SSCP : System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) : Part 32
-
As per the Orange Book, what are two types of system assurance?
- Operational Assurance and Architectural Assurance.
- Design Assurance and Implementation Assurance.
- Architectural Assurance and Implementation Assurance.
- Operational Assurance and Life-Cycle Assurance.
Explanation:
Are the two types of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
The following answers are incorrect:
Operational Assurance and Architectural Assurance. Is incorrect because Architectural Assurance is not a type of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
Design Assurance and Implementation Assurance. Is incorrect because neither are types of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
Architectural Assurance and Implementation Assurance. Is incorrect because neither are types of assurance mentioned in the Orange book.
-
Which must bear the primary responsibility for determining the level of protection needed for information systems resources?
- IS security specialists
- Senior Management
- Senior security analysts
- systems Auditors
Explanation:If there is no support by senior management to implement, execute, and enforce security policies and procedure, then they won’t work. Senior management must be involved in this because they have an obligation to the organization to protect the assests . The requirement here is for management to show “due diligence” in establishing an effective compliance, or security program. It is senior management that could face legal repercussions if they do not have sufficient controls in place.
The following answers are incorrect:
IS security specialists. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. Senior management bears the primary responsibility for determining the level of protection needed.
Senior security analysts. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. Senior management bears the primary responsibility for determining the level of protection needed.
systems auditors. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer, system auditors are responsible that the controls in place are effective. Senior management bears the primary responsibility for determining the level of protection needed.
-
The security of a computer application is most effective and economical in which of the following cases?
- The system is optimized prior to the addition of security.
- The system is procured off-the-shelf.
- The system is customized to meet the specific security threat.
- The system is originally designed to provide the necessary security.
Explanation:The earlier in the process that security is planned for and implement the cheaper it is. It is also much more efficient if security is addressed in each phase of the development cycle rather than an add-on because it gets more complicated to add at the end. If security plan is developed at the beginning it ensures that security won’t be overlooked.
The following answers are incorrect:
The system is optimized prior to the addition of security. Is incorrect because if you wait to implement security after a system is completed the cost of adding security increases dramtically and can become much more complex.
The system is procured off-the-shelf. Is incorrect because it is often difficult to add security to off-the shelf systems.
The system is customized to meet the specific security threat. Is incorrect because this is a distractor. This implies only a single threat.
-
Who is ultimately responsible for the security of computer based information systems within an organization?
- The tech support team
- The Operation Team.
- The management team.
- The training team.
Explanation:If there is no support by management to implement, execute, and enforce security policies and procedure, then they won’t work. Senior management must be involved in this because they have an obligation to the organization to protect the assests . The requirement here is for management to show “due diligence” in establishing an effective compliance, or security program.
The following answers are incorrect:
The tech support team. Is incorrect because the ultimate responsibility is with management for the security of computer-based information systems.
The Operation Team. Is incorrect because the ultimate responsibility is with management for the security of computer-based information systems.
The Training Team. Is incorrect because the ultimate responsibility is with management for the security of computer-based information systems.
Reference(s) used for this question:
OIG CBK Information Security Management and Risk Management (page 20 – 22) -
The major objective of system configuration management is which of the following?
- system maintenance.
- system stability.
- system operations.
- system tracking.
Explanation:A major objective with Configuration Management is stability. The changes to the system are controlled so that they don’t lead to weaknesses or faults in th system.
The following answers are incorrect:
system maintenance. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. Configuration Management does control the changes to the system but it is not as important as the overall stability of the system.
system operations. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer, the overall stability of the system is much more important.
system tracking. Is incorrect because while tracking changes is important, it is not the best answer. The overall stability of the system is much more important.
-
An Architecture where there are more than two execution domains or privilege levels is called:
- Ring Architecture.
- Ring Layering
- Network Environment.
- Security Models
Explanation:In computer science, hierarchical protection domains, often called protection rings, are a mechanism to protect data and functionality from faults (fault tolerance) and malicious behavior (computer security). This approach is diametrically opposite to that of capability-based security.
Computer operating systems provide different levels of access to resources. A protection ring is one of two or more hierarchical levels or layers of privilege within the architecture of a computer system. This is generally hardware-enforced by some CPU architectures that provide different CPU modes at the hardware or microcode level. Rings are arranged in a hierarchy from most privileged (most trusted, usually numbered zero) to least privileged (least trusted, usually with the highest ring number). On most operating systems, Ring 0 is the level with the most privileges and interacts most directly with the physical hardware such as the CPU and memory.
Special gates between rings are provided to allow an outer ring to access an inner ring’s resources in a predefined manner, as opposed to allowing arbitrary usage. Correctly gating access between rings can improve security by preventing programs from one ring or privilege level from misusing resources intended for programs in another. For example, spyware running as a user program in Ring 3 should be prevented from turning on a web camera without informing the user, since hardware access should be a Ring 1 function reserved for device drivers. Programs such as web browsers running in higher numbered rings must request access to the network, a resource restricted to a lower numbered ring.
Ring Architecture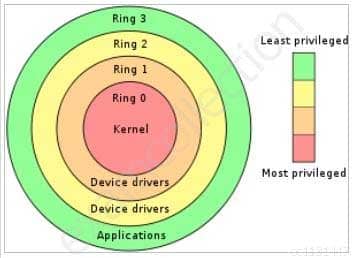
SSCP System Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP) Part 32 Q06 035 All of the other answers are incorrect because they are detractors.
References:
OIG CBK Security Architecture and Models (page 311)
and
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ring_%28computer_security%29 -
Which of the following is commonly used for retrofitting multilevel security to a database management system?
- trusted front-end.
- trusted back-end.
- controller.
- kernel.
Explanation:If you are “retrofitting” that means you are adding to an existing database management system (DBMS). You could go back and redesign the entire DBMS but the cost of that could be expensive and there is no telling what the effect will be on existing applications, but that is redesigning and the question states retrofitting. The most cost effective way with the least effect on existing applications while adding a layer of security on top is through a trusted front-end.
Clark-Wilson is a synonym of that model as well. It was used to add more granular control or control to database that did not provide appropriate controls or no controls at all. It is one of the most popular model today. Any dynamic website with a back-end database is an example of this today.
Such a model would also introduce separation of duties by allowing the subject only specific rights on the objects they need to access.
The following answers are incorrect:
trusted back-end. Is incorrect because a trusted back-end would be the database management system (DBMS). Since the question stated “retrofitting” that eliminates this answer.
controller. Is incorrect because this is a distractor and has nothing to do with “retrofitting”.
kernel. Is incorrect because this is a distractor and has nothing to do with “retrofitting”. A security kernel would provide protection to devices and processes but would be inefficient in protecting rows or columns in a table.
-
If an operating system permits shared resources such as memory to be used sequentially by multiple users/application or subjects without a refresh of the objects/memory area, what security problem is MOST likely to exist?
- Disclosure of residual data.
- Unauthorized obtaining of a privileged execution state.
- Data leakage through covert channels.
- Denial of service through a deadly embrace.
Explanation:Allowing objects to be used sequentially by multiple users without a refresh of the objects can lead to disclosure of residual data. It is important that steps be taken to eliminate the chance for the disclosure of residual data.
Object reuse refers to the allocation or reallocation of system resources to a user or, more appropriately, to an application or process. Applications and services on a computer system may create or use objects in memory and in storage to perform programmatic functions. In some cases, it is necessary to share these resources between various system applications. However, some objects may be employed by an application to perform privileged tasks on behalf of an authorized user or upstream application. If object usage is not controlled or the data in those objects is not erased after use, they may become available to unauthorized users or processes.
Disclosure of residual data and Unauthorized obtaining of a privileged execution state are both a problem with shared memory and resources. Not clearing the heap/stack can result in residual data and may also allow the user to step on somebody’s session if the security token/identify was maintained in that space. This is generally more malicious and intentional than accidental though. The MOST common issue would be Disclosure of residual data.
The following answers are incorrect:
Unauthorized obtaining of a privileged execution state. Is incorrect because this is not a problem with Object Reuse.
Data leakage through covert channels. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer. A covert channel is a communication path. Data leakage would not be a problem created by Object Reuse. In computer security, a covert channel is a type of computer security attack that creates a capability to transfer information objects between processes that are not supposed to be allowed to communicate by the computer security policy. The term, originated in 1973 by Lampson is defined as “(channels) not intended for information transfer at all, such as the service program’s effect on system load.” to distinguish it from Legitimate channels that are subjected to access controls by COMPUSEC.
Denial of service through a deadly embrace. Is incorrect because it is only a detractor.
References:
Hernandez CISSP, Steven (2012-12-21). Official (ISC)2 Guide to the CISSP CBK, Third Edition ((ISC)2 Press) (Kindle Locations 4174-4179). Auerbach Publications. Kindle Edition.
and
https://www.fas.org/irp/nsa/rainbow/tg018.htm
and
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covert_channel -
The Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (ITSEC) was written to address which of the following that the Orange Book did not address?
- integrity and confidentiality.
- confidentiality and availability.
- integrity and availability.
- none of the above.
Explanation:TCSEC focused on confidentiality while ITSEC added integrity and availability as security goals.
The following answers are incorrect:
integrity and confidentiality. Is incorrect because TCSEC addressed confidentiality.
confidentiality and availability. Is incorrect because TCSEC addressed confidentiality.
none of the above. Is incorrect because ITSEC added integrity and availability as security goals. -
What does “System Integrity” mean?
- The software of the system has been implemented as designed.
- Users can’t tamper with processes they do not own.
- Hardware and firmware have undergone periodic testing to verify that they are functioning properly.
- Design specifications have been verified against the formal top-level specification.
Explanation:System Integrity means that all components of the system cannot be tampered with by unauthorized personnel and can be verified that they work properly.
The following answers are incorrect:
The software of the system has been implemented as designed. Is incorrect because this would fall under Trusted system distribution.
Users can’t tamper with processes they do not own. Is incorrect because this would fall under Configuration Management.
Design specifications have been verified against the formal top-level specification. Is incorrect because this would fall under Specification and verification.
References:
AIOv3 Security Models and Architecture (pages 302 – 306)
DOD TCSEC – http://www.cerberussystems.com/INFOSEC/stds/d520028.htm -
The Orange Book states that “Hardware and software features shall be provided that can be used to periodically validate the correct operation of the on-site hardware and firmware elements of the TCB [Trusted Computing Base].” This statement is the formal requirement for:
- Security Testing.
- Design Verification.
- System Integrity.
- System Architecture Specification.
Explanation:This is a requirement starting as low as C1 within the TCSEC rating.
The Orange book requires the following for System Integrity Hardware and/or software features shall be provided that can be used to periodically validate the correct operation of the on-site hardware and firmware elements of the TCB.
NOTE FROM CLEMENT:
This is a question that confuses a lot of people because most people take for granted that the orange book with its associated Bell LaPadula model has nothing to do with integrity. However you have to be careful about the context in which the word integrity is being used. You can have Data Integrity and you can have System Integrity which are two completely different things.Yes, the Orange Book does not specifically address the Integrity requirements, however it has to run on top of systems that must meet some integrity requirements.
This is part of what they call operational assurance which is defined as a level of confidence of a trusted system’s architecture and implementation that enforces the system’s security policy. It includes:
System architecture
Covert channel analysis
System integrity
Trusted recoveryDATA INTEGRITY
Data Integrity is very different from System Integrity. When you have integrity of the data, there are three goals:
1. Prevent authorized users from making unauthorized modifications
2. Preven unauthorized users from making modifications
3. Maintaining internal and external consistancy of the dataBell LaPadula which is based on the Orange Book address does not address Integrity, it addresses only Confidentiality.
Biba address only the first goal of integrity.
Clark-Wilson addresses the three goals of integrity.In the case of this question, there is a system integrity requirement within the TCB. As mentioned above here is an extract of the requirements: Hardware and/or software features shall be provided that can be used to periodically validate the correct operation of the on-site hardware and firmware elements of the TCB.
The following answers are incorrect:
Security Testing. Is incorrect because Security Testing has no set of requirements in the Orange book.
Design Verification. Is incorrect because the Orange book’s requirements for Design Verification include: A formal model of the security policy must be clearly identified and documented, including a mathematical proof that the model is consistent with its axioms and is sufficient to support the security policy.
System Architecture Specification. Is incorrect because there are no requirements for System Architecture Specification in the Orange book.
The following reference(s) were used for this question:
Trusted Computer Security Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC), DoD 5200.28-STD, page 15, 18, 25, 31, 40, 50.
Harris, Shon (2012-10-25). CISSP All-in-One Exam Guide, 6th Edition, Security Architecture and Design, Page 392-397, for users with the Kindle Version see Kindle Locations 28504-28505.
and
DOD TCSEC – http://www.cerberussystems.com/INFOSEC/stds/d520028.htm -
Which of the following are required for Life-Cycle Assurance?
- System Architecture and Design specification.
- Security Testing and Covert Channel Analysis.
- Security Testing and Trusted distribution.
- Configuration Management and Trusted Facility Management.
Explanation:Security testing and trusted distribution are required for Life-Cycle Assurance.
The following answers are incorrect:
System Architecture and Design specification. Is incorrect because System Architecture is not requried for Life-Cycle Assurance.
Security Testing and Covert Channel Analysis. Is incorrect because Covert Channel Analysis is not requried for Life-Cycle Assurance.
Configuration Management and Trusted Facility Management. Is incorrect because Trusted Facility Management. is not requried for Life-Cycle Assurance.
-
Memory management in TCSEC levels B3 and A1 operating systems may utilize “data hiding”. What does this mean?
- System functions are layered, and none of the functions in a given layer can access data outside that layer.
- Auditing processes and their memory addresses cannot be accessed by user processes.
- Only security processes are allowed to write to ring zero memory.
- It is a form of strong encryption cipher.
Explanation:Data Hiding is protecting data so that it is only available to higher levels this is done and is also performed by layering, when the software in each layer maintains its own global data and does not directly reference data outside its layers.
The following answers are incorrect:
Auditing processes and their memory addresses cannot be accessed by user processes. Is incorrect because this does not offer data hiding.
Only security processes are allowed to write to ring zero memory. This is incorrect, the security kernel would be responsible for this.
It is a form of strong encryption cipher. Is incorrect because this does not conform to the definition of data hiding.
-
Which of the following exemplifies proper separation of duties?
- Operators are not permitted modify the system time.
- Programmers are permitted to use the system console.
- Console operators are permitted to mount tapes and disks.
- Tape operators are permitted to use the system console.
Explanation:This is an example of Separation of Duties because operators are prevented from modifying the system time which could lead to fraud. Tasks of this nature should be performed by they system administrators.
AIO defines Separation of Duties as a security principle that splits up a critical task among two or more individuals to ensure that one person cannot complete a risky task by himself.
The following answers are incorrect:
Programmers are permitted to use the system console. Is incorrect because programmers should not be permitted to use the system console, this task should be performed by operators. Allowing programmers access to the system console could allow fraud to occur so this is not an example of Separation of Duties..
Console operators are permitted to mount tapes and disks. Is incorrect because operators should be able to mount tapes and disks so this is not an example of Separation of Duties.
Tape operators are permitted to use the system console. Is incorrect because operators should be able to use the system console so this is not an example of Separation of Duties.
References:
OIG CBK Access Control (page 98 – 101)
AIOv3 Access Control (page 182) -
The control of communications test equipment should be clearly addressed by security policy for which of the following reasons?
- Test equipment is easily damaged.
- Test equipment can be used to browse information passing on a network.
- Test equipment is difficult to replace if lost or stolen.
- Test equipment must always be available for the maintenance personnel.
Explanation:Test equipment must be secured. There are equipment and other tools that if in the wrong hands could be used to “sniff” network traffic and also be used to commit fraud. The storage and use of this equipment should be detailed in the security policy for this reason.
The following answers are incorrect:
Test equipment is easily damaged. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer, and from a security point of view not relevent.
Test equipment is difficult to replace if lost or stolen. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer, and from a security point of view not relevent.
Test equipment must always be available for the maintenance personnel. Is incorrect because it is not the best answer, and from a security point of view not relevent.
References:
OIG CBK Operations Security (pages 642 – 643) -
Which of the following can be used as a covert channel?
- Storage and timing.
- Storage and low bits.
- Storage and permissions.
- Storage and classification.
Explanation:The Orange book requires protection against two types of covert channels, Timing and Storage.
The following answers are incorrect:
Storage and low bits. Is incorrect because, low bits would not be considered a covert channel.
Storage and permissions. Is incorrect because, permissions would not be considered a covert channel.
Storage and classification. Is incorrect because, classification would not be considered a covert channel. -
Configuration Management controls what?
- Auditing of changes to the Trusted Computing Base.
- Control of changes to the Trusted Computing Base.
- Changes in the configuration access to the Trusted Computing Base.
- Auditing and controlling any changes to the Trusted Computing Base.
Explanation:All of these are components of Configuration Management.
The following answers are incorrect:
Auditing of changes to the Trusted Computing Base. Is incorrect because it refers only to auditing the changes, but nothing about controlling them.
Control of changes to the Trusted Computing Base. Is incorrect because it refers only to controlling the changes, but nothing about ensuring the changes will not lead to a weakness or fault in the system.
Changes in the configuration access to the Trusted Computing Base. Is incorrect because this does not refer to controlling the changes or ensuring the changes will not lead to a weakness or fault in the system.
-
Which of the following is used by RADIUS for communication between clients and servers?
- TCP
- SSL
- UDP
- SSH
Explanation:Source: TIPTON, Harold F. & KRAUSE, MICKI, Information Security Management Handbook, 4th Edition, Volume 2, 2001, CRC Press, NY, Page 33. -
Which security model is based on the military classification of data and people with clearances?
- Brewer-Nash model
- Clark-Wilson model
- Bell-LaPadula model
- Biba model
Explanation:The Bell-LaPadula model is a confidentiality model for information security based on the military classification of data, on people with clearances and data with a classification or sensitivity model. The Biba, Clark-Wilson and Brewer-Nash models are concerned with integrity.
Source: HARE, Chris, Security Architecture and Models, Area 6 CISSP Open Study Guide, January 2002. -
What mechanism automatically causes an alarm originating in a data center to be transmitted over the local municipal fire or police alarm circuits for relaying to both the local police/fire station and the appropriate headquarters?
- Central station alarm
- Proprietary alarm
- A remote station alarm
- An auxiliary station alarm
Explanation:Auxiliary station alarms automatically cause an alarm originating in a data center to be transmitted over the local municipal fire or police alarm circuits for relaying to both the local police/fire station and the appropriate headquarters. They are usually Municipal Fire Alarm Boxes are installed at your business or building, they are wired directly into the fire station.
Central station alarms are operated by private security organizations. It is very similar to a proprietary alarm system (see below). However, the biggest difference is the monitoring and receiving of alarm is done off site at a central location manned by non staff members. It is a third party.
Proprietary alarms are similar to central stations alarms except that monitoring is performed directly on the protected property. This type of alarm is usually use to protect large industrials or commercial buildings. Each of the buildings in the same vincinity has their own alarm system, they are all wired together at a central location within one of the building acting as a common receiving point. This point is usually far away from the other building so it is not under the same danger. It is usually man 24 hours a day by a trained team who knows how to react under different conditions.
A remote station alarm is a direct connection between the signal-initiating device at the protected property and the signal-receiving device located at a remote station, such as the fire station or usually a monitoring service. This is the most popular type of implementation and the owner of the premise must pay a monthly monitoring fee. This is what most people use in their home where they get a company like ADT to receive the alarms on their behalf.
A remote system differs from an auxiliary system in that it does not use the municipal fire of police alarm circuits.
Reference(s) used for this question:
ANDRESS, Mandy, Exam Cram CISSP, Coriolis, 2001, Chapter 11: Physical Security (page 211).
and
Great presentation J.T.A. Stone on SlideShare