1.2.8.5 Check Your Understanding – Data Storage Devices Answers 2025 Full 100%
1.2.8.5 Check Your Understanding – Data Storage Devices Answers 2025 Full 100%
Are you looking for the correct answers to “1.2.8.5 Check Your Understanding – Data Storage Devices Answers” in 2025? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide, we provide accurate and verified answers to help you understand different types of data storage devices, including HDDs, SSDs, USB flash drives, optical discs, and cloud storage. Whether you’re preparing for an IT exam or just want to expand your knowledge, these answers will ensure you achieve 100% success. Read on to find the complete solutions and explanations!
-
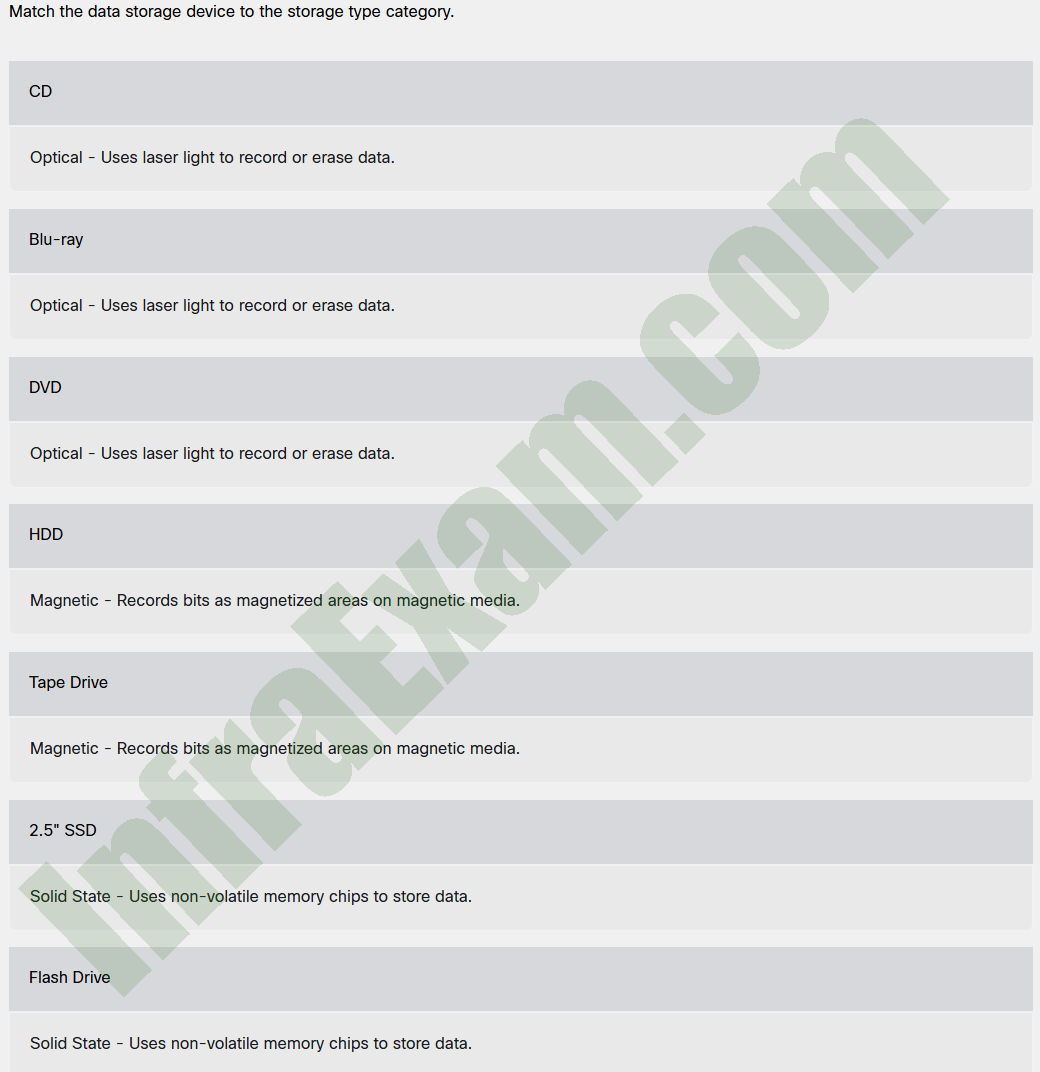
Match the data storage device to the storage type category.
Understanding Data Storage Devices and Their Categories
Data storage devices play a critical role in modern computing, allowing users to store, retrieve, and manage digital information efficiently. Different types of storage devices exist, categorized based on their storage technology. This article explores various data storage devices and their respective categories, providing a comprehensive understanding of their functions, advantages, and limitations.
1. Optical Storage Devices
Optical storage devices use laser light to read and write data. These devices are primarily used for storing multimedia files, software, and backups. The three main types of optical storage devices are CDs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs.
Compact Disc (CD)
A Compact Disc (CD) is an optical storage device that uses laser technology to store and retrieve data. CDs were widely used for music distribution, software installation, and data storage. They have a typical storage capacity of 700 MB, which is suitable for small-sized files and applications.
- Technology Used: Laser light reads and writes data.
- Common Uses: Music albums, software distribution, small file storage.
- Advantages: Portable, inexpensive, widely compatible.
- Limitations: Limited storage, prone to scratches and damage.
Digital Versatile Disc (DVD)
A Digital Versatile Disc (DVD) is an advancement over CDs, offering significantly higher storage capacity. DVDs can store up to 4.7 GB on a single layer and 8.5 GB on a dual-layer disc. They are commonly used for video storage, including movies and high-quality multimedia content.
- Technology Used: Laser light reads and writes data (shorter wavelength than CDs, allowing higher data density).
- Common Uses: Movies, video games, software installation, backups.
- Advantages: Higher capacity than CDs, widely supported format.
- Limitations: Still prone to physical damage, slower read/write speeds than solid-state storage.
Blu-ray Disc
A Blu-ray Disc is a high-capacity optical storage medium developed for high-definition video and data storage. It uses a blue-violet laser, which has a shorter wavelength than the red laser used in DVDs and CDs, enabling higher data density. Standard Blu-ray discs hold 25 GB (single-layer) or 50 GB (dual-layer).
- Technology Used: Blue-violet laser for data reading/writing.
- Common Uses: High-definition movies, PlayStation game storage, high-capacity backups.
- Advantages: Large storage capacity, high-quality media playback.
- Limitations: More expensive than DVDs, requires Blu-ray-compatible hardware.
2. Magnetic Storage Devices
Magnetic storage devices use magnetized regions to store data. They have been widely used for data storage in computers, especially for large-capacity requirements. Examples include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Tape Drives.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
A Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is one of the most common magnetic storage devices. It consists of spinning magnetic platters and read/write heads. Data is written and retrieved using an electromagnet. HDDs have been the primary storage solution for decades due to their affordability and high storage capacity.
- Technology Used: Spinning magnetic platters with read/write heads.
- Common Uses: Operating system storage, applications, large data storage.
- Advantages: Cost-effective per GB, high capacity (from hundreds of GBs to multiple TBs).
- Limitations: Slower than SSDs, mechanical parts prone to failure, power consumption is high.
Tape Drive
A Tape Drive is a data storage device that uses magnetic tape as a medium for storing digital information. It is commonly used for backup and archival purposes due to its high capacity and long-term reliability. Tape drives are widely utilized in enterprise environments where large amounts of data need to be stored securely over long periods.
- Technology Used: Magnetic tape for sequential data storage.
- Common Uses: Enterprise data backup, long-term storage, archival purposes.
- Advantages: High storage capacity, reliable for long-term storage, cost-effective for bulk data.
- Limitations: Slow data retrieval, sequential access makes searching inefficient.
3. Solid-State Storage Devices
Solid-state storage devices use non-volatile memory chips to store data, making them significantly faster and more durable than magnetic and optical storage devices. Examples include Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Flash Drives.
2.5″ Solid-State Drive (SSD)
A 2.5″ SSD is a storage device that replaces traditional hard drives in laptops and desktops. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, relying instead on NAND flash memory to store data, which allows for much faster read and write speeds.
- Technology Used: NAND flash memory for non-volatile data storage.
- Common Uses: Laptop and desktop storage, gaming, professional applications requiring fast speeds.
- Advantages: Faster read/write speeds than HDDs, energy efficient, shock-resistant.
- Limitations: More expensive than HDDs, limited write cycles can reduce lifespan.
Flash Drive (USB Drive)
A Flash Drive, also known as a USB Drive, is a portable storage device that uses flash memory. Flash drives are widely used for transferring and storing files due to their compact size and ease of use.
- Technology Used: NAND flash memory.
- Common Uses: Transferring files, temporary storage, bootable drives.
- Advantages: Portable, no moving parts, fast data access.
- Limitations: Limited storage capacity compared to SSDs and HDDs, susceptible to loss due to small size.
Comparison Table of Data Storage Devices
| Storage Device | Type | Capacity | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD | Optical | ~700MB | Portable, inexpensive | Limited storage, prone to scratches |
| DVD | Optical | 4.7GB – 8.5GB | More storage than CDs | Still limited compared to HDDs & SSDs |
| Blu-ray | Optical | 25GB – 50GB | High-definition media storage | Requires Blu-ray-compatible hardware |
| HDD | Magnetic | 500GB – 10TB+ | Cost-effective, high capacity | Slower, mechanical parts can fail |
| Tape Drive | Magnetic | Several TBs | Reliable for long-term storage | Slow retrieval time |
| 2.5″ SSD | Solid State | 128GB – 4TB | Fast, durable, energy efficient | Expensive compared to HDDs |
| Flash Drive | Solid State | 4GB – 1TB | Portable, convenient | Limited storage, easy to lose |
Conclusion
Understanding different storage devices and their categories is essential for choosing the right storage solution based on your needs. Optical storage is still useful for media playback and software distribution, while magnetic storage offers cost-effective high-capacity solutions. Solid-state storage, on the other hand, provides speed and durability, making it ideal for modern computing. Whether you need storage for everyday computing, backup, or enterprise applications, knowing the strengths and weaknesses of each technology helps you make informed decisions.