CCSK Module 1 Unit 6 Answers – Shared Responsibilities Knowledge Check Quiz Full 100% 2023
-
In which service model does the cloud consumer have the least amount of control over security?
- Platform as a Service
- Security as a Service
- Infrastructure as a Service
- Software as a Service
Answers Explanation & Hints:
In the service model where the cloud consumer has the least amount of control over security, it is typically Software as a Service (SaaS).
In a SaaS model, the cloud provider delivers software applications over the internet, and the consumer accesses and uses the software through a web browser or a thin client interface. In this model, the cloud consumer has limited control over the underlying infrastructure, network, and security configurations. The provider is responsible for managing and securing the application, including infrastructure, platform, and software stack.
While the consumer can control certain aspects related to user access, data management, and application-specific security settings, they have less control over the overall security architecture, infrastructure-level security controls, and backend systems. These aspects are managed and maintained by the cloud provider.
On the other hand, in Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), the cloud consumer has more control over security compared to SaaS. In IaaS, the consumer has access to virtualized infrastructure resources, such as servers, storage, and networking components, and they can configure and manage security measures at the infrastructure level.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) falls between SaaS and IaaS in terms of control over security. In PaaS, the cloud consumer has control over the applications and data they develop and deploy on the platform, but the provider is responsible for managing the underlying infrastructure and security controls related to the platform.
Security as a Service (SecaaS) refers to security-related services provided by a third-party cloud provider. While the consumer may rely on the provider for security services, they can still have control over configuring and managing security settings within their own infrastructure and applications.
-
In which cloud service model is the cloud consumer responsible for ensuring that the hypervisor is not vulnerable to attack?
- Software as a Service
- None of the above
- Infrastructure as a Service
- Platform as a Service
-
Answers Explanation & Hints:
If none of the provided options is correct, then it means there isn’t a specific cloud service model where the cloud consumer is responsible for ensuring the hypervisor’s security.
In traditional cloud service models, such as Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), the responsibility for securing the hypervisor typically lies with the cloud provider. They are responsible for ensuring the security and integrity of the underlying infrastructure, including the hypervisor.
If none of the options provided align with your scenario, it may be a specialized or unique deployment model where the responsibility for hypervisor security differs from the typical cloud service models. In such cases, it is important to clarify the specific context or deployment model to provide a more accurate response.
-
When should you define the security controls when building a cloud deployment?
- Before determining the service and deployment models
- Before selecting the provider
- After identifying requirements
- After identifying control gaps
-
Answers Explanation & Hints:
To clarify, the correct order of steps is to define security controls after identifying control gaps, not before.
The revised sequence is as follows:
- Identify Requirements: Understand the organization’s specific security requirements, compliance obligations, data protection needs, and risk tolerance.
- Determine Service and Deployment Models: Based on the requirements, determine the appropriate service and deployment models that align with the organization’s needs.
- Select Provider: Once the service and deployment models are determined, select a cloud service provider that meets the organization’s requirements.
- Identify Control Gaps: After selecting the provider, assess the control gaps between the organization’s desired security controls and the controls provided by the cloud service provider. Identify any additional security measures or controls that need to be implemented to bridge these gaps.
- Define Security Controls: After identifying the control gaps, define the necessary security controls that address the identified gaps and align with the organization’s requirements. This includes determining measures such as network security, access controls, encryption, data protection, vulnerability management, and incident response.
By following this revised sequence, organizations can identify any gaps between their desired security controls and the controls provided by the cloud service provider. They can then define and implement the necessary security controls to address these gaps and ensure the security of their cloud deployment.
-
Click and drag the items to the correct category.
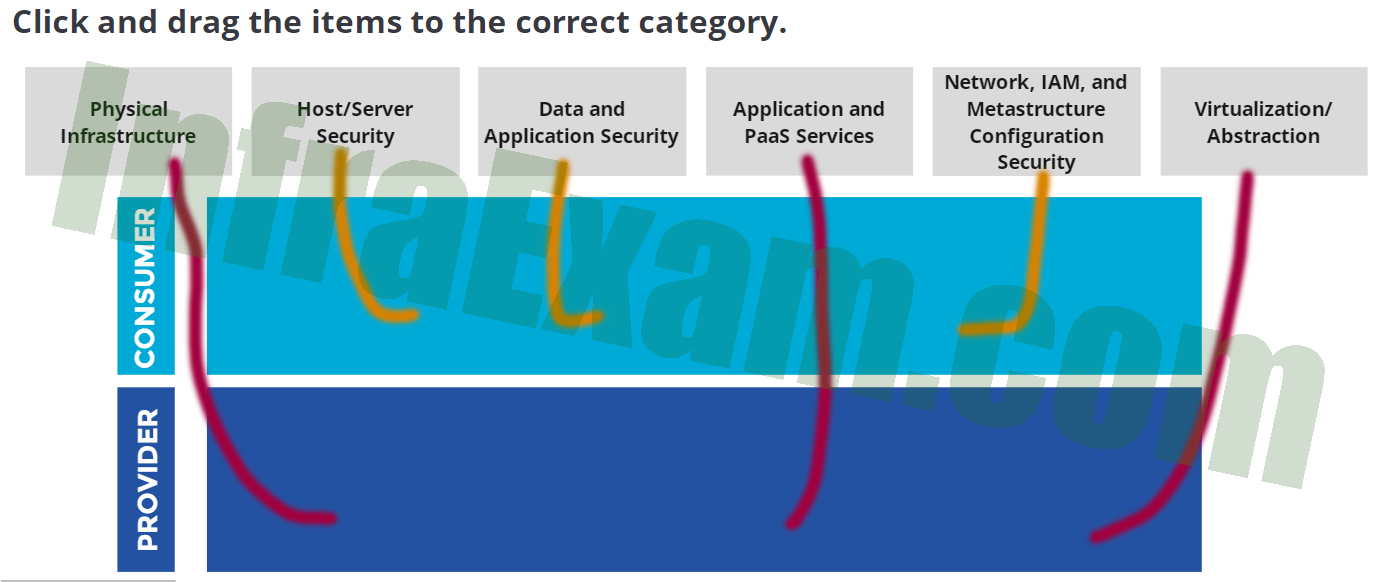
CCSK Module 1 Unit 5 Answers – Shared Responsibilities Knowledge Check Quiz 001 -
Answers Explanation & Hints:
- Host/Server Security: The responsibility for securing the underlying hosts and servers that run the cloud infrastructure and services typically lies with the cloud consumer. They are responsible for ensuring the security of the virtual machines (VMs) or servers they deploy and configure within the cloud environment.
- Data and Applications Security: The security of data and applications is primarily the responsibility of the cloud consumer. They are responsible for implementing appropriate security measures to protect their data, including encryption, access controls, and application-level security.
- Network, IAM, and Metastructure Configuration Security: The consumer is responsible for configuring and managing the network, Identity and Access Management (IAM), and metastructure components within the cloud environment. This includes setting up firewalls, managing user access and permissions, and securing the overall configuration of the cloud infrastructure.
- Physical Infrastructure: The responsibility for securing the physical infrastructure, including data centers, servers, networking equipment, and storage devices, typically lies with the cloud provider. They are responsible for implementing physical security measures to protect the infrastructure.
- Application and PaaS Services: The provider is responsible for securing the application and platform services offered to the consumer as part of the Platform as a Service (PaaS) model. This includes ensuring the availability, integrity, and security of the PaaS environment.
- Virtualization/Abstraction: The provider is responsible for securing the virtualization or abstraction layer that enables the creation and management of virtual resources in the cloud infrastructure.
Please note that the division of security responsibilities may vary depending on the specific cloud service models, deployment models, and the terms outlined in the service-level agreements (SLAs) between the consumer and provider.
-