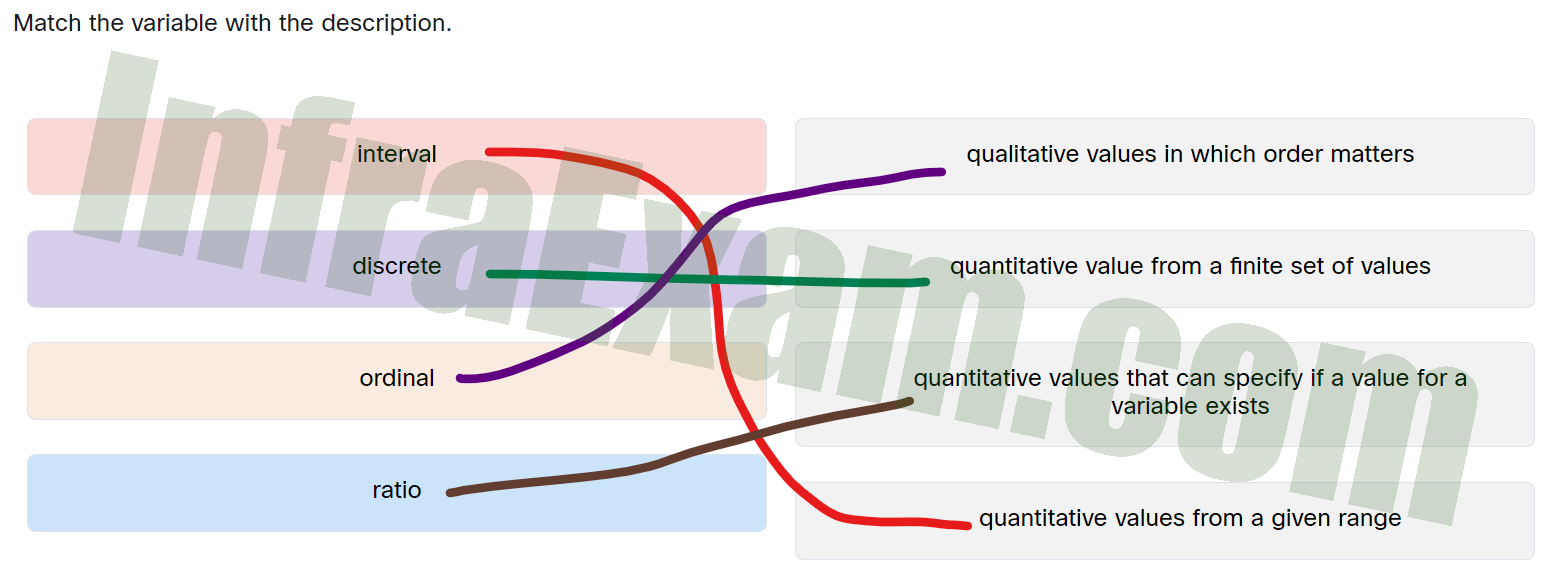
Answers Explanation & Hints:
- Nominal variable: This is a type of variable that describes data that is qualitative or categorical, meaning it is based on the identity of an object. For example, colors, gender, or type of product are all examples of nominal variables. They do not have an inherent order or ranking.
- Ordinal variable: This is a type of variable that describes data that is also qualitative or categorical, but the values are ordered in some way. For example, letter grades such as A, B, C, D, or E, or customer satisfaction ratings such as “very satisfied,” “somewhat satisfied,” “neutral,” “somewhat dissatisfied,” or “very dissatisfied” are examples of ordinal variables.
- Discrete variable: This is a type of variable that describes data that is quantitative and has a finite set of values. Discrete variables usually represent counts of items, such as the number of students in a classroom, the number of cars in a parking lot, or the number of items sold by a business.
- Continuous variable: This is a type of variable that describes data that is also quantitative but has an infinite range of possible values. Continuous variables are usually measurements of some kind, such as height, weight, or temperature. They can take on any value within a range, and they are often represented on a scale with decimal points.
|