CSSLP : Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional : Part 08
-
Which of the following processes describes the elements such as quantity, quality, coverage, timelines, and availability, and categorizes the different functions that the system will need to perform in order to gather the documented mission/business needs?
- Human factors
- Functional requirements
- Performance requirements
- Operational scenarios
Explanation:
The functional requirements categorize the different functions that the system will need to perform in order to gather the documented mission/business needs. The functional requirements describe the elements such as quantity, quality, coverage, timelines, and availability.
Answer: C is incorrect. The performance requirements comprise of speed, throughput, accuracy, humidity tolerances, mechanical stresses such as vibrations or noises. Answer: A is incorrect. Human factor consists of factors, which affect the operation of the system or component, such as design space, eye movement, or ergonomics. Answer: D is incorrect. The operational scenarios provide assistance to the system designers and form the basis of major events in the acquisition phases, such as testing the products for system integration. The customer classifies and defines the operational scenarios, which indicate the range of anticipated uses of system products. -
Which of the following are the benefits of information classification for an organization? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
- It helps reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
- It helps identify which protections apply to which information.
- It helps identify which information is the most sensitive or vital to an organization.
- It ensures that modifications are not made to data by unauthorized personnel or processes.
Explanation:Following are the benefits of information classification for an organization: It helps identify which protections apply to which information. It helps identify which information is the most sensitive or vital to an organization. It supports the tenets of confidentiality, integrity, and availability as it pertains to data.
Answer: D is incorrect. The concept of integrity ensures that modifications are not made to data by unauthorized personnel or processes. It also ensures that unauthorized modifications are not made to data by authorized personnel or processes. Answer: A is incorrect. Information classification cannot reduce the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). -
A number of security patterns for Web applications under the DARPA contract have been developed by Kienzle, Elder, Tyree, and Edwards-Hewitt. Which of the following patterns are applicable to aspects of authentication in Web applications?b Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Authenticated session
- Secure assertion
- Partitioned application
- Password authentication
- Account lockout
- Password propagation
Explanation:The various patterns applicable to aspects of authentication in the Web applications are as follows: Account lockout: It implements a limit on the incorrect password attempts to protect an account from automated password-guessing attacks. Authenticated session: It allows a user to access more than one access-restricted Web page without re-authenticating every page. It also integrates user authentication into the basic session model. Password authentication: It provides protection against weak passwords, automated password-guessing attacks, and mishandling of passwords. Password propagation: It offers a choice by requiring that a user’s authentication credentials be verified by the database before providing access to that user’s data. Answer: B and C are incorrect. Secure assertion and partitioned application patterns are applicable to software assurance in general. -
Which of the following steps of the LeGrand Vulnerability-Oriented Risk Management method determines the necessary compliance offered by risk management practices and assessment of risk levels?
- Assessment, monitoring, and assurance
- Vulnerability management
- Risk assessment
- Adherence to security standards and policies for development and deployment
Explanation:Assessment, monitoring, and assurance determines the necessary compliance that are offered by risk management practices and assessment of risk levels. -
Which of the following NIST Special Publication documents provides a guideline on questionnaires and checklists through which systems can be evaluated for compliance against specific control objectives?
- NIST SP 800-37
- NIST SP 800-26
- NIST SP 800-53A
- NIST SP 800-59
- NIST SP 800-53
- NIST SP 800-60
Explanation:NIST SP 800-26 (Security Self-Assessment Guide for Information Technology Systems) provides a guideline on questionnaires and checklists through which systems can be evaluated for compliance against specific control objectives. Answer: A, E, C, D, and F are incorrect. NIST has developed a suite of documents for conducting Certification & Accreditation (C&A). These documents are as follows:
NIST Special Publication 800-37: This document is a guide for the security certification and accreditation of Federal Information Systems. NIST Special Publication 800-53: This document provides a guideline for security controls for Federal Information Systems. NIST Special Publication 800-53A. This document consists of techniques and procedures for verifying the effectiveness of security controls in Federal Information System. NIST Special Publication 800-59: This document is a guideline for identifying an information system as a National Security System. NIST Special Publication 800-60: This document is a guide for mapping types of information and information systems to security objectives and risk levels. -
To help review or design security controls, they can be classified by several criteria. One of these criteria is based on time. According to this criteria, which of the following controls are intended to prevent an incident from occurring?
- Corrective controls
- Adaptive controls
- Detective controls
- Preventive controls
Explanation:Preventive controls are the security controls that are intended to prevent an incident from occurring, e.g., by locking out unauthorized intruders. Answer: C is incorrect. Detective controls are intended to identify and characterize an incident in progress, e.g., by sounding the intruder alarm and alerting the security guards or police. Answer: A is incorrect. Corrective controls are intended to limit the extent of any damage caused by the incident, e.g., by recovering the organization to normal working status as efficiently as possible. Answer: B is incorrect. There is no such categorization of controls based on time. -
Which of the following processes does the decomposition and definition sequence of the Vee model include? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. Choose all that apply.
- Component integration and test
- System security analysis
- Security requirements allocation
- High level software design
Explanation:Decomposition and definition sequence includes the following processes: System security analysis Security requirements allocation Software security requirements analysis High level software design Detailed software design Answer: A is incorrect. This process is included in the integration and verification sequence of the Vee model. -
A part of a project deals with the hardware work. As a project manager, you have decided to hire a company to deal with all hardware work on the project. Which type of risk response is this?
- Exploit
- Mitigation
- Transference
- Avoidance
Explanation:When you are hiring a third party to own risk, it is known as transference risk response. Transference is a strategy to mitigate negative risks or threats. In this strategy, consequences and the ownership of a risk is transferred to a third party. This strategy does not eliminate the risk but transfers responsibility of managing the risk to another party. Insurance is an example of transference. Answer: B is incorrect. The act of spending money to reduce a risk probability and impact is known as mitigation. Answer: A is incorrect. Exploit is a strategy that may be selected for risks with positive impacts where the organization wishes to ensure that the opportunity is realized. Answer: D is incorrect. When extra activities are introduced into the project to avoid the risk, this is an example of avoidance. -
You work as a security manager for BlueWell Inc. You are performing the external vulnerability testing, or penetration testing to get a better snapshot of your organization’s security posture. Which of the following penetration testing techniques will you use for searching paper disposal areas for unshredded or otherwise improperly disposed-of reports?
- Sniffing
- Scanning and probing
- Dumpster diving
- Demon dialing
Explanation:Dumpster diving technique is used for searching paper disposal areas for unshredded or otherwise improperly disposed-of reports. Answer: B is incorrect. In scanning and probing technique, various scanners, like a port scanner, can reveal information about a network’s infrastructure and enable an intruder to access the network’s unsecured ports. Answer: D is incorrect. Demon dialing technique automatically tests every phone line in an exchange to try to locate modems that are attached to the network. Answer: A is incorrect. In sniffing technique, protocol analyzer can be used to capture data packets that are later decoded to collect information such as passwords or infrastructure configurations. -
What are the differences between managed and unmanaged code technologies? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose two.
- Managed code is referred to as Hex code, whereas unmanaged code is referred to as byte code.
- C and C++ are the examples of managed code, whereas Java EE and Microsoft.NET are the examples of unmanaged code.
- Managed code executes under management of a runtime environment, whereas unmanaged code is executed by the CPU of a computer system.
- Managed code is compiled into an intermediate code format, whereas unmanaged code is compiled into machine code.
Explanation:Programming languages are categorized into two technologies: 1.Managed code: This computer program code is compiled into an intermediate code format. Managed code is referred to as byte code. It executes under the management of a runtime environment. Java EE and Microsoft.NET are the examples of managed code. 2.Unmanaged code: This computer code is compiled into machine code. Unmanaged code is executed by the CPU of a computer system. C and C++ are the examples of unmanaged code. Answer: A is incorrect. Managed code is referred to as byte code. Answer: B is incorrect. C and C++ are the examples of unmanaged code, whereas Java EE and Microsoft.NET are the examples of managed code. -
Which of the following security objectives are defined for information and information systems by the FISMA? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. Choose all that apply.
- Authenticity
- Availability
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
Explanation:FISMA defines the following three security objectives for information and information systems: Confidentiality: It means that the data should only be accessible to authorized users. Access includes printing, displaying, and other such forms of disclosure, including simply revealing the existence of an object. Integrity: It means that only authorized users are able to modify data. Modification admits changing, changing the status, deleting, and creating. Availability: It means that the data should only be available to authorized users. Answer: A is incorrect. Authenticity is not defined by the FISMA as one of the security objectives for information and information systems. -
Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E) is a component of risk assessment. It is useful in discovering system vulnerabilities. For what purposes is ST&E used? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- To implement the design of system architecture
- To determine the adequacy of security mechanisms, assurances, and other properties to enforce the security policy
- To assess the degree of consistency between the system documentation and its implementation
- To uncover design, implementation, and operational flaws that may allow the violation of security policy
Explanation:Security Test and Evaluation (ST&E) is a component of risk assessment. It is useful in discovering system vulnerabilities. According to NIST SP 800-42 (Guideline on Network Security Testing), ST&E is used for the following purposes: To assess the degree of consistency between the system documentation and its implementation To determine the adequacy of security mechanisms, assurances, and other properties to enforce the security policy To uncover design, implementation, and operational flaws that may allow the violation of security policy Answer: A is incorrect. ST&E is not used for the implementation of the system architecture. -
Which of the following describes a residual risk as the risk remaining after a risk mitigation has occurred?
- DIACAP
- SSAA
- DAA
- ISSO
Explanation:DIACAP describes a residual risk as the risk remaining after a risk mitigation has occurred. The Department of Defense Information Assurance Certification and Accreditation Process (DIACAP) is a process defined by the United States Department of Defense (DoD) for managing risk. DIACAP replaced the former process, known as DITSCAP (Department of Defense Information Technology Security Certification and Accreditation Process), in 2006. DoD Instruction (DoDI) 8510.01 establishes a standard DoD-wide process with a set of activities, general tasks, and a management structure to certify and accredit an Automated Information System (AIS) that will maintain the Information Assurance (IA) posture of the Defense Information Infrastructure (DII) throughout the system’s life cycle. DIACAP applies to the acquisition, operation, and sustainment of any DoD system that collects, stores, transmits, or processes unclassified or classified information since December 1997. It identifies four phases: 1.System Definition 2.Verification 3.Validation 4.Re-Accreditation Answer: D is incorrect. An Information System Security Officer (ISSO) plays the role of a supporter. The responsibilities of an Information System Security Officer (ISSO) are as follows: Manages the security of the information system that is slated for Certification & Accreditation (C&A). Insures the information systems configuration with the agency’s information security policy. Supports the information system owner/information owner for the completion of security-related responsibilities. Takes part in the formal configuration management process. Prepares Certification & Accreditation (C&A) packages. Answer: C is incorrect. The Designated Approving Authority (DAA), in the United States Department of Defense, is the official with the authority to formally assume responsibility for operating a system at an acceptable level of risk. The DAA is responsible for implementing system security. The DAA can grant the accreditation and can determine that the system’s risks are not at an acceptable level and the system is not ready to be operational. Answer: B is incorrect. System Security Authorization Agreement (SSAA) is an information security document used in the United States Department of Defense (DoD) to describe and accredit networks and systems. The SSAA is part of the Department of Defense Information Technology Security Certification and Accreditation Process, or DITSCAP (superseded by DIACAP). The DoD instruction (issues in December 1997, that describes DITSCAP and provides an outline for the SSAA document is DODI 5200.40. The DITSCAP application manual (DoD 8510.1-M), published in July 2000, provides additional details. -
You work as a system engineer for BlueWell Inc. You want to verify that the build meets its data requirements, and correctly generates each expected display and report. Which of the following tests will help you to perform the above task?
- Performance test
- Functional test
- Reliability test
- Regression test
Explanation:The various types of internal tests performed on builds are as follows: Regression tests: It is also known as the verification testing. These tests are developed to confirm that capabilities in earlier builds continue to work correctly in the subsequent builds. Functional test: These tests emphasizes on verifying that the build meets its functional and data requirements and correctly generates each expected display and report. Performance tests: These tests are used to identify the performance thresholds of each build. Reliability tests: These tests are used to identify the reliability thresholds of each build. -
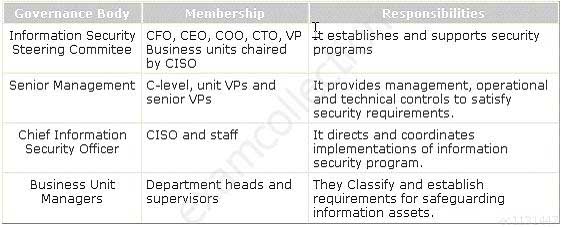
Which of the following governance bodies provides management, operational and technical controls to satisfy security requirements?
- Senior Management
- Business Unit Manager
- Information Security Steering Committee
- Chief Information Security Officer
Explanation: -
The Chief Information Officer (CIO), or Information Technology (IT) director, is a job title commonly given to the most senior executive in an enterprise. What are the responsibilities of a Chief Information Officer? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Facilitating the sharing of security risk-related information among authorizing officials
- Preserving high-level communications and working group relationships in an organization
- Establishing effective continuous monitoring program for the organization
- Proposing the information technology needed by an enterprise to achieve its goals and then working within a budget to implement the plan
Explanation:A Chief Information Officer (CIO) plays the role of a leader. The responsibilities of a Chief Information Officer are as follows: Establishes effective continuous monitoring program for the organization. Facilitates continuous monitoring process for the organizations. Preserves high-level communications and working group relationships in an organization.
Confirms that information systems are covered by a permitted security plan and monitored throughout the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Manages and delegates decisions to employees in large enterprises. Proposes the information technology needed by an enterprise to achieve its goals and then works within a budget to implement the plan. Answer: A is incorrect. A Risk Executive facilitates the sharing of security risk-related information among authorizing officials. -
Which of the following security architectures defines how to integrate widely disparate applications for a world that is Web-based and uses multiple implementation platforms?
- Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture
- Enterprise architecture
- Service-oriented architecture
- Service-oriented modeling and architecture
Explanation:In computing, a service-oriented architecture (SOA) is a flexible set of design principles used during the phases of systems development and integration. A deployed SOA-based architecture will provide a loosely-integrated suite of services that can be used within multiple business domains. SOA also generally provides a way for consumers of services, such as web-based applications, to be aware of available SOA-based services. For example, several disparate departments within a company may develop and deploy SOA services in different implementation languages; their respective clients will benefit from a well understood, well defined interface to access them. XML is commonly used for interfacing with SOA services, though this is not required. SOA defines how to integrate widely disparate applications for a world that is Web-based and uses multiple implementation platforms. Rather than defining an API, SOA defines the interface in terms of protocols and functionality. An endpoint is the entry point for such an SOA implementation.
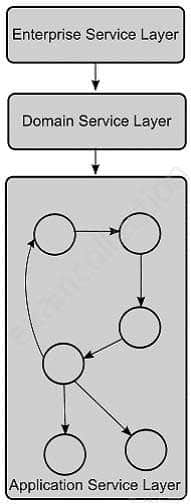
CSSLP Certified Secure Software Lifecycle Professional Part 08 Q17 010 (Layer interaction in Service-oriented architecture) Answer: A is incorrect. SABSA (Sherwood Applied Business Security Architecture) is a framework and methodology for Enterprise Security Architecture and Service Management. SABSA is a model and a methodology for developing risk-driven enterprise information security architectures and for delivering security infrastructure solutions that support critical business initiatives. The primary characteristic of the SABSA model is that everything must be derived from an analysis of the business requirements for security, especially those in which security has an enabling function through which new business opportunities can be developed and exploited. Answer: D is incorrect. The service-oriented modeling and architecture (SOMA) includes an analysis and design method that extends traditional object-oriented and component-based analysis and design methods to include concerns relevant to and supporting SOA. Answer: B is incorrect. Enterprise architecture describes the terminology, the composition of subsystems, and their relationships with the external environment, and the guiding principles for the design and evolution of an enterprise.
-
Which of the following recovery plans includes specific strategies and actions to deal with specific variances to assumptions resulting in a particular security problem, emergency, or state of affairs?
- Disaster recovery plan
- Business continuity plan
- Continuity of Operations Plan
- Contingency plan
Explanation:A contingency plan is a plan devised for a specific situation when things could go wrong. Contingency plans include specific strategies and actions to deal with specific variances to assumptions resulting in a particular problem, emergency, or state of affairs. They also include a monitoring process and triggers for initiating planned actions. Answer: A is incorrect. Disaster recovery is the process, policies, and procedures related to preparing for recovery or continuation of technology infrastructure critical to an organization after a natural or human-induced disaster. Answer: B is incorrect. It deals with the plans and procedures that identify and prioritize the critical business functions that must be preserved. Answer: C is incorrect. It includes the plans and procedures documented that ensure the continuity of critical operations during any period where normal operations are impossible. -
Henry is the project manager of the QBG Project for his company. This project has a budget of $4,576,900 and is expected to last 18 months to complete. The CIO, a stakeholder in the project, has introduced a scope change request for additional deliverables as part of the project work. What component of the change control system would review the proposed changes’ impact on the features and functions of the project’s product?
- Configuration management system
- Scope change control system
- Cost change control system
- Integrated change control
Explanation:The configuration management system ensures that proposed changes to the project’s scope are reviewed and evaluated for their affect on the project’s product. Configuration Management System is a subsystem of the overall project management system. It is a collection of formal documented procedures used to identify and document the functional and physical characteristics of a product, result, service, or component of the project. It also controls any changes to such characteristics, and records and reports each change and its implementation status. It includes the documentation, tracking systems, and defined approval levels necessary for authorizing and controlling changes. Audits are performed as part of configuration management to determine if the requirements have been met. Answer: B is incorrect. The scope change control system focuses on reviewing the actual changes to the project scope. When a change to the project’s scope is proposed, the configuration management system is also invoked. Answer: C is incorrect. The cost change control system is responsible for reviewing and controlling changes to the project costs. Answer: D is incorrect. Integrated change control examines the affect of a proposed change on the project as a whole. -
Which of the following are Service Level Agreement (SLA) structures as defined by ITIL? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Component Based
- Service Based
- Segment Based
- Customer Based
- Multi-Level
Explanation:ITIL defines 3 types of Service Level Agreement (SLA) structures, which are as follows: 1.Customer Based: It covers all services used by an individual customer group. 2.Service Based: It is one service for all customers. 3.Multi-Level: Some examples of Multi-Level SLA are 3 Tier SLA encompassing Corporate and Customer & Service Layers. Answer: C and A are incorrect. There are no such SLA structures as Segment Based and Component Based.