H12-211 : HCIA Routing & Switching : Part 21
-
If the IPv4 address of a host on a local area network (LAN) is 192.168.1.1/30, which of the following destination IPv4 addresses can be carried in data packets that the host can decapsulate?
- 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.2
- 192.168.1.3
- 255.255.255.255
-
Which of the following statements are true about the blackhole MAC address table?
- Entries are manually configured and delivered to each interface card. The entries cannot be aged out.
- After a device is reset, an interface card is hot swapped, or an interface card is reset, the saved entries on the device or interface card are not lost.
- After a blackhole MAC address is configured on a device, the device discards packets whose source or destination MAC address is the blackhole MAC address.
- Blackhole MAC address entries can be used to filter out unauthorized users.
-
Which of the following fields exist in both IPv6 and IPv4 packet headers?
- Source Address
- Destination Address
- Version
- Next Header
-
Which of the following is/are the characteristic(s) of HDLC?
- HDLC supports point-to-point links.
- HDLC does not support IP address negotiation.
- HDLC does not support authentication.
- HDLC supports point-to-multipoint links.
-
Which of the following types of routes can be used by a router to establish a routing table?
- Direct route
- Dynamic route
- Static route
- Aggregated route
-
On the network shown in the figure, which of the following commands can be used to enable host A to successfully ping host B?
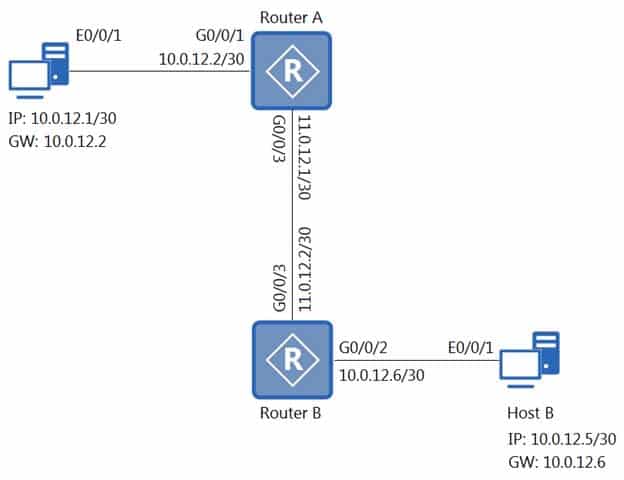
H12-211 HCIA Routing & Switching Part 21 Q06 086 - Router A : ip route-static 10.0.12.5 255.255.255.252 11.0.12.2
Router B : ip route-static 10.0.12.1 255.255.255.252 11.0.12.1 - Router A : ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 11.0.12.2
Router B : ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 11.0.12.1 - Router A : ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 11.0.12.1
Router B : ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 11.0.12.2 - Router A : ip route-static 10.0.12.5 255.255.255.252 11.0.12.1
Router B : ip route-static 10.0.12.1 255.255.255.252 11.0.12.2
- Router A : ip route-static 10.0.12.5 255.255.255.252 11.0.12.2
-
Which of the following packets are OSPF packets?
- HELLO
- LSU
- LSR
- LSA
-
Which of the following port status may exist on an STP-enabled switch?
- Forwarding
- Listening
- Discarding
- Disabled
-
One of the reasons that segment routing (SR) is introduced is that traditional LDP has some restrictions.
Which of the following statements about LDP restrictions are true?
- LDP does not support automatic label allocation.
- LDP supports path computation only based on IGP SPF (minimum cost), not based on traffic engineering.
- LDP path computation depends on an IGP. If the IGP and LDP are not synchronized, black holes are generated, affecting services.
- LDP has 11 types of protocol packets, which greatly increases link bandwidth consumption and device CPU usage.
-
The following shows the command output on a router.
Which of the following statements are true?
display startup
MainBoard:
Startup system software: flash:/AR2220E-V200R007C00SPC600.cc
Next startup system software: flash:/AR2220E-V200R007C00SPC600.cc
Backup system software for next startup: null
Startup saved-configuration file: flash:/vrpcfg.zip
Next startup saved-configuration file: flash:/backup.zip
Startup license file: null
Next startup license file: null
Startup patch package: null
Next startup patch package: null
Startup voice-files: null
Next startup voice-files: null- The current VRP version file is the same as the VRP file for next startup.
- The current VRP version file is different from the VRP file for next startup.
- The current configuration file is the same as the configuration file for next startup.
- The current configuration file is different from the configuration file for next startup.
-
Which of the following statements about Ethernet sub-interfaces is/are true?
- The sub-interface ID must be the same as the VLAN ID.
- A sub-interface can be bound to multiple VLANs.
- The sub-interface cannot be configured with an IP address.
- The IP addresses for sub-interfaces must not be on the same network segment.
-
Which of the following statements are true about the static MAC address table?
- After a device is reset, an interface card is hot swapped, or an interface card is reset, the saved entries on the device or interface card are not lost.
- After an interface is statically bound to a MAC address, other interfaces discarded a packet whose source MAC address is the bound MAC address.
- Each static MAC address entry can be bound only to one outbound interface.
- You can check whether data is forwarded between two connected devices by checking the static MAC address entries.
-
On a network running Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), which of the following ports are in Discarding state when the topology is stable?
- Root port
- Designated port
- Alternate port
- Backup port
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest