300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 11
-
Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
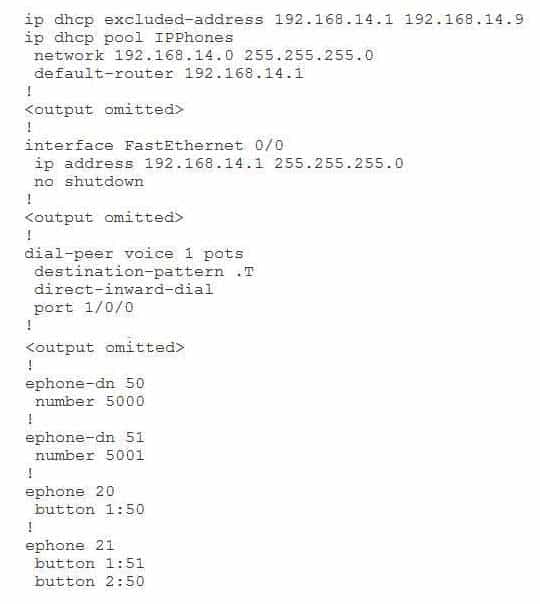
300-835 Part 11 Q01 044 How many phones will ring if a user dials extension 5001? (Select the best answer.)
- none
- one
- two
- three
Explanation:
One phone will ring if a user dials extension 5001 because only one IP phone has a line button that is configured to use extension 5001. By contrast, both the phone associated with ephonedn 50 and the phone associated with ephonedn 51 will ring when a user dials extension 5000 because both phones have buttons that are configured to use that extension. The following command set configures two phones to ring simultaneously when a call is received on extension 5000:
ephonedn 50
number 5000
!ephonedn 51
number 5001
!ephone 20
button 1:50
!ephone 21
button 1:51
button 2:50You can configure which ephonedn is given preference by issuing the preference command in ephonedn configuration mode. When multiple ephonedns are configured with the same extension number, the ephonedn with the lowest preference value will receive the call. The preference can be set to a value from 0 to 10; an ephonedn is set to a preference of 0 by default. An ephonedn with a preference of 0 is preferred over an ephonedn with a preference of 1.
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:
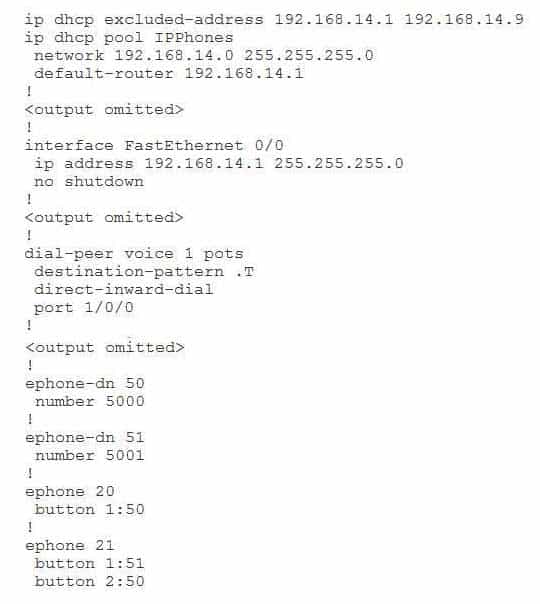
300-835 Part 11 Q02 045 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
Which of the following statements is true? (Select the best answer.)
- There will be no delay after the phone number is dialed.
- There will be no dial tone on the voice port.
- There will be an IP conflict between the CME router and an IP phone.
- Only the first dialed digit will be matched.
Explanation:
There will be no dial tone on the voice port, because the dial peer has been configured with the direct-inwarddial command. The directinwarddial command and the shutdown command can both disable dial tones on a voice port. You should issue the directinwarddial command on a plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peer to enable direct inward dialing (DID) for an incoming number. DID uses the incoming dialed number to match an outgoing dial peer. For example, you can use DID to map a POTS telephone number to a four digit extension on a Voice over IP (VoIP) network so that callers from POTS numbers can bypass the automated attendant or menu system and reach the internal VoIP extension directly. When DID is enabled on a POTS dial peer, the caller will not hear a dial tone on the voice port that is associated with that dial peer.
If you issue the shutdown command on a voice port, the port enters the shutdown state, meaning that no voice or data packets can traverse the port and, therefore, no dial tone can be heard by a caller who is attempting to place a call on the port. You can reenable a voice port by issuing the no shutdown command in interface configuration mode.
If you do not hear a dial tone on an IP phone even though directinwarddial has not been configured on the dial peer and the no shutdown command has been issued on the voice port, it is probable that you have not assigned an ephonedn to the line that is associated with the IP phone. You can assign a directory number (dn) to an IP phone in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) by issuing the button button-number:dntag command in ephone configuration mode, where dntag is the number that has been assigned to the ephonedn and buttonnumber is the number of the line button on the IP phone to which you want to associate the dn. In this scenario, the ephonedn 50 has been assigned to button 1 on ephone 20.
There will be a delay after the phone number is dialed. In addition, up to 32 digits will be matched by the destination pattern, not just the first digit. The dial peer command destinationpattern .T is used to indicate any string of up to 32 digits. The T character is used at the end of a string to instruct the router to wait for the complete dial string to be entered before matching a call to a dial peer. Cisco recommends that you use the destinationpattern .T command rather than the destinationpattern T command because the destination-pattern .T command requires that the caller dial a digit. A dial peer with the destinationpattern T command will be matched if an outbound caller takes the phone offhook for 10 seconds. Destination patterns that do not use the T wildcard do not experience a delay between the completion of the dialed string and the connection of the call; the dialed string is matched on a digitbydigit basis, and the call is connected as soon as a match is found.
There will not be a conflict between the CME router and an IP phone. The following commands configure the router with a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) pool that will be used to assign IP addresses to an IP phone:
ip dhcp pool IPPhones
network 192.168.14.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 192.168.14.1In addition, the ip address 192.168.14.1 255.255.255.0 command configures the FastEthernet 0/0 interface on the CME router with the IP address 192.168.14.1. In addition, the ip dhcp excludedaddress 192.168.14.1 192.168.14.9 command prevents the CME router from assigning the IP address 192.168.14.1 to an IP phone.
-
You issue the show running-config command on a CME router and receive the following partial output:
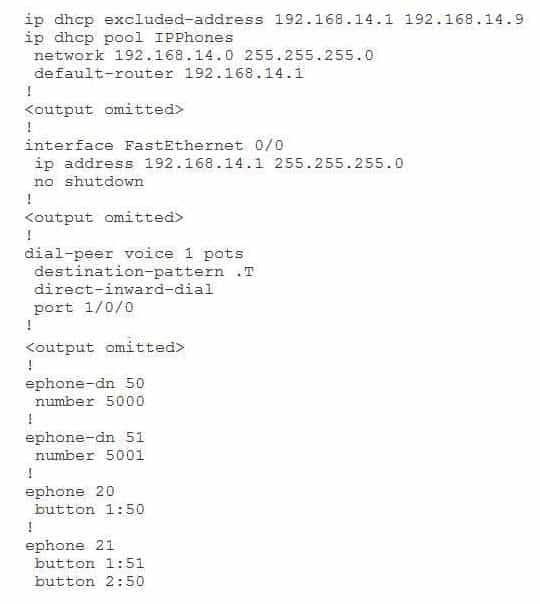
300-835 Part 11 Q03 046 Examine the output, and use the information you gather to answer the question.
Which of the following best describes port 1/0/0 in this configuration? (Select the best answer.)- an analog FXO port
- an analog FXS port
- a SIP trunk port
- a VoIP port
Explanation:
Port 1/0/0 is an analog foreign exchange office (FXO) port. An FXO interface is typically used to connect an analog device to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). In addition, if a public branch exchange (PBX) is configured with a foreign exchange station (FXS) port, the FXO interface on an analog device can terminate an analog trunk line from a PBX. FXO interfaces are commonly found on standard telephones, fax machines, and analog modems.
The port command is used by a voice router to match inbound plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peers and to determine where to route outgoing POTS dial peers. The dial peer voice command is used to define how calls are routed to destination endpoints on either the PSTN or a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. To define call routing for the PSTN, you should issue the dialpeer voice command with the pots keyword. To define call routing for a VoIP network, you should issue the dialpeer voice command with the voip keyword. In this scenario, dial peer 1 is configured as a pots dial peer. Therefore, the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router port that is connected to the PSTN is FXO port 1/0/0.
Port 1/0/0 is not an analog FXS port. An analog trunk line from the central office (CO) typically originates from an FXS interface on a phone switch. The switch provides dial tone, ring voltage, and line voltage for the customer site. Because the FXS interface on the phone switch provides power, it cannot be connected to another FXS interface; instead, the FXS interface must be connected to a device with an FXO interface, such as an analog telephone or a legacy voice mail system.
Port 1/0/0 is neither a Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunk port nor a VoIP port. SIP is the signaling method that is most commonly used by Internet telephony service providers (ITSPs). ITSPs enable customers to use VoIP to make phone calls over the Internet. SIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol that is supported by a wide variety of IP telephony vendors. The configuration methods for SIP trunking among ITSPs vary. To configure a CME dial peer for SIP trunking in Cisco IOS, you should issue the session protocol sipv2 command in dial peer configuration mode. For example, the following configuration creates dial peer 5012 to handle an outgoing call to a SIP trunk connected to the PSTN:dialpeer voice 5012 voip
session protocol sipv2
session target ipv4:10.11.12.13
dtmfrelay sipnotify
no vadThe configuration above sets the trunking protocol for the dial peer to SIP version 2, identifies the SIP trunk as having the IP address 10.11.12.13, specifies that dualtone multifrequency (DTMF) dialed digits should be relayed through SIP’s NOTIFY messages, and disables voice activity detection (VAD) for the dial peer. Because no codecconfiguration command is issued, the default G.729 codec will be used for the dial peer.
-
Which of the following Cisco UCM Mobility features is user configurable? (Select the best answer.)
- Application Dial Rules
- Remote Destination Profile
- Remote Destination
- SNR assignment schedule
Explanation:
Of the available choices, only the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Single Number Reach (SNR) assignment schedule is user configurable. SNR allows a user to specify an alternate number that will be automatically called when the user receives a call through UCM. SNR assignment schedules enable users to configure specific days and spans of time during which a given SNR configuration will be enabled. For example, if a user wanted to ensure that a given SNR was operational Monday through Friday from 8 a.m. until 6 p.m., the user could configure an SNR assignment schedule for those days and times.End users are not capable of configuring a Remote Destination Profile or a Remote Destination in UCM.
However, before a user can enable SNR, an administrator must perform the following actions:
-Create a Remote Destination Profile
-Create a Remote Destination
-Enable Mobility on the end user’s phoneEnd users are not capable of configuring Application Dial Rules. Application Dial Rules are used within UCM to add or remove digits from numbers that users dial.
-
You issue the following commands on a CME router:
Dial-peer voice 1 pots
Destination-pattern 9….
Forward-digits 3
prefix 9
port 1/0/0Which of the following digits will be forwarded to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267? (Select the best answer.)
- 426
- 942
- 4267
- 9267
- 94267
Explanation:
The following command set issued on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router will forward the digits 9267 to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) when a caller dials 94267:Dial-peer voice 1 pots
Destination-pattern 9….
Forward-digits 3
prefix 9
port 1/0/0The dialpeer voice command is used to define how calls are routed to destination endpoints on either the PSTN or a Voice over IP (VoIP) network. To define call routing for the PSTN, you should issue the dialpeer voice command with the pots keyword.
The destinationpattern command is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers. The sequence of dialed digits that will be matched for a dial peer can contain the digits 0 through 9, the asterisk (*), and the pound sign (#). In addition, you can use a period (.) as a wildcard symbol to refine the dialing pattern or to match multiple dial strings for a single dial peer. The command set in this scenario configures a dial peer on a CME router to match fivedigit patterns beginning with 9. By default, CME only forwards digits matched by wildcards in a destination pattern, not digits that are explicitly defined in the destination pattern. Therefore, the destinationpattern 9…. command configures CME to forward the digits 4267 in the destination pattern
when a user dials 94267. However, theforwarddigits 3 and prefix 9 commands will modify the digits that are forwarded to the PSTN.
The forwarddigits command configures a dial peer to forward the rightmost number of digits matched by the destination pattern, even if the digits are explicitly matched. The number of digits forwarded by CME depends on the value configured in the forwarddigits command. In this scenario, the forwarddigits 3 command configures CME to forward only the rightmost three digits, which are 267, of the dialed string. However, the prefix 9 command will modify the digits that are forwarded to the PSTN.
The prefix command is used to add one or more digits to the front of the dial string before the dial string is forwarded to the destination network. Issuing the prefix 9 command in this scenario will add the digit 9 to the front of the dial string. Therefore, the dial string 9267 will be forwarded to the PSTN.
Issuing the forwarddigits implicit command or the no forwarddigits command configures a dial peer to perform its default behavior of stripping digits that are explicitly matched in the destination pattern. Issuing the forwarddigits all command configures a dial peer to forward every digit that matches the destination pattern, even if the digits are explicitly matched.
The router will not forward the digits 94267 when a caller dials 94267. Any of the following command sets will configure the router to forward the digits 94267 to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267:
dialpeer voice 1 pots
destinationpattern …..
port 1/0/0dialpeer voice 1 pots
destinationpattern 9….
prefix 9
port 1/0/0dialpeer voice 1 pots
destinationpattern 9….
forwarddigits all
port 1/0/0The router will not forward the digits 4267 when a caller dials 94267. The following command set will configure the router to forward the digits 4267 to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267:
dialpeer voice 1 pots
destinationpattern 9….
port 1/0/0The router will not forward the digits 942 to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267. The following command set will configure the router to forward the digits 942 to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267:
dialpeer voice 1 pots
destinationpattern 94267
prefix 942 port 1/0/0The router will not forward the digits 426 to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267. The following command set will configure the router to forward the digits 426 to the PSTN when a caller dials 94267:
dialpeer voice 1 pots
destinationpattern 9…7
port 1/0/0The command set above explicitly defines the digits 9 and 7 in the destination pattern. Because the forwarddigits command has not been issued and because no prefix command has been issued, the dialed digits that match the three wildcards in the destination pattern string will be forwarded to the PSTN.
-
You issue the no auto-reg-ephone command on a CME router.
Which of the following is true? (Select the best answer.)
- No phones can automatically register with CME.
- Phones explicitly listed in the configuration can automatically register with CME.
- Phones can be registered in CME only by using the webbased GUI.
- The MAC addresses of phones that cannot automatically register will not be recorded.
Explanation:
Only phones that are explicitly listed in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) configuration can automatically register with CME if you issue the no autoregephone command on a CME router. When the no autoregephone command is issued in telephonyservice configuration mode, phones that do not have a Media Access Control (MAC) address explicitly listed in the configuration will be blocked and not able to automatically register with CME. However, phones with MAC addresses that are explicitly listed in the configuration will still be able to automatically register.
The autoregephone command, which is issued by default on a CME router, configures a router to automatically assign an ephone to an IP phone even if the phone’s MAC address is not explicitly listed in the configuration. When an IP phone registers with a router that is configured with the autoregephone command, the router will associate the MAC address of the IP phone with the first unassigned ephone on the router. If all the ephones on the router are associated with IP phones, the router will create a new ephone, provided that the number of configured ephones does not exceed the value of the max-ephonecommand.
On a Cisco 1700 router that is running IOS 12.4(4)XC, the CME graphical user interface (GUI) will display a dialog box that includes the words “no new phone to add” and a button labeled OK if you attempt to add a phone when autoregistration has been disabled on the router. Autoregistration can be disabled by issuing the no autoregephone command in telephonyservice configuration mode in the router’s commandline interface (CLI). However, you can register phones in ways other than the CME webbased GUI if auto-registration is disabled. For example, you can issue the macaddressmacaddresscommand in ephone configuration mode in the CLI to manually register an IP phone with CME. The only workaround for the CME GUI error is to enable autoregistration by issuing the autoregephone command in telephonyservice configuration mode in the CLI.
The MAC addresses of phones that cannot automatically register will be recorded by the CME router if the no autoregephone command has been issued on the CME router. In this scenario, IP phones that are not explicitly listed in the configuration are blocked by CME when they attempt to automatically register. CME records the MAC address of each blocked IP phone. You can display a list of blocked IP phones by issuing the show ephone attemptedregistrations command in privileged EXEC mode. You can erase the record of blocked IP phone registration attempts by issuing the clear telephonyservice ephoneattemptedregistrations command in privileged EXEC mode. -
How many Publisher servers can be added to a UCM cluster? (Select the best answer.)
- one
- two
- six
- eight
Explanation:
A Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) cluster supports one Publisher server. The Publisher server in a UCM cluster has two roles. It holds the master writable copy of the IBM Informix database for the cluster, and it acts as a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server for IP phone configuration downloads. The Publisher server is the only server that contains a writable copy of the IBM Informix database that stores directory numbers (dns), calling permissions, route plans, and other information. The Publisher server replicates the data that is stored in the master database to the Subscriber servers, all of which then store their own readonly copies of the database.
A UCM cluster can support up to eight Subscriber servers. Subscriber servers typically handle call routing, dial tone, receiving digits, and the streaming of onhold music in a UCM cluster. In medium to large environments, the Subscriber servers perform most of the work in connecting and maintaining calls so that the performance of the Publisher server is not hindered. A UCM cluster is an environment that contains a Publisher server and up to eight Subscriber servers. Each server in the UCM cluster has a unique configuration.
A Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) server cluster can support up to six servers. CUPS is server software that centralizes network traffic from several different communications services so that it can all be transmitted over the same Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network. CUPS uses industry standard Jabber XCP for communication between different instant messaging (IM) clients? Extensible Message and Presence Protocol (XMPP) is the protocol that establishes the IM sessions. In addition, Jabber XCP facilitates other features such as file and application sharing and video conferencing. -
Which of the following occurs when you press the **# keypad sequence at the Settings menu on a Cisco IP phone? (Select the best answer.)
- The phone will unlock the Settings menu options.
- The phone will be restored to the factory default settings.
- The phone will restart.
- The phone will reset.
- The phone will dial the voice mail pilot number
Explanation:
The IP phone’s settings will be unlocked if you press the **# keypad sequence at the Settings menu on a Cisco IP phone. You can access the Settings menu by pressing the settings button on the phone’s keypad. You might need to unlock the IP phone’s settings in order to make manual changes, such as manually deleting the phone’s Certificate Trust List (CTL) file. CTL files are a component of a secure Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) configuration. They are used as part of the device, file, and signaling authentication process. When a phone initializes, it downloads the CTL file from the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server.You might need to delete a CTL file from an IP phone if you move the phone to a different UCM cluster or to storage. You might also need to delete a CTL file from an IP phone if the secure cluster’s configuration changes or you lose the security tokens with which the CTL was signed.
The phone will not reset when you press the **# keypad sequence from the Settings menu. The phone will reset when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. An IP phone reset will reinitialize the phone, which means that the phone will reboot, contact the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to obtain network configuration information, and then download its configuration file from the TFTP server. The IP phone will also unregister and reregister with the Cisco call processor platform.The phone will not restart when you press the **# keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. An IP phone restart is different from a reset because a restart does not contact the DHCP server. Instead, the phone will store and reuse the network configuration information that was previously obtained from the DHCP server. However, a restarted phone does connect to the TFTP server to download configuration updates. In addition, the IP phone will unregister and reregister with the Cisco call processor platform. Because restarting an IP phone circumvents the DHCP server, a restart brings the phone back to working order faster than a reset.
The phone will not be restored to the factory default settings when you press the **# keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. The method you use to restore a Cisco IP phone to factory default settings varies by phone model. However, no Cisco IP phone can be restored to the factory default settings by pressing the **# sequence at the Settings menu. When an IP phone is restored to the factory default settings, any configuration changes that might be stored on the IP phone itself are restored to the factory default settings.
The phone will not dial the voice mail pilot number when you press the **# keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. To access voice mail from an IP phone, you should press the messages button on the IP phone keypad. The IP phone should automatically dial the voice mail pilot number. If the phone’s handset is on the hook, the voice mail system will use the IP phone’s builtin speaker to provide the audio for the voice mail session. -
Which of the following dial peer commands will match dial strings 1777 and 3777? (Select 3 choices.)
- destinationpattern .777
- destinationpattern *777
- destinationpattern (13)777
- destinationpattern [13]777
- destinationpattern [13]777
Explanation:
The following dial peer commands will match dial strings 1777 and 3777:
-destinationpattern .777
-destinationpattern [13]777
-destinationpattern [13]777The destination-npattern command is used to match both inbound and outbound dial peers; a dial peer defines a logical route to a telephony endpoint. Outbound dial peers are matched to destination patterns on a digit-by-digit basis as the caller dials the destination number. If multiple dial peers explicitly match the destination pattern, the most specific match for the pattern will be used. The sequence of dialed digits that will be matched for a dial peer can contain the digits 0 through 9, the asterisk (*), and the pound sign (#). In addition, you can use the following symbols to refine the dialing pattern or to match multiple dial strings for a single dial peer:
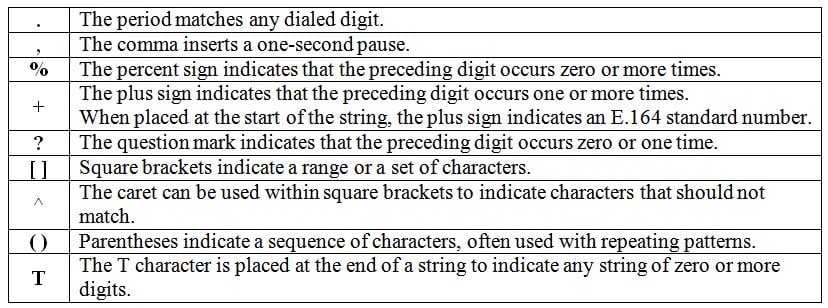
300-835 Part 11 Q09 047 The dial peer command destinationpattern .777 matches any fourdigit dial string that ends with 777. The period is used as a wildcard character that matches any digit. Not only will the destinationpattern .777 command match 1777 and 3777, it will also match 0777, 2777, 4777, 5777, and so on.
The dial peer command destinationpattern [13]777 matches only the dial strings 1777 and 3777. When square brackets contain a set of digits without a dash, the pattern will match any of the bracketed digits for that digit position. For example, the destinationpattern [135]777 command matches the dial strings 1777, 3777, and 5777. The caret (^) can be used within the brackets to indicate characters that should not match. For example, the destinationpattern [^01479]777 command matches the dial strings 2777, 3777, 5777, 6777, and 8777, but the command does not match the dial strings 0777, 1777, 4777, 7777, and 9777.
The dial peer command destinationpattern [13]777 matches the dial strings 1777, 2777, and 3777. The dash indicates a range of characters. You can also use the dash along with a set of characters. For example, the destinationpattern [135]777 command matches the dial strings 1777, 3777, 4777, and 5777.
The dial peer command destinationpattern *777 does not match the dial strings 1777 and 3777. The * character is not used as a wildcard character? it is used to indicate the asterisk on the telephone keypad. Therefore, the destinationpattern *777 command matches only the dial string *777.
The dial peer command destinationpattern (13)777 does not match the dial strings 1777 and 3777. Parentheses are used to indicate a specific sequence of characters. Therefore, the destinationpattern (13) 777 command matches only the dial string 13777. Parentheses are often used with the %, +, and ? characters to indicate a repeating pattern. For example, the destinationpattern (13)+777 command matches 13777, 1313777, 131313777, and so on. -
Which of the following problems is most likely caused by acoustic coupling between the earpiece and microphone in an IP phone handset when an IP phone user places a call to a PSTN user? (Select the best answer.)
- The PSTN phone user hears echo.
- The IP phone user hears echo.
- The PSTN phone user experiences delay.
- The IP phone user experiences delay.
Explanation:
The public switch telephone network (PSTN) user hears an echo when there is acoustic coupling between the earpiece and the microphone in the IP phone user’s handset. Acoustic coupling occurs when sound from a local user’s handset or headset speaker is picked up by the same device’s microphone, which then transmits that sound to the remote user. This causes the remote user to experience an echo.An IP phone user will hear an echo from telephone hybrids on the PSTN. The PSTN typically uses a four-wire method of transmitting bidirectional audio. However, homes and small businesses with analog devices often combine audio signals on two wires. A telephone hybrid converts between the two systems.
Delay, or latency, has a number of causes on both the PSTN and IP networks. Contributors to delay are conversion from analog to digital or viceversa, buffering, codec conversion, and more. However, acoustic coupling is more likely to cause echo for the remote user than delay. -
Your company has segregated UCM users into four partitions by region. You are configuring Cisco Unity Connection user templates.
Which of the following are you most likely to configure? (Select the best answer.)
- a single template for all regions
- a unique template for each search space
- a unique template for each region
- a unique template for each user
Explanation:
Most likely, you will configure a unique Cisco Unity Connection user template for each region if your company has segregated Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) users into four partitions by region. A partition is a logical grouping of Voice over IP (VoIP) route patterns and directory numbers (dns). A Cisco Unity Connection user template is a collection of settings that are applied to each user who is created based on the given template.
When users are separated into partitions, it is likely that certain settings, such as time zones, might be the same for the users within the partition but different for users in another partition. Therefore, you should consider creating separate Cisco Unity Connection user templates for users who exist in different partitions so that such settings can be applied to all users within a given partition with minimal administrative overhead. Other reasons you might create a separate user template include the use of a different call handler by some users or the use of a different phone system by some users. -
Which of the following is not a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition? (Select the best answer.)
- determining user availability by using presence status
- sending CDR reports to administrators or management
- reverting transferred calls back to the operator if the call is unanswered
- support for conferencing a single third party into an existing call
Explanation:
Sending Call Detail Records (CDR) reports to administrators or management is not a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. Cisco Unified Attendant Console is a software application that enables human operators to streamline the process of routing incoming calls across a Cisco IP phone network. There are several versions of Cisco Unified Attendant Console, including Compact Edition, Business Edition, Department Edition, Enterprise Edition, and Premium Edition.
Some features of Cisco Unified Attendant Console are common to all versions. Others require a specific version in order to use the feature set. For example, in Cisco Unified Attendant Console Enterprise Edition, it is possible to configure the Night Service feature, which enables the definition of operator working hours. If incoming calls arrive outside of the operator’s working hours, those calls can be automatically redirected to an answering service or a voice mail system.
Determining user availability by using presence status is a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. Operators can determine the presence of a given contact by selecting the contact from the corporate directory and then pressing the F2 key on the keyboard. The IP phone user’s presence and line status are indicated by various phone icons.
Reverting transferred calls back to the operator if the call is unanswered is a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. Cisco Unified Attendant Console will return a call to the application’s Call Progress area if the call is not answered by the user at the destination. From there it will move to Active Calls, at which point the operator can right click on the call and choose from one of several options for handling the call.
Support for conferencing a single third party into an existing call is a function of Cisco Unified Attendant Console Business Edition. You can add a third party to an existing call by clicking the party’s extension in the application and then clicking Start Conference. If the third party you attempt to add does not want to participate in the conference or does not answer, the call automatically reverts back to the original two participants. -
A caller presses an IP phone softkey labeled QRT. The caller is not logged in to the IP phone.
Which of the following will not be sent to an administrator? (Select the best answer.)
- the time stamp
- the category
- the reason
- the source user name
- the destination user name
- the source IP address
- the destination IP address
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the source user name will not be sent to an administrator if a user presses an IP phone softkey labeled QRT and is not logged in to the IP phone. The Cisco Quality Report Tool (QRT) can be configured as an extended function to enable users to send QRT information to Cisco Unified Communications administrators directly from the user’s IP phone. The report can then be displayed from the Tools menu within Cisco Unified Serviceability. However, if the user is not logged in to the IP phone at the time the data is sent, the user name, or source device owner field, will be null.
The QRT tool collects a variety of available source device information, destination device information, Real-time Information Server (RIS) information, Cisco Call Manager service and CTIManager service information, Call Manager database information, and enduser information when a user presses the QRT softkey. An administrator can then analyze that information to troubleshoot quality issues or other issues that occurred during a given call.
There is not enough information to determine whether the destination user name will be sent to the administrator. If the call’s recipient is logged in to the destination IP phone, the destination user name will be sent to the administrator. However, if the recipient is not logged in to the IP phone, the destination user name will be null.
Enduser information, such as the time stamp, the category, and the reason, will be sent to the administrator. In addition, the source IP address and the destination IP address will be sent to the administrator. -
A caller from the voice VLAN attempts to connect to an extension that does not exist on your company’s VoIP network.
Which of the following settings in the Call Forward and Pickup Settings section of the UCM Administration Directory NumberConfiguration page would direct such callers to voice mail? (Select the best answer.)
- Forward All
- Forward Busy External
- Forward Busy Internal
- Forward No Answer External
- Forward Unregistered External
- Forward Unregistered Internal
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the Forward Unregistered Internal setting would forward internal callers to a specific voice mailbox if the internal caller dialed a nonexistent directory number (dn). The Forward Unregistered Internal setting in the Call Forward and Pickup Settings section of the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Administration Directory Number Configuration page would direct a caller from the internal network, or voice virtual LAN (VLAN), to voice mail if that caller attempted to connect to an extension that does not exist on your company’s Voice over IP (VoIP) network. The Directory Number Configuration page enables a UCM administrator to configure several settings related to dns, including the following: call forwarding, call pickup, call waiting, line display text, ring settings, and voice mailboxes. In contrast to the Forward Unregistered Internal setting, the Forward Unregistered External setting forwards callers from the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to a specific voice mailbox if the internal caller dialed a nonexistent dn.The Forward All setting forwards all callers, internal or external, to a specific voice mailbox. This is the same behavior as the CFwdAll softkey that appears on a Cisco IP phone. However, an administrator can configure this behavior for a user by accessing the Directory Number Configuration page if the user for some reason does not have access to the CFwdAll softkey.
The Forward Busy External setting forwards any calls from the PSTN that arrive while the given dn is already in use. Similarly, the Forward Busy Internal setting forwards any internal calls that arrive while the given dn is already in use.
The Forward No Answer External setting forwards any calls from the PSTN that go unanswered by the user. Similarly, the Forward No Answer Internal setting forwards any internal calls that go unanswered by the user. -
Which of the following can you display by clicking System Reports in the CAR GUI? (Select 4 choices.)
- the current number of billing errors
- the call volume for a given period of time
- malicious call details
- QoS rating information for inbound calls
- Route and Line Group Utilization
- the top number of users by maximum length of calls
Explanation:
You can display the current number of billing errors, the call volume for a given period of time, malicious call details, and Quality of Service (QoS) rating information for inbound calls by clicking System Reports in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) graphical user interface (GUI). You can view information about the current number of billing errors by using the System Reports> CDR Error report in the CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view the number of errors that occurred when CDR data was loaded into the reporting system.
You can view the call volume for a given period of time by clicking System Reports > Traffic > Summary by Phone Number in the CAR GUI. The Summary by Phone Number report enables a CAR administrator to choose a range of time and IP phone extension numbers from which to view call volume information, thereby enabling an administrator to view what extensions were in use at a specific time.
You can view malicious call details by using the System Reports > Malicious Call Details report in the CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view call information that is tracked by the UCM Malicious Call Identification (MCID) service. An administrator can choose to view MCID information over a period of time.
You can view QoS information for inbound calls by using the System Reports > QoS > Detail report in the CAR GUI. The Detail report enables a CAR administrator to choose a UCM network and a period of time for which to view QoS ratings for both inbound and outbound calls. The Detail report can be used to monitor QoS at a user level.
The Route and Line Group Utilization report can be accessed by clicking Device Reports > Route Patterns/ Hunt Pilots in the Cisco CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view Route and Line Group Utilization as a percentage? the report can also be used to determine whether capacity needs to be added to an existing Voice over IP (VoIP) implementation.
You can view information about the top number of users by maximum length of calls by using the User Reports menu. The By Duration report can be accessed by clicking User Reports > Top N in the CAR GUI. This report enables a CAR administrator to view users who have made the longest calls over a given period of time, starting with the user who placed the longest call. -
Cisco Unity is sending messages that are destined for a Microsoft Exchange user’s mailbox to the Unaddressed Messages distribution list instead.
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the problem? (Select the best answer.)
- The Issue Warning storage limit has been exceeded.
- The Prohibit Send storage limit has been exceeded.
- The Prohibit Send and Receive storage limit has been exceeded.
- The Cisco Unity user’s dn does not match the dn configured in UCM.
- The Message Age limit has been exceeded.
Explanation:
Most likely, the Prohibit Send and Receive storage limit has been exceeded if Cisco Unity is sending messages that are destined for a Microsoft Exchange user’s mailbox to the Unaddressed Messages distribution list instead. Cisco Unity integrates voice messaging with email services provided by Microsoft Exchange. In a Cisco Unity and Microsoft Exchange environment, voice messages, email, and fax messages can all be accessed from the same client, such as a PC or a touchtone phone. When a user’s mailbox exceeds Microsoft Exchange storage limit thresholds, Cisco Unity can notify the user by using the phone conversation.
Microsoft Exchange has three different storage limit thresholds that can be configured systemwide or on a peruser basis. When a user’s mailbox size exceeds a configured threshold, Microsoft Exchange and Cisco Unity carry out different actions depending on the storage limit that applies.
When the Prohibit Send and Receive storage limit is exceeded, neither Microsoft Exchange nor Cisco Unity will allow the user to send or receive messages. In addition, Cisco Unity will forward any messages that cannot be delivered to its Unaddressed Messages distribution list. Messages that are forwarded to the Unaddressed Messages distribution list will not be delivered to the intended recipients.
It is not likely that the Message Age limit has been exceeded. If a Message Age limit were exceeded, voice mail messages would either be moved to the Deleted Items folder or be permanently deleted by Cisco Unity, which would prevent the mailbox from becoming full. Message Aging is a Cisco Unity option that can be used to move voice mail messages of a given age to the Deleted Items folder, or delete them permanently. This option is disabled by default. However, you can enable this option as a more permanent solution for a user who has a high volume of inbound voice mail messages that are never manually deleted.
It is not likely that the Issue Warning storage limit has been exceeded. When the Issue Warning threshold is exceeded, both Cisco Unity and Microsoft Exchange will send a notification to the user that the mailbox has exceeded the threshold. The warning gives users an opportunity to delete or archive old messages before stricter mailbox size enforcement measures are activated.
It is not likely that the Prohibit Send storage limit has been exceeded. When the Prohibit Send threshold is exceeded, neither Cisco Unity nor Microsoft Exchange will allow the user to send messages. However, messages will still be delivered to the user’s mailbox.
It is not likely that the Cisco Unity user’s directory number (dn) does not match the dn configured in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). Mismatched dns can become a problem when UCM users are imported into Cisco Unity Connection, not Cisco Unity. When a user’s dn in UCM does not match the same user’s dn in Cisco Unity Connection, the user will not be able to receive voice mail messages and will not be able to log in to voice mail services. -
You want to add a user to a CME router. The router has been assigned the IP address of 192.168.51.50. Which of the following interfaces cannot be used to accomplish your task? (Select the best answer.)
- CCP
- CLI
- http://192.168.51.50/ccme.html
- TUI
Explanation:
You cannot use the telephone user interface (TUI) to add a user to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router. The TUI is a voice-prompted interface that enables users to perform actions by pressing a number or a specific sequence of numbers on a telephone keypad. A typical function for a TUI on a Voice over IP (VoIP) system is to enable voice mail users to authenticate to the voice mail system and check messages. You can also use a telephone’s keypad to perform some configuration tasks, such as modifying network settings or restarting an IP phone.You can use Cisco Configuration Professional (CCP) to add a user to the CME router. You should click Configure > Unified Communications > Users, Phones, and Extensions > Phones and Users in the graphical user interface (GUI) to add a user or to add a phone if you are using CCP. CCP is a graphical device management tool that is installed as an application on a Windows computer. CCP can be used to configure voice systems, such as CME routers, and other Cisco networking products. When properly installed and configured, CCP enables you to make configuration changes to phones or users by modifying the options on the Phones and Users summary page. You can create, edit, delete, restart, and reset one or more phones from the Phones and Users summary page in CCP. In addition, you can create, edit, and delete one or more phone system users from the Phones and Users summary page in CCP.
You can use the CME command line interface (CLI) to add a user to the CME router. To create a phone user by using the CLI, issue the username username password password command in ephone configuration mode, where username is the user name that you want to assign to the user and password is the password that you want to assign to the user. You should issue the username username password password command only in ephone configuration mode of the device that you want to assign to the user you are creating. For example, if you want user John to be able to manage the device settings of ephone 5 by using the CME GUI, you should issue the following commands on the CME router:
CME1(config)#ephone 5
CME1(configephone)#username john password b0s0n
The ephone 5 command places the router into ephone configuration mode for ephone 5. The username john password b0s0n command creates a new user name of john for ephone 5 and assigns that user name the password b0s0n.
You can use the web address of http://192.168.51.50/ccme.html to add a user to the CME router in this scenario. CME routers support the configuration of phones and users by using a webbased GUI. After the GUI is enabled, you can access it by typing the CME router’s IP address followed by /ccme.html into a browser’s location bar. To create a phone user account in the CME GUI, you should click Configure Phones Add Phone, which opens the Add Phone window. In the Login Account area of the Add Phone window, assign the phone user a user name and password and then associate the phone user with either an existing device or a new device? you can create a new device by filling out the devicerelated fields in the Add Phone window. -
Which of the following statements are true about Cisco Unified RTMT? (Select 2 choices.)
- RTMT can send email alerts.
- RTMT can perform system backups.
- RTMT can reboot a UCM cluster.
- RTMT can display PerfMon counter information.
- RTMT can display CAR database information.
Explanation:
Cisco Unified RealTime Monitoring Tool (RTMT) can send email alerts. In addition, RTMT can display performance monitoring (PerfMon) counter information that is stored by Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM). RTMT is a reporting tool that can be installed as an application on Windows or Linux clients? it uses Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to connect to Cisco Unified Communications devices.
UCM stores performance counter information, known as PerfMon counters, that RTMT can access to monitor system performance. The counters include information about the number of registered phones, the number of active calls, and port usage. An administrator can configure RTMT to generate email alerts when counters either exceed or fall below a certain threshold. The severity of a specific alert can be specified when the alert is configured. By default, performance counter alerts are configured with a Syslog severity level of warning.
Because it is a reporting and analysis tool, RTMT does not support system administration functions such as rebooting UCM clusters and performing system backups. RTMT also does not provide the same type of reporting as Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR), which is available under the Tools menu of the webbased Cisco Unified Serviceability troubleshooting tool. -
Your company policy indicates that voice mail messages from internal users can be no longer than 120 seconds. Your company policy also indicates that voice mail messages from outside callers can be no longer than 300 seconds.
All UCM voice mail message length options are currently set to the defaults.
Which of the following options should you modify in Cisco Unity Connection? (Select the best answer.)- Message Settings > Maximum Message Length
- Class of Service > Recorded Name-Maximum Length
- Class of Service > Message Length-Maximum Length
- Advanced > Conversations > System Broadcast Message: Maximum Recording Length in Milliseconds
Explanation:
You should modify the Class of Service > Message Length Maximum Length field in Cisco Unity Connection to configure a 120second voice mail recording limit for internal users. The Class of Service > Message Length Maximum Length field sets a maximum length in seconds for users who are assigned to the specific Class of Service (CoS) that is being modified. Cisco Unity Connection enables an administrator to limit voice mail recording lengths for internal users separately from outside callers. Therefore, you can configure Unity Connection so that outside callers can leave longer messages than internal users. By default, both outside callers and internal users are limited to 300second voice mail messages. Therefore, you only need to configure the Class of Service > Message Length Maximum Length field to 120 to meet your company’s requirements. CoS settings can be modified for multiple users by using the Phone section of a Unity Connection user template or by using Bulk Edit Mode.
You should not modify the Message Settings > Maximum Message Length field, because this field limits the length of voice mail messages that are left by outside callers. By default, the Maximum Message Length field is configured to 300 seconds, which is your company’s requirement; therefore, you need not modify this field. However, if you were to modify the Maximum Message Length field value for a single user, you would edit the field on the Message Settings page of the user’s account. There are three typical ways to create users in Unity Connection: local manual creation, import from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), or synchronization by using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP).
You can also modify the setting for a number of users at once by editing the Maximum Message Length field in Bulk Edit Mode. In addition, you can configure the Maximum Message Length field on the Message Settings page of a voice mail user template to apply a nondefault maximum message length to any new user accounts that are based on the template.
You should not modify the Class of Service > Recorded Name Maximum Length field. This field applies to users who have been assigned to the CoS and limits the length of time allotted to a user for recording the voice mailbox name that will be announced to callers who reach that user’s voice mail. By default, the Recorded Name Maximum Length field is set to 30 seconds; the field’s configurable range is from one through 100 seconds.
You should not modify the Advanced > Conversations > System Broadcast
Message: Maximum Recording Length in Milliseconds field, because this field limits the length of system broadcast messages that are played for all voice mail users. System broadcast messages are typically used for announcements and can be scheduled to start and end on specific dates and times. By default, the maximum length of a broadcast message is configured to 300,000 milliseconds, which is 300 seconds or five minutes. -
Which of the following will occur when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone? (Select the best answer.)
- The phone will dial the voice mail pilot number.
- The phone will be restored to the factory default settings.
- The phone will restart.
- The phone will reset.
Explanation:
The phone will reset when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. You can access the Settings menu by pressing the settings button on the phone’s keypad. An IP phone reset will reinitialize the phone, which means that the phone will reboot, contact the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server to obtain network configuration information, and then download its configuration file from the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server. The IP phone will also unregister and reregister with the Cisco call processor platform. You can also reset an IP phone in IOS on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router by issuing the reset command in ephone configuration mode. You can reset all IP phones on a network by issuing the reset all command in telephony services configuration mode. You can perform a reset in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) graphical user interface (GUI) by clicking Device > Phone > Reset.
You must reset a phone after performing the following tasks:Updating the phone’s firmware
Modifying the DHCP scope
Changing the IP address of the TFTP server
Changing Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
Changing the date and time settings
Changing the language displayed on the phone
Changing the call progress tones for the phone
Changing the voice mail access numberThe phone will not restart when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. An IP phone restart is different from a reset because a restart does not contact the DHCP server. Instead, the phone will store and reuse the network configuration information that was previously obtained from the DHCP server. However, a restarted phone does connect to the TFTP server to download configuration updates. In addition, the IP phone will unregister and reregister with the Cisco call processor platform. Because restarting an IP phone circumvents the DHCP server, a restart brings the phone back to working order faster than a reset. You can restart an IP phone by issuing the restart command in ephone configuration mode on a CME router. You can also restart all IP phones at once by issuing the restart all command in telephony services configuration mode.
You can either reset or restart a phone after performing the following tasks:Adding or deleting a phone button
Associating a button with a new ephonedn
Modifying an extension on an ephonedn
Modifying speeddial numbers on an ephone
Enabling call parkThe phone will not be restored to the factory default settings when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. The method you use to restore a Cisco IP phone to factory default settings varies by phone model. However, no Cisco IP phone can be restored to the factory default settings by pressing the **#** sequence at the Settings menu. When an IP phone is restored to the factory default settings, any configuration changes that might be stored on the IP phone itself are restored to the factory default settings.
The phone will not dial the voice mail pilot number when you press the **#** keypad sequence at the Settings menu of a Cisco IP phone. To access voice mail from an IP phone, you should press the messages button on the IP phone keypad. The IP phone should automatically dial the voice mail pilot number. If the phone’s handset is on the hook, the voice mail system will use the IP phone’s builtin speaker to provide the audio for the voice mail session.