DP-900 : Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals : Part 01
-
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q01 001 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q01 001 Answer -
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q02 002 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q02 002 Answer -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q03 003 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q03 003 Answer Explanation:In the ELT pipeline, the transformation occurs in the target data store. ELT only works well when the target system is powerful enough to transform the data efficiently.
Incorrect Answers:
– The data does not need to be fully processed: Often, the three ETL phases are run in parallel to save time. For example, while data is being extracted, a transformation process could be working on data already received and prepare it for loading, and a loading process can begin working on the prepared data, rather than waiting for the entire extraction process to complete.
– The target does need to be a relational database. -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q04 004 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q04 004 Answer -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q05 005 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q05 005 Answer -
DRAG DROP
Match the types of analytics that can be used to answer the business questions.
To answer, drag the appropriate analytics type from the column on the left to its question on the right. Each analytics type may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q06 006 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q06 006 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Diagnostic
Diagnostic Analytics: At this stage you can begin to answer some of those why questions. Historical data can begin to be measured against other data to answer the question of why something happened in the past. This is the process of gathering and interpreting different data sets to identify anomalies, detect patters, and determine relationships.Box 2: Prescriptive
Prescriptive analytics is a combination of data, mathematical models, and various business rules to infer actions to influence future desired outcomes.Incorrect Answer:
Predictive analytics, broadly speaking, is a category of business intelligence that uses descriptive and predictive variables from the past to analyze and identify the likelihood of an unknown future outcomeBox 3: Descriptive
Generally speaking, data analytics comes in four types:
Descriptive, to answer the question: What’s happening?
Diagnostic, to answer the question: Why’s happening?
Predictive, to answer the question: What will happen?
Prescriptive, to answer the question: What actions should we take?
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q06 007 -
HOTSPOT
You have the following JSON document.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q07 008 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the JSON document.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q07 009 Question 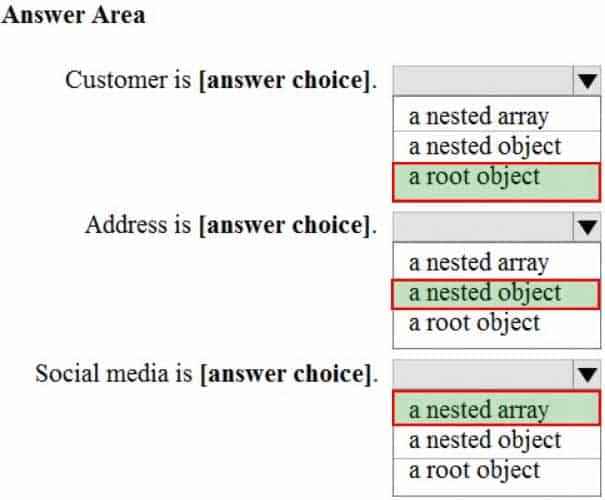
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q07 009 Answer -
HOTSPOT
You are reviewing the data model shown in the following exhibit.
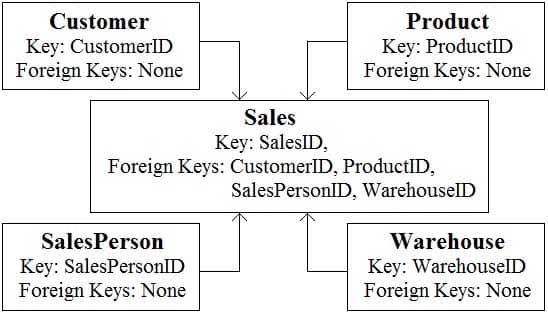
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q08 010 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q08 011 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q08 011 Answer Explanation:Box 1: star schema
In computing, the star schema is the simplest style of data mart schema and is the approach most widely used to develop data warehouses and dimensional data marts. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of dimension tables. The star schema is an important special case of the snowflake schema, and is more effective for handling simpler queries.
Example: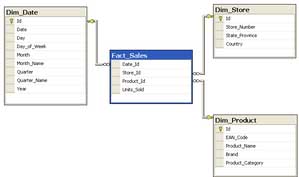
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q08 012 Incorrect Answers:
The data in the question is not normalized.
The snowflake schema is a variation of the star schema, featuring normalization of dimension tables. Example: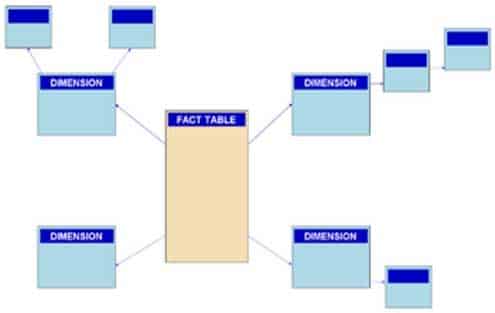
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q08 013 Note: A snowflake schema is a logical arrangement of tables in a multidimensional database such that the entity relationship diagram resembles a snowflake shape. The snowflake schema is represented by centralized fact tables which are connected to multiple dimensions.[citation needed]. “Snowflaking” is a method of normalizing the dimension tables in a star schema. When it is completely normalized along all the dimension tables, the resultant structure resembles a snowflake with the fact table in the middle.
Box 2: dimension
The star schema consists of one or more fact tables referencing any number of dimension tables. -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q09 014 Question 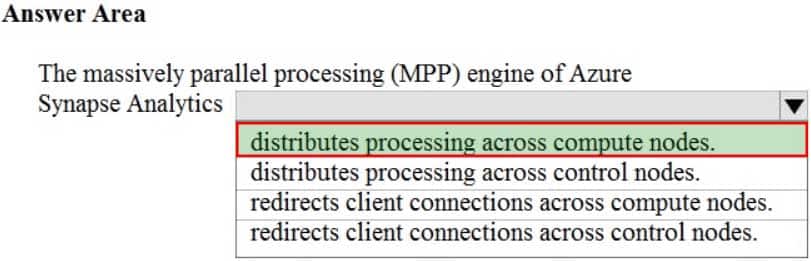
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q09 014 Answer -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q10 015 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q10 015 Answer -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q11 016 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q11 016 Answer Explanation:Disadvantages of non-relational databases include: Data Consistency — non-relational databases do not perform ACID transactions.
Note: Relational databases are optimized for writes. They are optimized for consistency and availability. Advantages of relational databases include simplicity, ease of data retrieval, data integrity, and flexibility.
Incorrect Answers:
Use a relational database when data that you work with is structured, and the structure is not subject to frequent changes.
Use Cloud storage (no relational database) for geographically distributed writes. -
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q12 017 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q12 017 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Yes
Big data solutions often use long-running batch jobs to filter, aggregate, and otherwise prepare the data for analysis. Usually these jobs involve reading source files from scalable storage (like HDFS, Azure Data Lake Store, and Azure Storage), processing them, and writing the output to new files in scalable storage.Box 2: No
Box 3: No
-
DRAG DROP
Your company plans to load data from a customer relationship management (CRM) system to a data warehouse by using an extract, load, and transform (ELT) process.
Where does data processing occur for each stage of the ELT process? To answer, drag the appropriate locations to the correct stages. Each location may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q13 018 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q13 018 Answer Explanation:Box 1: The CRM system
Data is extracted from the CRM system.Box 2: The data warehouse
Data is loaded to the data warehouse.Box 3: An in-memory data integration tool
The data transformation that takes place usually involves various operations, such as filtering, sorting, aggregating, joining data, cleaning data, deduplicating, and validating data.
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q13 019 -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q14 020 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q14 020 Answer Explanation:Generally speaking, data analytics comes in four types (Figure 1):
Descriptive, to answer the question: What’s happening?
Diagnostic, to answer the question: Why’s happening?
Predictive, to answer the question: What will happen?
Prescriptive, to answer the question: What actions should we take? -
DRAG DROP
Match the types of visualizations to the appropriate descriptions.
To answer, drag the appropriate visualization type from the column on the left to its description on the right. Each visualization type may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
NOTE: Each correct match is worth one point.
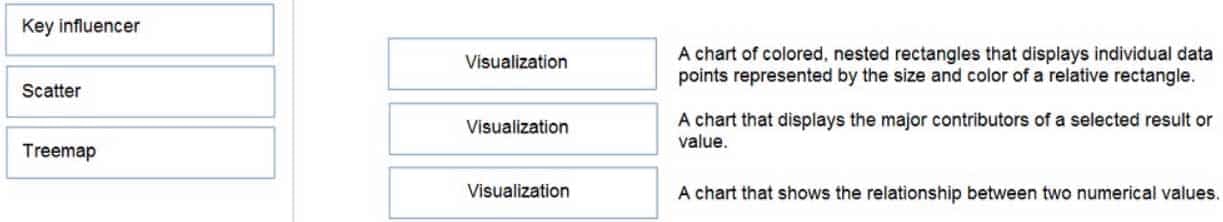
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q15 021 Question 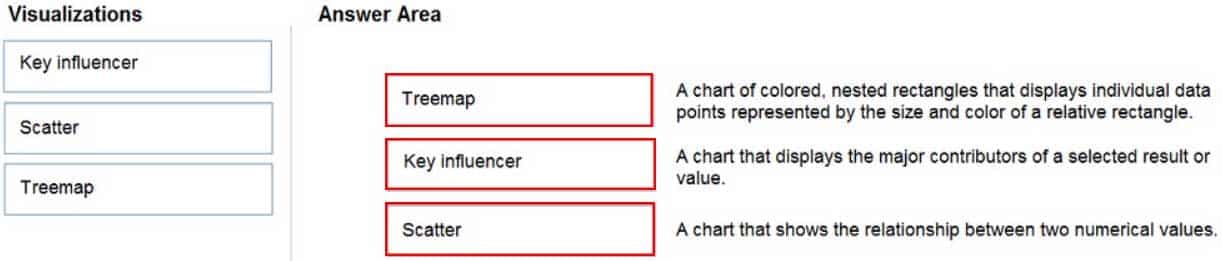
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q15 021 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Tree map
Treemaps are charts of colored rectangles, with size representing value. They can be hierarchical, with rectangles nested within the main rectangles.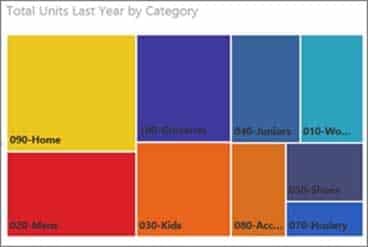
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q15 022 Box 2: Key influencer
A key influencer chart displays the major contributors to a selected result or value.Box 3: Scatter
Scatter and Bubble charts display relationships between 2 (scatter) or 3 (bubble) quantitative measures — whether or not, in which order, etc. -
You need to create an Azure Storage account.
Data in the account must replicate outside the Azure region automatically.
Which two types of replication can you use for the storage account? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- zone-redundant storage (ZRS)
- read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS)
- locally-redundant storage (LRS)
- geo-redundant storage (GRS)
Explanation:D: Azure Storage offers two options for copying your data to a secondary region:
– Geo-redundant storage (GRS)
– Geo-zone-redundant storage (GZRS)B: With GRS or GZRS, the data in the secondary region isn’t available for read or write access unless there is a failover to the secondary region. For read access to the secondary region, configure your storage account to use read-access geo-redundant storage (RA-GRS) or read-access geo-zone-redundant storage (RA-GZRS).
-
HOTSPOT
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q17 023 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q17 023 Answer Explanation:Box 1: Yes
Like IaaS, PaaS includes infrastructure – servers, storage, and networking – but also middleware, development tools, business intelligence (BI) services, database management systems, and more. PaaS is designed to support the complete web application lifecycle: building, testing, deploying, managing, and updating.
PaaS allows you to avoid the expense and complexity of buying and managing software licenses, the underlying application infrastructure and middleware, container orchestrators such as Kubernetes, or the development tools and other resourcesBox 2: Yes
You manage the applications and services you develop, and the cloud service provider typically manages everything else.
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q17 024 Box 3: No
There really is no way to pause / stop billing for your Azure SQL Database.
Microsoft’s official answer “Yes, you can export your database. Delete the Azure SQL database and that will pause billing. Then when you need it you can create a new database and import your previously exported DB.” -
Which statement is an example of Data Manipulation Language (DML)?
- REVOKE
- DISABLE
- INSERT
- GRANT
Explanation:
Data Manipulation Language (DML) statements:
– DELETE
– INSERT
– UPDATE -
You have a SQL query that combines customer data and order data. The query includes calculated columns.
You need to persist the SQL query so that other users can use the query.
What should you create?
- an index
- a view
- a scalar function
- a table
Explanation:
A view is a virtual table whose contents are defined by a query. A view acts as a filter on the underlying tables referenced in the view. The query that defines the view can be from one or more tables or from other views in the current or other databases. -
HOTSPOT
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.

DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q20 025 Question 
DP-900 Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals Part 01 Q20 025 Answer Explanation:Box 1: simple lookups
A key/value store associates each data value with a unique key. Most key/value stores only support simple query, insert, and delete operations. To modify a value (either partially or completely), an application must overwrite the existing data for the entire value. In most implementations, reading or writing a single value is an atomic operation.An application can store arbitrary data as a set of values. Any schema information must be provided by the application. The key/value store simply retrieves or stores the value by key.