Match the description to the Linux term. (Not all options are used.)
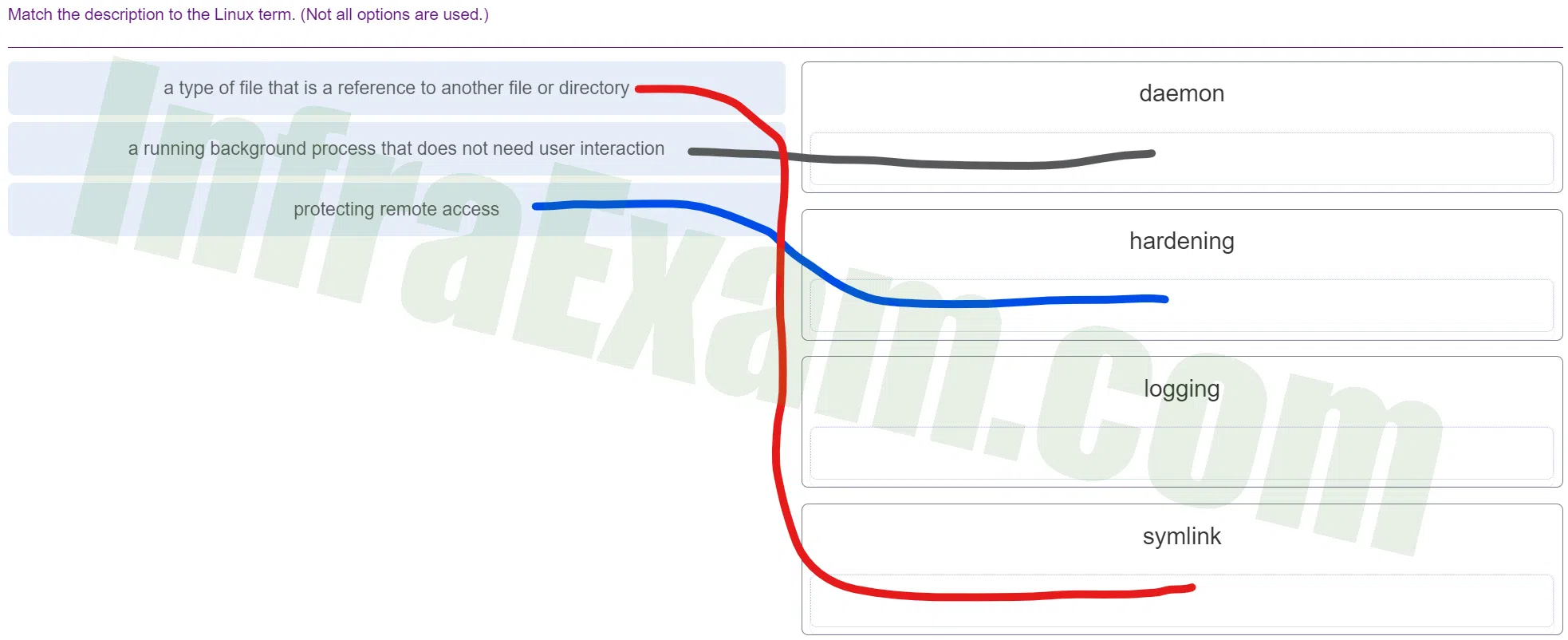
- a type of file that is a reference to another file or directory ==> symlink
- a running background process that does not need user interaction ==> daemon
- protecting remote access ==> hardening
|
Explanation & Hint:
|
For more Questions and Answers:
CA – CyberOps Associate v1.0 – Modules 3 – 4: Operating System Overview Group Exam Answers Full 100%
CyberOps Associate (200-201) Certification Practice Exam Answers Full 100%
Match the description to the Linux term. (Not all options are used.)
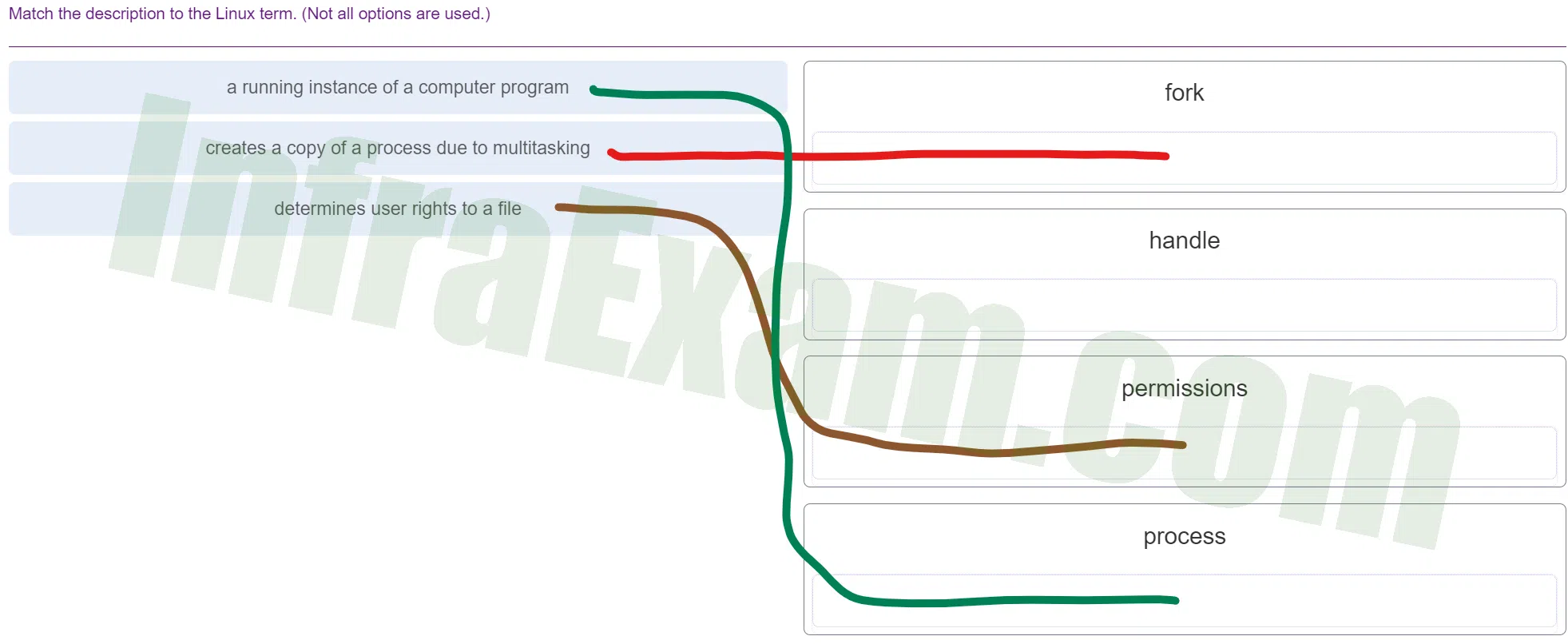
- a running instance of a computer program ==> process
- creates a copy of a process due to multitasking ==> fork
- determines user rights to a file ==> permissions
|
Explanation & Hint:
|