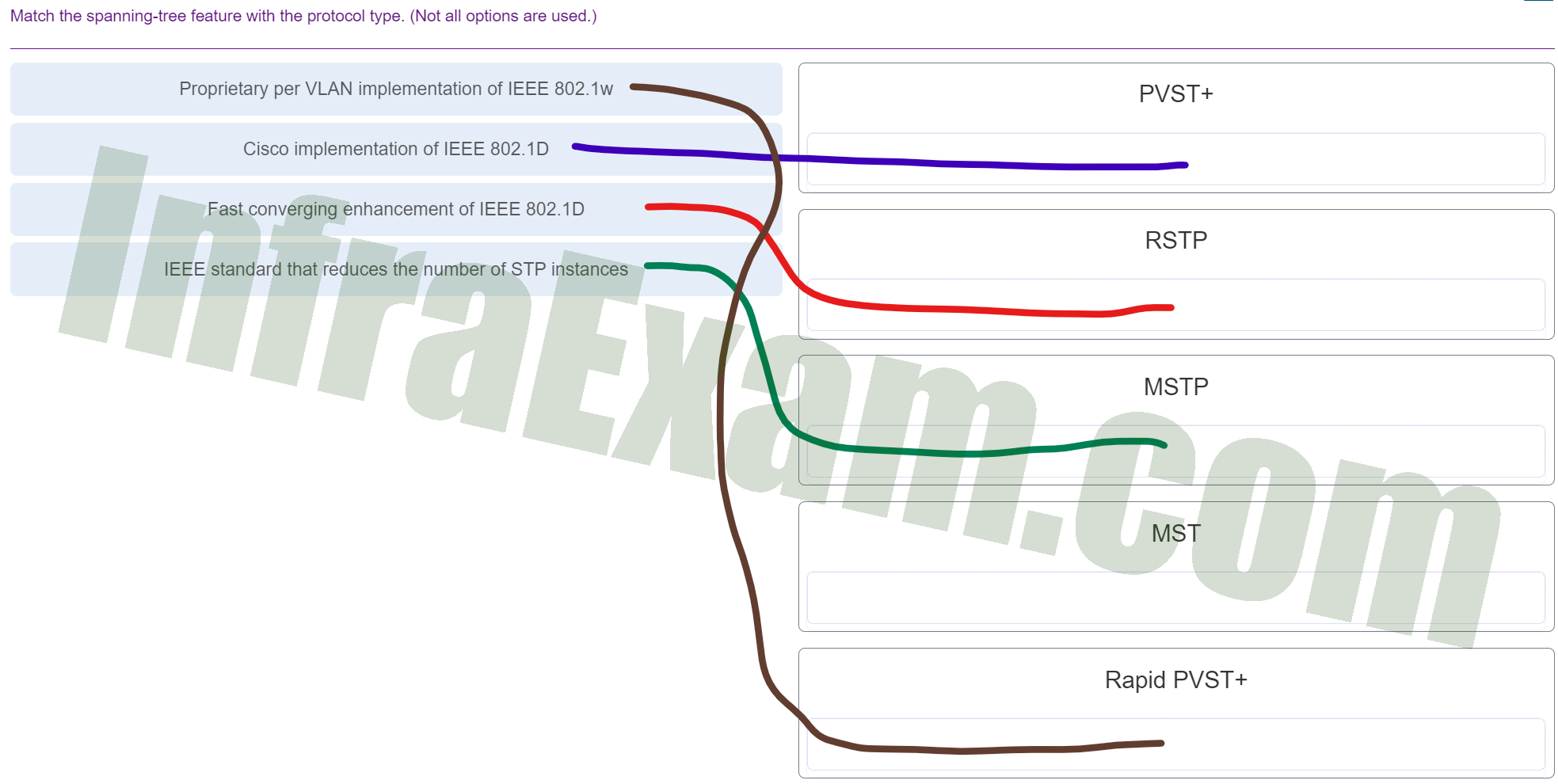
| Answers Explanation & Hints:
MST is the Cisco implementation of MSTP (IEEE 802.1s).
PVST+ (Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus):
- PVST+ is a Cisco proprietary protocol that is an extension of the original IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). It is used in Ethernet networks to prevent loops and create a loop-free topology.
- PVST+ operates by creating a separate spanning tree for each VLAN in the network. This means that it can calculate multiple spanning trees in parallel, one for each VLAN. This approach allows for load balancing and redundancy on a per-VLAN basis.
RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol):
- RSTP, defined by IEEE 802.1w, is a standard protocol designed to improve the convergence time of the original STP. It provides faster recovery from network topology changes.
- RSTP achieves rapid convergence by using features like port roles (e.g., discarding, learning, or forwarding), better BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units) with proposal and agreement mechanisms, and faster aging of MAC address table entries.
- RSTP retains backward compatibility with STP, which means it can interact with switches running the original STP or PVST+.
MSTP (Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol):
- MSTP, defined by IEEE 802.1s, is a standard protocol that provides a more efficient way to manage multiple VLANs in a network. It is vendor-neutral and designed to overcome some of the limitations of PVST+ and RSTP.
- MSTP allows network administrators to group VLANs into one or more instances (also known as “regions”), and each instance has its own spanning tree. This allows for better load balancing and redundancy control, especially in networks with numerous VLANs.
MST (Multiple Spanning Tree):
- MST is the practical implementation of MSTP, where VLANs are grouped into instances, and each instance has its own spanning tree topology. MSTP calculates the minimum number of spanning tree instances necessary to cover all VLANs in the network, reducing the computational overhead.
Rapid PVST+ (Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree Plus):
- Rapid PVST+ is a Cisco proprietary extension of the original PVST+ protocol. It combines the benefits of PVST+ and RSTP to create a faster-converging, loop-free network.
- Similar to PVST+, Rapid PVST+ creates a separate spanning tree for each VLAN, allowing for per-VLAN load balancing and redundancy. However, it incorporates RSTP features to achieve faster convergence in response to network topology changes.
In summary, PVST+ is Cisco’s proprietary per-VLAN STP, RSTP is a standard protocol for faster STP convergence, MSTP is a standard protocol for efficient management of multiple VLANs, MST is the practical implementation of MSTP, and Rapid PVST+ is Cisco’s enhanced version of PVST+ with rapid convergence capabilities. Each of these protocols serves to prevent network loops and optimize network performance. |