Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 | Checkpoint Exam: The Internet Protocol Answers 2025 Full 100%
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 | Checkpoint Exam: The Internet Protocol Answers Full 100% 2025
This Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 section for Checkpoint Exam: The Internet Protocol Answers which is provided with the correct answers to 100% of the questions. This module 8-11 exam answer is used for the Cisco SkillsForAll platform which is the latest version just released in 2025. Review all the questions and answers here, then you will meet randomly 20 questions from all here.
-
True or False?
Every device on a network needs an IP address to identify itself and communicate on the network.
- true
- false
Explanation: All network devices must have an IP address to communicate on the network. The IP address is used to uniquely identify each device on the network.
-
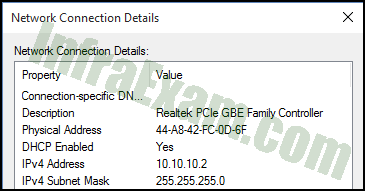
Refer to the exhibit. The IP address settings of a host are shown. What is the host number of the IP address?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 01 - 10
- 1
- 2
- 255
Explanation: An IP address consists of two parts. The first part is the network number and the second part is the host number. The length of the network number is defined by the subnet mask. For each 255 in the subnet mask, that much of the IP address represents the network part. For each 0 on the right part of the subnet mask, that part of the IP address identifies the host number. In this example the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 means that 10.10.10.0 is the network number and 2 is the host number.
-
How many bits make up an IPv4 address?
- 128
- 32
- 64
- 48
Explanation: An IPv4 address is a 32-bit logical address.
-
When IPv4 is configured for a computer on a network, what does the subnet mask identify?
- the part of the IP address that identifies the network
- the device that the computer uses to access another network
- the pool of addresses assigned within the network
- the dynamic subnetwork configuration
Explanation: The IP addressing system is a hierarchical addressing system. An IP address is made up of two parts: the network address and the host address. For IPv4, the subnet mask is used to identify which portion of an IPv4 address is the network address and which portion is the host address.
-
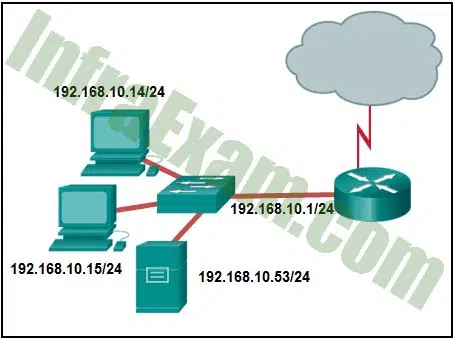
Refer to the exhibit. What is the network number of the LAN that is shown?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 02 - 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.0.0
- 192.168.10.0
- 255.255.255.0
Explanation: All of the hosts have IP addresses with 192.168.10.__/24 in common. The last digit can be any number in the range from 0 to 255. The first number of the range represents the network number and the last number in the range represents the broadcast address. Hosts can be assigned any number from 1 to 254. The network number in this case is 192.168.10.0
-
A student is helping a friend with a home computer that can no longer access the Internet. Upon investigation, the student discovers that the computer has been assigned the IP address 169.254.100.88. What could cause a computer to get such an IP address?
- interference from surrounding devices
- static IP addressing with incomplete information
- unreachable DHCP server
- reduced computer power supply output
Explanation: When a PC does not have a static IP address or cannot pick one up from a DHCP server, Windows will automatically assign the PC an IP address using APIPA, that uses the range of addresses 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255.
-
What is the purpose of the subnet mask in conjunction with an IP address?
- to mask the IP address to outsiders
- to determine the subnet to which the host belongs
- to identify whether the address is public or private
- to uniquely identify a host on a network
Explanation: With the IPv4 address, a subnet mask is also necessary. A subnet mask is a special type of IPv4 address that coupled with the IP address determines the subnet of which the device is a member.
-
What are the three ranges of IP addresses that are reserved for internal private use? (Choose three.)
- 192.168.0.0/16
- 127.16.0.0/12
- 64.100.0.0/14
- 10.0.0.0/8
- 192.31.7.0/24
- 172.16.0.0/12
Explanation: The private IP address blocks that are used inside companies are as follows:
- 10.0.0.0 /8 (any address that starts with 10 in the first octet)
- 172.16.0.0 /12 (any address that starts with 172.16 in the first two octets through 172.31.255.255)
- 192.168.0.0 /16 (any address that starts with 192.168 in the first two octets)
-
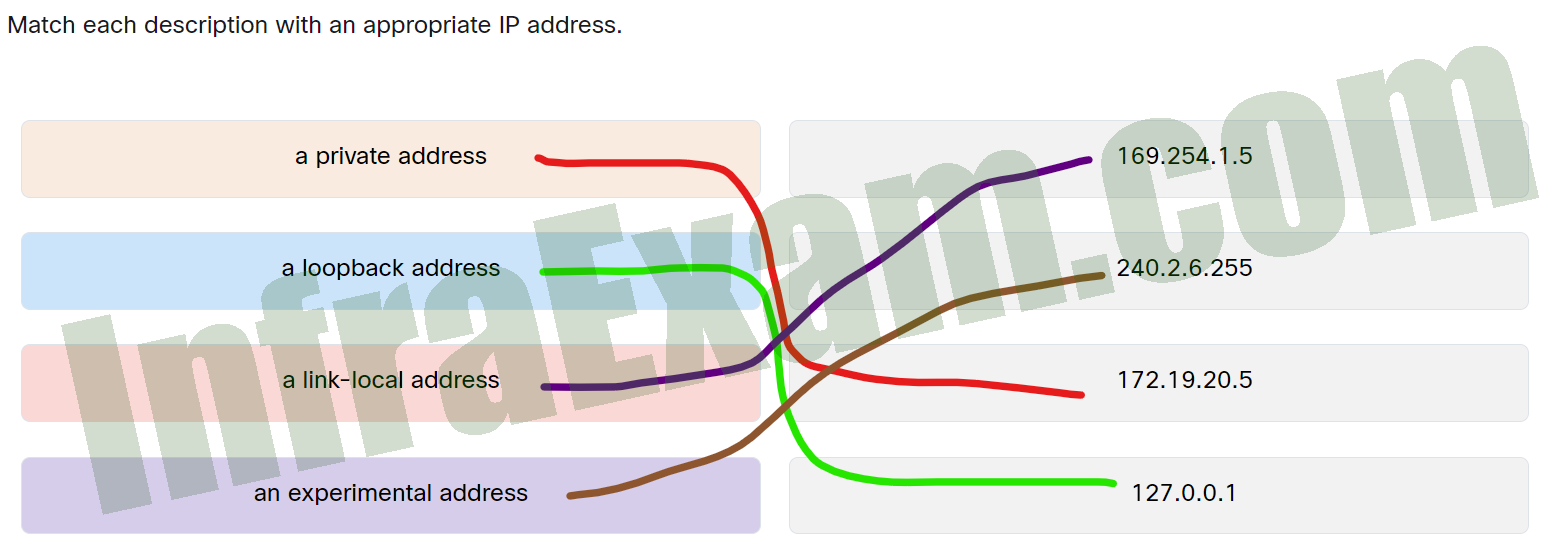
Match each description with an appropriate IP address.
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 001 - a private address —> 172.19.20.5
- a loopback address —> 127.0.0.1
- a link-local address —> 169.254.1.5
- an experimental address —> 240.2.6.255
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
A link-local address 169.254.1.5 An experimental address 240.2.6.255 A private address 172.19.20.5 A loopback address 127.0.0.1
-
What are two reasons a network administrator might want to create subnets? (Choose two.)
- simplifies network design
- improves network performance
- reduction in number of routers needed
- reduction in number of switches needed
- easier to implement security policies
Explanation: Two reasons for creating subnets include reduction of overall network traffic and improvement of network performance. Subnets also allow an administrator to implement subnet-based security policies. The number of routers or switches is not affected. Subnets do not simplify network design.
-
What is one factor increasing the adoption of IPv6 network addresses?
- IoT adds millions of network-ready sensors that need IP addresses.
- IPv4 addresses cannot coexist with IPv6 addresses on the internet.
- Devices communicate faster using IPv6 addresses than when using IPv4.
- IPv4 will no longer be supported on mobile devices.
Explanation: Factors that are driving an increase in IPv6 adoption are an increasing internet population, a limited IPv4 address space, issues with NAT and the large number of internet-ready IoT devices.
-
Which shortened address is an accurate representation of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:ab00:0000:0000:0000?
- 2001:db8:0:0:ab::
- 2001:db8::ab00::
- 2001:db8:0:ab00:0
- 2001:db8:0:0:ab00::
Explanation: There are two rules to help reduce the notation of IPv6 addresses. The first one is to omit any leading 0s (zeros) in any hextet. The second one is that a double colon (::) can replace any single, contiguous string of one or more 16-bit hextets consisting of all zeros, but the double colon (::) can only be used once within an address. If an address has more than one contiguous string of all-0 hextets, the best practice is to use the double colon (::) on the longest string. So, applying the first rule in the IPv6 address we have 2001:db8:0:0:ab00:0:0:0, and applying the second rule results in 2001:db8:0:0:ab00::
-
How many binary bits exist within an IPv6 address?
- 48
- 128
- 32
- 64
- 256
Explanation: IPv4 addressing space is exhausted by the rapid growth of the Internet and the devices connected to the Internet. IPv6 expands the IP addressing space by increasing the address length from 32 bits to 128 bits.
-
What is the valid most compressed format possible of the IPv6 address 2001:0DB8:0000:AB00:0000:0000:0000:1234?
- 2001:DB8:0:AB00::1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB:0:1234
- 2001:DB8:0:AB::1234
- 2001:DB8::AB00::1234
Explanation: There are two rules defining how an IPv6 address can be compressed. The first rule states that leading zeros in a hextet can be eliminated. The second rule states that a single :: can be used to represent one or more contiguous all zero hextets. There can be one and only one :: in an IPv6 address.
-
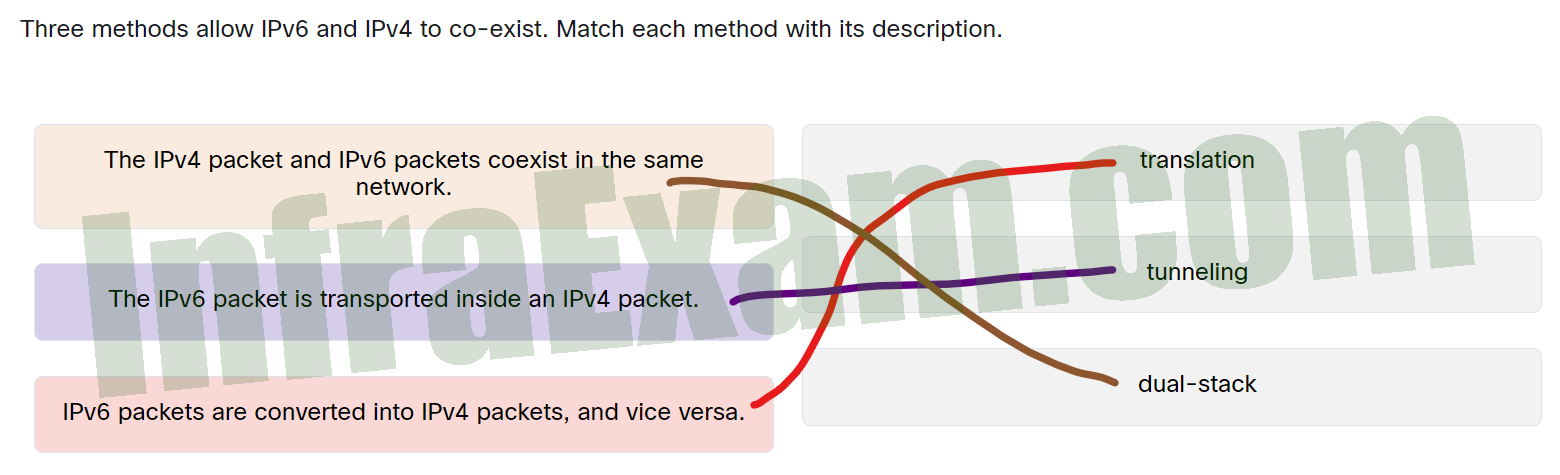
Three methods allow IPv6 and IPv4 to co-exist. Match each method with its description.
Networking Essentials 3.0 Module 8-11 Checkpoint Exam The Internet Protocol Answers 002 - IPv6 packets are converted into IPv4 packets, and vice versa. —> translation
- The IPv6 packet is transported inside an IPv4 packet. —> tunneling
- The IPv4 packet and IPv6 packets coexist in the same network. —> dual-stack
Explanation: Place the options in the following order:
IPv6 packets are converted into IPv4 packets, and vice versa. Translation The IPv6 packet is transported inside an IPv4 packet. Tunneling The IPv4 packet and IPv6 packets coexist in the same network. Dual-stack
-
A DHCP-enabled client PC has just booted. During which two steps will the client PC use broadcast messages when communicating with a DHCP server? (Choose two.)
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPNAK
Explanation: All DHCP messages between a DHCP-enabled client and a DHCP server are using broadcast messages until after the DHCPACK message. The DHCPDISCOVER and DHCPREQUEST messages are the only messages that are sent by a DHCP-enabled client. All DHCP messages between a DHCP-enabled client and a DHCP server use broadcast messages when the client is obtaining a lease for the first time.
-
Which DHCPv4 message will a client send to accept an IPv4 address that is offered by a DHCP server?
- broadcast DHCPACK
- unicast DHCPREQUEST
- unicast DHCPACK
- broadcast DHCPREQUEST
Explanation: When a DHCP client receives DHCPOFFER messages, it will send a broadcast DHCPREQUEST message for two purposes. First, it indicates to the offering DHCP server that it would like to accept the offer and bind the IP address. Second, it notifies any other responding DHCP servers that their offers are declined.
-
What is the destination IP address when an IPv4 host sends a DHCPDISCOVER message?
- 224.0.0.1
- 255.255.255.255
- 192.168.1.1
- 0.0.0.0
Explanation: Because a DHCP client does not have a valid IPv4 address, it must use a broadcast IP address of 255.255.255.255 as the destination address to communicate with the DHCP server. The DHCPDISCOVER message sent by the client is the first message sent in order to make initial contact with a DHCP server.
-
Which statement is true about DHCP operation?
- A client must wait for lease expiration before it sends another DHCPREQUEST message.
- When a device that is configured to use DHCP boots, the client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway.
- If the client receives several DHCPOFFER messages from different servers, it sends a unicast DHCPREQUEST message to the server from which it chooses to obtain the IP information.
Explanation: The client broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to identify any available DHCP servers on the network. A DHCP server replies with a DHCPOFFER message. This message offers to the client a lease that contains such information as the IP address and subnet mask to be assigned, the IP address of the DNS server, and the IP address of the default gateway. After the client receives the lease, the received information must be renewed through another DHCPREQUEST message prior to the lease expiration.
-
If more than one DHCP server is available on the local network, in which order will DHCP messages be sent between a host and a DHCP server?
- request, discover, offer, acknowledgment
- discover, offer, request, acknowledgment
- acknowledgment, request, offer, discover
- request, acknowledgment, discover, offer
Explanation: A DHCP host broadcasts a DHCP discover message to locate available servers. If more than one DHCP server is available, each server will respond to the host with a unicast DHCP offer message, which offers a lease to the client. The client then broadcasts a DHCP request message that identifies the specific server and offer that the client will accept. The identified server will unicast a DHCP acknowledgment message to finalize the offer.
-
Consider the group of five IPv4 addresses with the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Select three of them that belong to the same logical network.
- 172.16.45.35
- 172.16.45.12
- 172.16.35.45
- 172.16.45.56
- 173.16.45.18
Explanation & Hint:
-
When the IETF began development of IPv6, what was the goal of implementing this technology?
- to increase the limiting 128 bits available in IPv4 to facilitate the growing Internet
- to provide more address space in the Internet Names Registry
- to relieve IPv4 address depletion
- to make reading a 32-bit address easier
Explanation & Hint: IPv6 is designed to be the successor to IPv4. IPv6 has a larger 128 bit address space to provide many more addresses than IPv4.
-
Which two types of devices are typically assigned static IP addresses? (Choose two.)
- web servers
- hubs
- printers
- laptops
- workstations
Explanation & Hint: Servers and peripherals are often accessed by an IP address, so these devices need predictable IP addresses. End-user devices often have dynamic addresses that are assigned. Hubs do not require IPv4 addresses to operate as intermediary devices.
-
Which two reasons generally make DHCP the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks? (Choose two.)
- It eliminates most address configuration errors.
- It ensures that addresses are only applied to devices that require a permanent address.
- It guarantees that every device that needs an address will get one.
- It provides an address only to devices that are authorized to be connected to the network.
- It reduces the burden on network support staff.
Answers Explanation & Hints: DHCP is generally the preferred method of assigning IP addresses to hosts on large networks because it reduces the burden on network support staff and virtually eliminates entry errors. However, DHCP itself does not discriminate between authorized and unauthorized devices and will assign configuration parameters to all requesting devices. DHCP servers are usually configured to assign addresses from a subnet range, so there is no guarantee that every device that needs an address will get one.
-
Which destination IPv4 address does a DHCPv4 client use to send the initial DHCP Discover packet when the client is looking for a DHCP server?
- 127.0.0.1
- 224.0.0.1
- 255.255.255.255
- the IP address of the default gateway
Answers Explanation & Hints: Broadcast communications on a network may be directed or limited. A directed broadcast is sent to all hosts on a specific network. A limited broadcast is sent to 255.255.255.255. When a DHCP client needs to send a DHCP Discover packet in order to seek DHCP servers, the client will use this IP address of 255.255.255.255 as the destination in the IP header because it has no knowledge of the IP addresses of DHCP servers.
-
Which characteristic describes the default gateway of a host computer?
- the logical address of the router interface on the same network as the host computer
- the physical address of the switch interface connected to the host computer
- the physical address of the router interface on the same network as the host computer
- the logical address assigned to the switch interface connected to the router
Answers Explanation & Hints: The default gateway is the IP address of an interface on the router on the same network as the sending host.
-
Typically, which network device would be used to perform NAT for a corporate environment?
- DHCP server
- host device
- router
- server
- switch
Answers Explanation & Hints: Typically, the translation from private IP addresses to public IP addresses is performed on routers in corporate environments. In a home environment, this device might be an access point that has routing capability or the DSL or cable router.
-
Which network technology allows devices to communicate using both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing at the same time?
- SLAAC
- NAT64
- dual stack
- tunneling
Answers Explanation & Hints: Dual stack allows IPv4 and IPv6 protocol stacks to function on devices at the same time. This allows devices to communicate on a network that uses both IPv4 addressing and IPv6 addressing simultaneously.
-
What is the IPv6 prefix that is used for link-local addresses?
- 2001::/3
- FC00::/7
- FE80::/10
- FF01::/8
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IPv6 link-local prefix is FE80::/10 and is used to create a link-local IPv6 address on an interface.
-
What type of applications are best suited for using UDP?
- applications that are sensitive to delay
- applications that need reliable delivery
- applications that require retransmission of lost segments
- applications that are sensitive to packet loss
Answers Explanation & Hints: UDP is not a connection-oriented protocol and does not provide retransmission, sequencing, or flow control mechanisms. It provides basic transport layer functions with a much lower overhead than TCP. Lower overhead makes UDP suitable for applications which are sensitive to delay.
-
A destination PC receives an email message with the sequence numbers on packets out of order. Which layer of the TCP/IP model is responsible for reassembling the packets of the message in the correct order?
- internet
- transport
- application
- network access
Answers Explanation & Hints: The transport layer of the TCP/IP model is responsible for ensuring that all packets in a message are received, reassembling the message in the correct order after all packets are received, and identifying which applications are sending and receiving network data.
-
Which action is performed by a client when establishing communication with a server via the use of UDP at the transport layer?
- The client sets the window size for the session.
- The client sends an ISN to the server to start the 3-way handshake.
- The client randomly selects a source port number.
- The client sends a synchronization segment to begin the session.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because a session does not have to be established for UDP, the client selects a random source port to begin a connection. The random port number selected is inserted into the source port field of the UDP header.
-
A client device has initiated a secure HTTP request to a web browser. Which well-known port address number is associated with the destination address?
- 404
- 80
- 443
- 110
Answers Explanation & Hints: Port numbers are used in TCP and UDP communications to differentiate between the various services running on a device. The well-known port number used by HTTPs is port 443.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol allows a user to type www.cisco.com instead of an IP address to access the web server?
Modules 9 – 12 Data Communications and Network Services Pre-Test Exam Answers 01 - DNS
- FTP
- HTML
- HTTP
- SNMP
Answers Explanation & Hints: Web servers are assigned static IP addresses. They are also registered with domain names so people can remember them easily. However, web servers are connected through their IP addresses. DNS provides the service to map the domain name to its IP address.
-
Which protocol is used to transfer web pages from a server to a client device?
- HTML
- SMTP
- HTTP
- SSH
- POP
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) provides services between a web browser requesting web pages and a web server responding to the requests. HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a markup language to instruct a web browser how to interpret and display a web page.
-
What two characteristics describe an FTP connection? (Choose two.)
- A large file requires more than two connections between the client and the server to successfully download it.
- The server establishes the first connection with the client to control traffic that consists of server commands and client replies.
- Files can be downloaded from or uploaded to the server.
- The client needs to run a daemon program to establish an FTP connection with a server.
- The first connection established is for traffic control and the second connection is created to transfer a file.
Answers Explanation & Hints: An FTP client is an application that runs on a computer used to push and pull files from a server running an FTP daemon. To transfer files, FTP requires two connections between the client and the server: one for commands and replies and another for the actual file transfer. The client establishes the first connection to the server for control traffic and the second connection for the actual file transfer. This connection is created every time there is a file to be transferred. The client can download a file from or upload a file to the server.
-
Which protocol retains a message in a mailbox on a server, even after the message is accessed by a user on a local client device?
- IMAP4
- DNS
- SMTP
- POP3
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IMAP4 protocol will keep any message accessed by a client device in the mailbox on the server. The message is removed from the mailbox only after it is deleted by a user on the client device.
-
Which three types of nodes should be assigned static IP addresses on a network? (Choose three.)
- servers
- desktop PCs
- mobile laptops
- printers
- gateways
- tablets
Answers Explanation & Hints: Servers, printers, and intermediary devices, such as routers, switches, and access points should have statically assigned IP addresses so that they are accessible to users and available for remote management.
-
Why is DHCP for IPv4 preferred for use on large networks?
- Large networks send more requests for domain to IP address resolution than do smaller networks.
- DHCP uses a reliable transport layer protocol.
- It prevents sharing of files that are copyrighted.
- It is a more efficient way to manage IPv4 addresses than static address assignment is.
- Hosts on large networks require more IPv4 addressing configuration settings than do hosts on small networks.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Static IPv4 address assignment requires personnel to configure each network host with addresses manually. Large networks can change frequently and have many more hosts to configure than do small networks. DHCP provides a much more efficient means of configuring and managing IPv4 addresses on large networks than does static address assignment.
-
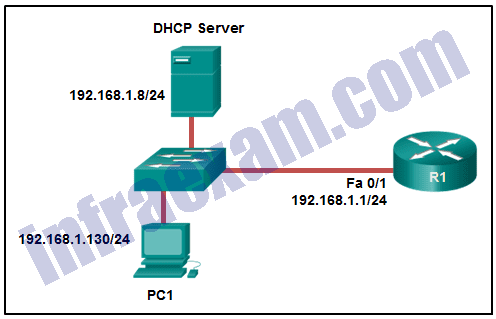
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 is configured to obtain a dynamic IP address from the DHCP server. PC1 has been shut down for two weeks. When PC1 boots and tries to request an available IP address, which destination IP address will PC1 place in the IP header?
Modules 9 – 12 Data Communications and Network Services Group Exam Answers 01 - 192.168.1.1
- 192.168.1.8
- 192.168.1.255
- 255.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a host boots and has been configured for dynamic IP addressing, the device tries to obtain a valid IP address. It sends a DHCPDISCOVER message. This is a broadcast message because the DHCP server address is unknown (by design). The destination IP address in the IP header is 255.255.255.255 and the destination MAC address is FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF.
-
Which message does an IPv4 host use to reply when it receives a DHCPOFFER message from a DHCP server?
- DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the client receives the DHCPOFFER from the server, it sends back a DHCPREQUEST broadcast message. On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the server replies with a unicast DHCPACK message.
-
A host PC is attempting to lease an address through DHCP. What message is sent by the server to let the client know it is able to use the provided IP information?
- DHCPDISCOVER
- DHCPOFFER
- DHCPREQUEST
- DHCPACK
- DHCPNACK
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a host uses DHCP to automatically configure an IP address, the typically sends two messages: the DHCPDISCOVER message and the DHCPREQUEST message. These two messages are usually sent as broadcasts to ensure that all DHCP servers receive them. The servers respond to these messages using DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK, and DHCPNACK messages, depending on the circumstance.
-
How is a DHCPDISCOVER transmitted on a network to reach a DHCP server?
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the DHCP server as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with a multicast IP address that all DHCP servers listen to as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the broadcast IP address as the destination address.
- A DHCPDISCOVER message is sent with the IP address of the default gateway as the destination address.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The DHCPDISCOVER message is sent by a DHCPv4 client and targets a broadcast IP along with the destination port 67. The DHCPv4 server or servers respond to the DHCPv4 clients by targeting port 68.
-
A DHCP server is used to assign IP addresses dynamically to the hosts on a network. The address pool is configured with 172.30.8.0/24. There are 7 printers on this network that need to use reserved static IP addresses from the pool. How many IP addresses in the pool are left to be assigned to other hosts?
- 254
- 247
- 251
- 249
Answers Explanation & Hints: If the block of addresses allocated to the pool is 172.30.8.0/24, there are 254 IP addresses to be assigned to hosts on the network. As there are 7 printers which need to have their addresses assigned statically, then there are 247 IP addresses left for assignment.
-
An employee is having connectivity issues. Why might a network technician try to ping the default gateway from the employee laptop?
- to verify that an IP address was provided by the DHCP server
- to determine if the laptop address is included in the DNS server
- to verify that the SVI interface on the switch is configured correctly
- to verify connectivity with the device that provides access to remote networks
Answers Explanation & Hints: The default gateway address is usually the address of the router interface. The router provides access to remote networks, so a successful ping to the default gateway would mean that the laptop is able to communicate with the router.
-
What is the result if the default gateway address is misconfigured on a PC?
- The PC cannot communicate with any devices.
- The PC can communicate with devices both in remote networks and in the same network.
- The PC can communicate with devices in the same network but not with those in remote networks.
- The PC can communicate with devices in remote networks but not with those in the same network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The default gateway for a PC is the closest networking device that can forward traffic to other networks. If a PC has an incorrect or nonexistent default gateway address, it will not be able to communicate with devices in remote networks. However, communication would occur between devices in the same network with or without a default gateway.
-
Which statement accurately describes dynamic NAT?
- It always maps a private IP address to a public IP address.
- It provides an automated mapping of inside local to inside global IP addresses.
- It provides a mapping of internal host names to IP addresses.
- It dynamically provides IP addressing to internal hosts.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Dynamic NAT provides a dynamic mapping of inside local to inside global IP addresses. NAT is merely the one-to-one mapping of one address to another address without taking into account whether the address is public or private. DHCP is automatic assignment of IP addresses to hosts. DNS is mapping host names to IP addresses.
-
What purpose does NAT64 serve in IPv6?
- It converts IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
- It translates private IPv6 addresses into public IPv6 addresses.
- It enables companies to use IPv6 unique local addresses in the network.
- It converts regular IPv6 addresses into 64-bit addresses that can be used on the Internet.
- It converts the 48-bit MAC address into a 64-bit host address that can be used for automatic host addressing.
Answers Explanation & Hints: NAT64 is typically used in IPv6 when networks are being transitioned from IPv4 to IPv6. It allows the IPv6 networks to connect to IPv4 networks (such as the Internet), and works by translating the IPv6 packets into IPv4 packets.
-
Which type of IPv6 address is not routable and used only for communication on a single subnet?
- global unicast address
- link-local address
- loopback address
- unique local address
- unspecified address
Answers Explanation & Hints: Link-local addresses have relevance only on the local link. Routers will not forward packets that include a link-local address as either the source or destination address.
-
How many bits make up the single IPv6 hextet :10CD:?
- 4
- 8
- 16
- 32
Answers Explanation & Hints: A hextet consists of 4 hexadecimal characters. Each hexadecimal character is represented by four bits, giving a total of 16 bits.
-
Which three pieces of information are identified by a URL? (Choose three.)
- the MAC address of the web server
- the protocol that is being used
- the domain name that is being accessed
- the IP address of the gateway
- the version of the browser
- the location of the resource
Answers Explanation & Hints: URLs are used to access specific content on a web server through a web browser. The URL identifies the protocol that is being used such as HTTP or FTP, the domain of the server, and the location of the resource on the server.
-
What is an advantage of UDP over TCP?
- UDP communication requires less overhead.
- UDP communication is more reliable.
- UDP reorders segments that are received out of order.
- UDP acknowledges received data.
Answers Explanation & Hints: TCP is a more reliable protocol and uses sequence numbers to realign packets that arrive out of order at the destination. Both UDP and TCP use port numbers to identify applications. UDP has less overhead than TCP because the UDP header has fewer bytes and UDP does not confirm the receipt of packets.
-
Which type of applications are best suited to use UDP as the transport layer protocol?
- applications that require flow control
- applications that require data to be reassembled in a specific order
- applications that require minimal transmission delay
- applications that require stateful sessions
Answers Explanation & Hints: UDP is a light-weight connectionless protocol that is well-suited for applications that are susceptible to delay or that do not need the features provided by TCP (guaranteed delivery, flow control, or sequencing).
-
What layer of the TCP/IP suite makes sure that all the data packets of a message arrive safely at the destination?
- internet
- transport
- application
- network access
Answers Explanation & Hints: The transport layer is responsible for managing the delivery of packets. TCP monitors the packets and if a packet is missing, it will request that it be sent again.
-
How does a client computer determine what source port number to assign to a UDP header?
- The port number is random within the range of dynamic port numbers.
- The port number is based on the application that created the data.
- The port number is based on a well-known port number that is open on the destination device.
- The port number is based on a well-known port number that is assigned to the application on the sending device.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The destination port number is normally a well-known or registered port number that is open on the destination device such as a server. The source port is randomly generated by the client computer from the 49152 to 65535 range.
-
What is a socket?
- the combination of the source and destination IP address and source and destination Ethernet address
- the combination of a source IP address and port number or a destination IP address and port number
- the combination of the source and destination sequence and acknowledgment numbers
- the combination of the source and destination sequence numbers and port numbers
Answers Explanation & Hints: A socket is a combination of the source IP address and source port or the destination IP address and the destination port number.
-
What is the purpose of using a source port number in a TCP communication?
- to notify the remote device that the conversation is over
- to assemble the segments that arrived out of order
- to keep track of multiple conversations between devices
- to inquire for a nonreceived segment
Answers Explanation & Hints: The source port number in a segment header is used to keep track of multiple conversations between devices. It is also used to keep an open entry for the response from the server. The incorrect options are more related to flow control and guaranteed delivery.
-
Which two protocols are used in the process of sending and receiving emails? (Choose two.)
- HTTP
- POP
- SSH
- SMTP
- FTP
Answers Explanation & Hints: POP and SMTP are protocols used for email. POP is Post Office Protocol and is used by clients to retrieve email messages from a server. SMTP is Simple Mail Transfer Protocol and is used by clients to send email messages to a server.
-
What is a function of a DNS server?
- It determines the IP address that is associated with a specific host domain name.
- It maps IP addresses to physical addresses.
- It translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses.
- It assigns logical address information to host computers.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Hosts are assigned with IP addresses in order to communicate over the network. Hosts are registered with domain names so people can remember and recognize them easily. However, computers are connected through their IP addresses. DNS provides the service to map the domain name to its IP address.
-
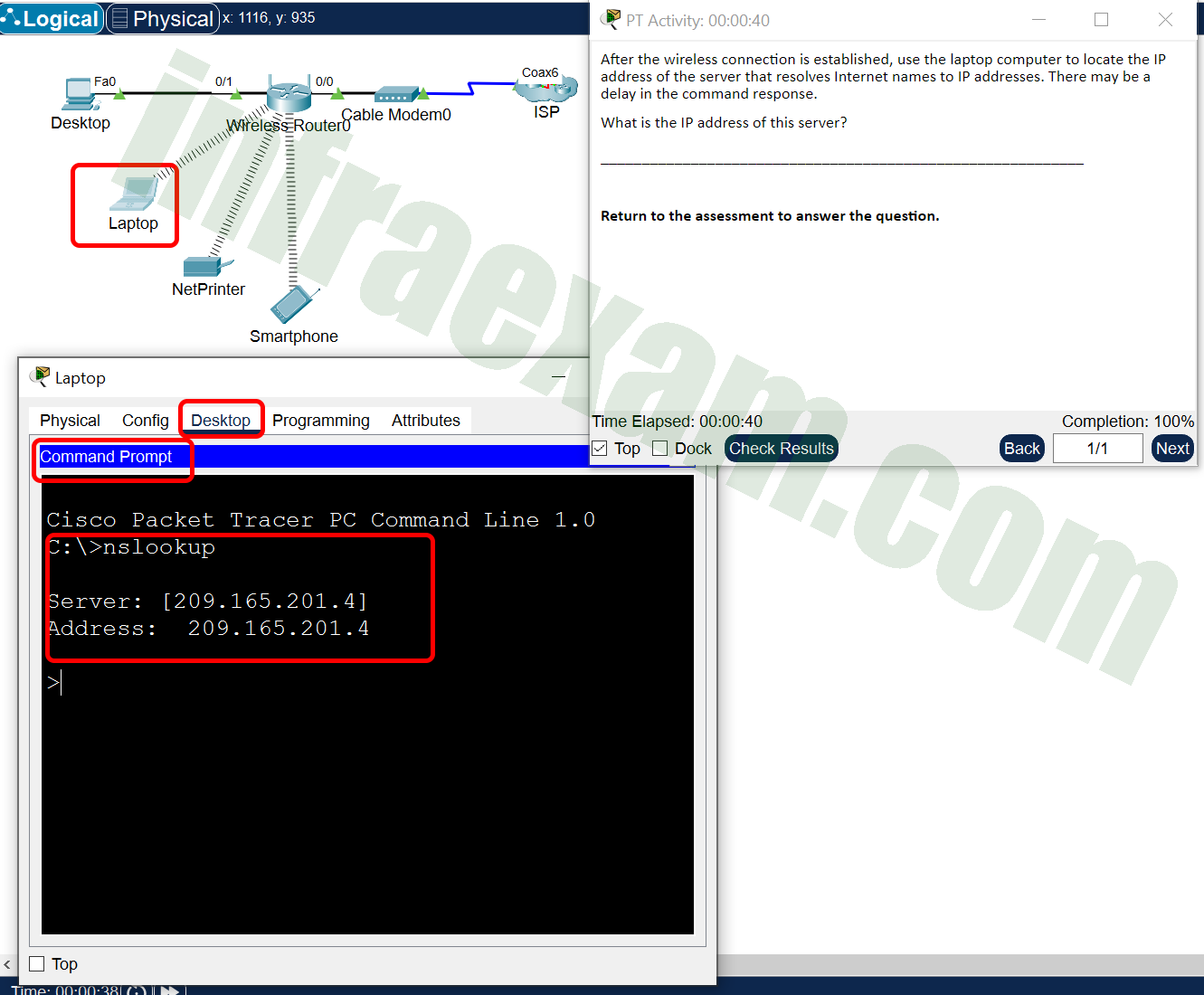
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Modules 9 – 12 Data Communications and Network Services Group Exam Answers PT 002 What is the IP address of this server?
- 192.168.10.1
- 192.168.10.100
- 209.165.201.3
- 209.165.201.4
Answers Explanation & Hints: The DNS server resolves Internet names to associated IP addresses.
-
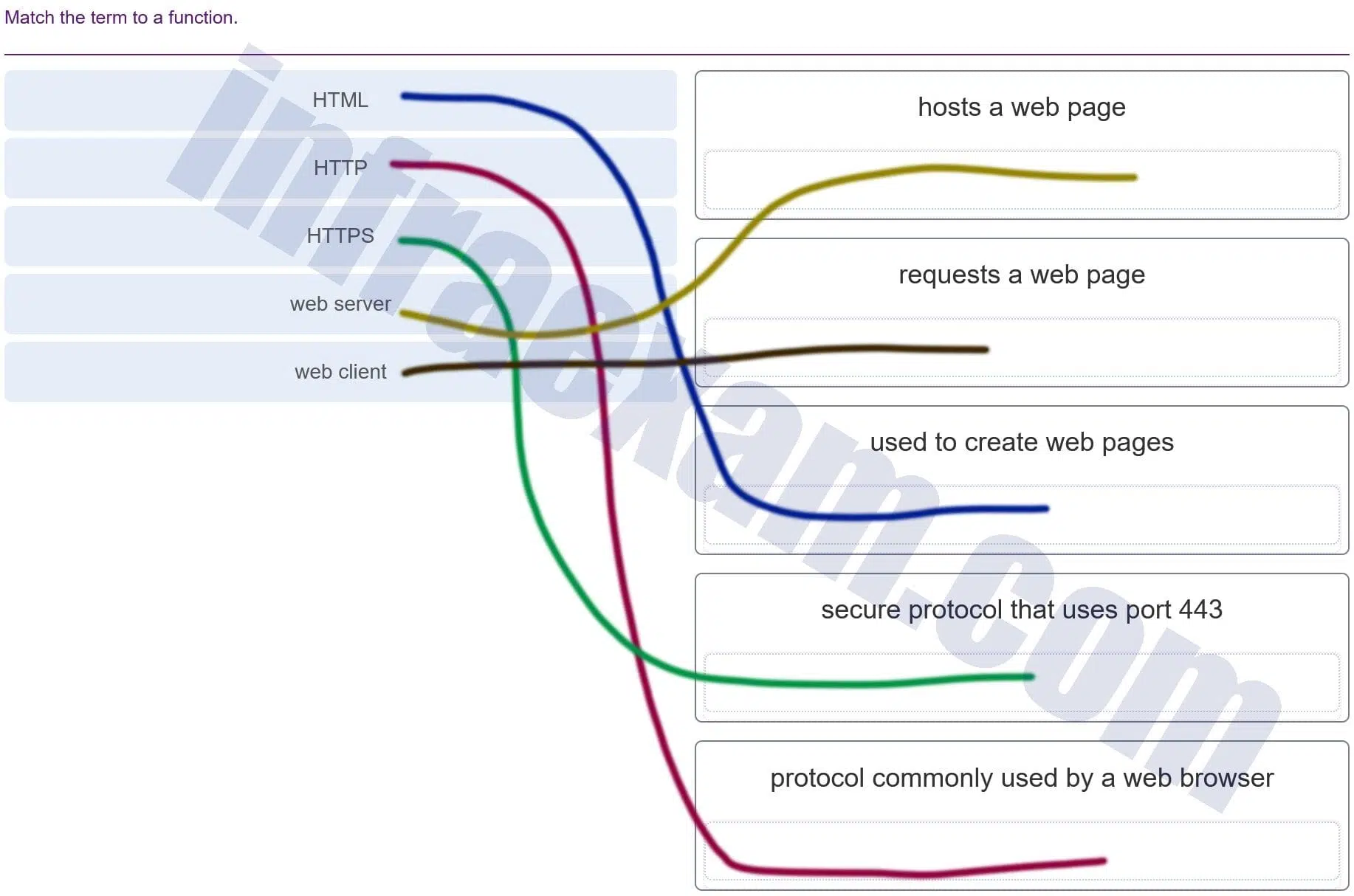
Match the term to a function.
Modules 9 – 12 Data Communications and Network Services Group Exam Answers 001 -
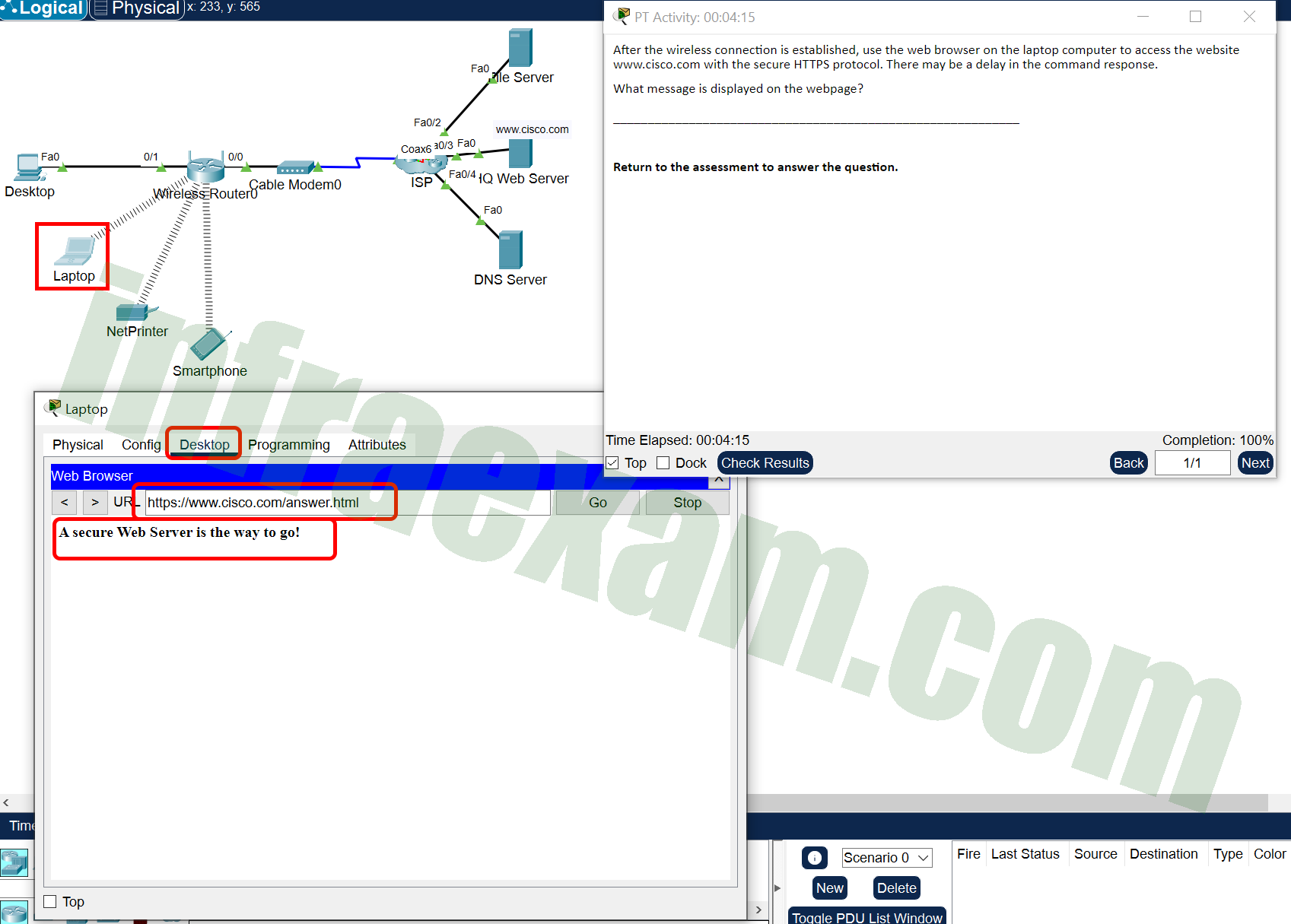
Open the PT Activity. Perform the tasks in the activity instructions and then answer the question.
Modules 9 – 12 Data Communications and Network Services Group Exam Answers PT 001 What message is displayed on the webpage?
- A secure web server is the way to go!
- A web server should run secure services!
- A web server provides secure communication!
- A secure web server is running!
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because the HQ web server runs a secure web service, the protocol HTTPS must be used to access the website. This means that the URL of https://www.cisco.com must be used to access the HQ web server and locate the message.
-
Which two applications provide virtual terminal access to remote servers? (Choose two.)
- SSH
- DNS
- DHCP
- SMTP
- Telnet
Answers Explanation & Hints: Telnet and SSH are two services that provide virtual terminal services to servers. DNS maps a domain name to its IP address. DHCP provides dynamic IP addressing information. SMTP provides email service.
-
What type of server would use IMAP?
- DNS
- DHCP
- FTP
- Telnet
Answers Explanation & Hints: SMTP, IMAP, and POP are three application layer protocols for email applications.