98-366 : Networking Fundamentals : Part 06
-
A university has network links between various locations. Where would a T3 connection be appropriate?
- Server to network in the main campus server room
- Main campus to a large satellite campus
- Computer lab PC to lab printer
- Library laptop PC to Internet
Explanation:T3 lines are a common aggregation of 28 T1 circuits that yields 44.736 Mbps total network bandwidth . Besides being used for long-distance traffic, T3 lines are also often used to build the core of a business network at its headquarters
-
HOTSPOT
You cannot get to any site on the Internet or on the school’s intranet. Your school uses DHCP.You check your network settings, which are configured as shown in the following image:

98-366 Part 06 Q02 015 You need to change the settings to access websites.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q02 016 Question 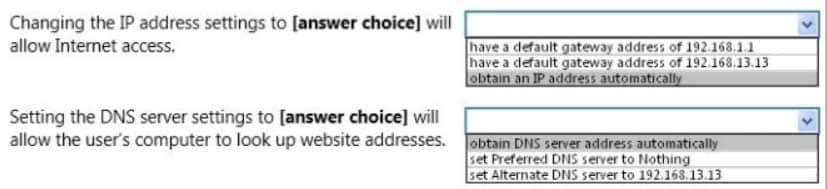
98-366 Part 06 Q02 016 Answer Explanation:The configuration must be set to obtain both IP and DNS server address automatically.
-
DRAG DROP
Match each network type to its corresponding definition.To answer, drag the appropriate network type from the column on the left to its definition on the right. Each network type may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q03 017 Question 
98-366 Part 06 Q03 017 Answer Explanation:* An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from outside of an organization’s intranet. Extranets are used for specific use cases including business-to-business (B2B).
* An intranet is a private network that is contained within an enterprise
* The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks -
DRAG DROP
Match the VPN connection type to the corresponding definition.To answer, drag the appropriate VPN term from the column on the left to its definition on the right. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q04 018 Question 
98-366 Part 06 Q04 018 Answer Explanation:* An SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer virtual private network) is a form of VPN that can be used with a standard Web browser. In contrast to the traditional Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) VPN, an SSL VPN does not require the installation of specialized client software on the end user’s computer. It’s used to give remote users with access to Web applications, client/server applications and internal network connections.
* A site-to-site VPN allows offices in multiple fixed locations to establish secure connections with each other over a public network such as the Internet.
* Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs. It does not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself. -
DRAG DROP
Match each set of characteristics to the corresponding 802.11 standard.To answer, drag the appropriate set of characteristics from the column on the left to its 802.11 standard on the right. Each set may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.
98-366 Part 06 Q05 019 Question 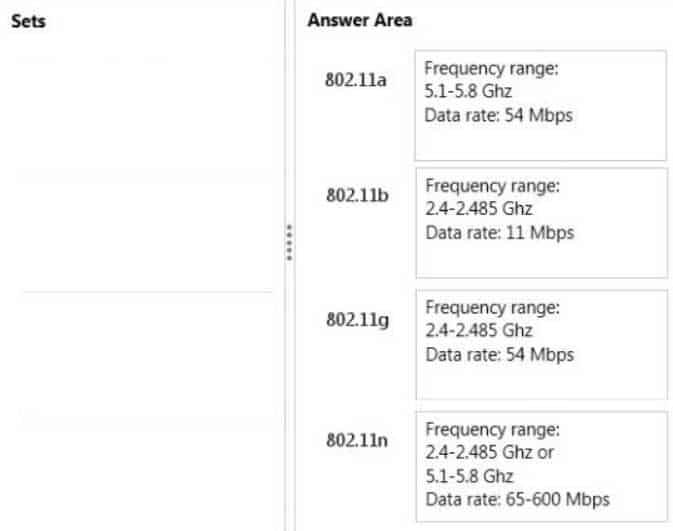
98-366 Part 06 Q05 019 Answer Explanation:* 802.11a
5.8 GHz
allow transmission and reception of data at rates of 1.5 to 54 Mbit/s.* 802.11b
2.4 GHz
The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s.* 802.11g
works in the 2.4 GHz band (like 802.11b)
maximum physical layer bit rate of 54 Mbit/s -
You work at a coffee shop. Your supervisor asks you to help set up a computer network.
The network needs to have the following items:
A public facing web server
A Wi-Fi network for customers
A private network for the point of sale terminals
An office PC
A file/print server
A network printerYou need to set up a perimeter network to protect the network.
Which two items should you include in the perimeter network? (Choose two.)
- Network printer
- Web server
- File server
- Wi-Fi network
- Point of sale terminals
Explanation:Put the web server and the network printer on the perimeter network.
The file server, wifi-network, and the Point of sale terminals should not be accessible from the internet.Note: A network perimeter is the boundary between the private and locally managed-and-owned side of a network and the public and usually provider-managed side of a network.
-
DRAG DROP
Match the networking topologies to their corresponding characteristics.To answer, drag the appropriate topology from the column on the left to its characteristic on the right. Each topology may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.
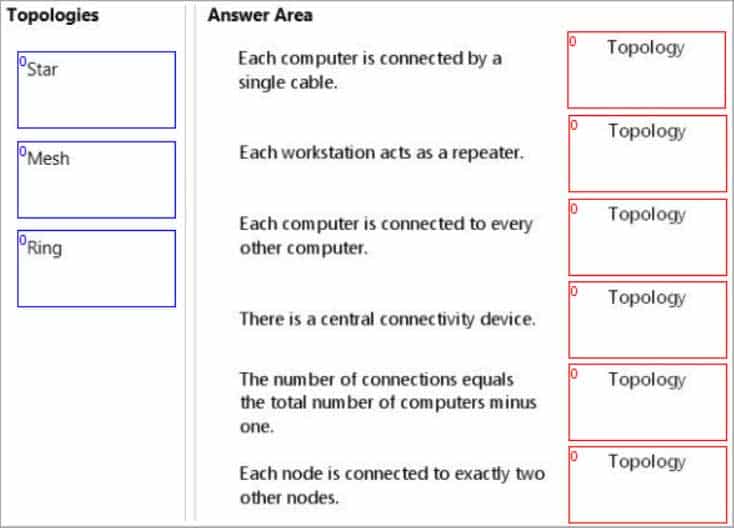
98-366 Part 06 Q07 020 Question 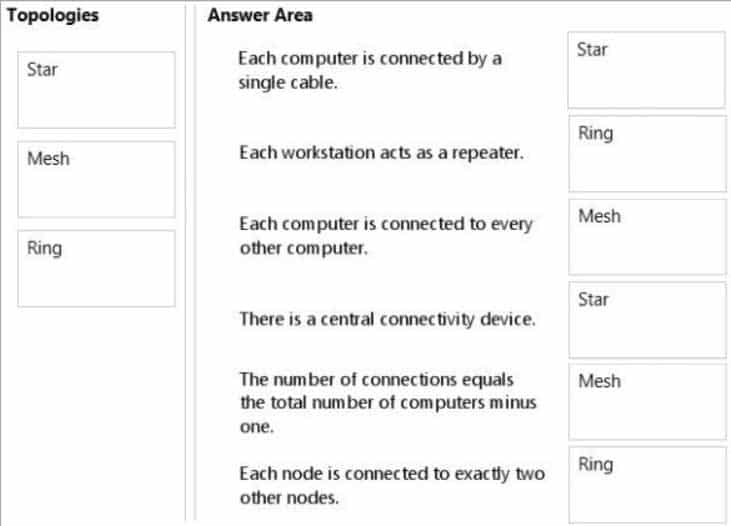
98-366 Part 06 Q07 020 Answer Explanation:* Star
In star topology, every node (computer workstation or any other peripheral) is connected to a central node called a hub or switch.
* Ring
Each device present in Ring Topology is incorporated with a REPEATER.
* Mesh
Fully connected mesh topology: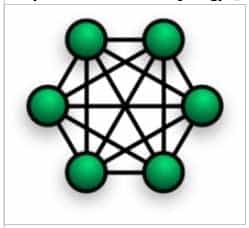
98-366 Part 06 Q07 021 A fully connected network is a communication network in which each of the nodes is connected to each other.
* Star
In star topology, every node (computer workstation or any other peripheral) is connected to a central node called a hub or switch.* mesh (full)
The major disadvantage is that the number of connections grows quadratically with the number of nodes,as per the formula: c=n(n-1)/2* Ring
Ring Topology: In this type of Topology, data is passed from one node to another in a series. Here each device has dedicated Point-to-Point connection, with only two devices present on either side of it. -
Which two features of a Windows Server 2008 R2 server should you install to use that server as a software router? (Choose two.)
- Network Policy and Access Services
- Routing and Remote Access Services
- Remote Administration
- DirectAccess
Explanation:To install the Routing and Remote Access service
– In the Server Manager main window, under Roles Summary, click Add roles.
— OR —
– In the Initial Configuration Tasks window, under Customize This Server, click Add roles.
– In the Add Roles Wizard, click Next.
– In the list of server roles, select Network Policy and Access Services. Click Next twice.
– In the list of role services, select Routing and Remote Access Services to select all of the role services. You can also select individual server roles.
– Proceed through the steps in the Add Roles Wizard to complete the installation. -
What are two characteristics of fiber optic cable? (Choose two.)
- Conducts electricity
- Requires metal conduit
- Supports splicing
- Requires a polish for end connectors
Explanation:C: A mechanical splice is a junction of two or more optical fibers that are aligned and held in place by a self-contained assembly (usually the size of a large carpenter’s nail).[1] The fibers are not permanently joined, just precisely held together so that light can pass from one to another.
D: Modern connectors typically use a “physical contact” polish on the fiber and ferrule end. This is a slightly convex surface with the apex of the curve accurately centered on the fiber, so that when the connectors are mated the fiber cores come into direct contact with one another.
Note: Optical fiber connectors are used to join optical fibers where a connect/disconnect capability is required. Due to the polishing and tuning procedures that may be incorporated into optical connector manufacturing, connectors are generally assembled onto optical fiber in a supplier’s manufacturing facility.
-
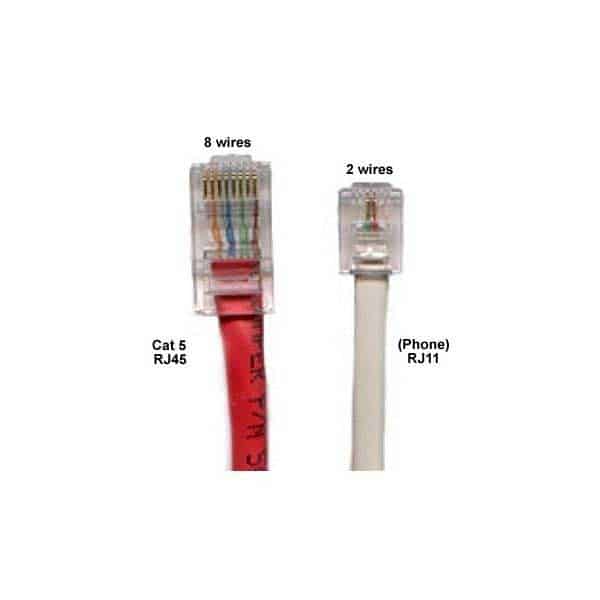
HOTSPOT
Identify the network cable type and connector in the following graphic:
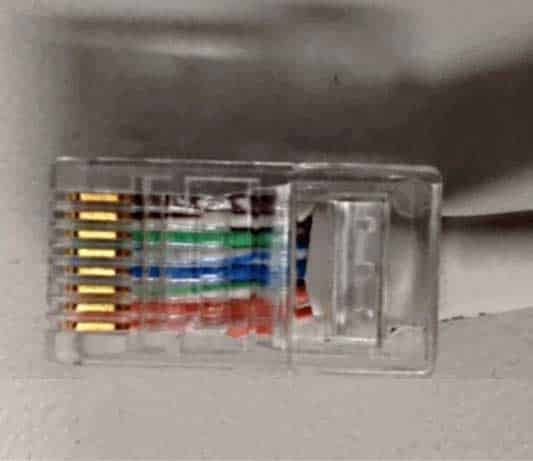
98-366 Part 06 Q10 022 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that answers each question. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q10 023 Question 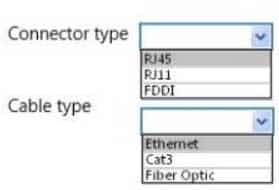
98-366 Part 06 Q10 023 Answer -
Which Microsoft network service can you use to establish a connection to a corporate LAN without any user action?
- VPN
- Remote Desktop
- DirectAccess
- Nap
Explanation:DirectAccess allows remote users to securely access internal network file shares, Web sites, and applications without connecting to a virtual private network (VPN). An internal network is also known as a private network or intranet. DirectAccess establishes bi-directional connectivity with an internal network every time a DirectAccess-enabled computer connects to the Internet, even before the user logs on. Users never have to think about connecting to the internal network and IT administrators can manage remote computers outside the office, even when the computers are not connected to the VPN.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q12 025 Question 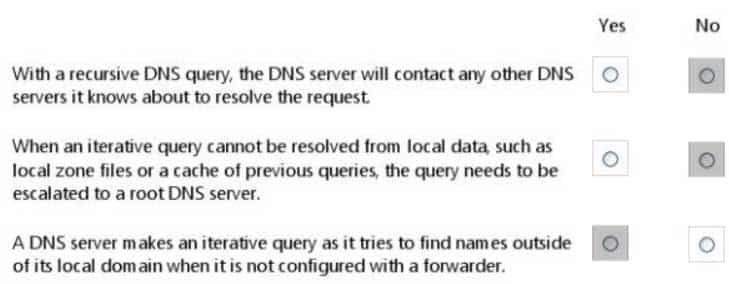
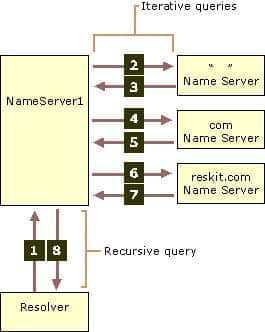
98-366 Part 06 Q12 025 Answer Explanation:* No.
With a recursive name query , the DNS client requires that the DNS server respond to the client with either the requested resource record or an error message stating that the record or domain name does not exist. The DNS server cannot just refer the DNS client to a different DNS server.
* No. * Yes.
An iterative name query is one in which a DNS client allows the DNS server to return the best answer it can give based on its cache or zone data. If the queried DNS server does not have an exact match for the queried name, the best possible information it can return is a referral (that is, a pointer to a DNS server authoritative for a lower level of the domain namespace). The DNS client can then query the DNS server for which it obtained a referral. It continues this process until it locates a DNS server that is authoritative for the queried name, or until an error or time-out condition is met.Example:
-
DRAG DROP
Match the IPv4 address type to the corresponding definition.To answer, drag the appropriate definition from the column on the left to the address type on the right. Each definition may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.
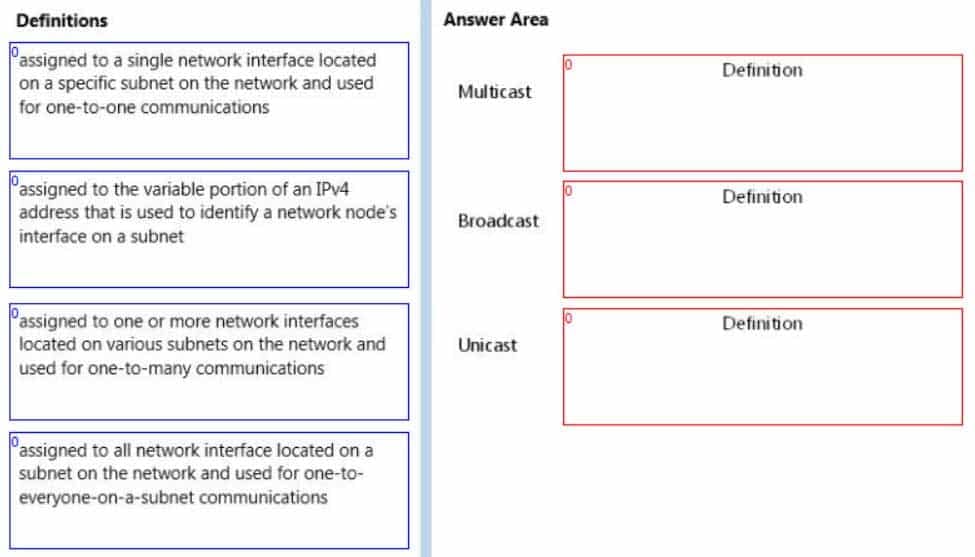
98-366 Part 06 Q13 027 Question 
98-366 Part 06 Q13 027 Answer Explanation:* Multicast
Multicast is communication between a single sender and multiple receivers on a network.
* Broadcast
Broadcasting sends a message to everyone on the network.
* Unicast
Unicast is a one-to one connection between the client and the server. -
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
A “secondary zone” is the first DNS zone to which all updates for the records that belong to that zone are written.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- Primary zone
- Stub zone
- Conditional forwarding zone
- No change is needed.
Explanation:When a zone that this DNS server hosts is a primary zone, the DNS server is the primary source for information about this zone, and it stores the master copy of zone data in a local file or in AD DS.
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q15 028 Question 
98-366 Part 06 Q15 028 Answer Explanation:* TRACERT prints out an ordered list of the routers in the path that returned the ICMP Time Exceeded message.
* Ping, not tracert, determines packet loss.
* Tracert just displays the path to the target, not all connections.Note
* Example:
tracert 11.1.0.1Tracing route to 11.1.0.1 over a maximum of 30 hops
1 2 ms 3 ms 2 ms 157.54.48.1
2 75 ms 83 ms 88 ms 11.1.0.67
3 73 ms 79 ms 93 ms 11.1.0.1Trace complete.
* The TRACERT diagnostic utility determines the route taken to a destination by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets with varying IP Time-To-Live (TTL) values to the destination. Each router along the path is required to decrement the TTL on a packet by at least 1 before forwarding it, so the TTL is effectively a hop count. When the TTL on a packet reaches 0, the router should send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source computer.
-
You are setting up a network computer game.
You need to open up ports on your firewall so your friends can join the network.
Which command displays the ports that your computer is listening for?
- nslookup
- nbtstat
- ping
- netstat
Explanation:netstat (network statistics) is a command-line tool that displays network connections for the Transmission Control Protocol (both incoming and outgoing), routing tables, and a number of network interface (network interface controller or software-defined network interface) and network protocol statistics.
Incorrect:
not A: nslookup is used for DNS troubleshooting.
Not B: Nbtstat is designed to help troubleshoot NetBIOS name resolution problems.
Not C: ping is used to troubleshoot network connectivity. -
DRAG DROP
Match the TCP ports to the corresponding service.To answer, drag the appropriate port number from the column on the left to its service on the right. Each port number may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.
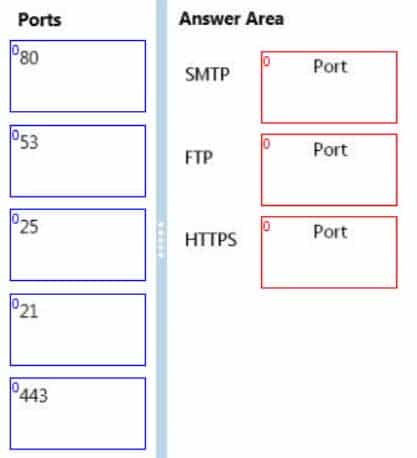
98-366 Part 06 Q17 029 Question 
98-366 Part 06 Q17 029 Answer Explanation:25 SMTP (Send Mail Transfer Protocol)
21 FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
443 Hypertext Transfer Protocol over TLS/SSL (HTTPS) -
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. Each correct selection is worth one point.

98-366 Part 06 Q18 030 Question 
98-366 Part 06 Q18 030 Answer Explanation:* The localhost (loopback) address, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, and the IPv6 unspecified address, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0, are reduced to ::1 and ::, respectively.
* A unique local address (ULA) is an IPv6 address in the block fc00::/7, defined in RFC 4193. It is the approximate IPv6 counterpart of the IPv4 private address.
* Link-local addresses for IPv4 are defined in the address block 169.254.0.0/16, in CIDR notation. In IPv6, they are assigned with the fe80::/10 prefix.
-
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct.
When a client computer is unable to reach a DHCP server, it will automatically assign an IP address in the “10.0.0.0 -10.0.0.255” range.
Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
- 127.0.0.0-127.0.0.255
- 169.254.0.0-169.254.255.255
- 192168.100.0 -192.168.100.255
- No change is needed
Explanation:169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255 is the APIPA address range. An APIPA address is used when the DHCP server is not available.
-
A node within a local area network (LAN) must have which two of the following? (Choose two.)
- Username and password
- Share name
- NIC
- IP address
- Table of all network nodes
Explanation:A node must be able to access the LAN through a network interface.
A node must also have an IP address.