Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 | Checkpoint Exam: Network Addressing Answers 2025 Full 100%
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 | Checkpoint Exam: Network Addressing Answers Full 100% 2025
This Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 section for Checkpoint Exam: Characteristics of Network Addressing Answers is provided with the correct answers to 100% of the questions. This module 21-23 exam answer is used for the Cisco SkillsForAll platform which is the latest version just released in 2025. Review all the questions and answers here, then you will meet randomly 21 questions from all here.
-
When a computer assembles a frame to be sent over the network, what is the maximum size of an Ethernet frame?
- 64 bytes
- 1518 bytes
- 1024 bytes
- 128 bytes
Explanation: Ethernet standards define a frame size with a minimum of 64 bytes and a maximum of 1518 bytes including fields of destination MAC address, source MAC, Length/Type, data payload, and FCS.
-
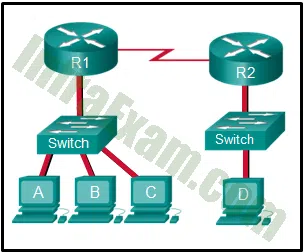
Refer to the exhibit. The switches have a default configuration. Host A needs to communicate with host D, but host A does not have the MAC address for the default gateway. Which network devices will receive the ARP request sent by host A?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 Checkpoint Exam Network Addressing Answers 05 - only router R1
- only hosts A, B, and C
- only hosts B and C
- only hosts B, C, and router R1
- only host D
- only hosts A, B, C, and D
Explanation: Because host A does not have the MAC address of the default gateway in the ARP table, host A sends an ARP broadcast. The ARP broadcast would be sent to every device on the local network. Hosts B, C, and router R1 would receive the broadcast. Router R1 would not forward the message.
-
When would a switch record multiple entries for a single switch port in its MAC address table?
- when another switch is connected to the switch port
- when multiple ARP broadcasts have been forwarded
- when a router is connected to the switch port
- when the switch is configured for Layer 3 switching
Explanation: When another switch or a hub is connected to a switch port then frames could be received from the multiple nodes connected to the other switch or the hub. This will result in the MAC address for each of those multiple nodes to be recorded in the MAC address table against that one port. When a router is connected to a switch port, only the MAC address of the router interface would be recorded against the switch port. ARP broadcasts are used to associate MAC addresses with IP addresses and such broadcasts would not directly result in multiple MAC addresses being recorded against a single switch port. Configuring the switch to perform Layer 3 switching will not result in multiple MAC addresses being recorded against a single switch port. The ARP table associated with the Layer 3 switch port may contain multiple IP address to MAC address mappings but this is to enable the correct framing of Layer 3 packets, not the Layer 2 frame switching function.
-
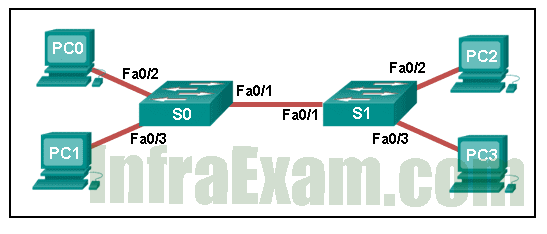
Refer to the exhibit. A ping to PC3 is issued from PC0, PC1, and PC2 in this exact order. Which MAC addresses will be contained in the S1 MAC address table that is associated with the Fa0/1 port?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 Checkpoint Exam Network Addressing Answers 01 - just the PC0 MAC address
- just the PC1 MAC address
- just PC0 and PC1 MAC addresses
- PC0, PC1, and PC2 MAC addresses
- just the PC2 MAC address
Explanation: Switch S1 builds a MAC address table based on the source MAC address in the frame and the port upon which the frame enters the switch. The PC2 MAC address will be associated with port FA0/2. Because port FA0/1 of switch S1 connects with another switch, port FA0/1 will receive frames from multiple different devices. The MAC address table on switch S1 will therefore contain MAC addresses associated with each of the sending PCs.
-
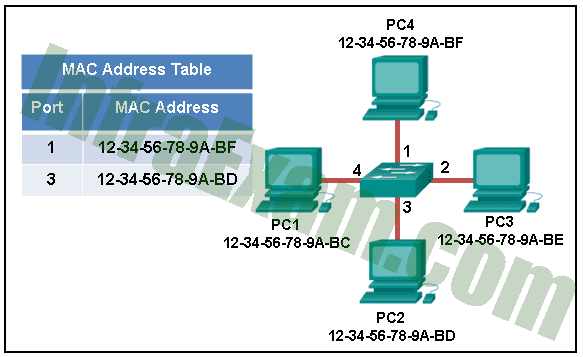
Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 Checkpoint Exam Network Addressing Answers 03 - The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
- The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
Explanation: The MAC address of PC3 is not present in the MAC table of the switch. Because the switch does not know where to send the frame that is addressed to PC3, it will forward the frame to all the switch ports, except for port 4, which is the incoming port.
-
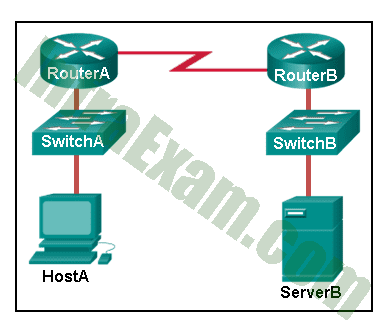
Refer to the exhibit. ServerB is attempting to contact HostA. Which two statements correctly identify the addressing that ServerB will generate in the process? (Choose two.)
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 Checkpoint Exam Network Addressing Answers 06 - ServerB will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of SwitchB.
- ServerB will generate a packet with the destination IP address of HostA.
- ServerB will generate a packet with the destination IP address of RouterB.
- ServerB will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of RouterA.
- ServerB will generate a frame with the destination MAC address of RouterB.
- ServerB will generate a packet with the destination IP address of RouterA.
Explanation: In order to send data to HostA, ServerB will generate a packet that contains the IP address of the destination device on the remote network and a frame that contains the MAC address of the default gateway device on the local network.
-
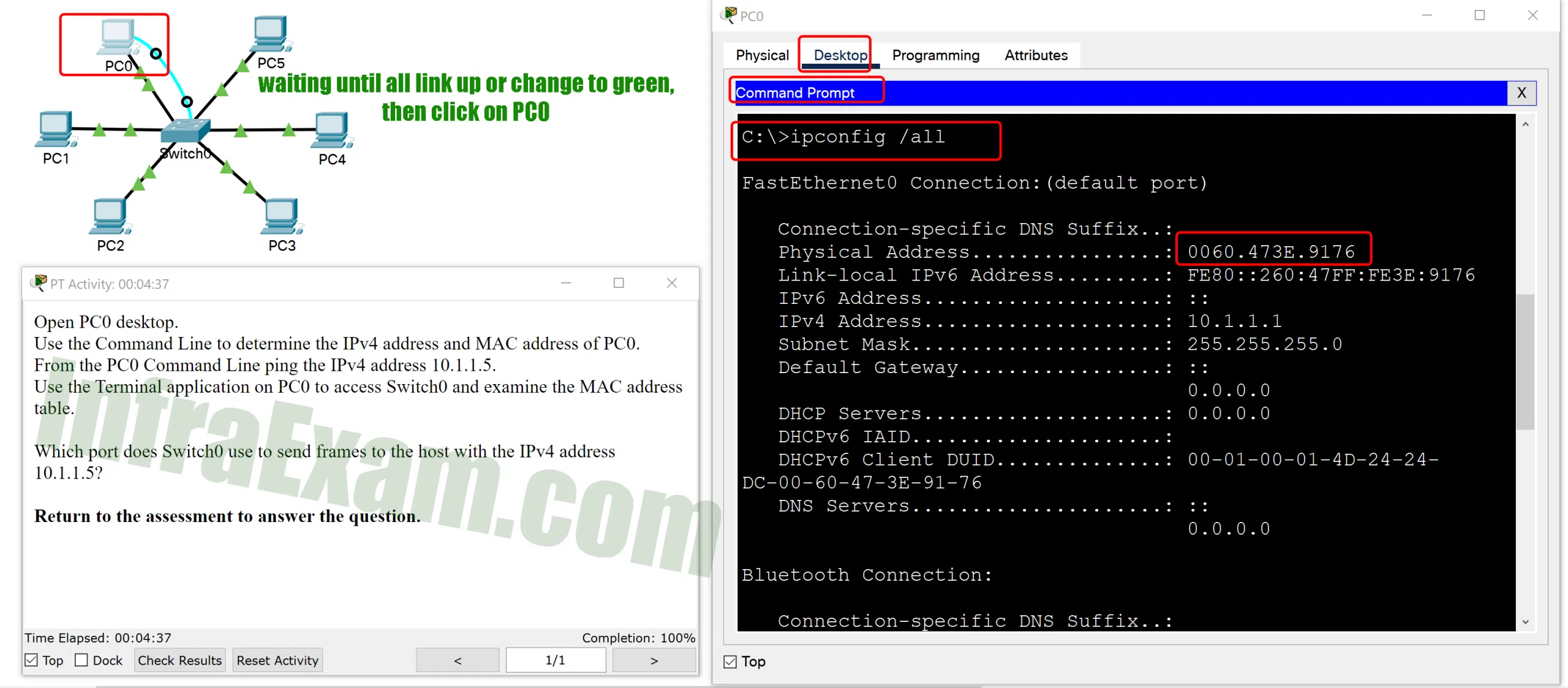
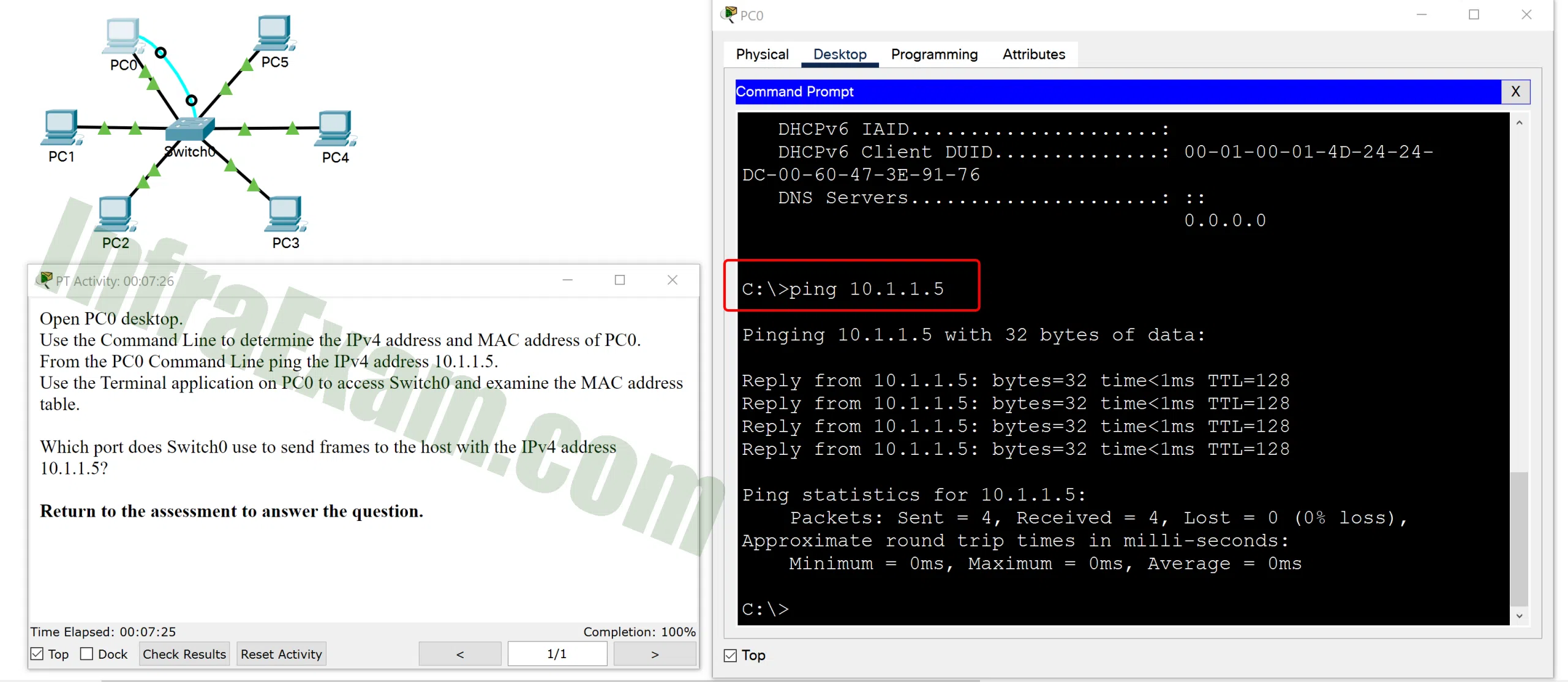
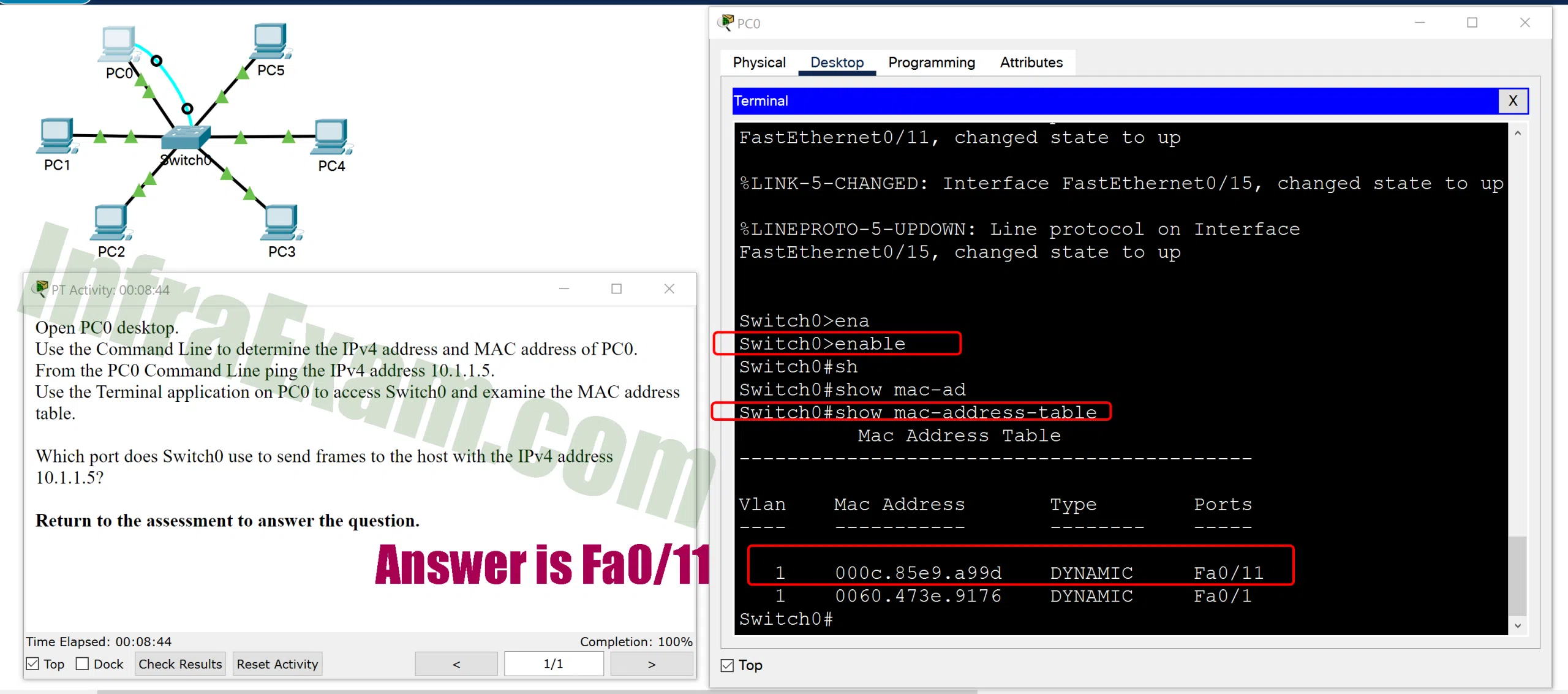
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5 PT-A Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5 PT-B Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5 PT-C Which port does Switch0 use to send frames to the host with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5?
- Fa0/5
- Fa0/11
- Fa0/1
- Fa0/9
Explanation: Issuing the command ipconfig /all from the PC0 command prompt displays the IPv4 address and MAC address. When the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5 is pinged from PC0, the switch stores the source MAC address (from PC0) along with the port to which PC0 is connected. When the destination reply is received, the switch takes the destination MAC address and compares to MAC addresses stored in the MAC address table. Issuing the show mac-address-table on the PC0 Terminal application displays two dynamic MAC address entries. The MAC address and port entry that does not belong to PC0 must be the MAC address and port of the destination with the IPv4 address 10.1.1.5.
-
What is correct in relation to NAT for IPv6?
- NAT64 has been deprecated by IETF in favor of NAT-PT.
- It is a temporary mechanism to assist in the migration from IPv4 to IPv6.
- Dual stack is an example of implementation of NAT for IPv6.
- It is used to convert private IPv6 addresses to public IPv6 addresses.
Explanation: NAT for IPv6 is a temporary measure to aid in the move from IPv4 to IPv6. NAT64 is replacing NAT-PT. Dual stack is a method for running IPv4 and IPv6 on the same network.
-
Which field in an IPv6 packet is used by the router to determine if a packet has expired and should be dropped?
- Address Unreachable
- TTL
- Hop Limit
- No Route to Destination
Explanation: ICMPv6, like IPv4, sends a Time Exceeded message if the router cannot forward an IPv6 packet because the packet has expired. However, the IPv6 packet does not have a TTL field. Instead, it uses the Hop Limit field to determine if the packet has expired.
-
Match the characteristics with the correct IP protocol version.
- 12 basic header fields
IPv4 - 128-bit address space
IPv6 - 40 octets header
IPv6 - 20 octets header
IPv4 - 8 header fields
IPv6 - 32-bit address space
IPv4Explanation: Options matched to the correct selection.
IPv4 IPv6 12 basic header fields 128-bit address space 20 octets header 40 octets header 32-bit address space 8 header fields
- 12 basic header fields
-
What IPv6 header field is used to indicate the upper layer protocol or extension header that is included in the packet?
- Payload Length
- Next Header
- Flow Label
- Traffic Class
Explanation: There are eight fields in an IPv6 header.
- Version
- Traffic Class
- Flow Label
- Payload Length
- Next Header
- Hop Limit
- Source Address
- Destination Address
The next header field contains an 8-bit value that indicates the upper layer or extension header that is contained within the IPv6 packet.
-
What is one advantage that the IPv6 simplified header offers over IPv4?
- little requirement for processing checksums
- smaller-sized source and destination IP addresses
- smaller-sized header
- efficient packet handling
Explanation: The IPv6 simplified header offers several advantages over IPv4:
· Better routing efficiency and efficient packet handling for performance and forwarding-rate scalability
· No requirement for processing checksums
· Simplified and more efficient extension header mechanisms (as opposed to the IPv4 Options field)
· A Flow Label field for per-flow processing with no need to open the transport inner packet to identify the various traffic flows
-
What are two functions that are provided by the network layer? (Choose two.)
- carrying data between processes that are running on source and destination hosts
- directing data packets to destination hosts on other networks
- providing end devices with a unique network identifier
- placing data on the network medium
- providing dedicated end-to-end connections
Explanation: The network layer is primarily concerned with passing data from a source to a destination on another network. IP addresses supply unique identifiers for the source and destination. The network layer provides connectionless, best-effort delivery. Devices rely on higher layers to supply services to processes.
-
Which IPv4 header field is responsible for defining the priority of the packet?
- traffic class
- flags
- flow label
- differentiated services
Explanation: Differentiated services (DiffServ) is an IPv4 header field that is used to define the priority of each packet. The first 6 bits identify the value that is used by the QoS mechanism, and the last 2 bits identify the value that can be used to avoid packet dropping during network congestion. Traffic class is an IPv6 header field that is equivalent to the IPv4 differentiated services (DiffServ) field. Flow label is also an IPv6 header field that can be used to tell routers and switches to keep the same path for the packet flow to avoid packet reordering. Flags is an IPv4 header field that identifies how the packet is fragmented.
-
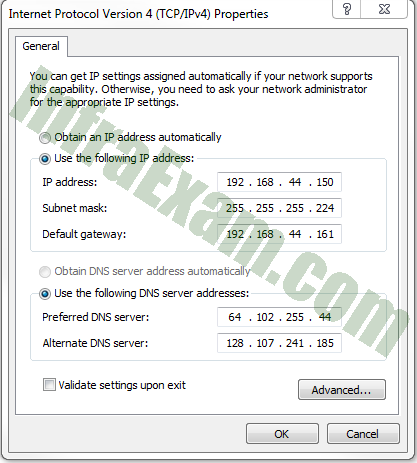
Refer to the exhibit. A computer that is configured with the IPv4 address as shown in the exhibit is unable to access the internet. What is the problem?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 Checkpoint Exam Network Addressing Answers 02 - The IP address is a broadcast address.
- The gateway address is in the wrong subnet.
- The IP address is a network address.
- The settings were not validated.
Explanation: The subnet mask of 255.255.255.224 identifies the network of 192.168.44.128. The usable range for the network is 192.168.44.129 through 192.168.44.158. The default gateway address of 192.168.44.161 exists on a separate network from the PC it is configured on.
-
Consider the group of five IPv4 addresses each with the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Which two IPv4 addresses belong to the same local network? (Choose two.)
- 193.168.10.16
- 192.168.10.2
- 192.167.10.74
- 192.168.10.56
- 192.168.100.62
Explanation: The subnet mask determines which part of the IP address is the network number. Because the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the first three sets of numbers in each IPv4 address indicate the network number. IPv4 addresses with the same network number are considered in the same local network.
-
A network engineer subnets the network 192.168.100.0 /24 into 16 subnets. How many usable host addresses will be available on each of the subnets?
- 6
- 30
- 14
- 62
Explanation: When network 192.168.100.0 /24 is subnetted into 16 subnets, each subnet will have a new network mask of 255.255.255.240. This new mask will leave four bits of the address available for hosts. Four host bits yield 16 host addresses. However, two of those addresses are reserved, the lowest for the subnet and the highest for the subnet broadcast. This leaves 14 addresses for host configuration.
-
What subnet mask would be associated with the IPv4 prefix of /28?
- 255.255.255.252
- 255.255.255.240
- 255.255.255.224
- 255.255.255.0
- 255.255.255.248
Explanation: /28 represents the number of consecutive 1s in the subnet mask. 24 1s makes the 255.255.255 part of the subnet mask. The last 4 1s in the mask is where it gets a little tricky. Add the values that these 4 1s represent to get the last octet of the mask: 128 + 64 + 32 + 16 = 240. /28 = 255.255.255.240
-
Which two hosts exist on the same subnet? (Choose two.)
- host 172.16.101.199/23
- host 172.16.97.78/23
- host 172.16.102.237/23
- host 172.16.98.250/23
- host 172.16.100.4/23
Explanation: Hosts 172.16.100.4/23 and 172.16.101.199/23 both exist in network 172.16.100.0/23. This network includes all addresses from 172.16.100.1 through 172.16.101.255.
-
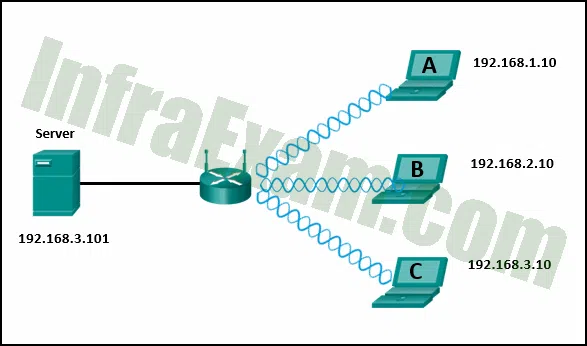
Refer to the exhibit. If all devices are using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, which laptop would have an IP address with the same network number as the server?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 21-23 Checkpoint Exam Network Addressing Answers 04 - C
- B
- A
Explanation: The subnet mask shows which part of the IP address is the network number. Because all the devices have a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, the first three sets of numbers in each IP address indicate the network number. The server and laptop C both have network numbers of 192.168.3.0.
-
Why does a Layer 3 device perform the ANDing process on a destination IP address and subnet mask?
- to identify faulty frames
- to identify the host address of the destination host
- to identify the network address of the destination network
- to identify the broadcast address of the destination network
Explanation: ANDing allows us to identify the network address from the IP address and the network mask.
-
Which information does a switch use to populate the MAC address table?
- the source MAC address and the incoming port
- the destination MAC address and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the incoming port
- the source and destination MAC addresses and the outgoing port
- the source MAC address and the outgoing port
- the destination MAC address and the outgoing port
Explanation & Hint: To maintain the MAC address table, the switch uses the source MAC address of the incoming packets and the port that the packets enter. The destination address is used to select the outgoing port.
-
Which two hosts exist on the same subnet? (Choose two.)
- host 172.16.97.78/23
- host 172.16.102.237/23
- host 172.16.98.250/23
- host 172.16.101.199/23
- host 172.16.100.4/23
Explanation & Hint: Hosts 172.16.100.4/23 and 172.16.101.199/23 both exist in network 172.16.100.0/23. This network includes all addresses from 172.16.100.1 through 172.16.101.255.
-
Which field in the IPv6 header points to optional network layer information that is carried in the IPv6 packet?
- version
- traffic class
- flow label
- next header
Explanation & Hint: Optional Layer 3 information about fragmentation, security, and mobility is carried inside of extension headers in an IPv6 packet. The next header field of the IPv6 header acts as a pointer to these optional extension headers if they are present.