SSCP : System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) : Part 17
-
Which of the following is NOT an advantage that TACACS+ has over TACACS?
- Event logging
- Use of two-factor password authentication
- User has the ability to change his password
- Ability for security tokens to be resynchronized
Explanation:
Although TACACS+ provides better audit trails, event logging is a service that is provided with TACACS.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 121).
-
Which of the following remote access authentication systems is the most robust?
- TACACS+
- RADIUS
- PAP
- TACACS
Explanation:TACACS+ is a proprietary Cisco enhancement to TACACS and is more robust than RADIUS. PAP is not a remote access authentication system but a remote node security protocol.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 122). -
Which of the following devices enables more than one signal to be sent out simultaneously over one physical circuit?
- Router
- Multiplexer
- Channel service unit/Data service unit (CSU/DSU)
- Wan switch
Explanation:Multiplexers are devices that enable enables more than one signal to be sent out simultaneously over one physical circuit.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 118). -
What layer of the ISO/OSI model do routers normally operate at?
- Data link layer
- Session layer
- Transport layer
- Network layer
Explanation:Routers are switching devices that operate at the network layer (layer 3) by examining network addresses.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 111). -
Which of the following offers security to wireless communications?
- S-WAP
- WTLS
- WSP
- WDP
Explanation:Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS) is a communication protocol that allows wireless devices to send and receive encrypted information over the Internet. S-WAP is not defined. WSP (Wireless Session Protocol) and WDP (Wireless Datagram Protocol) are part of Wireless Access Protocol (WAP).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 173).
-
A Wide Area Network (WAN) is basically everything outside of:
- a Local Area Network (LAN).
- a Campus Area Network (CAN).
- a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN).
- the Internet.
Explanation:A WAN is basically everything outside of a LAN.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 99. -
Which of the following is true about link encryption?
- Each entity has a common key with the destination node.
- Encrypted messages are only decrypted by the final node.
- This mode does not provide protection if anyone of the nodes along the transmission path is compromised.
- Only secure nodes are used in this type of transmission.
Explanation:In link encryption, each entity has keys in common with its two neighboring nodes in the transmission chain.
Thus, a node receives the encrypted message from its predecessor, decrypts it, and then re-encrypts it with a new key, common to the successor node. Obviously, this mode does not provide protection if anyone of the nodes along the transmission path is compromised.
Encryption can be performed at different communication levels, each with different types of protection and implications. Two general modes of encryption implementation are link encryption and end-to-end encryption.
Link encryption encrypts all the data along a specific communication path, as in a satellite link, T3 line, or telephone circuit. Not only is the user information encrypted, but the header, trailers, addresses, and routing data that are part of the packets are also encrypted. The only traffic not encrypted in this technology is the data link control messaging information, which includes instructions and parameters that the different link devices use to synchronize communication methods. Link encryption provides protection against packet sniffers and eavesdroppers.
In end-to-end encryption, the headers, addresses, routing, and trailer information are not encrypted, enabling attackers to learn more about a captured packet and where it is headed.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition (pp. 845-846). McGraw-Hill.
And:
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 4: Cryptography (page 132). -
Which of the following protects Kerberos against replay attacks?
- Tokens
- Passwords
- Cryptography
- Time stamps
Explanation:A replay attack refers to the recording and retransmission of packets on the network. Kerberos uses time stamps, which protect against this type of attack.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 8: Cryptography (page 581).
-
Which xDSL flavour delivers both downstream and upstream speeds of 1.544 Mbps over two copper twisted pairs?
- HDSL
- SDSL
- ADSL
- VDSL
Explanation:High-rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL) delivers 1.544 Mbps of bandwidth each way over two copper twisted pairs. SDSL also delivers 1.544 Mbps but over a single copper twisted pair. ADSL and VDSL offer a higher bandwidth downstream than upstream.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 115). -
Which xDSL flavour can deliver up to 52 Mbps downstream over a single copper twisted pair?
- VDSL
- SDSL
- HDSL
- ADSL
Explanation:Very-high data-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) can deliver up to 52 Mbps downstream over a single copper twisted pair over a relatively short distance (1000 to 4500 feet).
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a modem technology for broadband data access over ordinary copper telephone lines (POTS) from homes and businesses. xDSL refers collectively to all types of DSL, such as ADSL (and G.Lite), HDSL, SDSL, IDSL and VDSL etc. They are sometimes referred to as last-mile (or first mile) technologies because they are used only for connections from a telephone switching station to a home or office, not between switching stations.xDSL is similar to ISDN in as much as both operate over existing copper telephone lines (POTS) using sophisticated modulation schemes and both require the short runs to a central telephone office
Graphic below from: http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm
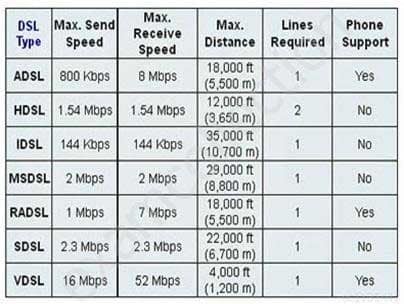
SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 17 Q10 008 DSL speed chart
The following are incorrect answers:
Single-line Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) deliver 2.3 Mbps of bandwidth each way.
High-rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL) deliver 1.544 Mbps of bandwidth each way.
ADSL delivers a maximum of 8 Mbps downstream for a total combined speed of almost 9 Mbps up and down.Reference used for this question:
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm
and
http://www.javvin.com/protocolxDSL.html
and
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 115). -
Which xDSL flavour, appropriate for home or small offices, delivers more bandwidth downstream than upstream and over longer distance?
- VDSL
- SDSL
- ADSL
- HDSL
Explanation:Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is designed to provide more bandwidth downstream (1 to 8 Mbps) than upstream (16 to 800Kb).
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a modem technology for broadband data access over ordinary copper telephone lines (POTS) from homes and businesses. xDSL refers collectively to all types of DSL, such as ADSL (and G.Lite), HDSL, SDSL, IDSL and VDSL etc. They are sometimes referred to as last-mile (or first mile) technologies because they are used only for connections from a telephone switching station to a home or office, not between switching stations.xDSL is similar to ISDN in as much as both operate over existing copper telephone lines (POTS) using sophisticated modulation schemes and both require the short runs to a central telephone office
Graphic below from: http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm
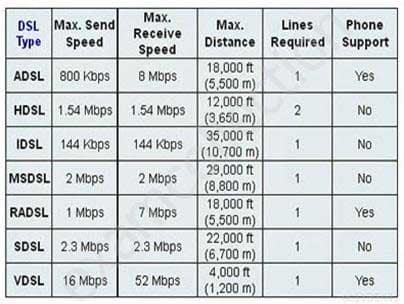
SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 17 Q11 009 DSL speed chart
The following are incorrect answers:
Single-line Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) deliver 2.3 Mbps of bandwidth each way.
High-rate Digital Subscriber Line (HDSL) deliver 1.544 Mbps of bandwidth each way.Very-high data-rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) can deliver up to 52 Mbps downstream over a single copper twisted pair over a relatively short distance (1000 to 4500 feet).
Reference used for this question:
http://computer.howstuffworks.com/vdsl3.htm
and
http://www.javvin.com/protocolxDSL.html
and
KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 115). -
What ISO/OSI layer do switches primarily operate at?
Do take note that this question makes reference to a plain vanilla switch and not one of the smart switches that is available on the market today.
- Physical layer
- Network layer
- Data link layer
- Session layer
Explanation:Switches primarily operate at the data link layer (layer 2), although intelligent, extremely fast Layer 3 switching techniques are being more frequently used.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 111). -
Which of the following is the simplest type of firewall ?
- Stateful packet filtering firewall
- Packet filtering firewall
- Dual-homed host firewall
- Application gateway
Explanation:A static packet filtering firewall is the simplest and least expensive type of firewalls, offering minimum security provisions to a low-risk computing environment.
A static packet filter firewall examines both the source and destination addresses of the incoming data packet and applies ACL’s to them. They operates at either the Network or Transport layer. They are known as the First generation of firewall.
Older firewalls that were only packet filters were essentially routing devices that provided access control functionality for host addresses and communication sessions. These devices, also known as stateless inspection firewalls, do not keep track of the state of each flow of traffic that passes though the firewall; this means, for example, that they cannot associate multiple requests within a single session to each other. Packet filtering is at the core of most modern firewalls, but there are few firewalls sold today that only do stateless packet filtering. Unlike more advanced filters, packet filters are not concerned about the content of packets. Their access control functionality is governed by a set of directives referred to as a ruleset. Packet filtering capabilities are built into most operating systems and devices capable of routing; the most common example of a pure packet filtering device is a network router that employs access control lists.
There are many types of Firewall:
Application Level Firewalls – Often called a Proxy Server. It works by transferring a copy of each accepted data packet from one network to another. They are known as the Second generation of firewalls.An application-proxy gateway is a feature of advanced firewalls that combines lower-layer access control with upper-layer functionality. These firewalls contain a proxy agent that acts as an intermediary between two hosts that wish to communicate with each other, and never allows a direct connection between them. Each successful connection attempt actually results in the creation of two separate connections—one between the client and the proxy server, and another between the proxy server and the true destination. The proxy is meant to be transparent to the two hosts—from their perspectives there is a direct connection. Because external hosts only communicate with the proxy agent, internal IP addresses are not visible to the outside world. The proxy agent interfaces directly with the firewall ruleset to determine whether a given instance of network traffic should be allowed to transit the firewall.
Stateful Inspection Firewall – Packets are captured by the inspection engine operating at the network layer and then analyzed at all layers. They are known as the Third generation of firewalls.
Stateful inspection improves on the functions of packet filters by tracking the state of connections and blocking packets that deviate from the expected state. This is accomplished by incorporating greater awareness of the transport layer. As with packet filtering, stateful inspection intercepts packets at the network layer and inspects them to see if they are permitted by an existing firewall rule, but unlike packet filtering, stateful inspection keeps track of each connection in a state table. While the details of state table entries vary by firewall product, they typically include source IP address, destination IP address, port numbers, and connection state information.
Web Application Firewalls – The HTTP protocol used in web servers has been exploited by attackers in many ways, such as to place malicious software on the computer of someone browsing the web, or to fool a person into revealing private information that they might not have otherwise. Many of these exploits can be detected by specialized application firewalls called web application firewalls that reside in front of the web server.
Web application firewalls are a relatively new technology, as compared to other firewall technologies, and the type of threats that they mitigate are still changing frequently. Because they are put in front of web servers to prevent attacks on the server, they are often considered to be very different than traditional firewalls.Host-Based Firewalls and Personal Firewalls – Host-based firewalls for servers and personal firewalls for desktop and laptop personal computers (PC) provide an additional layer of security against network-based attacks. These firewalls are software-based, residing on the hosts they are protecting—each monitors and controls the incoming and outgoing network traffic for a single host. They can provide more granular protection than network firewalls to meet the needs of specific hosts.
Host-based firewalls are available as part of server operating systems such as Linux, Windows, Solaris, BSD, and Mac OS X Server, and they can also be installed as third-party add-ons. Configuring a host-based firewall to allow only necessary traffic to the server provides protection against malicious activity from all hosts, including those on the same subnet or on other internal subnets not separated by a network firewall. Limiting outgoing traffic from a server may also be helpful in preventing certain malware that infects a host from spreading to other hosts.11 Host-based firewalls usually perform logging, and can often be configured to perform address-based and application-based access controls
Dynamic Packet Filtering – Makes informed decisions on the ACL’s to apply. They are known as the Fourth generation of firewalls.
Kernel Proxy – Very specialized architecture that provides modular kernel-based, multi-layer evaluation and runs in the NT executive space. They are known as the Fifth generation of firewalls.
The following were incorrect answers:
All of the other types of firewalls listed are more complex than the Packet Filtering Firewall.
Reference(s) used for this question:
HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, 6th Edition, Telecommunications and Network Security, Page 630.
and
NIST Guidelines on Firewalls and Firewalls policies, Special Publication 800-4 Revision 1 -
Upon which of the following ISO/OSI layers does network address translation operate?
- Transport layer
- Session layer
- Data link layer
- Network layer
Explanation:Network address translation (NAT) is concerned with IP address translation between two networks and operates at the network layer (layer 3).
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 440). -
What is the framing specification used for transmitting digital signals at 1.544 Mbps on a T1 facility?
- DS-0
- DS-1
- DS-2
- DS-3
Explanation:Digital Signal level 1 (DS-1) is the framing specification used for transmitting digital signals at 1.544 Mbps on a T1 facility. DS-0 is the framing specification used in transmitting digital signals over a single 64 Kbps channel over a T1 facility. DS-3 is the framing specification used for transmitting digital signals at 44.736 Mbps on a T3 facility. DS-2 is not a defined framing specification.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, John Wiley & Sons, 2001, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 114).
-
Which of the following is the biggest concern with firewall security?
- Internal hackers
- Complex configuration rules leading to misconfiguration
- Buffer overflows
- Distributed denial of service (DDOS) attacks
Explanation:Firewalls tend to give a false sense of security. They can be very hard to bypass but they need to be properly configured. The complexity of configuration rules can introduce a vulnerability when the person responsible for its configuration does not fully understand all possible options and switches. Denial of service attacks mainly concerns availability.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, Chapter 3: Telecommunications and Network Security (page 412). -
Which of the following packets should NOT be dropped at a firewall protecting an organization’s internal network?
- Inbound packets with Source Routing option set
- Router information exchange protocols
- Inbound packets with an internal address as the source IP address
- Outbound packets with an external destination IP address
Explanation:Normal outbound traffic has an internal source IP address and an external destination IP address.
Traffic with an internal source IP address should only come from an internal interface. Such packets coming from an external interface should be dropped.
Packets with the source-routing option enabled usually indicates a network intrusion attempt.
Router information exchange protocols like RIP and OSPF should be dropped to avoid having internal routing equipment being reconfigured by external agents.
Source: STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 10: The Perfect Firewall.
-
Why does fiber optic communication technology have significant security advantage over other transmission technology?
- Higher data rates can be transmitted.
- Interception of data traffic is more difficult.
- Traffic analysis is prevented by multiplexing.
- Single and double-bit errors are correctable.
Explanation:It would be correct to select the first answer if the world “security” was not in the question.
Source: TIPTON, Hal, (ISC)2, Introduction to the CISSP Exam presentation. -
Which of the following is the primary security feature of a proxy server?
- Virus Detection
- URL blocking
- Route blocking
- Content filtering
Explanation:In many organizations, the HTTP proxy is used as a means to implement content filtering, for instance, by logging or blocking traffic that has been defined as, or is assumed to be nonbusiness related for some reason.
Although filtering on a proxy server or firewall as part of a layered defense can be quite effective to prevent, for instance, virus infections (though it should never be the only protection against viruses), it will be only moderately effective in preventing access to unauthorized services (such as certain remote-access services or file sharing), as well as preventing the download of unwanted content. HTTP Tunneling.
HTTP tunneling is technically a misuse of the protocol on the part of the designer of such tunneling applications. It has become a popular feature with the rise of the first streaming video and audio applications and has been implemented into many applications that have a market need to bypass user policy restrictions.
Usually, HTTP tunneling is applied by encapsulating outgoing traffic from an application in an HTTP request and incoming traffic in a response. This is usually not done to circumvent security, but rather, to be compatible with existing firewall rules and allow an application to function through a firewall without the need to apply special rules, or additional configurations.
The following are incorrect choices:
Virus Detection A proxy is not best at detection malware and viruses within content. A antivirus product would be use for that purpose.
URL blocking This would be a subset of Proxying, based on the content some URL’s may be blocked by the proxy but it is not doing filtering based on URL addresses only. This is not the BEST answer.
Route blocking This is a function that would be done by Intrusion Detection and Intrusion prevention system and not the proxy. This could be done by filtering devices such as Firewalls and Routers as well. Again, not the best choice.
Reference(s) used for this question:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 6195-6201). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition. -
In the context of network enumeration by an outside attacker and possible Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which of the following firewall rules is not appropriate to protect an organization’s internal network?
- Allow echo reply outbound
- Allow echo request outbound
- Drop echo request inbound
- Allow echo reply inbound
Explanation:Echo replies outbound should be dropped, not allowed. There is no reason for any internet users to send ICMP ECHO Request to your interal hosts from the internet. If they wish to find out if a service is available, they can use a browser to connect to your web server or simply send an email if they wish to test your mail service.
Echo replies outbound could be used as part of the SMURF amplification attack where someone will send ICMP echo requests to gateways broadcast addresses in order to amplify the request by X number of users sitting behind the gateway.
By allowing inbound echo requests and outbound echo replies, it makes it easier for attackers to learn about the internal network as well by performing a simply ping sweep. ICMP can also be used to find out which host has been up and running the longest which would indicates which patches are missing on the host if a critical patch required a reboot.
ICMP can also be use for DDoS attacks, so you should strictly limit what type of ICMP traffic would be allowed to flow through your firewall.
On top of all this, tools such as LOKI could be use as a client-server application to transfer files back and forward between the internat and some of your internal hosts. LOKI is a client/server program published in the online publication Phrack. This program is a working proof-of-concept to demonstrate that data can be transmitted somewhat secretly across a network by hiding it in traffic that normally does not contain payloads. The example code can tunnel the equivalent of a Unix RCMD/RSH session in either ICMP echo request (ping) packets or UDP traffic to the DNS port. This is used as a back door into a Unix system after root access has been compromised. Presence of LOKI on a system is evidence that the system has been compromised in the past.
The outbound echo request and inbound echo reply allow internal users to verify connectivity with external hosts.
The following answers are incorrect:
Allow echo request outbound The outbound echo request and inbound echo reply allow internal users to verify connectivity with external hosts.
Drop echo request inbound There is no need for anyone on the internet to attempt pinging your internal hosts.
Allow echo reply inbound The outbound echo request and inbound echo reply allow internal users to verify connectivity with external hosts.
Reference(s) used for this question:
http://www.phrack.org/issues.html?issue=49&id=6
STREBE, Matthew and PERKINS, Charles, Firewalls 24seven, Sybex 2000, Chapter 10: The Perfect Firewall.