300-835 : Automating Cisco Collaboration Solutions (CLAUTO) : Part 12
-
You issue the following commands on a CME router:
CME1#configure terminal CME1(config)#ephone 6 CME1(config-ephone)#username john password b0s0n CME1(config-ephone)#end
Which of the following best describes the type of CME user you just configured? (Select the best answer.
- a customer administrator
- an LDAP user
- a phone user
- a system administrator
Explanation:
You have configured a phone user if you issued the commands in this scenario on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router. A CME environment supports three types of users: system administrator, customer administrator, and phone user. Phone users can manage IP phone settings either by using the telephone keypad or by logging on to the CME browserbased graphical user interface (GUI). In order for a phone user to log on to the GUI, a system administrator must create a phone user account for that user and associate that account with a device. The phone user can then access the GUI by using the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) http://ipaddress/ccme.html, where ipaddress is the IP address of the CME router.
To create a phone user by using the command line interface (CLI), you should issue the username user – name password password command in ephone configuration mode, where username is the user name you want to assign to the user and password is the password you want to assign to the user. You should issue the username username password password command only in ephone configuration mode of the device that you want to assign to the user you are creating. For example, if you want user John to be able to manage the device settings of ephone 6 by using the CME GUI, you should issue the following commands on the CME router:
ephone 6
username john password b0s0n
To create a phone user account in the CME GUI, you should click Configure > Phones >Add Phone in the GUI, which opens the Add Phone window. In the Login Account area of the Add Phone window, you should assign the phone user a user name and password and then associate the phone user with either an existing device or a new device. Finally, click the Change button to create the user. You can also change an existing user’s password by clicking Configure > Phones in the GUI. Scroll through the list of Media Access Control (MAC) addresses in the Phone Physical ID (MAC Address) column until you find the phone you want to modify. Click the phone you want to modify, change the password, and then click the Change button.
You have not created a customer administrator. Customer administrator accounts are configured in the CLI by issuing the web admin customer name user name password string command in telephony service configuration mode, where username is the user name you want to assign to the customer administrator and string is the password you want to associate with the user name. In addition, you can configure a customer administrator in the GUI by clicking Administrator’s Login Account in the Configure System Parameters menu. After you have entered values in the Admin User Name (username) field, the Admin User Type (Customer) field, and both password fields, click the Change button to create the user.
You have not created a system administrator. The system administrator account must be configured from the CLI before the system administrator account can access the GUI. You can enable GUI access for a system administrator by issuing the web admin system name admin password string command in telephony service configuration mode.
You have not created a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) user account. You cannot directly synchronize users in an LDAP directory, such as Microsoft Active Directory, with CME. However, you can synchronize users in an LDAP directory with other Cisco Unified Communications products, such as Cisco Unity Connection. -
Which of the following Cisco Unity Connection Port Monitor fields are most likely to display a value of Idle? (Select 3 choices.)
- Application Status
- Conversation Status
- Display Status
- Connected To
- Port Ext
Explanation:
Of the available choices, the Application Status field, the Conversation Status field, and the Display Status field are all likely to display a value of Idle. The Cisco Unity Connection Port Monitor is a Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) option that can be used to monitor activity on each Cisco Unity Connection port in real time.
The Application Status field displays the name of the conversation being played on the given call. The Idle value indicates that the given port is not currently handling a call.
The Display Status field is used to display the action that is currently being performed in a conversation.
The Idle value indicates that the given port is not currently handling a call.
The Conversation Status field displays details about actions that the conversation is performing on a call.
The Idle value indicates that the given port is not currently handling a call.
Neither the Connected To field nor the Port Ext field displays an Idle value. The Connected To field displays the IP address and port of the UCM server to which the port is registered when the port is Skinny Control Client Protocol (SCCP)integrated. The Port Ext field displays the extension that is associated with the port. -
Which of the following commands are not required to configure basic telephony service on a CME router? (Select 2 choices.)
- dn-webedit
- max-dn
- max-ephones
- telephony-service
- mac-address
Explanation:
Neither the dnwebedit command nor the macaddress command is required to configure basic telephony service on a Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) router. The dnwebedit command enables the addition of ephone directory numbers (dns), or extensions, by using the browserbased graphical user interface (GUI). By default, you cannot add an extension to CME by using the browser based GUI. The dnwebedit command should be issued in telephony service configuration mode.The mac address mac address command associates a specific ephone number with the IP phone that has the specified Media Access Control (MAC) address. An ephone is a Cisco IOS representation of a physical IP phone device. However, you cannot configure ephones on a CME device until basic telephony service has been configured.
A CME router requires three values in order to configure basic telephony service: an IP address, a maxdn value, and a maxephones value. Issuing the telephony service command puts the router into telephony-service configuration mode, where you can issue commands that configure telephony settings on the router, such as the maxdn and maxephones commands.
The maxdn command configures the maximum number of dns, or extensions, that you can configure on a CME device. The maximum value of the maxdn parameter varies based on the router model, the IOS version, and the amount of memory. If you do not issue the maxdn command, you will not be able to configure any ephonedns on the router.
The maxephones command sets the maximum number of phones that you can configure on a router. Like the maxdn command, the maxephones command must be issued in telephony service configuration mode. The maximum value of the maxephone sparameter varies based on the router model and the IOS version. If you do not issue the maxephones command, you will not be able to configure any ephones on the router. -
Refer to the diagram.
300-835 Part 12 Q04 048 The IP phone at extension 1002 uses SCCP to communicate with the CME router. The IP phone at extension 1001 uses SIP to communicate with the CME router.
Which of the following protocols will the IP phones use to carry voice data during a call between extension 1001 and extension 1002? (Select the best answer.)- RTP
- SCCP
- SIP
- The phones will be unable to establish a call, because they do not use the same protocol to communicate with CME.
- RTCP
Explanation:
In this scenario, the phones will use Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP) to carry voice data during a call between extension 1001 and extension 1002. An IP phone can use Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) or Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to communicate with Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME). The signaling conversation between a CME router and an IP phone controls many of the IP phone’s functions, such as call initiation, call termination, and call waiting notification. CME can use SIP to communicate with one IP phone and SCCP to communicate with another? however, once CME has completed its signaling conversation with each IP phone, the phones will establish an RTP data stream between them to convey the voice traffic, as illustrated in the following diagram:
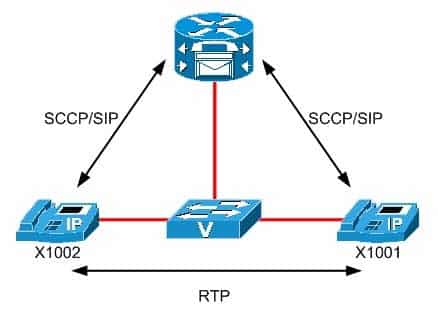
300-835 Part 12 Q04 049 Although the CME router is not directly involved in the voice data stream between the IP phones once the call has been established, CME continues to communicate with the IP phones for other functions related to the existing call and for any new calls. For example, if the CME router needs to notify extension 1001 of a second incoming call, CME can initiate a new SCCP or SIP conversation with extension 1001 while the original call is still active. This signaling conversation is in addition to the original SCCP or SIP conversation that CME used to set up the call and the RTP conversation between the two IP phones engaged in the call.
Realtime Transport Control Protocol (RTCP) is not used to carry voice streams between devices. RTCP is designed to report packet statistics between two devices engaged in an RTP session. Each RTP session is monitored by a corresponding RTCP session. Each RTCP session is established on the odd numbered User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port following the even numbered UDP port established by RTP. For example, if an RTP session is established on UDP port 23456, a corresponding RTCP session is established on UDP port 23457. -
You want to allow a traditional telephone handset to operate as an IP phone on a Cisco network.
Which of the following Cisco devices would accomplish this task? (Select the best answer.)
- ATA 190
- High Density Voice/Fax Network Module
- CUBE
- FXO Voice Interface Card
Explanation:
A Cisco Analog Telephone Adapter (ATA) 190 would allow a traditional telephone handset to operate as an IP phone on a Cisco network. The ATA 190 enables you to connect a traditional telephone handset to an Ethernet network. It houses two RJ11 traditional telephone ports and a single RJ45 Ethernet port. It is possible to connect both a traditional handset and an analog fax machine to the RJ11 ports. On the network, the ATA 190 behaves similarly to a normal Cisco IP phone.
Other Cisco IP telephony devices that can support analog ports for traditional handsets and fax machines include the Cisco Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Voice Interface Card, the Cisco VG 224 Analog Voice Gateway, and the Cisco VG350 Analog Voice Gateway. The FXS Voice Interface Card is an expansion card that enables a Cisco IP device to connect to RJ11 equipment.
The Cisco VG224 and the Cisco VG350 are both analog voice gateways. Each of them is capable of connecting traditional analog telephony devices to a Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network. The VG224 is an older gateway that supports 24 analog FXS ports and two Ethernet ports. The VG350 is a newer high-density gateway that is intended to connect traditional analog telephony equipment, including voice and fax, to an enterprise level voice network.
The Cisco Unified Border Element (CUBE) is a device that connects Cisco VoIP networks to service provider Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) trunks. Therefore, CUBE does not support traditional analog telephony devices.
A Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) Voice Interface Card enables a Cisco voice router to connect an RJ11 analog telephony device to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or to a private branch exchange (PBX). It does not enable traditional telephony devices to participate on a Cisco VoIP network.
The High Density Voice/Fax Network Module is an expansion for Cisco voice routers. This module supports only analog voice devices, not fax devices. -
You are integrating an existing Cisco Unity Connection user with an existing LDAP user. However, the user’s Unity Connection Alias field does not match the LDAP user ID.
Which of the following should you do prior to using the BAT to import the LDAP data? (Select the best answer.)
- Map the LDAP first name field to the Unity Connection first name field in the BAT.
- Map the LDAP last name field to the Unity Connection last name field in the BAT.
- Modify the user’s Alias field in Unity Connection.
- Modify the LDAP user ID in the CSV file prior to importing it with the BAT.
Explanation:
If you want to integrate an existing Cisco Unity Connection user with an existing Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) user, you should first ensure that the Aliasfield in Unity Connection matches the user ID in the LDAP directory. If the values do not match, as in this scenario, you should modify the user’s Alias field in Cisco Unity Connection.The Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) can be used to add, update, or remove users from Cisco Unified Communications platforms. When you integrate an existing Cisco Unity Connection account with an existing LDAP user, you must first export the LDAP user information to a comma-separated values (CSV) file. Next, you must import the CSV file into Unity Connection by using the BAT. The LDAP user ID field that is specified in the CSV is what the BAT will use to search the Unity Connection database. If the BAT finds no matching Unity Connection user alias, the action will fail and a failed objects report will be created.
You should not map the LDAP first name field to the Unity Connection first name field in the BAT. Even if it were possible to do so, multiple users could have the same first name. In addition, you should not map the LDAP last name field to the Unity Connection last name field in the BAT. Even if it were possible to do so, multiple users could have the same last name.
You should not modify the LDAP user ID in the CSV file prior to importing it with the BAT. The purpose of integrating a Unity Connection user account with an existing LDAP account is to ensure that the data between the two systems remains consistent. If you update the LDAP user ID value in the CSV, the value in the LDAP directory itself does not change. Therefore, the data between the two systems will not remain synchronized. -
Which of the following devices are not found in the endpoints layer in the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture? (Select 2 choices.)
- VoIP gateways
- analog gateways
- analog phones
- wireless phones
- IP phones
- IM clients
Explanation:
Voice over IP (VoIP) gateways and analog phones are not found in the endpoints layer in the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture. The Cisco Unified Communications Architecture divides the components of a VoIP solution into the following four layers:

300-835 Part 12 Q07 050 The endpoints layer generally contains devices that an end user is most likely to recognize and use. End users do not typically interface with VoIP gateways, which are found in the infrastructure layer. Analog phones are not capable of directly interfacing with a VoIP network; therefore, analog phones are not part of the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture.
Wireless phones, IP phones, and instant messaging (IM) clients are all found in the endpoints layer because end users commonly interface with these devices. An analog gateway is responsible for translating voice packets between VoIP networks and analog phones. The VoIP network does not extend beyond the analog gateway to the analog phone? therefore, the analog gateway is also considered an endpoint in the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture.
The applications layer of the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture contains devices and systems responsible for enhancing a Cisco VoIP solution with additional features, such as voice mail, fax delivery, and email integration. Systems that are found in the applications layer include Cisco Unity and Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS). Cisco Unity is a scalable messaging server that integrates with third party collaboration servers, such as Microsoft Exchange and Novell GroupWise. CUPS is an application that can assist a user in determining whether another user is currently on a call or available for a meeting.
The call processing layer of the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture contains devices that are responsible for determining what functions or signals must be generated for specific actions. Systems that are found in the call processing layer include Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME), and Unified Communications 500 (UC500). Each of these systems supports a different number of end users.
The infrastructure layer is the foundation of the Cisco Unified Communications Architecture. This layer contains devices that are responsible for routing and switching voice packets across a network. Systems that are found in the infrastructure layer include VoIP gateways, VoIP switches, and Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) firewalls. -
Which of the following UCM device settings fields identifies the specific hardware device that is being configured? (Select the best answer.)
- Device Pool
- Phone Security Profile
- MAC Address
- Phone Button Template
Explanation:
The MAC Address field is the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) field that identifies the specific hardware device that is being configured. The MAC Address field contains the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the device that you are provisioning. The MAC address is a hardware address that is assigned by the device manufacturer. When you are manually provisioning an IP phone in UCM Administration, you must fill in the MAC Address field, the Device Pool field, the Phone Button Template field, and the Phone Security Profile field.The Device Pool field does not identify the specific hardware device that is being configured. Although required when manually provisioning an IP phone in UCM Administration, the Device Pool field specifies a given set of characteristics that are to be applied to IP phones within the pool, such as region, date and time groups, softkey templates, and more.
The Phone Button Template field does not identify the specific hardware device that is being configured. Phone button templates are used to add or arrange IP phone buttons for a given device or group of devices. You can create or edit phone button templates by clicking Device > Device Settings > Phone Button Template in UCM.
The Phone Security Profile field does not identify the specific hardware device that is being configured. The Phone Security Profile field is used to create or modify the security configuration of devices to which the profile is applied. For example, you can assign a profile that supports UCM authentication or encryption to a device that supports those features. -
Which of the following support XMPP? (Select 3 choices.)
- a Cisco IP phone
- Cisco Unity Connection
- Cisco Unified MeetingPlace
- Cisco Unified Personal Communicator
- Cisco Jabber
- CUPS
Explanation:
Cisco Unified Personal Communicator, Cisco Jabber, and Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) all support Extensible Message and Presence Protocol (XMPP). Unified Personal Communicator is software that enables a user to connect to several different communication services from a single application. For example, you can use Unified Personal Communicator to place phone calls, download voice mails, and instant message (IM) another user.
Cisco Jabber is an application that is intended to integrate CUPS server services, such as user availability, with Microsoft Office. Cisco Jabber is also an IM client, a voice and video call client, and a desktop sharing client.
CUPS is server software that centralizes network traffic from several different communications services so that it can all be transmitted over the same Cisco Voice over IP (VoIP) network. CUPS uses XMPP to communicate with IM clients. However, CUPS uses Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) to communicate with collaboration endpoints.
Cisco IP phones support SIP and Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP), not XMPP. SCCP is a Cisco-proprietary, client/server call signaling protocol. SCCP must be used with a Cisco call processing platform, such as Unified Communications Manager (UCM), because SCCP is proprietary to Cisco. The firmware on Cisco IP phones is configured to use SCCP by default. SCCP must be used on Cisco IP phones to enable the phones to use Cisco’s full VoIP feature set. SIP is supported on Cisco IP phones with a firmware replacement.
Cisco Unity Connection uses Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP), not XMPP. IMAP can be used to retrieve email messages from a remote server. Many email clients support the use of either Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) or IMAP to retrieve email messages. Unity Connection uses IMAP to enable Unified Personal Communicator to download voice mails.
Cisco Unified Meeting Place uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or Secure HTTP (HTTPS), not XMPP. Unified Meeting Place is a collaboration tool that enables users to share information in the same manner that a conference room would? however, this solution comes together remotely with the use of a phone and browser based workstation desktop sharing. -
You administer the voice network shown above.
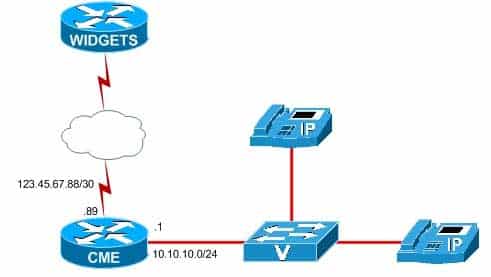
300-835 Part 12 Q10 051 You want to access the CME GUI from a workstation on your company’s private network. The browser on the workstation you are using does not have any bookmarks.
You type the URL http://10.10.10.1/cme.html into a browser location bar, but the browser reports an error.
There are no ACLs configured on the CME router.
Which of the following statements is true? (Select the best answer.)- The URL should be http://10.10.10.1/ccme.html.
- The URL should be http://123.45.67.89/cuadmin.
- The URL should be http://123.45.67.89/ccme.html.
- You have not enabled the CME browserbased GUI.
- A firewall is blocking access to the CME router from the workstation.
Explanation:
In this scenario, the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) should be http://10.10.10.1/ccme.html because you are accessing the Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME) browser based graphical user interface (GUI) from your company’s internal network. The CME router interface that is directly connected to your company’s internal network has been assigned the IP address 10.10.10.1. In addition, the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) page you should access to launch the CME GUI is named ccme.html. After you have logged in to the CME GUI, you can create users, add phones, or perform other operations. For example, to create a phone user account in the CME GUI, you should click Configure > Phones in the GUI.
The URL should not be http://123.45.67.89/cuadmin, because you are attempting to access the CME browser based GUI from your company’s internal network, which is on the 10.10.10.0/24 network. If you were a customer administrator who needed to access the CME GUI from outside the company’s internal network, you could use the URL http://123.45.67.89/ccme.html to do so, provided that the company has enabled a customer administrator account for you on the CME router. In addition, the HTML page you should access to launch the CME GUI is named ccme.html, not cuadmin. The cuadmin page could be used to launch the Cisco Unity Connection administration page if a Cisco Unity Connection server were to be installed on the network in this scenario.
Most likely, you have enabled the CME browser based GUI. In this scenario, you want to access the GUI from another workstation that does not contain your browser’s bookmarks. Therefore, it is most likely that you have mistyped the URL on the workstation you are using to access the GUI.
It is not likely that a firewall is blocking access to the CME router from the workstation. No access control lists (ACLs) have been configured on the router in this scenario, and no firewall exists on the private network between the workstations, the switch, and the CME router. Therefore, it is not likely that a firewall is preventing access to the browser based GUI on the CME. -
You administer a small VoIP network. You have registered one Cisco IP phone with UCM. Every other IP phone on the network is a thirdparty IP phone.
Which of the following statements is most likely true? (Select the best answer.)
- Only one H.323 endpoint is registered with UCM.
- Only one SCCP endpoint is registered with UCM.
- Only one SIP endpoint is registered with UCM.
- Only one MGCP endpoint is registered with UCM.
Explanation:
Most likely, only one Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) endpoint is registered with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) if you have registered one Cisco IP phone with UCM and every other IP phone on the network is a third party IP phone. By default, Cisco IP phones use SCCP, which is a Cisco-proprietary client/server call signaling protocol intended to be an alternative to H.323. A call signaling protocol is responsible for the setup, maintenance, and teardown of a voice call. For example, call signaling protocols can detect and report when a phone is offhook.Although a few third party IP phones support SCCP, Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is more widely supported on non Cisco IP phones. SIP is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol that is supported by a wide variety of IP telephony vendors. SIP can be supported by Cisco IP phones with a firmware replacement.
SIP uses a text based signaling method, which is easier to understand and troubleshoot than the binary method used by other protocols, such as SCCP and H.323. For example, SIP uses text based INVITE requests and ACK requests to invite a user to participate in a call and to acknowledge that user’s response to the INVITE, respectively. Although SIP is typically used as a peertopeer call signaling protocol, it can also operate in client/server mode. SIP is most commonly used by Internet telephony service providers (ITSPs). Therefore, many nonCisco IP phones and video phones are SIP phones.
Neither Cisco IP phones nor third party IP phones typically use H.323. H.323 is an International Telecommunication Union (ITU)standard, peertopeer call signaling protocol. Peertopeer call signaling protocols do not require a call processing platform, because the voice gateways provide their own call signaling and call routing. Therefore, you would be more likely to register a nonCisco SIP IP phone than an H.323 IP phone with UCM. Although UCM supports H.323, Cisco IP phones do not, because H.323 consumes a large amount of processor and memory resources.
Neither Cisco IP phones nor thirdparty IP phones typically use Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP). MGCP is a client/server call signaling protocol. MGCP is an IETF standard protocol that can be used on some Cisco IP phones with a firmware replacement. -
Which of the following best describes Connection Reports Data Harvester? (Select the best answer.)
- It synchronizes existing users with LDAP directory services.
- It enables administrators to import or modify users by using CSV files.
- It is the service required for Unity Connection report generation.
- It is the feature that an administrator can use to automatically populate certain settings of a new user account in Unity Connection.
Explanation:
Connection Reports Data Harvester is the service required for Cisco Unity Connection report generation. Unity Connection reports can be accessed in Cisco Unified Serviceability, which enables an administrator to view reports and manage other Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) features. Unity Connection is a voice messaging product that is typically installed as an appliance. Cisco Unified Serviceability is a browser based troubleshooting tool that uses Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) to access information that is provided by other reporting tools, such as Cisco Unified Real Time Monitoring Tool (RTMT) and Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) tool.
The Connection Reports Data Harvester service allows data to be collected from log files and entered into the Cisco Unified Serviceability Reports Archive, which holds information from which reports can be generated. You can verify that the Connection Reports Data Harvester service is running by clicking Navigation > Cisco Unified Serviceability from within the UCM graphical user interface (GUI) and then clicking Service Management from the Tools menu. The Connection Reports Data Harvester service can be found under Optional Services. If the service is deactivated, you can click Activate to turn it on.
The Bulk Administration Tool (BAT), not the Connection Reports Data Harvester, enables administrators to import or modify users by using commaseparated values (CSV) files. For example, to use the BAT to modify the voice mail message length limit, you could export the voice mail users to a CSV file, change the message length limit value for each user in the CSV file, and then import the CSV file again. You can access the BAT by clicking Tools> Bulk Administration Tool in the Unity Connection GUI.
The Cisco Directory Synchronization (DirSync) service, not the Connection Reports Data Harvester, synchronizes existing Unity Connection users with Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory services, such as Microsoft Active Directory. To enable Unity Connection to synchronize with an LDAP directory, you must select the Cisco DirSync check box in the Directory Services area of the Unity Connection GUI. In addition, you can import new users from LDAP by either using the BAT to import a CSV file or by using the Users > Import Users tool to import into Unity Connection LDAP information that was previously imported into UCM. Because Unity Connection stores users locally, a user that is synchronized with Unity Connection from LDAP will continue to be stored locally even if that user is later deleted from the LDAP database.
A user template, not the Connection Reports Data Harvester, is the feature that an administrator can use to automatically populate certain settings of a new user account in Unity Connection. Templates are created in Unity Connection by clicking Templates > User Templates and then clicking Add New. Next, you should choose an existing template to use as the base for the new template. The template you choose as the base template can be one of the Unity Connection default templates, such as the Voicemail User Template or the Administrator Template, or a custom template that you have previously configured. The new template will inherit all the settings of the base template except for settings that are unique to each template, such as the template alias and display name. -
Which of the following best describes jitter? (Select the best answer.)
- serialization delay
- variation in delay
- end-to-end delay
- dropped packets
- flapping links
Explanation:
Jitter is a variation in delay, which can cause packets to arrive out of sequence or at a different rate than they were sent. Voice over IP (VoIP) traffic is heavily affected by jitter because voice traffic is time sensitive and requires that the destination host receive the voice traffic in the order, and at the same rate, it was sent. When jitter is present, the end user might experience choppiness in the audio connection. A dejitter buffer at the destination is used to collect packets, sort them into the proper sequence based on Realtime Transport Protocol (RTP) time stamps, and release them to the voice application. Although a dejitter buffer can decrease jitter, it can increase delay as packets sit in the buffer. Jitter can be mitigated by increasing bandwidth, using Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms to prioritize time sensitive traffic, using Compressed RTP (cRTP) to compress headers, and using Stacker and Predictor to compress payloads.Jitter is not dropped packets, nor is it caused by dropped packets. Congested networks often cause dropped packets. Dropped packets can cause clips, or breaks, in the audio stream. However, voice traffic is more tolerant of dropped packets than of delayed packets, because a small amount of packet loss is not noticeable to the human ear. Packet loss can be mitigated by implementing QoS and congestion avoidance mechanisms, increasing bandwidth, and increasing buffer space. In addition, some codecs can correct small amounts of packet loss.
Jitter is not serialization delay. Serialization delay is the time required to place a packet onto a medium, such as a copper or fiberoptic cable. Serialization delay is directly related to the clocking method and the bandwidth of the line.
Jitter is not endtoend delay. Endtoend delay is the sum of the processing, queuing, serialization, and propagation delays in the traffic path between the source of the packet and the destination of the packet. Therefore, the total network delay between the source of the packet and its destination is considered endto-end delay. Endtoend delay can be mitigated by QoS mechanisms.
Jitter is not flapping links, although jitter can be caused by a flapping link. A flapping link is an interface that alternates between enabled and disabled, often because of a faulty cable or network card. Flapping links can cause packets to take different routes through a network, which can introduce jitter and packet loss. -
You want to configure a shared line configuration whereby two phones will ring simultaneously when a caller dials extension 301.
Which of the following command sets should you issue? (Select the best answer.)
-
CME(config)#ephonedn 21 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephonedn 22 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 1 CME(configephone)#button 1:21 2:22
-
CME(config)#ephonedn 21 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephonedn 22 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 1 CME(configephone)#button 1:21 CME(configephone)#ephone 2 CME(configephone)#button 1:22
-
CME(config)#ephonedn 21 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#preference 1 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 1 CME(configephone)#button 1:21 CME(configephone)#ephone 2 CME(configephone)#button 2:21
-
CME(config)#ephonedn 21 dualline CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 2 CME(configephone)#button 1:21
Explanation
You should issue the following command set to configure a shared line configuration whereby two phones will ring simultaneously when a caller dials extension 301:CME(config)#ephonedn 21 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#preference 1 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 1 CME(configephone)#button 1:21 CME(configephone)#ephone 2 CME(configephone)#button 2:21
The ephonedn 21 command creates ephonedn 21. The number 301 command
associates extension 301 with ephonedn 21. The ephone 1 command creates ephone 1, and the ephone 2 command creates ephone 2. The button 1:21 command associates button 1 on ephone 1 with ephonedn 21; similarly, the button 2:21 command associates button 2 on ephone 2 with ephonedn 21.
When multiple ephones are configured with the same extension number, as they are in this scenario, they are configured as shared lines. When a caller dials extension 301, ephonedn 21 will be matched and all of the ephones that are associated with ephonedn 21 will ring.
The preference 1 command is irrelevant to this configuration. The preference command is used to indicate the order in which ephone dns are selected when multiple ephonedns are configured with the same extension number. However, in this scenario, there is only one ephonedn.
It is also possible to configure phones with a shared line when those phones are registered with Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) instead of Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express (CME). To configure a shared line in UCM Administration, navigate to the phones on which you want to share the line and add the directory number (dn) for the shared line. For example, if User 1 has a primary dn of 2401 and User 2 has a primary dn of 2402, you can configure 2401 as a shared line by adding it as another dn on the User 2 phone.
You should not issue the following command set to configure a shared line configuration whereby two phones will ring simultaneously when a caller dials extension 301:CME(config)#ephonedn 21 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephonedn 22 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 1 CME(configephone)#button 1:21 2:22
This configuration has one ephone with two ephonedns. The button 1:21 2:22command associates button 1 with ephonedn 21 and button 2 with ephonedn 22. Because the ephonedns are not configured with the preference command, they will use the default preference value of 0. Both preference values are the same, so when a call is placed to extension 301, either ephonedn 21 or ephonedn 22 will be selected randomly. Therefore, either button 1 or button 2 on ephone 1 will ring.
You should not issue the following command set to configure a shared line configuration whereby two phones will ring simultaneously when a caller dials extension 301:CME(config)#ephonedn 21 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephonedn 22 CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 1 CME(configephone)#button 1:21 CME(configephone)#ephone 2 CME(configephone)#button 1:22
This configuration has two ephones, each with its own ephonedn. Button 1 of ephone 1 is associated with ephonedn 21, and button 1 of ephone 2 is associated with ephonedn 22. The ephonedns are not configured with the preference command, so they will use the default preference value of 0. As a result, either ephone-dn 21 or ephonedn 22 will be selected at random when a call is placed to extension 301, and only one phone will ring.
You should not issue the following command set to configure a shared line configuration whereby two phones will ring simultaneously when a caller dials extension 301:
CME(config)#ephonedn 21 dualline CME(configephonedn)#number 301 CME(configephonedn)#ephone 2 CME(configephone)#button 1:21
This is a dualline configuration with one ephone associated with one ephonedn. An ephonedn configured with the dualline keyword is capable of handling two calls simultaneously, thereby enabling the ephonedn to support call waiting, call conferencing, and consult transfers. The button 1:21 command associates button 1 of ephone 2 with ephonedn 21. When a call is placed to extension 301 while ephonedn 21 is in use, the receiver will hear a call waiting beep.
-
-
Which of the following is not a valid device name for a Cisco Unified Client Services Framework softphone device in UCM? (Select the best answer.)
- UPCJPUBLIC
- UPCJoanPublic
- JOANPUBLICUPC
- UPCJPSOFTPHONE
- JPUBLICSOFTPHONE
Explanation:
JPUBLICSOFTPHONE is not a valid device name for a Cisco Unified Client Services Framework softphone device in Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), because JPUBLICSOFTPHONE contains more than 15 characters. Neither the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type name nor the Cisco Unified Client Services Framework device type name can contain more than 15 characters. The Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type name can contain uppercase letters and numbers. By contrast, Cisco Unified Client Services Framework device type names can contain uppercase letters, lowercase letters, and numbers.
There are five steps to configuring an end user for Cisco Unified Personal Communicator:
1.Assign the user a license in UCM.
2.Create the end user in UCM.
3.Create the Client Services Framework device.
4.Associate the Client Services Framework device to the end user.
5.Associate a directory number (dn) to the end user.The Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type naming convention requires that the name begin with the letters UPC and be derived from the UCM user name. For example, if you were to configure the user Joan Public with a UCM user name of jpublic, the softphone device name associated with the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type would be UPCJPUBLIC. Similarly, the user name of j_public or j.public would have an associated softphone device name of UPCJPUBLIC. If two UCM user names are similar enough to result in identical softphone device names, softphone registration problems can occur in UCM. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator naming convention when you are assigning user names and configuring softphone devices. The Cisco Unified Client Services Framework device type name has no such naming convention.
A softphone is software that behaves like a phone, enabling a user to have voice conversations over a typical workstation network connection. Softphone mode is an operational mode that Unified Personal Communicator uses to act as a softphone. In order to use Unified Personal Communicator as a softphone with UCM, you must add a device to UCM that enables the registration of Unified Personal Communicator in softphone mode. You can configure a softphone device in UCM by clicking Device > Phone > Add New in the UCM administrative graphical user interface (GUI) and selecting either Cisco Unified Personal Communicator or Cisco Unified Client Services Framework from the Phone Type dropdown field. You must configure the Phone Type field with Cisco Unified Personal Communicator if the user is using Unified Personal Communicator version 7.0. You must configure the Phone Type field with Cisco Unified Client Services Framework if the user is using Unified Personal Communicator version 8.0 or later.
UPCJPUBLIC is a valid device name for both Cisco Unified Client Services Framework soft phone devices and Cisco Unified Personal Communicator softphone devices in UCM. The UPCJPUBLIC device name conforms to all the naming convention requirements of Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device types. Similarly, UPCJPSOFTPHONE is a valid device name for both softphone device types, provided that the UCM user name associated with the Cisco Unified Personal Communicator device type is jpsoftphone or something similar.
UPCJoanPublic is a valid device name for Cisco Unified Client Services Framework softphone devices in UCM because that device type allows lowercase letters. However, UPCJoanPublic is not a valid device name for Cisco Unified Personal Communicator devices, because that device type requires uppercase letters.
JOANPUBLICUPC is a valid device name for Cisco Unified Client Services Framework softphone devices in UCM because that device type has no naming convention that requires UPC to be at the front of the device name. However, JOANPUBLICUPC is not a valid device name for Cisco Unified Personal Communicator devices, because that device type has a naming convention that requires that device names begin with UPC. -
Which of the following protocols typically listens on TCP port 389? (Select the best answer.)
- LDAP
- SCCP
- SIP
- XMPP
Explanation:
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) listens on Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port 389 unencrypted. LDAP Secure (LDAPS) listens on TCP port 636 over Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). LDAP is a directory protocol that is used by other servers, such as Cisco Unified Presence (CUPS) to perform contact lookups.
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)standard call signaling protocol. Although SIP is typically used as a peertopeer call signaling protocol, it can also operate in client/ server mode. SIP is used for call signaling between Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) and thirdparty IP phones, or between UCM and Cisco SIPenabled IP phones. SIP is supported on Cisco IP phones with a firmware replacement.
Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) is a Ciscoproprietary, client/server call signaling protocol. SCCP must be used with a Cisco call processing platform, such as UCM, because SCCP is proprietary to Cisco. The firmware on Cisco IP phones is configured to use SCCP by default. SCCP must be used on Cisco IP phones to enable the phones to use Cisco’s full Voice over IP (VoIP) feature set.
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) is an open Extensible Markup Language (XML) instant messaging (IM) and presence protocol. CUPS uses XMPP to communicate with thirdparty IM clients -
Which of the following can administrators display by clicking Device Reports > Gatewayin the CAR GUI? (Select the best answer.)
- the Gateway Detail report
- the Gateway Summary report
- the Gateway Utilization report
- any of the Gateway device reports
Explanation:
Administrators can display any of the gateway reports by clicking Device Reports > Gateway in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM) Call Detail Records (CDR) Analysis and Reporting (CAR) graphical user interface (GUI). CAR provides three privilege levels for reporting: administrators, managers, and individual users. Only administrators are permitted to view Gateway device reports.
The Gateway Detail report can be used to examine issues with a specific gateway. The Gateway Summary report can be used to examine a summary of every call that was transmitted through the gateways. Therefore, the Gateway Summary report can be used to monitor traffic and Quality of Service (QoS). The Gateway Utilization report can be used to determine whether a given gateway or gateways are over utilized. Therefore, you can use the Gateway Utilization report to determine whether new gateways need to be added to the network. -
You issue the following commands on a Cisco voice router:
voice translation-rule 1
rule 1 /^615/ //
voice translation-profile VCE
translate called 1
dia-lpeer voice 101 pots
translation-profile incoming VCE
direct-inward-dial
port 1/0:21
Which of the following will occur when you issue the test voice translation-rule 1 6155550121 command from privileged EXEC mode? (Select the best answer.)
- The number will not change, because 615 is at the beginning of the string.
- The digits 615 will be stripped from the beginning of the string.
- An error will occur because the command syntax is not correct.
- The digits 615 will be added to the beginning of the string.
Explanation:
The digits 615 will be stripped from the beginning of the string when you issue the test voice translation rule 1 6155550121 command in this scenario. The command set in this scenario creates a voice translation rule with an ID of 1 that is then attached to a voice translation profile named VCE. The translation profile is then associated with plain old telephone service (POTS) dial peer 101 in the inbound direction.
The voice translationrule 1 command creates a voice translation rule with an ID of 1. The rule 1 /^615/ // command creates the first rule within voice translation rule 1. The first two slash marks in a translation rule contain the regular expression pattern that is to be matched within the string. In this scenario, the ^615 within the first set of slashes creates a pattern that matches the digits 615 as long as those digits are anchored at the beginning of the string.
The second set of slashes in the rule 1 command represents the values with which the rule should replace the matched digits. In this scenario, no value has been placed between the second set of slashes in the command. Therefore, the rule is designed to simply remove the digits 615 from the beginning of the string.
However, a voice translation rule alone will not automatically strip the digits. Voice translation rules must be applied to voice translation profiles. In this scenario, the following set of commands creates a voice translation profile named VCE and applies voice translation rule 1 to the profile:
voice translation-profile VCE
translate called 1After the voice translation profile has been created, the profile must be associated with a dial peer and applied in the appropriate direction. The following set of commands performs these actions:
dialpeer voice 101 pots
translationprofile incoming VCE
directinwarddial
port 1/0:21By using voice translation rules and voice translation profiles, a company that wants the local area code stripped from any incoming local calls can create a voice translation rule that matches the digits of the area code within the incoming Automatic Number Identification (ANI) string and replaces those digits with nothing. Performing this operation thus reduces the size of the string from 10 digits to seven.
-
Which of the following statements best describes DiffServ? (Select the best answer.)
- It prioritizes packets by traffic class.
- It is not a QoS model that is recommended by Cisco for voice traffic.
- It requires applications to reserve their endtoend bandwidth requirements.
- It is a traffic policing mechanism for when traffic exceeds minimum bandwidth limits.
Explanation:
Differentiated Services (DiffServ) is a Quality of Service (QoS) model that prioritizes packets by traffic class. QoS enables a network to treat a specific type of traffic with a different priority than other types of traffic. For example, QoS can ensure that voice traffic gets higher priority on a network than data traffic. QoS models include the besteffort model, the Integrated Services (IntServ) model, and the DiffServ model. Each QoS model handles packet flows in a different manner.
IntServ, not DiffServ, requires that applications reserve their endtoend bandwidth requirements. In addition, IntServ is not the QoS model that is recommended by Cisco. Cisco recommends using DiffServ instead of other QoS models when configuring QoS for voice traffic.
Committed Access Rate (CAR) is a traffic policing mechanism that you can use when traffic exceeds the configured bandwidth limitations. When CAR is used, packets that exceed the bandwidth limits are re-marked with a lower priority and forwarded instead of being dropped. -
All of your department’s IP phones are connected to a switch that does not support PoE. The IP phones have all been manually configured with IP addressing information. Another administrator power cycles the switch without warning. No calls are in progress.
Which of the following is most likely to occur? (Select the best answer.)
- The IP phones will power down until the switch restarts.
- The IP phones will not be affected by the power cycle.
- The IP phones will disappear from the UCM configuration.
- The IP phones will reset but retain IP configuration information.
Explanation:
Most likely, the IP phones will reset but retain IP configuration information when the administrator power cycles the switch because, in this scenario, the IP addressing information has been manually configured on each IP phone. When an IP phone is disconnected from Cisco Unified Communications Manager (UCM), the phone will automatically reset in an attempt to reestablish communication. Therefore, if an IP phone suddenly resets or is continuously attempting to register with UCM, it is important to first verify the phone’s connectivity to the network switch.
The IP phones will not disappear from the UCM configuration. You can verify that an IP phone exists in the UCM by clicking Device > Phone > Find in UCM Administration and searching for the particular IP phone’s Media Access Control (MAC) address. The IP phone will no longer be registered with UCM when it loses connectivity. However, the IP phone’s record in the UCM configuration will remain there.
The IP phones will not power down until the switch restarts, because the switch in this scenario does not support Power over Ethernet (PoE). Therefore, the IP phones in this scenario must be connected to individual power supplies in order to obtain power.
The IP phones will be affected by the power cycle. In addition to registration problems, IP configuration problems, and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) configuration problems, IP phones that are powered directly from a switch by using PoE will not be able to receive power until the switch has restarted.