CCSK Module 1 Unit 3 Answers – Cloud Essential Characteristics Knowledge Check Quiz Full 100% 2023 2024
This is CCSK Module 1 Unit 3 Answers – Cloud Essential Characteristics Knowledge Check Quiz. Our expert team has verified questions and answers with clear explanations to get a full score of 100%. You can review all these questions before taking the exam.
-
Click and drag the correct NIST model element to the appropriate category below.
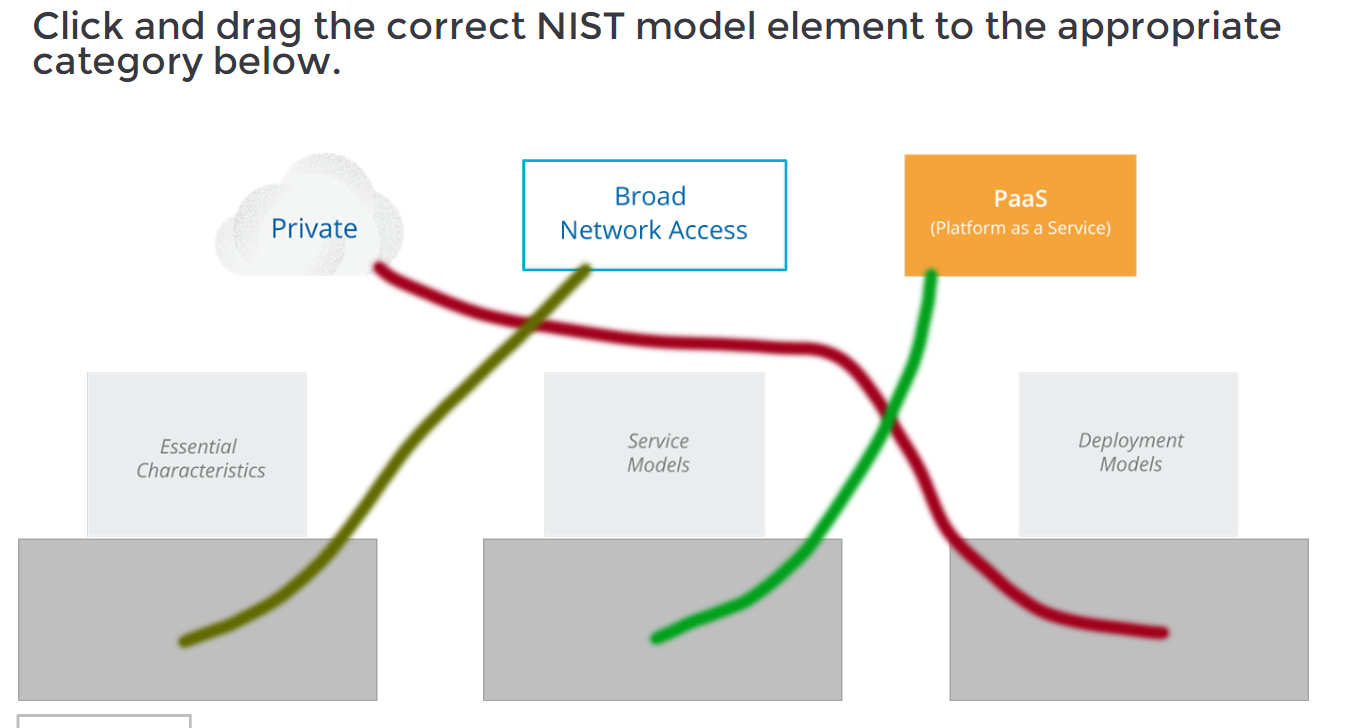
CCSK Module 1 Unit 3 Answers – Cloud Essential Characteristics Knowledge Check Quiz 001 Answers Explanation & Hints:
Private – Deployment Models: Private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization or entity. It is not shared with other organizations and offers more control and privacy over data and resources.
Broad Network Access – Essential Characteristics: Broad Network Access is one of the essential characteristics of cloud computing. It refers to the ability to access cloud services and resources over a network, typically the internet, using standard protocols and devices. It ensures that cloud services are accessible from a wide range of devices and platforms.
PaaS – Service Model: PaaS stands for Platform as a Service, which is a cloud computing service model. In the PaaS model, cloud providers offer a platform that includes the infrastructure, runtime environment, and development tools for building, testing, and deploying applications. It allows developers to focus on application development without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
In summary:
- Private is a deployment model.
- Broad Network Access is an essential characteristic.
- PaaS is a service model.
-
Services scaling out and scaling in quickly are an example of which essential characteristics of cloud.
- Measured Service
- Resource Pooling
- Rapid Elasticity
- Broad Network Access
- On-Demand Self Service
-
Answers Explanation & Hints:
The example you provided, services scaling out and scaling in quickly, is an example of the essential characteristic of cloud called “Rapid Elasticity.”
Rapid Elasticity refers to the ability of cloud resources to quickly and automatically scale up or down based on demand. It allows organizations to rapidly provision and release resources as needed, ensuring that the system can handle fluctuations in workload efficiently. In the case of services scaling out, additional resources are allocated to accommodate increased demand, while scaling in involves reducing resources when demand decreases. This elasticity enables cost optimization and ensures that applications or services can effectively handle varying levels of usage without any manual intervention.
To summarize, the ability to scale services quickly, both up and down, is an example of the essential characteristic of cloud known as Rapid Elasticity.
-
Click and drag the Essential Characteristics to the box below.
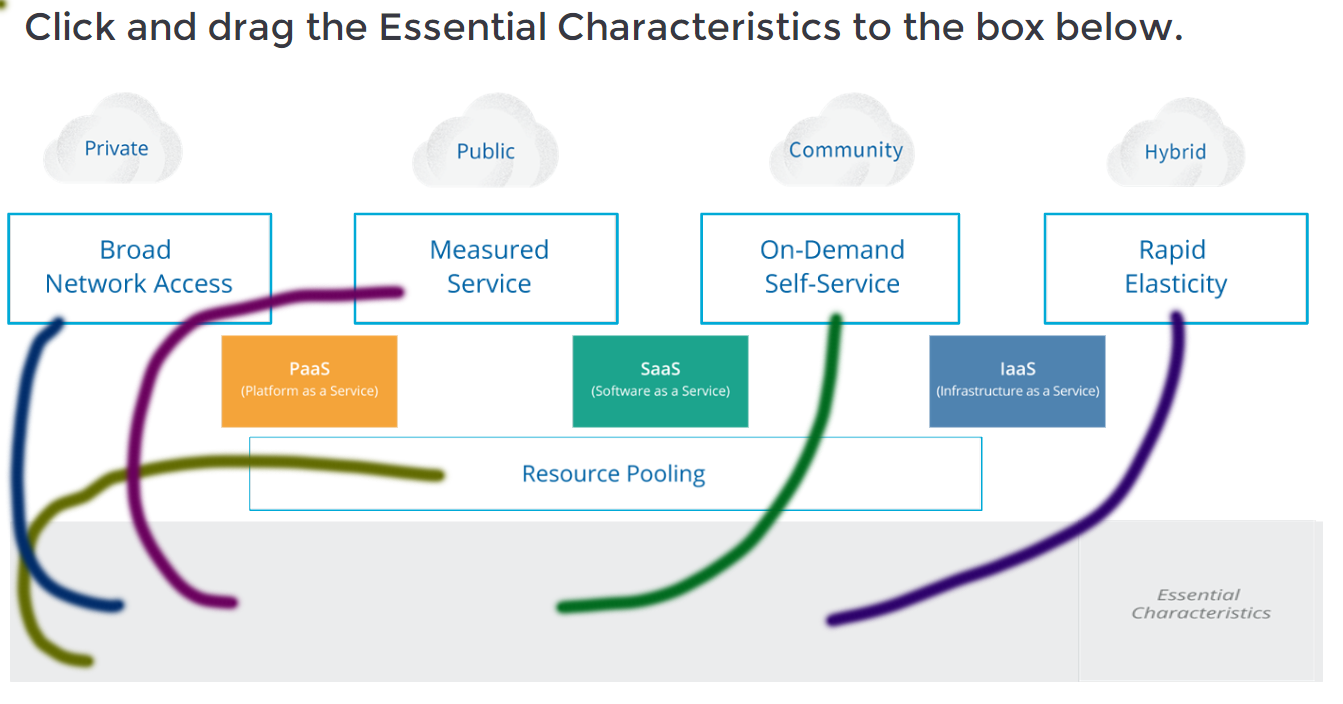
CCSK Module 1 Unit 3 Answers – Cloud Essential Characteristics Knowledge Check Quiz 002 -
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Here’s the matching of the given terms with the corresponding essential characteristics of cloud computing:
Private – Deployment Models Public – Deployment Models Community – Deployment Models Hybrid – Deployment Models Broad Network Access – Essential Characteristics Measured Service – Essential Characteristics On-Demand Self-Service – Essential Characteristics Rapid Elasticity – Essential Characteristics PaaS – Service Models SaaS – Service Models IaaS – Service Models Resource Pooling – Essential Characteristics
Explanation:
Private – Deployment Models: Private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization or entity. It is not shared with other organizations and offers more control and privacy over data and resources.
Public – Deployment Models: Public cloud refers to a cloud computing environment where services and resources are made available to the general public over the internet. It is owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers.
Community – Deployment Models: Community cloud refers to a cloud computing environment shared by several organizations with shared interests or requirements. It is managed and used by a community of organizations that have similar goals, such as industry-specific regulations or security requirements.
Hybrid – Deployment Models: Hybrid cloud refers to a combination of two or more cloud deployment models, such as private and public clouds, that remain distinct entities but are interconnected. It allows organizations to leverage the benefits of both private and public clouds and facilitates data and application portability.
Broad Network Access – Essential Characteristics: Broad Network Access is one of the essential characteristics of cloud computing. It refers to the ability to access cloud services and resources over a network, typically the internet, using standard protocols and devices. It ensures that cloud services are accessible from a wide range of devices and platforms.
Measured Service – Essential Characteristics: Measured Service is an essential characteristic of cloud computing that involves automatically measuring and monitoring resource usage. It enables cloud providers to optimize resource allocation, track usage for billing purposes, and provide transparency to customers.
On-Demand Self-Service – Essential Characteristics: On-Demand Self-Service is an essential characteristic that allows users to provision and manage cloud resources automatically without requiring interaction with cloud providers. Users can access and deploy resources as needed, such as virtual machines or storage, without manual intervention.
Rapid Elasticity – Essential Characteristics: Rapid Elasticity is an essential characteristic that enables cloud resources to quickly and automatically scale up or down based on demand. It allows organizations to rapidly provision and release resources as needed, ensuring efficient handling of workload fluctuations.
PaaS – Service Models: Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a service model where cloud providers offer a platform that includes the infrastructure, runtime environment, and development tools for building, testing, and deploying applications. It allows developers to focus on application development without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
SaaS – Service Models: Software as a Service (SaaS) is a service model where cloud providers offer software applications and services over the internet. Users can access and use the software applications without needing to install or manage them locally.
IaaS – Service Models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a service model where cloud providers offer virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks, over the internet. Users can manage and control these resources while leaving the underlying infrastructure management to the cloud provider.
Resource Pooling – Essential Characteristics: Resource Pooling is an essential characteristic that involves the aggregation of computing resources, such as processing power, storage, or network bandwidth, to serve multiple users or tenants. It allows for efficient utilization and sharing of resources among different users, often through virtualization techniques.
In summary:
- Private, Public, Community, and Hybrid are deployment models.
- Broad Network Access, Measured Service, On-Demand Self-Service, and Rapid Elasticity are essential characteristics.
- PaaS, SaaS, and IaaS are service models.
- Resource Pooling is an essential characteristic.
-
-
Which of the following is not an emergent property of resource pooling?
- Broad Network Access
- Segmentation
- Isolation
- Governance
-
Answers Explanation & Hints:
Among the options provided, “Broad Network Access” is not an emergent property of resource pooling.
Resource pooling is an essential characteristic of cloud computing where a provider’s computing resources are shared among multiple users, typically through virtualization techniques. It allows users to access and utilize a common pool of computing resources, such as processing power, storage, or network bandwidth.
Emergent properties of resource pooling refer to the characteristics that arise from the pooling of resources. These properties include:
- Segmentation: Resource pooling enables logical separation or segmentation of resources, allowing different users or applications to have their own isolated environments within the shared infrastructure.
- Isolation: Resource pooling provides mechanisms to ensure isolation between different users or tenants utilizing the shared resources. It ensures that one user’s activities or performance do not impact the resources or performance of other users.
- Governance: Resource pooling includes governance mechanisms that govern the allocation, management, and monitoring of the shared resources. This includes policies, rules, and controls to ensure fair and efficient utilization of resources among multiple users.
On the other hand, “Broad Network Access” is not an emergent property of resource pooling. Broad Network Access is an essential characteristic of cloud computing itself, which allows users to access cloud services and resources over a network, typically the internet, using standard protocols and devices. It is not a property that emerges from resource pooling specifically but is a fundamental feature of cloud computing as a whole.