SSCP : System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) : Part 22
-
A group of independent servers, which are managed as a single system, that provides higher availability, easier manageability, and greater scalability is:
- server cluster
- client cluster
- guest cluster
- host cluster
Explanation:
A server cluster is a group of independent servers, which are managed as a single system, that provides higher availability, easier manageability, and greater scalability.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 67. -
A server cluster looks like a:
- single server from the user’s point of view
- dual server from the user’s point of view
- triple server from the user’s point of view
- quardle server from the user’s point of view
Explanation:The cluster looks like a single server from the user’s point of view.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 67. -
One of the following statements about the differences between PPTP and L2TP is NOT true
- PPTP can run only on top of IP networks.
- PPTP is an encryption protocol and L2TP is not.
- L2TP works well with all firewalls and network devices that perform NAT.
- L2TP supports AAA servers
Explanation:L2TP is affected by packet header modification and cannot cope with firewalls and network devices that perform NAT.
“PPTP can run only on top of IP networks.” is correct as PPTP encapsulates datagrams into an IP packet, allowing PPTP to route many network protocols across an IP network.
“PPTP is an encryption protocol and L2TP is not.” is correct. When using PPTP, the PPP payload is encrypted with Microsoft Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) using MSCHAP or EAP-TLS.
“L2TP supports AAA servers” is correct as L2TP supports TACACS+ and RADIUS.
NOTE:
L2TP does work over NAT. It is possible to use a tunneled mode that wraps every packet into a UDP packet. Port 4500 is used for this purpose. However this is not true of PPTP and it is not true as well that it works well with all firewalls and NAT devices.References:
All in One Third Edition page 545
Official Guide to the CISSP Exam page 124-126 -
You have been tasked to develop an effective information classification program. Which one of the following steps should be performed first?
- Establish procedures for periodically reviewing the classification and ownership
- Specify the security controls required for each classification level
- Identify the data custodian who will be responsible for maintaining the security level of data
- Specify the criteria that will determine how data is classified
Explanation:According to the AIO 3rd edition, these are the necessary steps for a proper classification program:
1. Define classification levels.
2. Specify the criteria that will determine how data is classified.
3. Have the data owner indicate the classification of the data she is responsible for.
4. Identify the data custodian who will be responsible for maintaining data and its security level.
5. Indicate the security controls, or protection mechanisms, that are required for each classification level.
6. Document any exceptions to the previous classification issues.
7. Indicate the methods that can be used to transfer custody of the information to a different data owner.
8. Create a procedure to periodically review the classification and ownership. Communicate any changes to the data custodian.
9. Indicate termination procedures for declassifying the data.
10. Integrate these issues into the security-awareness program so that all employees understand how to handle data at different classification levels.Domain: Information security and risk management
Reference: AIO 3rd edition page 50
-
Which of the following methods of providing telecommunications continuity involves the use of an alternative media?
- Alternative routing
- Diverse routing
- Long haul network diversity
- Last mile circuit protection
Explanation:Alternative routing is a method of routing information via an alternate medium such as copper cable or fiber optics. This involves use of different networks, circuits or end points should the normal network be unavailable. Diverse routing routes traffic through split cable facilities or duplicate cable facilities. This can be accomplished with different and/or duplicate cable sheaths. If different cable sheaths are used, the cable may be in the same conduit and therefore subject to the same interruptions as the cable it is backing up. The communication service subscriber can duplicate the facilities by having alternate routes, although the entrance to and from the customer premises may be in the same conduit. The subscriber can obtain diverse routing and alternate routing from the local carrier, including dual entrance facilities. This type of access is time-consuming and costly. Long haul network diversity is a diverse long-distance network utilizing T1 circuits among the major long-distance carriers. It ensures long-distance access should any one carrier experience a network failure. Last mile circuit protection is a redundant combination of local carrier T1s microwave and/or coaxial cable access to the local communications loop. This enables the facility to have access during a local carrier communication disaster. Alternate local carrier routing is also utilized.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association, Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, chapter 5: Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity (page 259). -
Which port does the Post Office Protocol Version 3 (POP3) make use of?
- 110
- 109
- 139
- 119
Explanation:The other answers are not correct because of the following protocol/port numbers matrix:
Post Office Protocol (POP2) 109
Network News Transfer Protocol 119
NetBIOS 139 -
If any server in the cluster crashes, processing continues transparently, however, the cluster suffers some performance degradation. This implementation is sometimes called a:
- server farm
- client farm
- cluster farm
- host farm
Explanation:If any server in the cluster crashes, processing continues transparently, however, the cluster suffers some performance degradation. This implementation is sometimes called a “server farm.”
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 67. -
Which of the following is immune to the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and therefore has a much longer effective usable length?
- Fiber Optic cable
- Coaxial cable
- Twisted Pair cable
- Axial cable
Explanation:Fiber Optic cable is immune to the effects of electromagnetic interference (EMI) and therefore has a much longer effective usable length (up to two kilometers in some cases).
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 72. -
What is called an attack where the attacker spoofs the source IP address in an ICMP ECHO broadcast packet so it seems to have originated at the victim’s system, in order to flood it with REPLY packets?
- SYN Flood attack
- Smurf attack
- Ping of Death attack
- Denial of Service (DOS) attack
Explanation:Although it may cause a denial of service to the victim’s system, this type of attack is a Smurf attack. A SYN Flood attack uses up all of a system’s resources by setting up a number of bogus communication sockets on the victim’s system. A Ping of Death attack is done by sending IP packets that exceed the maximum legal length (65535 octets).
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 11: Application and System Development (page 789). -
What is the main difference between a Smurf and a Fraggle attack?
- A Smurf attack is ICMP-based and a Fraggle attack is UDP-based.
- A Smurf attack is UDP-based and a Fraggle attack is TCP-based.
- Smurf attack packets cannot be spoofed.
- A Smurf attack is UDP-based and a Fraggle attack is ICMP-based.
Explanation:Fraggle is an attack similar to Smurf, but instead of using ICMP, it uses UDP.
Source: HARRIS, Shon, All-In-One CISSP Certification Exam Guide, McGraw-Hill/Osborne, 2002, chapter 11: Application and System Development (page 790). -
Which of the following is a telecommunication device that translates data from digital to analog form and back to digital?
- Multiplexer
- Modem
- Protocol converter
- Concentrator
Explanation:A modem is a device that translates data from digital form and then back to digital for communication over analog lines.
Source: Information Systems Audit and Control Association,
Certified Information Systems Auditor 2002 review manual, Chapter 3: Technical Infrastructure and Operational Practices (page 114). -
Which of the following transmission media would NOT be affected by cross talk or interference?
- Copper cable
- Radio System
- Satellite radiolink
- Fiber optic cables
Explanation:Only fiber optic cables are not affected by crosstalk or interference.
For your exam you should know the information about transmission media:
Copper Cable
Copper cable is very simple to install and easy to tap. It is used mostly for short distance and supports voice and data.
Copper has been used in electric wiring since the invention of the electromagnet and the telegraph in the 1820s.The invention of the telephone in 1876 created further demand for copper wire as an electrical conductor.
Copper is the electrical conductor in many categories of electrical wiring. Copper wire is used in power generation, power transmission, power distribution, telecommunications, electronics circuitry, and countless types of electrical equipment. Copper and its alloys are also used to make electrical contacts. Electrical wiring in buildings is the most important market for the copper industry. Roughly half of all copper mined is used to manufacture electrical wire and cable conductors.Copper Cable

SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 22 Q12 016 Image Source – http://i00.i.aliimg.com/photo/v0/570456138/FRLS_HR_PVC_Copper_Cable.jpg
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax (pronounced ‘ko.aks), is a type of cable that has an inner conductor surrounded by a tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. Many coaxial cables also have an insulating outer sheath or jacket. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing a geometric axis. Coaxial cable was invented by English engineer and mathematician Oliver Heaviside, who patented the design in 1880.Coaxial cable differs from other shielded cable used for carrying lower-frequency signals, such as audio signals, in that the dimensions of the cable are controlled to give a precise, constant conductor spacing, which is needed for it to function efficiently as a radio frequency transmission line.Coaxial cable are expensive and does not support many LAN’s. It supports data and video
Coaxial Cable

SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 22 Q12 017 Image Source – http://www.tlc-direct.co.uk/Images/Products/size_3/CARG59.JPG
Fiber optics
An optical fiber cable is a cable containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed. Different types of cable are used for different applications, for example long distance telecommunication, or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.Fiber optics used for long distance, hard to splice, not vulnerable to cross talk and difficult to tap. It supports voice data, image and video.
Radio System
Radio systems are used for short distance,cheap and easy to tap.
Radio is the radiation (wireless transmission) of electromagnetic signals through the atmosphere or free space.Information, such as sound, is carried by systematically changing (modulating) some property of the radiated waves, such as their amplitude, frequency, phase, or pulse width. When radio waves strike an electrical conductor, the oscillating fields induce an alternating current in the conductor. The information in the waves can be extracted and transformed back into its original form.
Fiber Optics

SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 22 Q12 018 Image Source – http://aboveinfranet.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/fiber-optic-cables-above-infranet-solutions.jpg
Microwave radio system
Microwave transmission refers to the technology of transmitting information or energy by the use of radio waves whose wavelengths are conveniently measured in small numbers of centimetre; these are called microwaves.
Microwaves are widely used for point-to-point communications because their small wavelength allows conveniently-sized antennas to direct them in narrow beams, which can be pointed directly at the receiving antenna. This allows nearby microwave equipment to use the same frequencies without interfering with each other, as lower frequency radio waves do. Another advantage is that the high frequency of microwaves gives the microwave band a very large information-carrying capacity; the microwave band has a bandwidth 30 times that of all the rest of the radio spectrum below it. A disadvantage is that microwaves are limited to line of sight propagation; they cannot pass around hills or mountains as lower frequency radio waves can.Microwave radio transmission is commonly used in point-to-point communication systems on the surface of the Earth, in satellite communications, and in deep space radio communications. Other parts of the microwave radio band are used for radars, radio navigation systems, sensor systems, and radio astronomy.
Microwave radio systems are carriers for voice data signal, cheap and easy to tap.
Microwave Radio System

SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 22 Q12 019 Image Source – http://www.valiantcom.com/images/applications/e1_digital_microwave_radio.gif
Satellite Radio Link
Satellite radio is a radio service broadcast from satellites primarily to cars, with the signal broadcast nationwide, across a much wider geographical area than terrestrial radio stations. It is available by subscription, mostly commercial free, and offers subscribers more stations and a wider variety of programming options than terrestrial radio.Satellite radio link uses transponder to send information and easy to tap.
The following answers are incorrect:
Copper Cable – Copper cable is very simple to install and easy to tap. It is used mostly for short distance and supports voice and data.
Radio System – Radio systems are used for short distance,cheap and easy to tap.
Satellite Radio Link – Satellite radio link uses transponder to send information and easy to tap.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
CISA review manual 2014 page number 265 &
Official ISC2 guide to CISSP CBK 3rd Edition Page number 233 -
In telephony different types of connections are being used. The connection from the phone company’s branch office to local customers is referred to as which of the following choices?
- new loop
- local loop
- loopback
- indigenous loop
Explanation:Transmission on fiber optic wire requires repeating at distance intervals. The glass fiber requires more protection within an outer cable than copper. For these reasons and because the installation of any new wiring is labor-intensive, few communities yet have fiber optic wires or cables from the phone company’s branch office to local customers (local loop).
In telephony, a local loop is the wired connection from a telephone company’s central office in a locality to its customers’ telephones at homes and businesses. This connection is usually on a pair of copper wires called twisted pair. The system was originally designed for voice transmission only using analog transmission technology on a single voice channel. Today, your computer’s modem makes the conversion between analog signals and digital signals. With Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) or Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), the local loop can carry digital signals directly and at a much higher bandwidth than they do for voice only.
Local Loop diagram
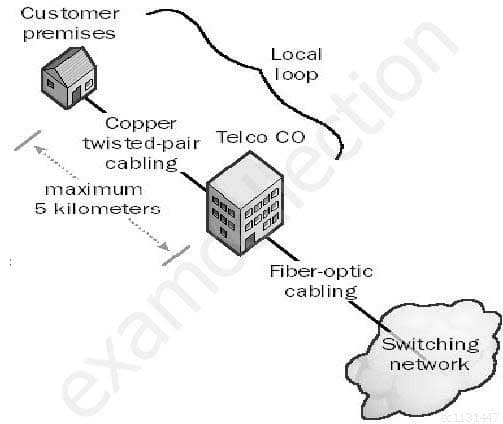
SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 22 Q13 020 Image from: http://www.thenetworkencyclopedia.com/entry/local-loop/
The following are incorrect answers:
New loop This is only a detractor and does not exist
Loopback In telephone systems, a loopback is a test signal sent to a network destination that is returned as received to the originator. The returned signal may help diagnose a problem.
Ingenious loop This is only a detractor and does not exist
Reference(s) used for this question:
http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/local-loop
and
STEINER, Kurt, Telecommunications and Network Security, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group (Domain Leader: skottikus), Page 14. -
Communications and network security relates to transmission of which of the following?
- voice
- voice and multimedia
- data and multimedia
- voice, data and multimedia
Explanation:From the published (ISC)2 goals for the Certified Information Systems Security Professional candidate:
The CISSP candidate should be familiar to communications and network security as it relates to voice, data, multimedia, and facsimile transmissions in terms of local area, wide area, and remote access.
Source: KRUTZ, Ronald L. & VINES, Russel D., The CISSP Prep Guide: Mastering the Ten Domains of Computer Security, 2001, John Wiley & Sons, Page 57.
-
Why are coaxial cables called “coaxial”?
- it includes two physical channels that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis.
- it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis
- it includes two physical channels that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another two concentric physical channels, both running along the same axis.
- it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running perpendicular and along the different axis
Explanation:Coaxial cable is called “coaxial” because it includes one physical channel that carries the signal surrounded (after a layer of insulation) by another concentric physical channel, both running along the same axis.
The outer channel serves as a ground. Many of these cables or pairs of coaxial tubes can be placed in a single outer sheathing and, with repeaters, can carry information for a great distance.
Source: STEINER, Kurt, Telecommunications and Network Security, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group (Domain Leader: skottikus), Page 14.
-
The International Standards Organization / Open Systems Interconnection (ISO/OSI) Layers does NOT have which of the following characteristics?
- Standard model for network communications
- Used to gain information from network devices such as count of packets received and routing tables
- Enables dissimilar networks to communicate
- Defines 7 protocol layers (a.k.a. protocol stack)
Explanation:The International Standards Organization / Open Systems Interconnection (ISO/OSI) Layers and Characteristics Standard model for network communications enables dissimilar networks to communicate, Defines 7 protocol layers (a.k.a. protocol stack) Each layer on one workstation communicates with its respective layer on another workstation using protocols (i.e. agreed-upon communication formats) “Mapping” each protocol to the model is useful for comparing protocols.
Mnemonics: Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away (bottom to top layer)
All People Seem To Need Data Processing (top to bottom layer).
Source: STEINER, Kurt, Telecommunications and Network Security, Version 1, May 2002, CISSP Open Study Group (Domain Leader: skottikus), Page 12. -
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is a protocol that one program can use to request a service from a program located in another computer in a network. Within which OSI/ISO layer is RPC implemented?
- Session layer
- Transport layer
- Data link layer
- Network layer
Explanation:The Answer: Session layer, which establishes, maintains and manages sessions and synchronization of data flow. Session layer protocols control application-to-application communications, which is what an RPC call is.
The following answers are incorrect:
Transport layer: The Transport layer handles computer-to computer communications, rather than application-to-application communications like RPC.
Data link Layer: The Data Link layer protocols can be divided into either Logical Link Control (LLC) or Media Access Control (MAC) sublayers. Protocols like SLIP, PPP, RARP and L2TP are at this layer. An application-to-application protocol like RPC would not be addressed at this layer.
Network layer: The Network Layer is mostly concerned with routing and addressing of information, not application-to-application communication calls such as an RPC call.
The following reference(s) were/was used to create this question:
The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol is implemented at the Session layer, which establishes, maintains and manages sessions as well as synchronization of the data flow.
Source: Jason Robinett’s CISSP Cram Sheet: domain2.Source: Shon Harris AIO v3 pg. 423
-
How do you distinguish between a bridge and a router?
- A bridge simply connects multiple networks, a router examines each packet to determine which network to forward it to.
- “Bridge” and “router” are synonyms for equipment used to join two networks.
- The bridge is a specific type of router used to connect a LAN to the global Internet.
- The bridge connects multiple networks at the data link layer, while router connects multiple networks at the network layer.
Explanation:A bridge operates at the Data Link Layer and a router operates at the Network Layer.
The following answers are incorrect:
A bridge simply connects multiple networks, a router examines each packet to determine which network to forward it to. Is incorrect because both forward packets this is not distinctive enough.
“Bridge” and “router” are synonyms for equipment used to join two networks. Is incorrect because the two are unique and operate at different layers of the OSI model.
The bridge is a specific type of router used to connect a LAN to the global Internet. Is incorrect because a bridge does not connect a LAN to the global internet, but connects networks together creating a LAN.
-
ICMP and IGMP belong to which layer of the OSI model?
- Datagram Layer.
- Network Layer.
- Transport Layer.
- Data Link Layer.
Explanation:The network layer contains the Internet Protocol (IP), the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), and the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
The following answers are incorrect:
Datagram Layer. Is incorrect as a distractor as there is no Datagram Layer.
Transport Layer. Is incorrect because it is used to data between applications and uses the TCP and UDP protocols.
Data Link Layer. Is incorrect because this layer deals with addressing hardware. -
Which of the following layers provides end-to-end data transfer service?
- Network Layer.
- Data Link Layer.
- Transport Layer.
- Presentation Layer.
Explanation:It is the Transport Layer that is responsible for reliable end-to-end data transfer between end systems.
The following answers are incorrect:
Network Layer. Is incorrect because the Network Layer is the OSI layer that is responsible for routing, switching, and subnetwork access across the entire OSI environment.
Data Link Layer. Is incorrect because the Data Link Layer is the serial communications path between nodes or devices without any intermediate switching nodes.
Presentation Layer. Is incorrect because the Presentation Layer is the OSI layer that determines how application information is represented (i.e., encoded) while in transit between two end systems.