Networking Essentials 3.0: Course Final Exam Answers 2025 Full 100%
Networking Essentials 3.0: Course Final Exam Answers 2025 Full 100%
This Networking Essentials 3.0: Course Final Exam Answers is provided with the correct answers to 100% of the questions. This Final Exam Answers is used for the Cisco NetAcad platform which is the latest version just released in 2025. Review all the questions and answers here, then you will meet randomly 60 questions from all here.
-
Which three types of nodes should be assigned static IP addresses on a network? (Choose three.)
- printers
- servers
- tablets
- mobile laptops
- gateways
- desktop PCs
Explanation & Hint: The three types of nodes that should be assigned static IP addresses on a network are:
- Printers: Printers are often accessed by multiple users, and assigning a static IP address to a printer ensures that it can always be found at the same network location.
- Servers: Servers are critical components of a network and should have a static IP address to ensure that they can always be found and accessed by clients.
- Gateways: Gateways are the entry and exit points of a network and are responsible for directing traffic between different networks. Assigning a static IP address to a gateway ensures that other devices on the network can always find it.
Note that while desktop PCs can also benefit from having a static IP address, it is not always necessary or practical to assign them one, especially in larger networks where IP address management can become more complex. Similarly, while tablets and mobile laptops may benefit from having a static IP address in some cases, they are typically assigned dynamic IP addresses by default.
-
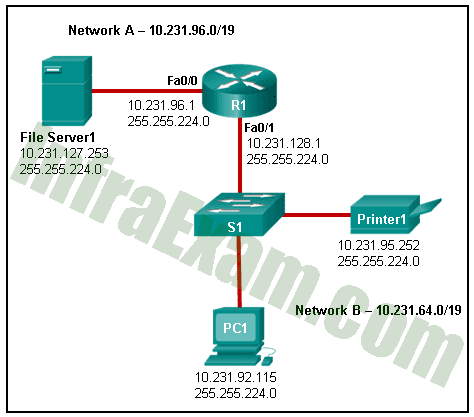
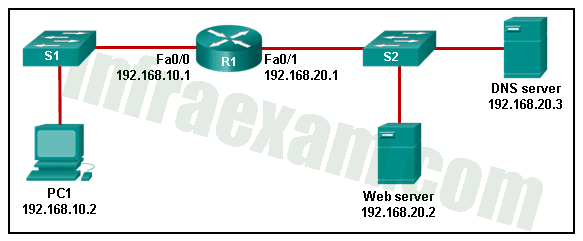
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator is troubleshooting connectivity on the office network. PC1 is able to send print jobs to Printer1, but is unable to access File Server1. Which action would correct the problem?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 07 - Change the R1 Fa0/0 interface subnet mask to 255.255.0.0.
- Change the R1 Fa0/1 interface IP address to 10.231.64.1.
- Change the PC1 IP address to 10.231.64.115.
- Change the File Server1 IP address to 10.231.96.253.
-
Explanation & Hint: Network B – 10.231.64.0/19
Network ID: 10.231.64.0
Usable IP Range: 10.231.64.1 – 10.231.95.254
Broadcast IP: 10.231.95.255
According to the exhibit, R1 => f0/1: 10.231.128.1 is out of the Network B range, so we have to change it to one of IP that is in the Network B range.
Based on the answer choices, 10.231.64.1 is the first IP in the Network B Range.
-
Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers? (Choose two.)
- The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
-
Explanation & Hint: - The Source Address field name is kept in IPv6 and is used to indicate the IPv6 address of the source node or device sending the packet.
- The Destination Address field is new in IPv6 and is used to indicate the IPv6 address of the destination node or device for the packet.
- The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6, as IPv6 uses a separate 4-bit field called the “Version” field in its header.
- The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6, which serves a similar purpose of preventing packets from circulating indefinitely in the network.
- The Header Checksum field name from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6, as IPv6 uses a different mechanism for ensuring data integrity called the “Authentication Header” (AH) and “Encapsulating Security Payload” (ESP).
-
Which statement is true regarding the UDP client process during a session with a server?
- Application servers have to use port numbers above 1024 in order to be UDP capable.
- A three-way handshake takes place before the transmission of data begins.
- A session must be established before datagrams can be exchanged.
- Datagrams that arrive in a different order than that in which they were sent are not placed in order.
-
Explanation & Hint: - UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a transport layer protocol that is connectionless, meaning it does not establish a session or perform a three-way handshake before transmitting data.
- Unlike TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), UDP does not guarantee delivery or order of datagrams. If datagrams are lost or arrive out of order, it is up to the application layer to handle any necessary retransmissions or reordering of data.
- Both the client and server processes using UDP can use any port number, and there is no requirement for applications to use ports above 1024. However, some well-known services such as DNS use specific port numbers.
- In summary, while a session does not need to be established before datagrams can be exchanged, and a three-way handshake does not take place, UDP does not guarantee delivery or order of datagrams.
-
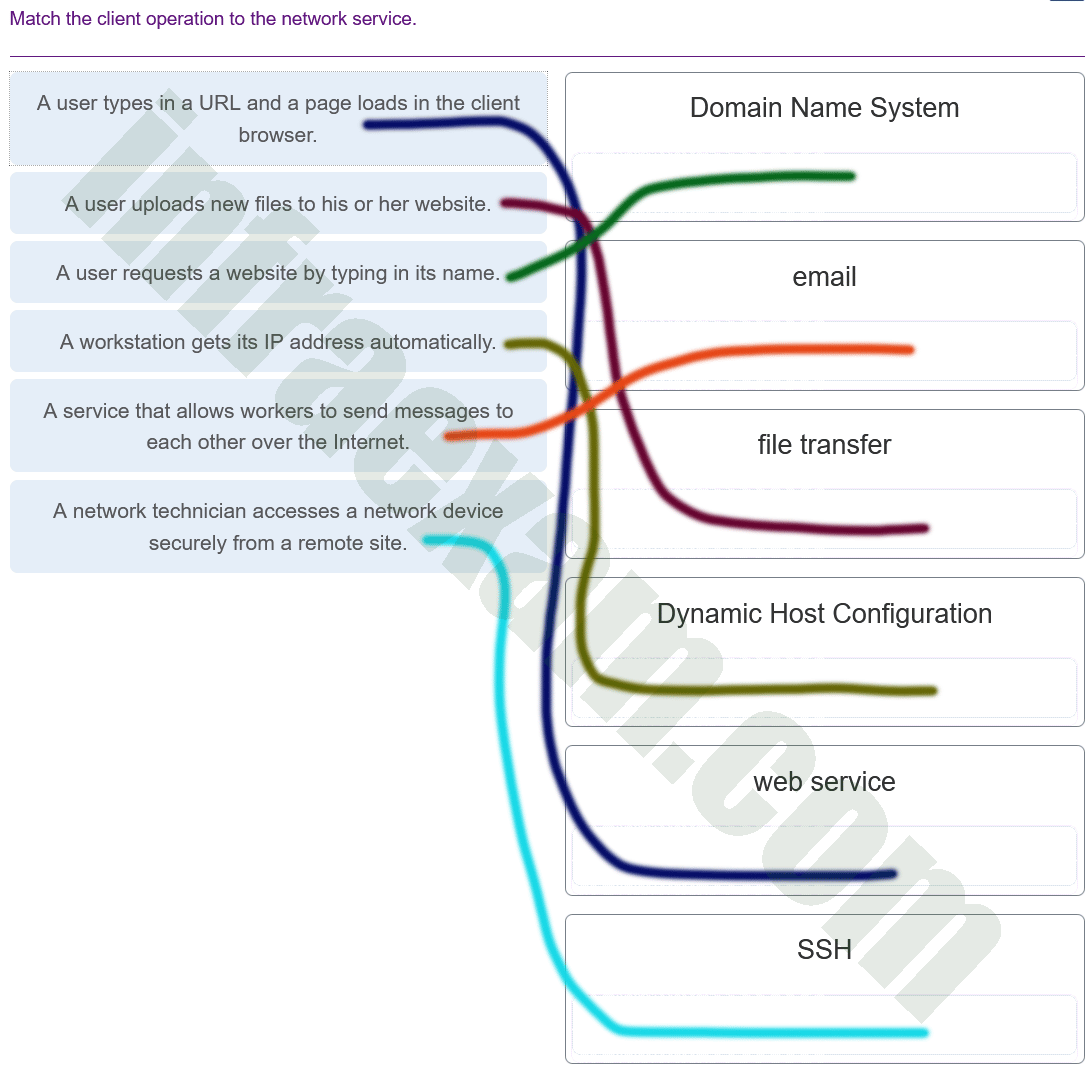
Match the definition to the type of cloud.
- made up of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures bound together by technology ==> hybrid cloud
- intended for a specific organization or entity, such as the government ==> private cloud
- intended for exclusive use by multiple organizations with shared functional needs ==> community
- services made available to the general population ==> public cloud
-
Explanation & Hint: - Public cloud: A public cloud is a type of cloud environment in which computing resources are made available to the general public over the internet. These resources are typically owned and operated by a third-party provider, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform, or Microsoft Azure. Public clouds are often used by companies or individuals who want to run applications or services on infrastructure that they do not own or manage.
- Private cloud: A private cloud is a type of cloud environment that is intended for a specific organization or entity. Private clouds are typically built and maintained by the organization’s IT department, and the infrastructure may be physically located on-premises or in a third-party data center. Private clouds offer more control and customization options than public clouds, but they require more upfront investment in terms of hardware, software, and personnel.
- Community cloud: A community cloud is a type of cloud environment that is intended for exclusive use by multiple organizations with shared functional needs. Community clouds may be owned and managed by one or more of the participating organizations, or they may be provided by a third-party vendor. Community clouds offer a way for organizations to share computing resources while maintaining greater control and security than they would have in a public cloud.
- Hybrid cloud: A hybrid cloud is a type of cloud environment that is made up of two or more distinct cloud infrastructures bound together by technology. This can include a combination of public and private clouds, as well as on-premises infrastructure. Hybrid clouds offer a way for organizations to take advantage of the scalability and flexibility of public clouds while maintaining greater control over sensitive data and applications.
-
What are two characteristics of RAM on a Cisco device? (Choose two.)
- RAM is able to store multiple versions of IOS and configuration files.
- RAM is a component in Cisco switches but not in Cisco routers.
- The configuration that is actively running on the device is stored in RAM.
- The contents of RAM are lost during a power cycle.
- RAM provides nonvolatile storage.
-
Explanation & Hint: RAM stands for Random Access Memory, which is volatile memory and stores the running configuration file, routing tables, ARP cache, packet buffers, and other temporary data. RAM provides fast access to data but does not provide permanent storage, so its contents are lost when the device is powered off or restarted. Cisco routers and switches both use RAM for temporary storage. RAM does not provide nonvolatile storage, as it is volatile memory.
-
Which statement describes the use of powerline networking technology?
- New “smart” electrical cabling is used to extend an existing home LAN.
- Wireless access points use powerline adapters to distribute data through the home LAN.
- A device connects to an existing home LAN using an adapter and an existing electrical outlet.
- A home LAN is installed without the use of physical cabling.
-
Explanation & Hint: Powerline networking technology allows network signals to be transmitted over the existing electrical wiring in a building. With this technology, a device can be connected to an existing home LAN by using an adapter that plugs into a wall socket, allowing network signals to be transmitted over the electrical wiring in the building. This technology is often used in situations where it is difficult or impossible to run physical network cables or where wireless signals are unreliable.
-
An employee is having connectivity issues. Why might a network technician try to ping the default gateway from the employee laptop?
- to verify that the SVI interface on the switch is configured correctly
- to verify connectivity with the device that provides access to remote networks
- to verify that an IP address was provided by the DHCP server
- to determine if the laptop address is included in the DNS server
-
Explanation & Hint: The default gateway is the device that enables communication between devices on the local network and devices on remote networks. If a device is having connectivity issues, one of the first steps a technician might take is to verify that the device can communicate with the default gateway. By pinging the default gateway from the employee laptop, the technician can determine if the issue is related to connectivity with the device that provides access to remote networks. If the ping is successful, then the connectivity issue may be related to other factors such as DNS or DHCP, which can be further investigated.
-
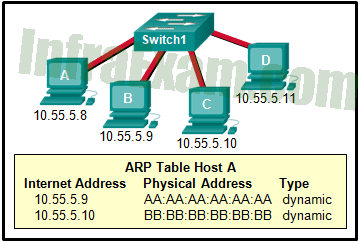
Refer to the exhibit. A switch with a default configuration connects four hosts. The ARP table for host A is shown. What happens when host A wants to send an IP packet to host D?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 08 - Host A sends an ARP request to the MAC address of host D.
- Host A sends out a broadcast of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. Every other host connected to the switch receives the broadcast and host D responds with its MAC address.
- Host D sends an ARP request to host A.
- Host A sends out the packet to the switch. The switch sends the packet only to the host D, which in turn responds.
-
Explanation & Hint: Host A sends out an ARP request to the MAC address of host D. Since the IP address of host D is not listed in the ARP table of host A, host A will need to send an ARP request to determine the MAC address of host D. Once host A receives the MAC address of host D from the ARP response, it can use that information to send the IP packet to host D.
-
Which type of static route creates a gateway of last resort?
- default static route
- floating static route
- summary static route
- standard static route
-
Explanation & Hint: A default static route is a type of static route that creates a gateway of last resort. It is used to route traffic to any destination that is not in the routing table, and is typically used when a router has only one path to the outside network. The default static route is also known as the 0.0.0.0/0 route, which means that it matches any destination address (0.0.0.0) with any subnet mask (/0). When a packet is received by the router that does not match any other route in the routing table, the router will forward the packet to the next hop specified in the default route. This is useful for routers that do not have specific knowledge of all the networks they might encounter, such as border routers or routers that connect to the internet.
-
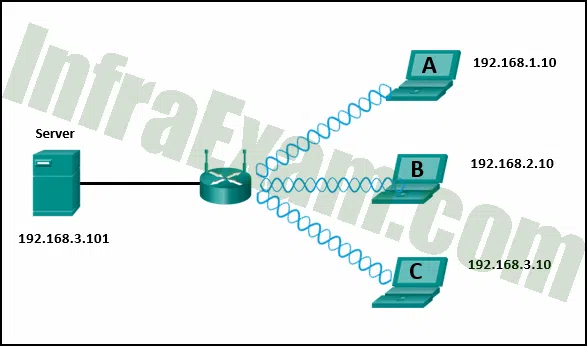
Refer to the exhibit. If all devices are using a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, which laptop would have an IP address with the same network number as the server?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 09 - B
- A
- C
-
Explanation & Hint: Laptop C (192.168.3.10) would have the same network number (192.168.3.0) as the server (192.168.3.101) because they both have the same network portion (the first three octets) in their IP addresses.
-
Which two scenarios would benefit the user the most by adding quality of service (QoS) to the network? (Choose two.)
- A student is communicating via Skype with a friend in another country.
- Students are updating information about their sport activities on the class Facebook page.
- A student is sending emails to a friend.
- Students are watching a lecture from a YouTube site.
-
Explanation & Hint: In both scenarios, real-time communication and streaming video are involved, which require a reliable and fast network with minimal delay, jitter, and packet loss. Implementing QoS can prioritize and manage the network traffic to ensure that these applications receive the necessary bandwidth and resources, while less critical traffic is given lower priority. This can improve the overall user experience and prevent issues such as choppy audio or video, dropped calls, and slow response times.
-
An attacker is sitting in front of a store and wirelessly copies emails and contact lists from nearby unsuspecting user devices. What type of attack is this?
- bluejacking
- bluesnarfing
- smishing
- RF jamming
-
Explanation & Hint: The attack described is called bluesnarfing. Bluesnarfing is a type of wireless attack in which an attacker gains unauthorized access to a Bluetooth-enabled device such as a mobile phone, laptop, or tablet and steals personal data such as contact lists, emails, and messages. This type of attack can be carried out with software tools that allow attackers to search for and connect to Bluetooth devices without the knowledge or permission of the device owner.
To protect against bluesnarfing and other Bluetooth-related attacks, users should ensure that their devices are not discoverable to other Bluetooth devices when they are not in use, use strong and unique PINs or passwords to authenticate Bluetooth connections, and avoid connecting to unknown or suspicious devices. Network administrators can also implement security measures such as Bluetooth scanning, access controls, and intrusion detection systems to monitor and prevent unauthorized access to Bluetooth-enabled devices on their networks.
-
What type of attack targets an SQL database using the input field of a user?
- XML injection
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting
- buffer overflow
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of attack that targets an SQL database using the input field of a user is called SQL injection. In this type of attack, an attacker attempts to inject malicious SQL code into a web application’s input field, which the application then sends to a backend database. This can allow the attacker to access or modify the contents of the database, bypass authentication, or execute other unauthorized actions. SQL injection attacks can be prevented by input validation and sanitization of user input, as well as using prepared statements and parameterized queries in code.
-
What is an example of cloud computing?
- a service that offers on-demand access to shared resources
- a network infrastructure that spans a large geographic area
- a continuous interaction between people, processes, data, and things
- an architectural style of the World Wide Web
-
Explanation & Hint: An example of cloud computing is a service that offers on-demand access to shared resources over the Internet. This could include services such as cloud storage, cloud-based software applications, and cloud-based virtual machines. Cloud computing allows users to access computing resources on an as-needed basis, without the need to invest in and maintain physical hardware and infrastructure. This makes it a flexible and cost-effective solution for businesses and individuals alike.
-
Which two criteria are used to help select a network medium for a network? (Choose two.)
- the types of data that need to be prioritized
- the distance the selected medium can successfully carry a signal
- the environment where the selected medium is to be installed
- the cost of the end devices that are used in the network
- the number of intermediate devices that are installed in the network
-
Explanation & Hint: The distance a medium can carry a signal is important in determining the type of medium to be used. For example, fiber optic cables can carry signals over longer distances than copper cables. The environment where the medium is to be installed is also an important consideration, as some media are more suitable for certain environments than others. For example, wireless networks may be more suitable in environments where physical cabling is difficult to install or may not be feasible. The types of data that need to be prioritized, the cost of the end devices used in the network, and the number of intermediate devices installed are not as critical in determining the type of network medium to be used.
-
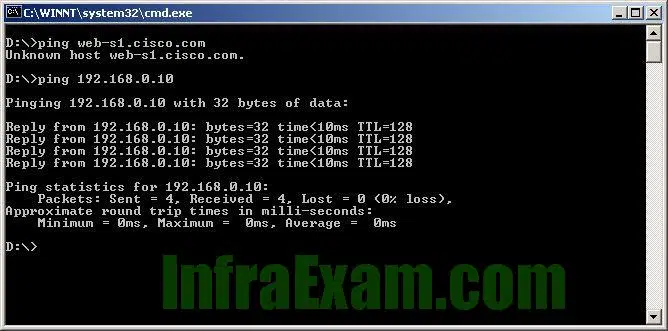
Refer to the exhibit. A web designer calls to report that the web server web-s1.cisco.com is not reachable through a web browser. The technician uses command line utilities to verify the problem and to begin the troubleshooting process. Which two things can be determined about the problem? (Choose two.)
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 10 - A router is down between the source host and the server web-s1.cisco.com.
- There is a problem with the web server software on web-s1.cisco.com.
- The default gateway between the source host and the server at 192.168.0.10 is down.
- The web server at 192.168.0.10 is reachable from the source host.
- DNS cannot resolve the IP address for the server web-s1.cisco.com.
-
Explanation & Hint: The output of the
pingcommand provides some useful information for troubleshooting network connectivity issues.In this particular case, the technician first attempted to ping the hostname “web-s1.cisco.com” but received the message “Unknown host web-s1.cisco.com”, indicating that the DNS (Domain Name System) server was unable to resolve the hostname to an IP address. This suggests that the problem may be related to DNS resolution.
Next, the technician pinged the IP address 192.168.0.10 and received four successful replies, indicating that the web server at that IP address is reachable from the source host. This rules out any issues with connectivity between the source host and the web server.
Based on these two pieces of information, it can be determined that the problem is likely related to DNS resolution, and specifically with the DNS server being used by the source host. The technician may need to investigate the configuration of the DNS server settings on the source host to ensure that they are configured correctly.
-
Which command would a technician use to display network connections on a host computer?
- ipconfig
- nslookup
- netstat
- tracert
-
Explanation & Hint: The command that a technician would use to display network connections on a host computer is
netstat. This command is used to show active network connections, routing tables, and other network statistics. By default, it displays all active TCP connections, both incoming and outgoing, and also UDP connections. Thenetstatcommand is available on both Windows and Unix-based operating systems. The output of thenetstatcommand can be used to troubleshoot network connectivity issues and identify potential security threats.
-
Which type of network model describes the functions that must be completed at a particular layer, but does not specify exactly how each protocol should work?
- reference model
- protocol model
- hierarchical design model
- TCP/IP model
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network model that describes the functions that must be completed at a particular layer, but does not specify exactly how each protocol should work is a reference model. The most well-known reference model is the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which divides network communication into seven layers, each of which performs specific functions necessary for communication. The OSI model provides a framework for how network protocols should interact and communicate with each other, but it does not define the actual protocols used to accomplish these tasks.
-
Which three IPv4 header fields have no equivalent in an IPv6 header? (Choose three.)
- protocol
- TTL
- fragment offset
- flag
- identification
- version
-
Explanation & Hint: The three IPv4 header fields that have no equivalent in an IPv6 header are:
- Fragment offset – IPv6 does not support fragmentation at the router level, so this field is no longer needed.
- Identification – Instead of using the identification field, IPv6 uses a combination of the Source Address, Destination Address, and Flow Label fields to identify and reassemble fragmented packets.
- TTL – In IPv6, the TTL field is replaced with a Hop Limit field, which functions in the same way, but with a different name.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
- Fragment offset
- Identification
- TTL
-
How are port numbers used in the TCP/IP encapsulation process?
- Source port and destination port numbers are randomly generated.
- Destination port numbers are assigned automatically and cannot be changed.
- If multiple conversations occur that are using the same service, the source port number is used to track the separate conversations.
- Source port numbers and destination port numbers are not necessary when UDP is the transport layer protocol being used for the communication.
-
Explanation & Hint: In the TCP/IP encapsulation process, port numbers are used to identify the processes or applications on the source and destination devices that are communicating with each other. The source device randomly generates a source port number, and the destination device uses a well-known port number for the service that it provides. The source and destination port numbers together create a unique identifier for the communication, allowing multiple conversations using the same service to occur simultaneously without interfering with each other. In UDP, the source and destination port numbers are also used to identify the processes on the source and destination devices, and they are necessary to direct the data to the correct application.
-
What is the key difference between a type 1 hypervisor and a type 2 hypervisor?
- A type 1 hypervisor runs on specialized systems and a type 2 hypervisor runs on desktop computers.
- A type 1 hypervisor supports all server OS virtualization and a type 2 hypervisor supports Linux and Mac virtualization.
- A type 1 hypervisor supports server virtualizations and a type 2 hypervisor only supports workstation virtualization.
- A type 1 hypervisor runs directly on the system hardware and a type 2 hypervisor requires a host OS to run.
-
Explanation & Hint: The key difference between a type 1 hypervisor and a type 2 hypervisor is that a type 1 hypervisor runs directly on the system hardware while a type 2 hypervisor requires a host operating system to run. Type 1 hypervisors are also known as bare-metal hypervisors and are installed directly on the server hardware. They have direct access to the underlying system hardware and manage the resources of the physical host, allowing multiple guest virtual machines to run on top. Type 2 hypervisors, on the other hand, run on top of a host operating system, such as Windows or Linux, and are also known as hosted hypervisors. They use the host OS to manage system resources and create a layer of abstraction between the guest virtual machines and the physical host.
-
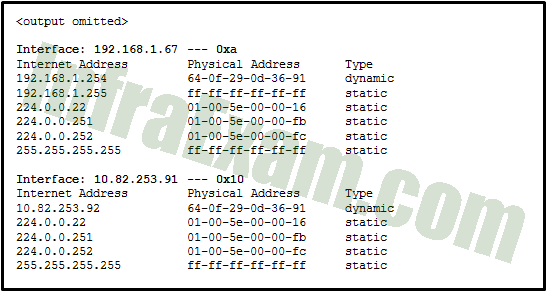
Refer to the exhibit. Which protocol was responsible for building the table that is shown?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 06 - DNS
- ARP
- DHCP
- ICMP
-
Explanation & Hint: The table in the exhibit shows the mapping of IP addresses to physical addresses on a local network segment. This mapping is accomplished through a protocol called Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). When a device needs to communicate with another device on the same local network segment, it uses ARP to determine the physical address (also known as the MAC address) of the destination device based on its IP address. Once the physical address is known, the source device can create a frame with the appropriate source and destination MAC addresses and transmit it over the local network to the destination device. ARP is a protocol that operates at the data link layer of the OSI model.
-
Which two types of messages are used in place of ARP for address resolution in IPv6? (Choose two.)
- neighbor solicitation
- neighbor advertisement
- broadcast
- echo reply
- echo request
- anycast
-
Explanation & Hint: In IPv6, ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) has been replaced with two messages, Neighbor Solicitation (NS) and Neighbor Advertisement (NA), which are used for address resolution. These two messages help nodes determine the link-layer (MAC) address of a neighbor on the same network segment. An NS message is used to query the link-layer address of a neighbor, while an NA message is used to respond to a query or to announce the link-layer address of the sender. The use of broadcast is also replaced with multicast addressing. Echo request and echo reply are messages used in ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) for ping tests, and anycast is a type of addressing used for routing packets to the nearest of a group of potential destination hosts.
-
A PC has sent an RS message to an IPv6 router attached to the same network. Which two pieces of information will the router send to the client? (Choose two.)
- DNS server IP address
- subnet mask in dotted decimal notation
- prefix
- administrative distance
- domain name
- prefix length
-
Explanation & Hint: An RS (Router Solicitation) message is used by an IPv6 client to obtain its own global unicast address by sending a multicast message to all routers on the network. When a router receives an RS message from a client, it will respond with an RA (Router Advertisement) message that includes the following information:
- Prefix: The prefix to be used for the network segment.
- Prefix length: The length of the prefix.
Therefore, the correct answers to this question are:
- Prefix
- Prefix length
-
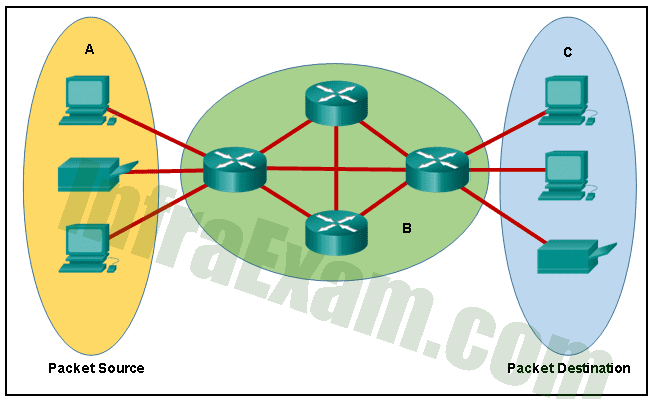
Refer to the exhibit. Which term correctly identifies the device type that is included in the area B?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 05 - transfer
- source
- intermediary
- end
-
Explanation & Hint: In the given exhibit, the area B is the middle circle that contains three interconnected routers. This indicates that the routers in this area are functioning as intermediary devices. An intermediary device is a networking device that acts as a bridge between multiple networks or devices, providing connectivity and forwarding data packets between them. In this case, the routers in area B are responsible for routing packets between the devices in areas A and C. The routers in area B may perform additional functions such as filtering, security, and quality of service (QoS) to optimize the network traffic flow.
-
A user can access a file share resource on a server located in the same office but cannot access the internet. What is the possible cause?
- The switch is malfunctioning.
- The default gateway address is misconfigured on the PC.
- The DHCP server is disconnected.
- The IPv4 address and subnet mask are misconfigured on the PC.
-
Explanation & Hint: The possible cause for a user to be able to access a file share resource on a server located in the same office but not access the internet is that the default gateway address is misconfigured on the PC. The default gateway is the IP address of the router that provides access to networks outside of the local network. If the default gateway is misconfigured or unavailable, the PC cannot access resources outside of the local network, such as the internet. However, it can still communicate with devices on the same local network. To resolve the issue, the default gateway address on the PC needs to be correctly configured.
-
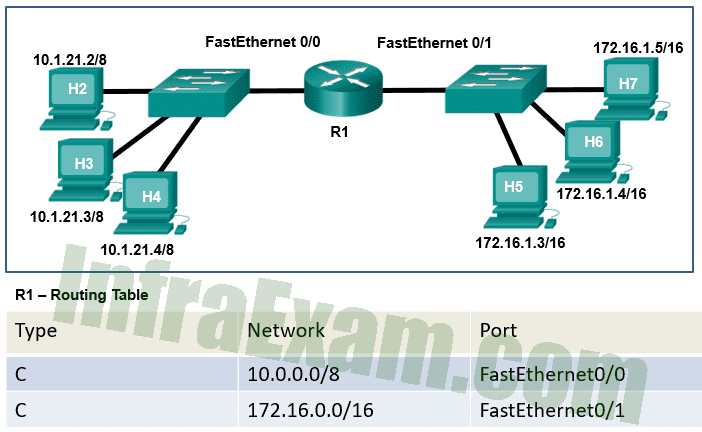
Refer to the exhibit. Host H2 sends a unicast message to host H6. Which destination IP address is contained in the header of the packet when it reaches host H6?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 04 - the IP address of the FastEthernet0/0 interface on router R1
- the IP address of the FastEthernet0/1 interface on router R1
- the IP address assigned to the network adapter on host H6
- the IP address assigned to the network adapter on host H2
-
Explanation & Hint: The destination IP address contained in the header of the packet when it reaches host H6 would be the IP address assigned to the network adapter on host H6, which is 172.16.1.4/16.
-
Refer to the exhibit. How many bits are represented by each group of four hexadecimal values contained between the colons in an IPv6 address?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 03 - 32
- 16
- 64
- 4
- 8
-
Explanation & Hint: Each group of four hexadecimal values contained between the colons in an IPv6 address represents 16 bits.
-
Which wireless technology allows a customer to connect to a payment terminal in the store with a smartphone?
- Wi-Fi
- GPS
- Bluetooth
- NFC
-
Explanation & Hint: The wireless technology that allows a customer to connect to a payment terminal in the store with a smartphone is Near Field Communication (NFC). NFC is a short-range wireless technology that enables two devices to communicate with each other when they are in close proximity, typically within a few centimeters. It is widely used for contactless payments, ticketing, and access control systems. The technology is based on radio frequency identification (RFID) technology and operates on the 13.56 MHz frequency band. Unlike Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, NFC does not require pairing or a network connection, which makes it more convenient and secure for mobile payments.
-
What data encoding technology is used in copper cables?
- modulation of light rays
- pulses of light
- electrical pulses
- modulation of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves
-
Explanation & Hint: Data encoding is the process of transforming digital information into a format suitable for transmission over a communication channel. In copper cables, the data is encoded using electrical pulses. Electrical pulses are used to represent binary digits, which can be transmitted over the copper cable as electrical signals.
The most commonly used data encoding technique for copper cables is called Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) encoding. In this technique, a high voltage represents a binary 1, and a low voltage represents a binary 0. The electrical pulses are transmitted over the copper cable using a specific protocol, such as Ethernet, which defines how the data is organized and transmitted.
Other data encoding techniques that can be used with copper cables include Manchester encoding, Differential Manchester encoding, and Bipolar encoding. These techniques are used to reduce errors and increase data transmission rates over the copper cable.
-
Which two TCP header fields are used to confirm receipt of data? (Choose two.)
- preamble
- acknowledgment number
- FCS
- checksum
- sequence number
-
Explanation & Hint: The two TCP header fields used to confirm receipt of data are:
- Acknowledgment Number: This field contains the sequence number of the next byte of data that the receiver is expecting from the sender. When the receiver receives a TCP segment, it sends an acknowledgment back to the sender with this field set to the next expected sequence number.
- Checksum: This field is used to ensure the integrity of the TCP segment. It is a 16-bit field that contains a checksum value calculated over the entire TCP segment. The sender calculates this value and includes it in the TCP segment header. The receiver recalculates the checksum and compares it to the value in the header to confirm that the segment was not corrupted in transit.
-
What are two characteristics of multicast transmission? (Choose two.)
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255.
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct characteristics of multicast transmission are:
- A single packet can be sent to a group of hosts.
- Multicast transmission can be used by routers to exchange routing information.
The other options are incorrect:
- Computers use multicast transmission to request IPv4 addresses: this is not true, DHCP is used to assign IPv4 addresses.
- Multicast messages map lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses: this statement is not correct, mapping of lower layer addresses to upper layer addresses is not related to multicast transmission.
- The source address of a multicast transmission is in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255: This statement is not accurate, the source address of a multicast transmission can be any valid unicast or multicast IP address. However, the destination IP address for multicast transmission must be in the range of 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
-
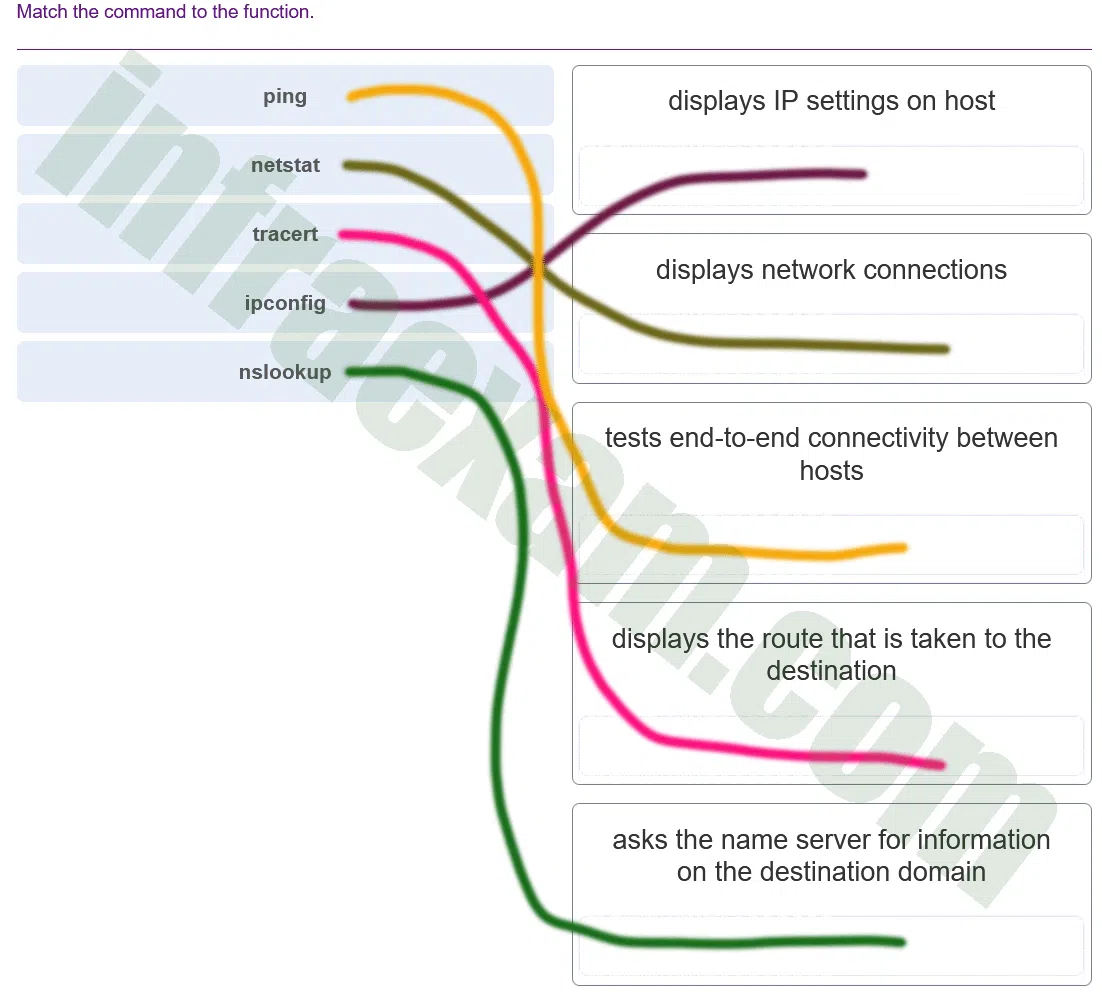
Which troubleshooting tool can be used to determine the current TCP open connections on a PC?
- netstat
- nslookup
- tracrt
- ping
- ipconfig
-
Explanation & Hint: The
netstatcommand is a network diagnostic tool that can be used to display various information about network connections on a computer. One of the pieces of information it can provide is the current TCP open connections on the PC.When you run the
netstatcommand, it will display a list of all the active network connections on your computer, along with information about the local and remote IP addresses and port numbers, the state of the connection, and the process ID (PID) of the application that is using the connection. By examining this information, you can determine which applications are using the most network resources, troubleshoot network connectivity issues, and monitor your network for unusual activity.
-
By having narrow viewing angles, an ATM mitigates what kind of attacks?
- quid pro quo
- identity fraud
- dumpster diving
- shoulder surfing
-
Explanation & Hint: By having narrow viewing angles, an ATM mitigates shoulder surfing attacks. Shoulder surfing is a form of direct observation attack in which an attacker looks over the shoulder of the victim to obtain sensitive information, such as PINs, passwords, or other confidential information. By limiting the viewing angles, an ATM makes it difficult for an attacker to observe the information entered by the user on the ATM screen or keypad. This reduces the risk of successful shoulder surfing attacks and helps to improve the security of ATM transactions.
-
Match the IPv6 field with its description.
- Payload Length ==> This 16-bit field indicates the length of the data portion of the IPv6 packet.
- Hop Limit ==> This 8-bit field uses a decremental counter to generate an IPv6 Time Exceeded message for the unsuccessful delivery of the message.
- Version ==> This field contains a 4-bit binary value set to 0110 that identifies this as an IP version 6 packet.
- Flow Label ==> This 20-bit flow label field in the IPv6 header is used by the source to label those packets for which the source requests special handling by the IPv6 routers.
- Next Header ==> This field indicates the data payload type that the packet is carrying, enabling the network layer to pass the data to the appropriate upper-layer protocol.
- Traffic Class ==> This 8-bit field is equivalent to the IPv4 Differentiated Services (DS) field.
-
Explanation & Hint: IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol (IP), and it is designed to address the limitations of IPv4, which is the current version of IP that most networks use today. IPv6 has a much larger address space than IPv4, allowing for the creation of more unique addresses, which is important as the number of internet-connected devices continues to grow.
One of the key features of IPv6 is the addition of several new header fields that provide additional functionality compared to IPv4. These header fields include the Payload Length, Hop Limit, Version, Flow Label, Next Header, and Traffic Class fields.
The Payload Length field is a 16-bit field that indicates the length of the data portion of the IPv6 packet, excluding the IPv6 header. This field allows the receiving device to know how much data to expect in the packet.
The Hop Limit field is an 8-bit field that uses a decremental counter to generate an IPv6 Time Exceeded message for the unsuccessful delivery of the message. This field is similar to the Time to Live (TTL) field in IPv4, but the Hop Limit field is incremented at each hop, while the TTL field is decremented.
The Version field is a 4-bit binary value set to 0110 that identifies the packet as an IPv6 packet. This field is used to differentiate IPv6 packets from IPv4 packets.
The Flow Label field is a 20-bit field that is used by the source to label those packets for which the source requests special handling by the IPv6 routers. This field is used to provide Quality of Service (QoS) guarantees for specific traffic flows.
The Next Header field is an 8-bit field that indicates the type of data payload that the packet is carrying, enabling the network layer to pass the data to the appropriate upper-layer protocol.
The Traffic Class field is an 8-bit field that is equivalent to the IPv4 Differentiated Services (DS) field. This field is used to provide different levels of service for different types of traffic.
-
Which nslookup command would return the DNS information of www.cisco.com?
- nslookup = cisco
- nslookup -type=mx www.cisco.com
- nslookup
- nslookup www.cisco.com
-
Explanation & Hint: To return the DNS information of www.cisco.com using the nslookup command, you can simply enter “nslookup www.cisco.com” in your command prompt or terminal. This will perform a DNS lookup for the domain and provide you with the relevant information.
Here’s an example of how the command would look:
nslookup www.cisco.com
Executing this command will display the DNS information for the specified domain, including the IP address associated with it.
-
Match the applications protocols to their respective transport protocols.
- HTTP ==> TCP
- SMTP ==> TCP
- FTP ==> TCP
- TFTP ==> UDP
-
Explanation & Hint: Application protocols are used to specify how data should be formatted, transmitted, and received between applications. These protocols operate at the application layer of the OSI model, which is the topmost layer responsible for application-to-application communication.
Transport protocols, on the other hand, operate at the transport layer of the OSI model and are responsible for the end-to-end delivery of data between hosts. There are two main transport protocols: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application protocol that is used for transmitting data over the World Wide Web. HTTP typically runs over TCP.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is an application protocol used to transmit electronic mail messages between servers. SMTP typically runs over TCP.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is an application protocol used for transferring files over the Internet. FTP can run over both TCP and UDP, but is more commonly used with TCP.
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) is a simpler version of FTP, used mainly for booting diskless workstations. TFTP runs over UDP.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Host A wants to send a packet to host D. Before sending the packet; host A needs to find out if host D is on the same local network. How does the source host find out if it has the same network portion as the destination host?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 02 - a binary anding between the R1 default gateway IP address and the R2 default gateway IP address
- a binary anding between the subnet mask of host A and the R2 default gateway IP address
- a binary anding between the subnet mask of host A and the host D IP destination address
- a binary anding between the subnet mask of host A and the R1 default gateway IP address
-
Explanation & Hint: The source host (Host A) will perform a binary AND operation between its own IP address and subnet mask, and the IP address of the destination host (Host D). This will give the network address of the destination host, and the source host will compare it to its own network address. If they match, the destination host is on the same local network as the source host, and the source host can send the packet directly to the destination host using ARP to resolve the MAC address. If they do not match, the source host will send the packet to its default gateway (Router R1), which will forward the packet to the next hop towards the destination host.
-
Which two addressing schemes use hexadecimal numbers? (Choose two.)
- IPv6 addresses
- IPv4 multicast addresses
- MAC addresses
- IPv4 broadcast addresses
- destination port numbers
-
Explanation & Hint: The two addressing schemes that use hexadecimal numbers are:
- MAC addresses – MAC addresses are 48-bit addresses used to identify devices on a local network, and are expressed in hexadecimal format.
- IPv6 addresses – IPv6 addresses are 128-bit addresses used to identify devices on a network and are also expressed in hexadecimal format.
-
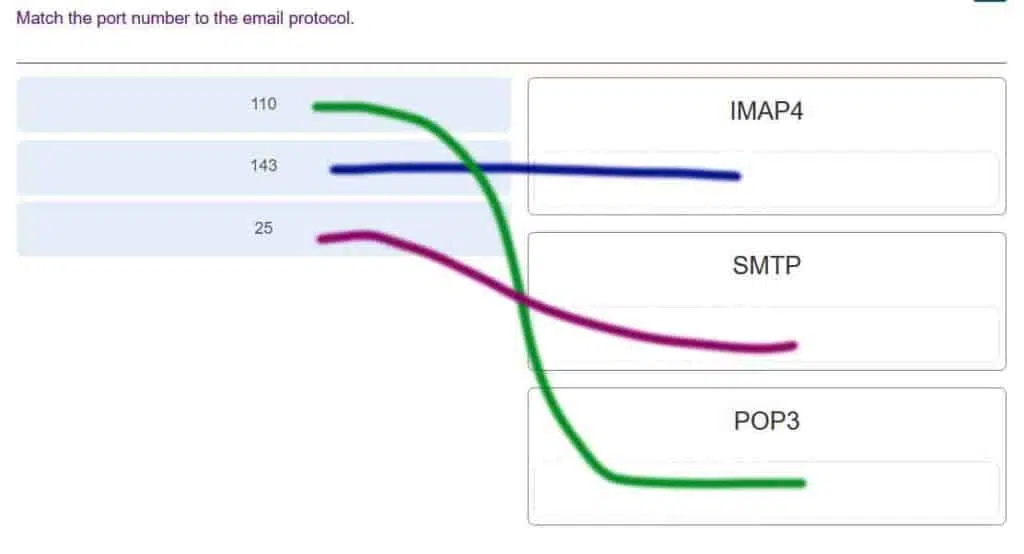
Which two application protocols retrieve emails from remote servers? (Choose two.)
- SSH
- IMAP
- POP
- SMTP
- FTP
-
Explanation & Hint: IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) and POP (Post Office Protocol) are two email retrieval protocols used to access emails stored on a remote email server.
IMAP allows a user to view and manipulate email messages as if they were stored locally on the user’s device. The email messages remain on the server and can be accessed and managed from different devices or email clients. IMAP also supports multiple mailboxes and folders, allowing users to organize and manage their emails more efficiently.
POP, on the other hand, downloads email messages from the server onto the user’s device and removes them from the server. Once downloaded, the email messages can only be accessed on that specific device. POP does not support multiple mailboxes or folders, making it less flexible than IMAP.
Both protocols use port numbers to communicate with the email server. IMAP uses port number 143 for unencrypted connections and port number 993 for encrypted connections (IMAP over SSL/TLS). POP uses port number 110 for unencrypted connections and port number 995 for encrypted connections (POP over SSL/TLS).
-
Which network connection type provides the highest data link speed?
- DSL
- fiber
- cable
- satellite
-
Explanation & Hint: Fiber provides the highest data link speed among the four network connection types mentioned. This is because fiber optic cables use light signals to transmit data, which can travel at very high speeds over long distances with minimal signal degradation. Compared to DSL, cable, and satellite connections, fiber optic connections can offer higher bandwidth and faster data transfer rates, making them ideal for high-speed Internet access and other bandwidth-intensive applications.
-
What are the two functions of the physical layer? (Choose two.)
- It adds the sending and destination IP addresses to the message.
- It scans incoming and outgoing signals for potential security breaches.
- It provides a connection to the network through the local media.
- It provides information about the type of user application used in the transmission.
- It encodes the signal to be transported based on the requirements of the local media.
-
Explanation & Hint: The physical layer of the OSI model is responsible for the following two functions:
- It provides a physical connection to the network through the local media. This includes the transmission of bits over a communication channel, the physical components used to transmit the signals (such as cables, connectors, and repeaters), and the characteristics of the physical media (such as the maximum transmission distance and the data transfer rate).
- It encodes the signal to be transported based on the requirements of the local media. This involves transforming the digital data into a format that can be transmitted over the specific physical medium being used. The encoding method depends on the type of medium being used (such as copper wire, fiber optic cable, or wireless radio waves).
-
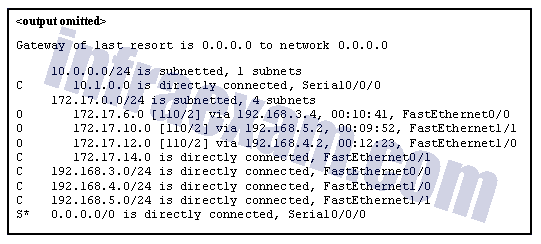
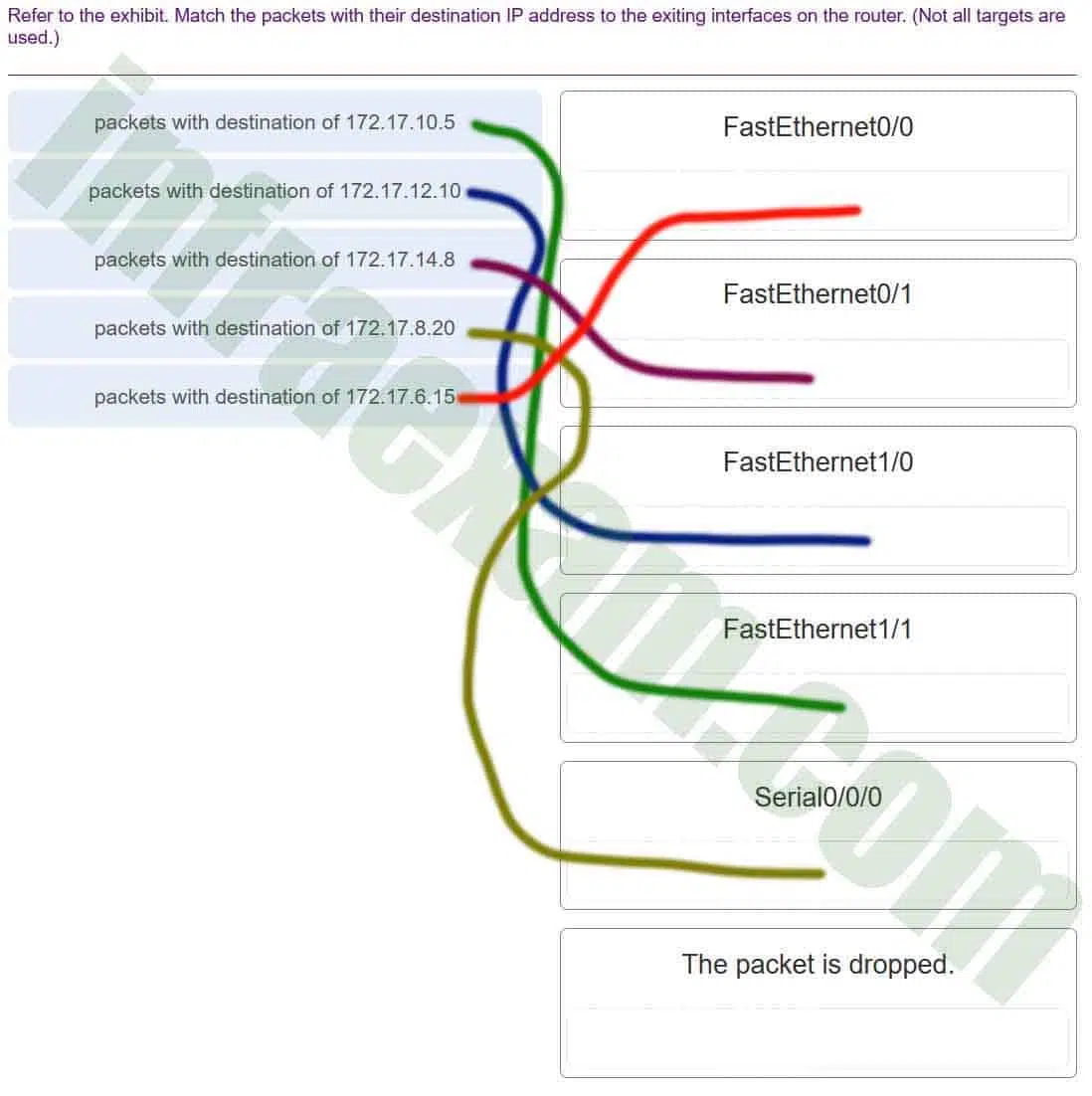
Refer to the exhibit. The router receives a packet with the destination IP address of 172.17.10.14. What will the router do with this packet?
Networking Essentials 3.0 Course Final Exam Answers 01 - Forward the packet through interface FastEthernet0/1.
- Drop the packet.
- Forward the packet through interface Serial0/0/0.
- Forward the packet through interface FastEthernet1/1.
-
Explanation & Hint: Based on the routing table shown in the exhibit, the router will forward the packet through interface FastEthernet1/1 since the destination IP address 172.17.10.14 is within the subnet 172.17.10.0/24, which is directly connected to the router via the FastEthernet1/1 interface.
-
Match the IPv6 addresses to the appropriate unicast category.
- Loopback ==> 1/128
- Unspecified ==> ::/128
- Link Local ==> fe80::530:3bff:fe22:70d5
- Global Unicast ==> 2001:db8:2626:ae44:208a:8899:6060:3be6
- Unique Local ==> fc00::/7
-
Explanation & Hint: IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol (IP) that is designed to replace IPv4. It uses a 128-bit address space that allows for a large number of unique addresses to be assigned to devices on a network. IPv6 addresses are divided into different categories, each with its own characteristics and uses.
- Loopback: This is a special address that points to the device itself. The loopback address is used for testing and diagnosing network issues. In IPv6, the loopback address is represented as ::1.
- Unspecified: This address is used to represent an uninitialized or unknown address. In IPv6, the unspecified address is represented as ::.
- Link-local: This address is used for communication between devices on the same local network segment, such as a LAN. The link-local address is automatically generated based on the device’s MAC address and is represented as fe80::/10.
- Global Unicast: This address is used for communication across the Internet or other wide area networks. Global unicast addresses are routable and unique, and are assigned by Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) or a regional Internet registry. They are represented as 2000::/3.
- Unique Local: This address is similar to a private address in IPv4, and is used for communication within a private network. Unique local addresses are not routable on the public Internet, but can be used to communicate with other private networks that use the same address space. They are represented as fc00::/7.
-
Host A wants to send a message to another host on the local IPv6 network. What are the first two steps Host A will take to determine the MAC address of the receiving host? (Choose two.)
- Host A will send a neighbor solicitation message to an all-nodes multicast address (FF02::1).
- Host A will sends a neighbor advertisement message to a broadcast address.
- Host A will check its ARP table entries to see if the destination host MAC information is already in the table.
- Host A will send a router solicitation message to the all-router multicast address (FF02::2).
- Host A will review entries in its neighbor cache to see if the destination host information is already in the cache.
- Host A will send a broadcast message to all hosts on the local network.
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct options are:
- Host A will send a neighbor solicitation message to an all-nodes multicast address (FF02::1).
- Host A will review entries in its neighbor cache to see if the destination host information is already in the cache.
When a host needs to send a message to another host on the same IPv6 network, it needs to determine the MAC address of the destination host to be able to send the message on the local network. To do this, Host A will send a neighbor solicitation message to the all-nodes multicast address (FF02::1), asking the receiving host to send a neighbor advertisement message with its MAC address. The neighbor solicitation message includes the IPv6 address of the destination host.
If Host A has previously communicated with the destination host, it might have the MAC address information cached in its neighbor cache. So, Host A will review the entries in its neighbor cache to see if the destination host information is already in the cache. If the MAC address is already in the neighbor cache, Host A can use it to send the message to the destination host.
-
A user purchases a new switch for the home office to accommodate faster speeds for a newly purchased laptop. The controller has 10/100/1000 MBPS ports, and the computer comes with a 10/100 NIC. What actual bandwidth will the laptop receive if it is plugged into a port on the switch?
- 100 MBPS
- 10 MBPS
- The laptop will not connect.
- 1000 MBPS
-
Explanation & Hint: The laptop will receive a maximum bandwidth of 100 MBPS since its NIC supports speeds up to 100 MBPS, which is the maximum speed that it can transmit or receive data from the network. Although the switch has 10/100/1000 MBPS ports, the laptop’s NIC cannot support the higher speed.
-
What are the two main functions of a layer 2 switch? (Choose two.)
- To provide payload scanning on the local network.
- To connect local devices to a default gateway.
- To provide wireless connectivity to the home network.
- To connect multiple remote routers to gigabit ports.
- To connect end-user devices on the same local network.
-
Explanation & Hint: A layer 2 switch is a networking device that operates at the data link layer (layer 2) of the OSI model. Its primary function is to connect end-user devices on the same local network, allowing these devices to communicate with each other.
The layer 2 switch works by reading the destination MAC address in the incoming Ethernet frame and then forwarding the frame only to the port that is connected to the destination device. This process is known as “switching” and is much faster than traditional network bridges, which operate at the same layer.
Another key function of a layer 2 switch is to provide network segmentation, which helps to improve network performance and security. By dividing a large network into smaller, more manageable segments, layer 2 switches can reduce network congestion and prevent network broadcasts from affecting all devices on the network.
In summary, the two main functions of a layer 2 switch are to connect end-user devices on the same local network and to provide network segmentation to improve network performance and security.
-
Which switch forwarding method provides the lowest latency?
- store-and-forward
- fast-forward
- store-and-forward with error checking disabled
- fragment-free
-
Explanation & Hint: The switch forwarding method with the lowest latency is “fast-forward.”
Fast-forward switching is a method where the switch begins forwarding a packet as soon as the destination MAC address is read. The switch does not wait for the entire frame to be received before forwarding, which results in lower latency and higher throughput. This method is commonly used in switches that have a higher bandwidth than the traffic volume they need to process.
In contrast, store-and-forward switching stores the entire frame in a buffer and performs a CRC error check before forwarding. This method introduces additional latency due to the error checking and waiting for the entire frame to be received before forwarding.
Fragment-free switching is a variant of store-and-forward switching where the switch only stores the first 64 bytes of the frame, which includes the frame header. This method reduces latency compared to store-and-forward but is slower than fast-forward switching.
-
Which three solutions are examples of physical access control? (Choose three.)
- protocol
- password
- motion detector
- smart card
- mantrap-style entry system
- video camera
-
Explanation & Hint: The three solutions that are examples of physical access control are:
- Motion detector: This device detects motion and can be used to trigger an alarm or open a door only when a person is detected.
- Smart card: This is a physical object, similar to a credit card, that contains an embedded microchip or magnetic stripe with information about the user. The smart card can be used to gain access to a building, room or network.
- Mantrap-style entry system: This is a physical access control system that uses a series of doors or gates to control the flow of people into a secure area. A person must be granted access through each door or gate to gain entry to the secure area.
-
Which is the advantage of using an automated patch service on an enterprise network?
- Administrators can obtain reports on the updates needed by each system.
- Each computer needs to connect to the vendor’s service to download patches.
- Administrators can only approve updates with the consent of the users.
- Users can disable or circumvent updates.
-
Explanation & Hint: The advantage of using an automated patch service on an enterprise network is that administrators can obtain reports on the updates needed by each system. This helps administrators to ensure that all systems are up to date with the latest security patches and fixes, which can improve overall security and reduce the risk of data breaches or other security incidents. Automated patching can also save time and reduce the workload for IT staff, as patches can be applied quickly and easily across all systems.
-
Which Apple security feature ensures that only authentic, digitally-signed software that an Apple-notarized software developer has created is permitted to be installed?
- Gatekeeper
- XProtect
- MRT
- Security-focused hardware
-
Explanation & Hint: Gatekeeper is an Apple security feature that ensures that only authentic, digitally-signed software that an Apple-notarized software developer has created is permitted to be installed. This is done by enforcing code signing and verifying that the digital signature of an application matches the developer’s signature, or the signature of the app’s designated distribution channel. Gatekeeper provides three security levels to choose from: App Store only, App Store and identified developers, and Anywhere. The default setting is “App Store and identified developers,” which means that only applications downloaded from the App Store or signed by identified developers are allowed to run. This feature helps to protect against malware and other malicious software by limiting the sources of software that can be installed on a Mac.
-
What is a characteristic of a nftables host-based firewall?
- to use a simple virtual machine in the Linux kernel
- to use a profile-based approach to firewall functionality
- to allow Linux system administrators to configure network access rules that are part of the Linux kernel Netfilter modules
- to be a rule-based access control and logging system for Linux
-
Explanation & Hint: nftables is a rule-based access control and logging system for Linux, which is used to configure network access rules that are part of the Linux kernel Netfilter modules. It provides the ability to filter and manipulate network traffic by creating and manipulating rules and filtering criteria. Unlike iptables, nftables uses a simpler syntax and provides more functionality, such as supporting IPv6 natively, being able to use sets, maps, and expressions, and providing better logging and monitoring capabilities. Therefore, nftables is a popular choice for Linux system administrators to configure host-based firewalls.
-
Which statement describes an advanced persistent threat (APT)?
- an attack by threat actors performing unauthorized network probing and port scanning on the targeted network
- an attack that modifies the operating system through malware and creates a backdoor on the infected system
- an attack that takes advantage of algorithms in a piece of legitimate software to generate unintended behaviors
- a continuous attack that uses elaborated espionage tactics involving multiple threat actors and sophisticated malware to gain access to the targeted network
-
Explanation & Hint: An advanced persistent threat (APT) is a continuous, targeted and sophisticated attack on a network or system, often involving multiple threat actors and sophisticated malware. The attack is usually carried out over a long period of time, during which the attackers gather intelligence about the target and use this information to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. APTs are often associated with state-sponsored attacks, although they can also be carried out by criminal organizations or other types of threat actors.
-
Which application attack replaces a Windows code file with a malicious one and launches an attack when a Windows application calls the code file?
- Replay
- XML injection
- LDAP injection
- DLL injection
-
Explanation & Hint: The application attack that replaces a Windows code file with a malicious one and launches an attack when a Windows application calls the code file is known as DLL injection.
-
Which two actions demonstrate effective active listening techniques when assisting a customer with a problem? (Choose two.)
- correcting the customer when they use incorrect technical terms or jargon
- stopping the customer so you can ask questions as you think of them
- re-asking questions the customer has already answered when describing the problem
- allowing the customer to explain the problem
- Let the customer know that you are listening by interjecting phrases such as “I understand,” “I see,” and “OK.”
-
Explanation & Hint: Allowing the customer to explain the problem and letting the customer know that you are listening by interjecting phrases such as “I understand,” “I see,” and “OK” are effective active listening techniques when assisting a customer with a problem.
-
A trouble ticket placed by a Ubuntu Linux user states that the wired network connection on the computer intermittently fails. Which command can be entered at the Linux CLI to quickly see the number of transmit and receive errors occurring on the Ethernet interface?
- ipconfig /all
- show interfaces eth0
- ifconfig
- show ip interface brief
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct command to view the number of transmit and receive errors on a Ubuntu Linux computer is:
ifconfig eth0
This command displays the network configuration of the eth0 interface, including the number of packets transmitted and received, as well as any errors that may have occurred. The user can then use this information to troubleshoot the intermittent network connection issue.
-
A user reports that the computer occasionally loses connectivity when streaming videos from the web. The technician suspects that a network hardware issue may exist in a device located between the computer and the internet edge router. Which documentation would the technician use to determine where network devices are located in the path from the user to the edge router?
- three-layer enterprise network design model
- logical topology map
- cloud service architecture diagram
- physical topology map
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician would use a physical topology map to determine where network devices are located in the path from the user to the edge router. A physical topology map provides a visual representation of the physical location of network devices and how they are connected to each other, which can help to identify the devices that are located between the user’s computer and the edge router. This information can be used to troubleshoot network connectivity issues and identify potential hardware problems.
-
Which statement accurately describes the measurement of the speed of network transmissions between a client and a server?
- Throughput equals the combined bandwidth of the links in the path from the client to the server.
- Bandwidth equals the speed at which a file can be downloaded from a server to a client.
- Internet speed tests measure the bandwidth of the links between a client and a server.
- Throughput is lower than bandwidth due to latency from client to server.
-
Explanation & Hint: Like bandwidth, throughput is the measure of the transfer of bits across the media over a given period of time. However, due to a number of factors, throughput does not usually match the specified bandwidth. Many factors influence throughput including:
- The amount of data being sent and received over the connection
- The types of data being transmitted
- The latency created by the number of network devices encountered between source and destination
Latency refers to the amount of time, including delays, for data to travel from one given point to another.
-
What are two characteristics of a remote-access SSL VPN? (Choose two.)
- clients have no awareness of the VPN
- a VPN gateway device is needed at both ends of the VPN tunnel
- the client initiates the VPN connection
- the VPN is established between the client PC and a VPN gateway
- traffic between the client and VPN gateway is sent in clear text
-
Explanation & Hint: The two characteristics of a remote-access SSL VPN are:
- The client initiates the VPN connection.
- The VPN is established between the client PC and a VPN gateway.
Clients have awareness of the VPN and a VPN gateway device is needed at only one end of the VPN tunnel. Traffic between the client and VPN gateway is encrypted, not sent in clear text.
-
Which three protocols operate at the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- ARP
- POP3
- TCP
- DHCP
- FTP
- UDP
Answers Explanation & Hints: FTP, DHCP, and POP3 are application layer protocols. TCP and UDP are transport layer protocols. ARP is a network layer protocol.
-
When is UDP preferred to TCP?
- when a client sends a segment to a server
- when an application can tolerate some loss of data during transmission
- when segments must arrive in a very specific sequence to be processed successfully
- when all the data must be fully received before any part of it is considered useful
-
What is the function of ARP?
- provides automatic IP address assignments to hosts
- sends error and operational information messages to hosts
- maps IPv4 addresses to MAC addresses
- resolves domain names to IP addresses
-
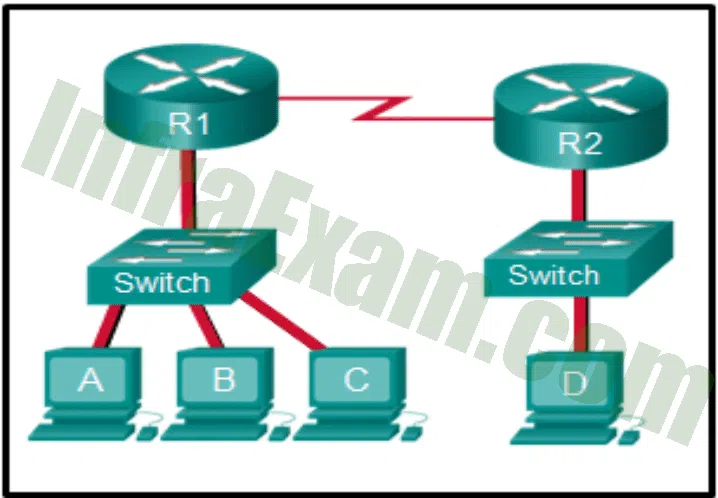
Refer to the exhibit. The exhibit shows a small switched network and the contents of the MAC address table of the switch. PC1 has sent a frame addressed to PC3. What will the switch do with the frame?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 02 - The switch will forward the frame only to port 2.
- The switch will discard the frame.
- The switch will forward the frame only to ports 1 and 3.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports except port 4.
- The switch will forward the frame to all ports.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The MAC address of PC3 is not present in the MAC table of the switch. Because the switch does not know where to send the frame that is addressed to PC3, it will forward the frame to all the switch ports, except for port 4, which is the incoming port.
-
Which network design solution will best extend access layer connectivity to host devices?
- implementing EtherChannel
- implementing redundancy
- implementing routing protocols
- implementing wireless connectivity
-
Which network server is malfunctioning if a user can ping the IP address of a web server but cannot ping the web server host name?
- the DHCP server
- the DNS server
- the FTP server
- the HTTP server
Explanation: If pings are successful to an IP address but not to a host name, then the problem may be that a DNS server cannot be accessed.
-
A PC is not able to connect to a wired network. Pinging the loopback address is successful, but the gateway cannot be reached. On the network switch all the interface lights are on, except for the interface connected to the PC. The LED on the network card is off. What is the most likely cause of this problem?
- The gateway needs to be fixed.
- The network cable is faulty.
- The PC has an incorrect IP address for the DNS server.
- The network switch is faulty.
Explanation: The network card is working if the loopback address can be pinged. The LED on the network card being off points towards a faulty cable or a bad connection.
-
Users are complaining that they are unable to browse certain websites on the Internet. An administrator can successfully ping a web server via its IP address, but cannot browse to the domain name of the website. Which troubleshooting tool would be most useful in determining where the problem is?
- nslookup
- ipconfig
- tracert
- netstat
Answers Explanation & Hints: The nslookup command can be used to look up information about a particular DNS name in the DNS server. The information includes the IP address of the DNS server being used as well as the IP address associated with the specified DNS name. This command can help verify the DNS that is used and if the domain name to IP address resolution works.
-
Which type of network is covered by the IEEE 802.11 standards?
- Internet
- Ethernet
- Wi-Fi
- WAN
-
What are two benefits of wireless networks over wired networks? (Choose two.)
- increased security
- anytime, anywhere connectivity
- immunity to interference
- speed
- mobility
-
Which technology is used to uniquely identify a WLAN network?
- MAC address table
- SSID
- WEP
- WPA
Explanation: When a wireless AP or router is being set up, an SSID is configured to uniquely identify the WLAN that is managed by the device.
-
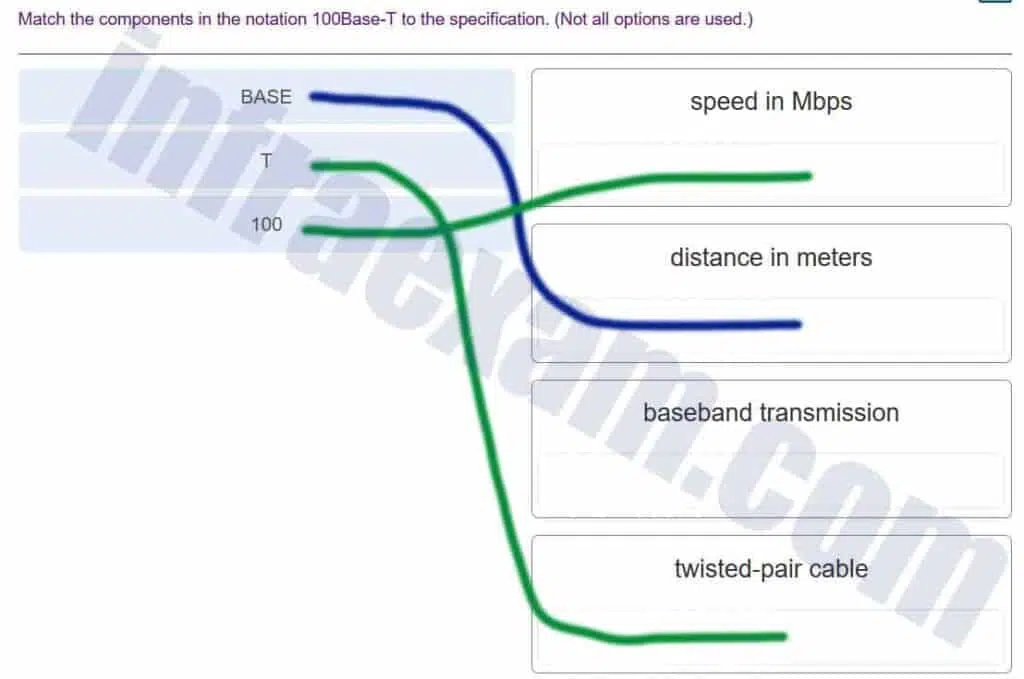
Match the components in the notation 100Base-T to the specification. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 001 -
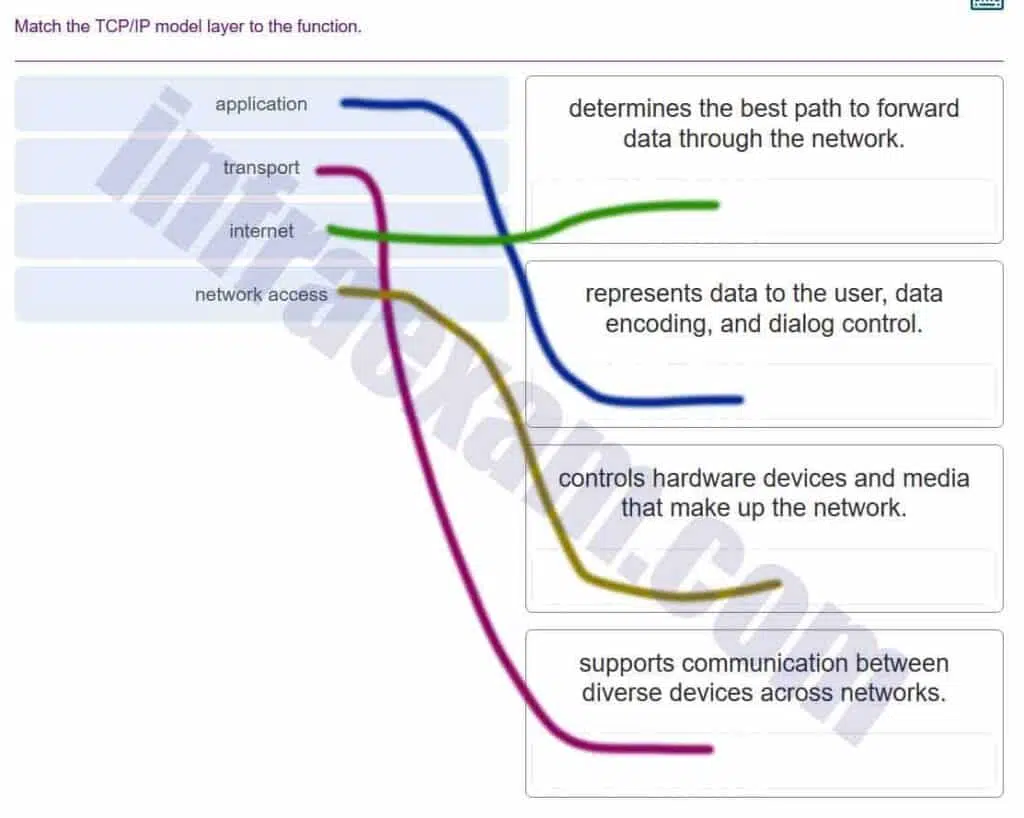
Match the TCP/IP model layer to the function.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 002 -
Which two OSI model layers have the same functionality as a single layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose two.)
- transport
- physical
- network
- data link
- session
Answers Explanation & Hints: The OSI data link and physical layers together are equivalent to the TCP/IP network access layer. The OSI transport layer is functionally equivalent to the TCP/IP transport layer, and the OSI network layer is equivalent to the TCP/IP internet layer. The OSI application, presentation, and session layers are functionally equivalent to the application layer within the TCP/IP model.
-
Which address is a valid IPv6 address that could be assigned to a host?
- 2001:db8::1111::200/80
- 2001:db8::1111::200/64
- 2001:db8:0:1111::200/44
- 2001:db8:0:1111::200/120
-
Which function does NAT perform in a wireless router?
- NAT takes an internal source IP address and translates it to a global IP address.
- NAT takes a source IP address and translates it to a default gateway address.
- NAT takes a destination IP address and translates it to a global IP address.
- NAT takes a local IP address and translates it to an internal source IP address.
-
What type of address is automatically assigned to an interface when IPv6 is enabled on that interface?
- unique local
- global unicast
- link-local
- loopback
Explanation: When IPv6 is enabled on any interface, that interface will automatically generate an IPv6 link-local address.
-
A network administrator investigates a user problem. The user can reach hosts on the same network, but is unable to communicate to remote networks.The network administrator tries to ping the gateway address configured on the host device and is unsuccessful. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
- The IP address of the user is incorrectly configured.
- The default gateway address is incorrect.
- The address of the remote device is incorrect.
- TCP/IP is not installed on the host device.
-
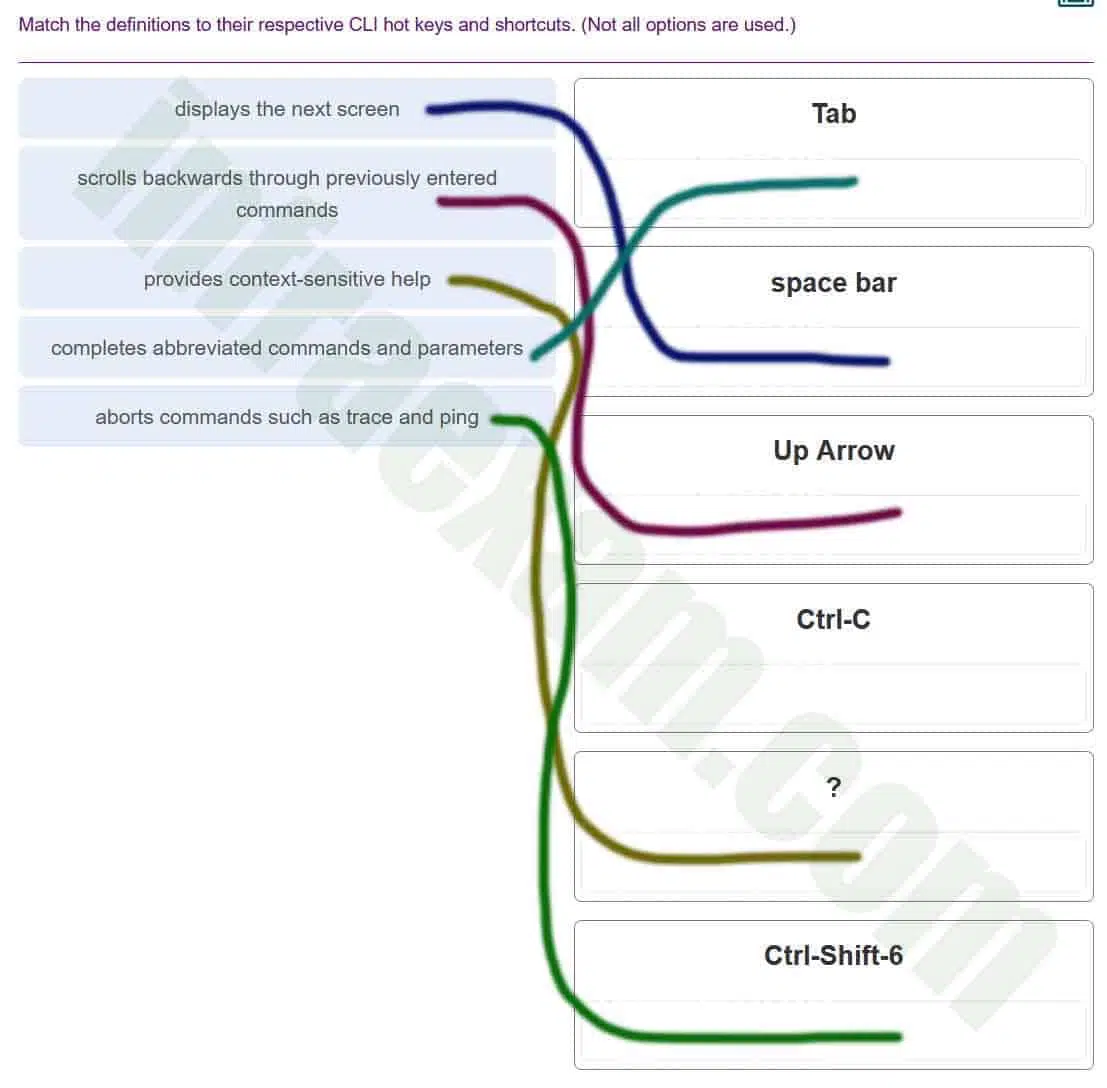
Match the definitions to their respective CLI hot keys and shortcuts. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 003 Explanation: The shortcuts with their functions are as follows:
– Tab – Completes the remainder of a partially typed command or keyword
– Space bar – displays the next screen
– ? – provides context-sensitive help
– Up Arrow – Allows user to scroll backward through former commands
– Ctrl-C – cancels any command currently being entered and returns directly to privileged EXEC mode
– Ctrl-Shift-6 – Allows the user to interrupt an IOS process such as ping or traceroute -
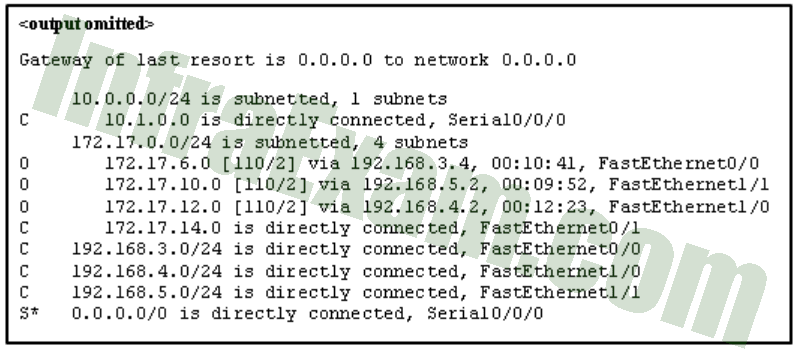
What does the letter C mean next to an entry in the output of the show ip route command?
- It identifies a network that is a static route.
- It identifies a network that is learned through OSPF.
- It identifies a network that is learned through EIGRP.
- It identifies a network that is directly connected to the router.
-
Which switch command would a network administrator use to determine if there are encapsulation or media errors on an interface?
- show line
- show ip interface
- show interfaces
- show arp
-
Which network device makes forwarding decisions based on the destination MAC address that is contained in the frame?
- switch
- hub
- router
- repeater
Explanation: Switches are the central connection point for a LAN and they maintain a MAC address table. The MAC address table has a port number associated with a MAC address for each particular device. The switch inspects a frame to look at the destination MAC address. The switch then looks in its MAC address table and if that MAC address is found, the switch forwards the data to the port that is associated with that particular MAC address.
-
Which interface allows remote management of a Layer 2 switch?
- the first Ethernet port interface
- the switch virtual interface
- the console port interface
- the AUX interface
Answers Explanation & Hints: In a Layer 2 switch, there is a switch virtual interface (SVI) that provides a means for remotely managing the device.
-
Which two statements correctly describe the components of a router? (Choose two.)
- ROM contains diagnostics executed on hardware modules.
- Flash memory does not lose its contents during a reboot.
- RAM permanently stores the configuration file used during the boot sequence.
- ROM contains the most current and most complete version of the IOS.
- Flash contains boot system commands to identify the location of the IOS.
- NVRAM stores a backup copy of the IOS used during the boot sequence.
-
Which feature is characteristic of MAC filtering in wireless networks?
- It restricts computer access to a wireless network.
- It encrypts data that is transmitted on a wireless network.
- It allows only authorized users to detect the network.
- It is configured on the computer rather than on the router.
Answers Explanation & Hints: MAC address filtering uses the MAC address to identify which devices are allowed to connect to the wireless network.
-
Which wireless security technology is difficult to crack and provides encryption of network traffic?
- MAC address filtering
- WEP
- WPA2
- EAP
-
Which two statements about a Service Set Identifier (SSID) are true? (Choose two.)
- It is responsible for determining the signal strength.
- It tells a wireless device to which WLAN it belongs.
- All wireless devices on the same WLAN must have the same SSID.
- It provides strong wireless security.
- It is used to encrypt data sent across the wireless network.
-
What are three characteristics of UTP cabling? (Choose three.)
- susceptible to EMI and RFI
- commonly used for Internet connectivity by a cable TV provider
- easiest type of networking cable to install
- commonly used between buildings
- uses light to transmit data
- most commonly used networking cable
-
Which three factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate network media? (Choose three.)
- the data security and fault tolerance requirement
- the environment in which the media is installed
- the amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
- the operating systems used on network devices in the network
- the distance between hosts that the media will connect
- the speed of the CPU and amount of memory in servers
Explanation: Several criteria should be considered when selecting network media: The cost of the media and installation
The environment in which the media is installed
The amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
The distance between hosts that the media will connect
-
What makes fiber preferable to copper cabling for interconnecting buildings? (Choose three.)
- easily terminated
- greater distances per cable run
- lower installation cost
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI
- greater bandwidth potential
- durable connections
Answers Explanation & Hints: Optical fiber cable transmits data over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than any other networking media. Unlike copper wires, fiber-optic cable can transmit signals with less attenuation and is completely immune to EMI and RFI.
-
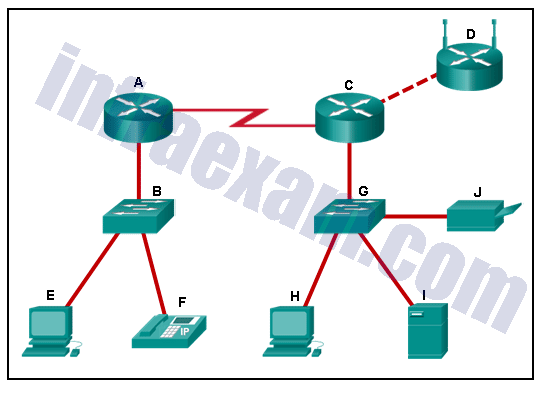
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only end devices?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 04 - D, E, F, H, I, J
- A, C, D
- B, E, G, H
- C, D, G, H, I, J
- E, F, H, I, J
-
What is an advantage of the peer-to-peer network model?
- high level of security
- scalability
- ease of setup
- centralized administration
-
Which three devices are considered intermediate devices in a network? (Choose three.)
- wireless access point
- network printer
- server
- switch
- workstation
- router
Explanation: Intermediate devices in a network provide network connectivity to end devices and transfer user data packets during data communications.
-
Which two methods are used to directly connect mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones to a data network? (Choose two.)
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- wired Ethernet
- cellular communications
- WiMax
-
Which two devices are shared peripherals? (Choose two.)
- touch-pad with digital stylus
- printer
- scanner
- tablet
- laptop
Explanation: A shared peripheral device does not connect directly to a network. This device is attached to a host (such as a PC) and the host connects to the network to share the peripheral device.
-
Which three configuration components are required to allow a host to communicate with other hosts on remote networks? (Choose three.)
- DHCP server address
- subnet mask
- IP address
- default gateway
- DNS server
- domain name
Explanation: An IP address, a subnet mask, and a default gateway are required on a host that must communicate with another host in a remote network. DNS server information is needed if mapping a domain name to an associated IP address. DHCP server information is dynamically learned and is not a required configuration for remote network reachability.
-
A user is looking for a wireless headphone for listening to songs stored on a smartphone. What wireless technology would the headphone use?
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- infrared
- 3G/4G
Answers Explanation & Hints: Bluetooth is a wireless technology for data exchange over a short distance. It is suitable for connecting devices with simple tasks, such as headsets, keyboards, mice, and printers. Wi-Fi is suitable for variety of applications with high speed wireless connectivity required or preferred. Infrared requires a direct line of sight between the transmitter and the receiver. 3G/4G are cellular network technologies to manage voice calls and data transmission between clients and service providers.
-
Which is a characteristic of a Type 2 hypervisor?
- does not require management console software
- has direct access to server hardware resources
- best suited for enterprise environments
- installs directly on hardware
-
A company has a few employees that are designers. The designers do not have the CAD application loaded on their local computer. Instead, the designers use a CAD application hosted by the application developer. Which type of virtualization is the company using?
- SaaS
- DaaS
- IaaS
- PaaS
-
A network administrator attempted to access the company website and received a “page not found” error. The next day the administrator checked the web server logs and noticed that during the same hour that the site failed to load, there was an unusually large number of requests for the website home page. All of the requests originated from the same IP address. Given this information, what might the network administrator conclude?
- The web server was turned off and was not able to service requests.
- It is normal web surfing activity.
- It is likely that someone attempted a DoS attack.
- The link to the website does not have enough capacity and needs to be increased.
-
Which three attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software? (Choose three.)
- pretexting
- worms
- phishing
- Trojan horses
- vishing
- viruses
-
What technique is used in social engineering attacks?
- sending junk email
- man-in-the-middle
- phishing
- buffer overflow
-
A file is downloaded from the Internet. After the user opens the downloaded file, the hard drive crashes and all information on the computer is lost. What type of attack occurred?
- denial of service
- virus
- worm
- Trojan horse
Explanation: Viruses are malicious programs that are spread by modifying other programs and files and can cause hard drives to crash and files to be lost.
-
What is the decimal equivalent to binary 11110000?
- 192
- 240
- 248
- 224
-
What does the IP address 172.17.4.250/24 represent?
- multicast address
- network address
- host address
- broadcast address
Explanation: The /24 shows that the network address is 172.17.4.0. The broadcast address for this network would be 172.17.4.255. Useable host addresses for this network are 172.17.4.1 through 172.17.4.254.
-
Which three IP addresses are considered private addresses? (Choose three.)
- 192.168.5.29
- 172.17.254.4
- 128.37.255.6
- 198.168.6.18
- 172.68.83.35
- 10.234.2.1
Explanation: The designated private IP addresses are within the three IP address ranges:
- 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
-
A network security administrator is writing documentation on the firewall requirements for allowing Telnet access to the remote server. Which two pieces of information should be included? (Choose two.)
- port 20
- port 23
- port 22
- UDP
- TCP
-
Which two application layer protocols manage the exchange of messages between a client with a web browser and a remote web server? (Choose two.)
- HTTPS
- HTML
- DHCP
- HTTP
- DNS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and HTTP Secure (HTTPS) are two application layer protocols that manage the content requests from clients and the responses from the web server. HTML (Hypertext Mark-up Language) is the encoding language that describes the content and display features of a web page. DNS is for domain name to IP address resolution. DHCP manages and provides dynamic IP configurations to clients.
-
Match the port number to the email protocol.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 004 -
Which protocol is used by a server that needs to send an email message to another server in order to support successful delivery of the message?
- SMTP
- DNS
- POP3
- IMAP4
-
What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses.
- It provides segmentation at Layer 2.
- A router connects multiple IP networks.
- It determines the best path to send packets.
- It builds a routing table based on ARP requests.
Explanation: Routers connect multiple networks, determine the best path to send packets, and forward packets based on a destination IP address.
-
Which statement describes a major characteristic of a local area network?
- A LAN is under one administrative control.
- A LAN is implemented in a corporation to connect all of its offices.
- A LAN connects remote users to the main corporate office.
- A LAN can contain up to 100 hosts.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 02 - subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
-
A law firm uses DHCPv4 to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses for staff workstations. The DHCP policy specifies that the lease period is 7 days. A staff member returns to the office after 2 weeks of vacation. When the employee turns on the workstation, which DHCPv4 message is sent by the workstation to obtain a valid IPv4 address?
- DHCPACK broadcast message
- DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message
- DHCPOFFER unicast message
- DHCPREQUEST unicast message
-
A company uses DHCP servers to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses to employee workstations. The address lease duration is set as 5 days. An employee returns to the office after an absence of one week. When the employee boots the workstation, it sends a message to obtain an IP address. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will the message contain?
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
- both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
- MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the lease of a dynamically assigned IPv4 address has expired, a workstation will send a DHCPDISCOVER message to start the process of obtaining a valid IP address. Because the workstation does not know the addresses of DHCP servers, it sends the message via broadcast, with destination addresses of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255.
-
The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway <ip address>.
-
Which two steps are required before SSH can be enabled on a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
- Give the router a host name and domain name.
- Create a banner that will be displayed to users when they connect.
- Enable SSH on the physical interfaces where the incoming connection requests will be received.
- Generate a set of secret keys to be used for encryption and decryption.
- Set up an authentication server to handle incoming connection requests.
Explanation: There are four steps to configure SSH on a Cisco router. First, set the host name and domain name. Second, generate a set of RSA keys to be used for encrypting and decrypting the traffic. Third, create the user IDs and passwords of the users who will be connecting. Lastly, enable SSH on the vty lines on the router. SSH does not need to be set up on any physical interfaces, nor does an external authentication server need to be used. While it is a good idea to configure a banner to display legal information for connecting users, it is not required to enable SSH.
-
Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 005 Answers Explanation & Hints: The enable command is entered in R1> mode. The login command is entered in R1(config-line)# mode. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered in R1# mode. The ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.0 command is entered in R1(config-if)# mode. The service password-encryption command is entered in global configuration mode.
-
Which three acronyms/initialisms represent standards organizations? (Choose three.)
- MAC
- IEEE
- IANA
- OSI
- IETF
- TCP/IP
Answers Explanation & Hints: TCP/IP is a protocol stack that contains a lot of other protocols such as HTTP, FTP, and DNS. The TCP/IP protocol stack is required to be used when communicating on the Internet. A MAC address is an address that is burned into an Ethernet network card. OSI is the 7 layer model that is used to explain how networking works.
-
Which three layers of the OSI model make up the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- presentation
- transport
- application
- network
- session
- data link
Answers Explanation & Hints: The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The top three layers of the OSI model: application, presentation, and session map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model.
-
A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- DNS server
- default gateway
- source port number
- source MAC address
- HTTP server
-
What are two characteristics of 802.11 wireless networks? (Choose two.)
- Stations can transmit at any time.
- They use CSMA/CA technology.
- They are collision-free networks.
- They use CSMA/CD technology.
- Collisions can exist in the networks.
-
A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
Answers Explanation & Hints: A directed broadcast is a message sent to all hosts on a specific network. It is useful for sending a broadcast to all hosts on a nonlocal network. A multicast message is a message sent to a selected group of hosts that are part of a subscribing multicast group. A limited broadcast is used for a communication that is limited to the hosts on the local network. A unicast message is a message sent from one host to another.
-
When a computer assembles a frame to be sent over the network, what is the maximum size of an Ethernet frame?
- 1024 bytes
- 1518 bytes
- 128 bytes
- 64 bytes
Answers Explanation & Hints: Ethernet standards define a frame size with a minimum of 64 bytes and a maximum of 1518 bytes including fields of destination MAC address, source MAC, Length/Type, data payload, and FCS
-
Which function is supplied by the access layer in a three-layer network design?
- application of policies
- backbone connectivity
- routing
- network access
- high-speed connectivity
Answers Explanation & Hints: The main purpose of devices in the access layer is to supply network access to end users. Distribution layer devices provide services such as routing and policy functions. The core layer provides high-speed backbone connectivity.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 05 Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 006 Answers Explanation & Hints: Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
-
When a router receives a packet, what information must be examined in order for the packet to be forwarded to a remote destination?
- destination MAC address
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source MAC address
Explanation: When a router receives a packet, it examines the destination address of the packet and uses the routing table to search for the best path to that network.
-
A user is setting up a home wireless network. A global address is to be used in NAT translations for traffic flowing through the wireless router. How is this global address assigned?
- The host devices will select an unused IP address on the LAN for performing NAT through the wireless router.
- The default gateway IP address of the LAN device is used as the global address for NAT translations through the wireless router.
- The network administrator will choose an available IP address from the LAN and configure the global addressing of the wireless router.
- The wireless router will act as a DHCP client in order to receive global addressing from the ISP.
-
When a LAN is connected to the internet using a wireless router, how do devices on the LAN communicate on the internet using NAT?
- Each LAN must select a single client device from the wireless router settings that can communicate to the internet via NAT.
- Only a small group of high priority client devices can be chosen by the wireless router to communicate to the internet using NAT.
- Each device must wait to receive a token from the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
- All devices must share the single public IPv4 address assigned to the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
-
What two default wireless router settings can affect network security? (Choose two.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 06 - The SSID is broadcast.
- MAC address filtering is enabled.
- WEP encryption is enabled.
- The wireless channel is automatically selected.
- A well-known administrator password is set.
Explanation: Default settings on wireless routers often include broadcasting the SSID and using a well-known administrative password. Both of these pose a security risk to wireless networks. WEP encryption and MAC address filtering are not set by default. The automatic selection of the wireless channel poses no security risks.
-
Which security function is provided by a firewall?
- passively monitors network traffic and logs intrusion attacks for security analysis
- passively monitors network traffic and automatically blocks intrusion attacks
- aggregates and correlates threat events, contextual information, and network device performance data
- allows or blocks traffic based on IP address, port number, or application
-
In what situation would a Layer 2 switch have an IP address configured?
- when the Layer 2 switch is the default gateway of user traffic
- when the Layer 2 switch is using a routed port
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to forward user traffic to another device
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to be remotely managed
Explanation: Layer 2 switches can be configured with an IP address so that they can be remotely managed by an administrator. Layer 3 switches can use an IP address on routed ports. Layer 2 switches do not need a configured IP address to forward user traffic or act as a default gateway.
-
When would the Cisco IOS image held in ROM be used to boot the router?
- when the full IOS cannot be found
- during a normal boot process
- when the running configuration directs the router to do this
- during a file transfer operation
-
A technician has been asked to troubleshoot a simple network problem that seems to be caused by software. Which troubleshooting approach should be used?
- divide and conquer
- bottom-up
- top-down
- substitution
-
A router with a valid operating system contains a configuration file stored in NVRAM. The configuration file has an enable secret password but no console password. When the router boots up, which mode will display?
- user EXEC mode
- privileged EXEC mode
- setup mode
- global configuration mode
Explanation: If a Cisco IOS device has a valid IOS and a valid configuration file, it will boot into user EXEC mode. A password will be required to enter privileged EXEC mode.
-
What action does a DNS server take if it does not have an entry for a requested URL?
- The server checks with another DNS server to see if it has an entry.
- The server drops the request.
- The server assigns a temporary IP address to the name and sends this IP address to the client.
- The server returns a “page not found” response to the client.
-
A new employee is attempting to configure a cell phone to connect to the email server of the company. What is the source port number when sending an email from a mobile device?
- The source port number is 110.
- The source port number is dynamically generated.
- The source port number is 25.
- The source port number is 143.
-
What is the purpose of the startup configuration file on a Cisco router?
- to facilitate the basic operation of the hardware components of a device
- to contain the configuration commands that the router IOS is currently using
- to provide a limited backup version of the IOS, in case the router cannot load the full featured IOS
- to contain the commands that are used to initially configure a router on startup
Explanation: The startup configuration file is stored in NVRAM and contains the commands needed to initially configure a router. It also creates the running configuration file that is stored in in RAM.
-
Which statement describes the ping and tracert commands?
- Tracert shows each hop, while ping shows a destination reply only.
- Tracert uses IP addresses; ping does not.
- Both ping and tracert can show results in a graphical display.
- Ping shows whether the transmission is successful; tracert does not.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ping utility tests end-to-end connectivity between the two hosts. However, if the message does not reach the destination, there is no way to determine where the problem is located. On the other hand, the traceroute utility ( tracert in Windows) traces the route a message takes from its source to the destination. Traceroute displays each hop along the way and the time it takes for the message to get to that network and back.
-
Which three features represent benefits of virtualization? (Choose three.)
- fewer security requirements
- less power consumption
- improved disaster recovery
- less equipment
- less device monitoring
- less employee technical training
-
Which three features represent benefits of virtualization? (Choose three.)
- fewer security requirements
- less power consumption
- improved disaster recovery
- less equipment
- less device monitoring
- less employee technical training
-
What is a difference between the functions of Cloud computing and virtualization?
- Cloud computing utilizes data center technology whereas virtualization is not used in data centers.
- Cloud computing provides services on web-based access whereas virtualization provides services on data access through virtualized
- Internet connections.
- Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware whereas virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware.
- Cloud computing requires hypervisor technology whereas virtualization is a fault tolerance technology.
Explanation: Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware. Virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware. Virtualization is a typical component within cloud computing. Virtualization is also widely used in data centers. Although the implementation of virtualization facilitates an easy server fault tolerance setup, it is not a fault tolerance technology by design. The Internet connection from a data center or service provider needs redundant physical WAN connections to ISPs.
-
Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a host requests a web page, transmission reliability and completeness must be guaranteed. Therefore, HTTP uses TCP as its transport layer protocol.
-
Which two types of devices provide dynamic IPv4 addressing for internal hosts on a local network? (Choose two.)
- ISP DHCP server
- PC-based DHCP client
- wireless router
- PC-based DHCP server
- ISP router
-
When designing an IP address scheme, what is a benefit of using DHCP to assign host addresses?
- A gateway address is not required for hosts on one subnet to communicate with hosts on another subnet.
- Hosts are permanently assigned an address by the DHCP server so that they are easier to manage
- Changing the subnetting scheme does not require manually reassigning individual host addresses.
- Devices on the Internet can easily locate the hosts and send data to them.
-
A technician uses an application to capture packets on the network. One such capture reveals the password that is used by a person in the classroom to initiate a Telnet session with a school network device. What recommendation could the technician make to the person who is using Telnet?
- If possible, enable the network device to use SSH instead of Telnet.
- If possible, configure the business firewall to filter port 23.
- If possible, encrypt the Telnet password on the classroom computer.
- If possible, use a VPN tunnel from the classroom computer to the network device.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
Explanation: Cloud computing extends IT’s capabilities without requiring investment in new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software. These services are available on-demand and delivered economically to any device anywhere in the world without compromising security or function. BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. Smart home technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated. Powerline networking is a trend for home networking that uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
-
A technician is tasked with connecting a printer directly to the network and making it accessible to all staff in the general vicinity. What type of network cable is most likely used to connect the printer?
- RJ-11
- fiber-optic
- coaxial
- twisted-pair
-
What benefit does DHCP provide to a network?
- DHCP allows users to refer to locations by a name rather than an IP address.
- Hosts always have the same IP address and are therefore always reachable.
- Hosts can connect to the network and get an IP address without manual configuration.
- Duplicate addresses cannot occur on a network that issues dynamic addresses using DHCP and has static assignments.
-
A medium-sized company uses APs, WLCs, and laptops for employee workstations. An employee reports the inability to connect to the Internet. A technician verifies that other workstations can successfully connect to the Internet. What are two possible reasons for the problem? (Choose two.)
- A default gateway is improperly configured on the AP.
- A bad cable exists between the client and the WLC.
- The workstation is out of range.
- The AP does not have power.
- The wireless client is not configured for DHCP.
-
What is the first step that a switch performs during the bootup sequence?
- Low-level CPU initialization begins.
- POST is initiated.
- The default IOS image is loaded.
- The boot loader is loaded.
-
Which scenario describes a peer-to-peer network?
- Users access shared files from a file server.
- A user visits a webpage on the company web site.
- A user has shared a printer attached to the workstation.
- Users print documents from a network printer that has a built-in NIC.
Explanation: In a peer-to-peer network there is no centralized or dedicated server. A user computer can be a client to request service from another user computer and a server to share a network resource (such as a printer) to other users.
-
What is the difference between the terms bandwidth and throughput?
- Bandwidth represents the data transfer rate in a local network and throughput represents the data transfer rate over the Internet.
- Bandwidth is the capacity of data transfer in a network and throughput is the actual data transfer rate.
- Bandwidth measures data transfer of web applications and throughput measures data transfer of video applications.
- Bandwidth is measured with Mb/s and throughput is measured in Kbps.
-
A network engineer working at a community building that provides free WiFi is holding an IT conference tomorrow evening. A previous conference with over 100 attendees just ended less than 24 hours ago and the network engineer is concerned about the availability of dynamic addressing. How will the network engineer ensure that there are enough IP addresses for the attendees arriving at the IT conference tomorrow?
- The network engineer will create a new pool of IP addresses and provide a new network subnet and router configuration for the conference.
- The network engineer will manually release each lease created by the conference attendees yesterday and statically assign the incoming devices at the conference.
- The network engineer will disconnect all devices using an IP address from the DHCP server in preparation for the conference.
- The network engineer will verify that the DHCP leasing time is set for a couple of hours.
-
A student is sending files from a phone to a computer across a network. Which layer of the TCP/IP model is responsible for reassembling these messages as they are received on the computer?
- application
- transport
- Internet
- network access
-
When a wireless router is being configured for the first time, what type of wired connection is used?
- Ethernet patch cable
- telephone cable
- console cable
- modem cable
Explanation: A straight-through Ethernet cable, or patch cable, is commonly used to connect to a wireless router for initial configuration.
-
Which advanced wireless security measure allows a network administrator to keep sensitive data secure as it travels over the air in a wireless network?
- MAC address filtering
- encryption
- authentication
- traffic filtering
Explanation: Encryption is used to secure plaintext data that would be viewable traveling over a wireless network.
-
Which logical binary operation is used by a network device to determine the network portion of an IPv4 address with a specified subnet mask?
- AND
- OR
- EQUAL
- NOT
-
Match the type of attack with the description. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 007 -
A router receives an incoming packet and cannot determine where to forward it. What will the router do?
- save it until a usable path is installed
- send it back to the source host
- drop it
- broadcast it to directly attached networks
-
Refer to the exhibit. A TCP segment was sent by PC1 to the web server via port 80. Because of an unexpected network failure, the data was forwarded by R1 but was not received by R2. Which statement is correct about this scenario?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 07 - The timer on R1 will expire and R1 will resend the segment to R2.
- R1 will request that PC1 resend the segment.
- The web server will not acknowledge this segment. The PC1 timer will expire and PC1 will resend the segment.
- R1 forwarded the data to R2 but R2 did not receive it. R2 will send a request to R1 to resend the segment.
Explanation: The TCP protocol works between end devices, not between each device on the network. Routers, switches, etc. do not participate in the packet recovery process. For each TCP segment (or group of segments) sent by a host, there is an acknowledgment. If the sender does not receive an acknowledgment within a period of time, the sender resends the segment.
-
A network technician is extending the network from the main office building over several hundred meters to a new security station. The security station needs a high speed connection to support video surveillance of the main building. What type of cable is best suited to connect the security station to the rest of the main office network?
- unshielded twisted pair
- fiber optic
- shielded twisted pair
- coax
-
A network administrator needs to monitor network traffic to and from servers in a data center. Which features of an IP addressing scheme should be applied to these devices?
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- random static addresses to improve security
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses
Explanation: When monitoring servers, a network administrator needs to be able to quickly identify them. Using a predictable static addressing scheme for these devices makes them easier to identify. Server security, redundancy, and duplication of addresses are not features of an IP addressing scheme.
-
What data representation is used when a computer or network device is processing data?
- binary
- readable
- text
- inferred
-
Match the client operation to the network service.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 008 -
Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 009 -
Which memory location on a Cisco router or switch stores the startup configuration file?
- ROM
- RAM
- flash
- NVRAM
-
What command will prevent all unencrypted passwords from displaying in plain text in a configuration file?
- (config)# enable password secret
- (config)# enable secret Encrypted_Password
- (config-line)# password secret
- (config)# enable secret Secret_Password
- (config)# service password-encryption
Answers Explanation & Hints: To prevent all configured passwords from appearing in plain text in configuration files, an administrator can execute the service password-encryption command. This command encrypts all configured passwords in the configuration file.
-
Which memory location on a Cisco router or switch will lose all content when the device is restarted?
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
- flash
Answers Explanation & Hints: RAM is volatile memory and will lose all contents if the router or switch is restarted or shutdown.
-
Match the command to the function.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 010 -
Which statement is correct about network protocols?
- They define how messages are exchanged between the source and the destination.
- Network protocols define the type of hardware that is used and how it is mounted in racks.
- They all function in the network access layer of TCP/IP.
- They are only required for exchange of messages between devices on remote networks.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Network protocols are implemented in hardware, or software, or both. They interact with each other within different layers of a protocol stack. Protocols have nothing to do with the installation of the network equipment. Network protocols are required to exchange information between source and destination devices in both local and remote networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 needs to resolve the host name of the web server into an IP address by using DNS. What destination IP address and destination port number will PC1 assign to the DNS query packet?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 08 - 192.168.10.1 port 53
- 192.168.20.3 port 80
- 192.168.20.3 port 53
- 192.168.20.2 port 80
- 192.168.20.2 port 53
-
Which statement describes the relationship of a physical network and logical IPv4 addressed networks?
- All devices connected to a physical network need to belong to the same IPv4 logical network.
- A physical network can connect multiple devices of different IPv4 logical networks.
- End devices on different IPv4 logical networks can communicate with each other if they all connect to the same switch.
- A local physical network supports one IPv4 logical network.
-
A DHCP configured PC boots up. What is the order of the messages that are sent and received by this PC in order to obtain an appropriate IP address?
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPACK
-
What are two ways to protect a computer from malware? (Choose two.)
- Empty the browser cache.
- Defragment the hard disk.
- Delete unused software.
- Use antivirus software.
- Keep software up to date.
-
Which wireless security technology is difficult to crack and provides encryption of network traffic?
- MAC address filtering
- WEP
- WPA2
- EAP
-
Which two statements about a Service Set Identifier (SSID) are true? (Choose two.)
- It is responsible for determining the signal strength.
- It tells a wireless device to which WLAN it belongs.
- All wireless devices on the same WLAN must have the same SSID.
- It provides strong wireless security.
- It is used to encrypt data sent across the wireless network.
-
What are three characteristics of UTP cabling? (Choose three.)
- susceptible to EMI and RFI
- commonly used for Internet connectivity by a cable TV provider
- easiest type of networking cable to install
- commonly used between buildings
- uses light to transmit data
- most commonly used networking cable
-
Which three factors should be considered when choosing the appropriate network media? (Choose three.)
- the data security and fault tolerance requirement
- the environment in which the media is installed
- the amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
- the operating systems used on network devices in the network
- the distance between hosts that the media will connect
- the speed of the CPU and amount of memory in servers
Explanation: Several criteria should be considered when selecting network media: The cost of the media and installation
The environment in which the media is installed
The amount of data and the data transfer rate desired
The distance between hosts that the media will connect
-
What makes fiber preferable to copper cabling for interconnecting buildings? (Choose three.)
- easily terminated
- greater distances per cable run
- lower installation cost
- limited susceptibility to EMI/RFI
- greater bandwidth potential
- durable connections
Answers Explanation & Hints: Optical fiber cable transmits data over longer distances and at higher bandwidths than any other networking media. Unlike copper wires, fiber-optic cable can transmit signals with less attenuation and is completely immune to EMI and RFI.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Which set of devices contains only end devices?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 04 - D, E, F, H, I, J
- A, C, D
- B, E, G, H
- C, D, G, H, I, J
- E, F, H, I, J
-
What is an advantage of the peer-to-peer network model?
- high level of security
- scalability
- ease of setup
- centralized administration
-
Which three devices are considered intermediate devices in a network? (Choose three.)
- wireless access point
- network printer
- server
- switch
- workstation
- router
Explanation: Intermediate devices in a network provide network connectivity to end devices and transfer user data packets during data communications.
-
Which two methods are used to directly connect mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones to a data network? (Choose two.)
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- wired Ethernet
- cellular communications
- WiMax
-
Which two devices are shared peripherals? (Choose two.)
- touch-pad with digital stylus
- printer
- scanner
- tablet
- laptop
Explanation: A shared peripheral device does not connect directly to a network. This device is attached to a host (such as a PC) and the host connects to the network to share the peripheral device.
-
Which three configuration components are required to allow a host to communicate with other hosts on remote networks? (Choose three.)
- DHCP server address
- subnet mask
- IP address
- default gateway
- DNS server
- domain name
Explanation: An IP address, a subnet mask, and a default gateway are required on a host that must communicate with another host in a remote network. DNS server information is needed if mapping a domain name to an associated IP address. DHCP server information is dynamically learned and is not a required configuration for remote network reachability.
-
A user is looking for a wireless headphone for listening to songs stored on a smartphone. What wireless technology would the headphone use?
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- infrared
- 3G/4G
Answers Explanation & Hints: Bluetooth is a wireless technology for data exchange over a short distance. It is suitable for connecting devices with simple tasks, such as headsets, keyboards, mice, and printers. Wi-Fi is suitable for variety of applications with high speed wireless connectivity required or preferred. Infrared requires a direct line of sight between the transmitter and the receiver. 3G/4G are cellular network technologies to manage voice calls and data transmission between clients and service providers.
-
Which is a characteristic of a Type 2 hypervisor?
- does not require management console software
- has direct access to server hardware resources
- best suited for enterprise environments
- installs directly on hardware
-
A company has a few employees that are designers. The designers do not have the CAD application loaded on their local computer. Instead, the designers use a CAD application hosted by the application developer. Which type of virtualization is the company using?
- SaaS
- DaaS
- IaaS
- PaaS
-
A network administrator attempted to access the company website and received a “page not found” error. The next day the administrator checked the web server logs and noticed that during the same hour that the site failed to load, there was an unusually large number of requests for the website home page. All of the requests originated from the same IP address. Given this information, what might the network administrator conclude?
- The web server was turned off and was not able to service requests.
- It is normal web surfing activity.
- It is likely that someone attempted a DoS attack.
- The link to the website does not have enough capacity and needs to be increased.
-
Which three attacks exploit vulnerabilities in software? (Choose three.)
- pretexting
- worms
- phishing
- Trojan horses
- vishing
- viruses
-
What technique is used in social engineering attacks?
- sending junk email
- man-in-the-middle
- phishing
- buffer overflow
-
A file is downloaded from the Internet. After the user opens the downloaded file, the hard drive crashes and all information on the computer is lost. What type of attack occurred?
- denial of service
- virus
- worm
- Trojan horse
Explanation: Viruses are malicious programs that are spread by modifying other programs and files and can cause hard drives to crash and files to be lost.
-
What is the decimal equivalent to binary 11110000?
- 192
- 240
- 248
- 224
-
What does the IP address 172.17.4.250/24 represent?
- multicast address
- network address
- host address
- broadcast address
Explanation: The /24 shows that the network address is 172.17.4.0. The broadcast address for this network would be 172.17.4.255. Useable host addresses for this network are 172.17.4.1 through 172.17.4.254.
-
Which three IP addresses are considered private addresses? (Choose three.)
- 192.168.5.29
- 172.17.254.4
- 128.37.255.6
- 198.168.6.18
- 172.68.83.35
- 10.234.2.1
Explanation: The designated private IP addresses are within the three IP address ranges:
- 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255
- 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255
-
A network security administrator is writing documentation on the firewall requirements for allowing Telnet access to the remote server. Which two pieces of information should be included? (Choose two.)
- port 20
- port 23
- port 22
- UDP
- TCP
-
Which two application layer protocols manage the exchange of messages between a client with a web browser and a remote web server? (Choose two.)
- HTTPS
- HTML
- DHCP
- HTTP
- DNS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and HTTP Secure (HTTPS) are two application layer protocols that manage the content requests from clients and the responses from the web server. HTML (Hypertext Mark-up Language) is the encoding language that describes the content and display features of a web page. DNS is for domain name to IP address resolution. DHCP manages and provides dynamic IP configurations to clients.
-
Match the port number to the email protocol.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 004 -
Which protocol is used by a server that needs to send an email message to another server in order to support successful delivery of the message?
- SMTP
- DNS
- POP3
- IMAP4
-
What are two functions of a router? (Choose two.)
- It controls the flow of data via the use of Layer 2 addresses.
- It provides segmentation at Layer 2.
- A router connects multiple IP networks.
- It determines the best path to send packets.
- It builds a routing table based on ARP requests.
Explanation: Routers connect multiple networks, determine the best path to send packets, and forward packets based on a destination IP address.
-
Which statement describes a major characteristic of a local area network?
- A LAN is under one administrative control.
- A LAN is implemented in a corporation to connect all of its offices.
- A LAN connects remote users to the main corporate office.
- A LAN can contain up to 100 hosts.
-
Refer to the exhibit. The network administrator for a small advertising company has chosen to use the 192.168.5.96/27 network for internal LAN addressing. As shown in the exhibit, a static IP address is assigned to the company web server. However, the web server cannot access the Internet. The administrator verifies that local workstations with IP addresses that are assigned by a DHCP server can access the Internet, and the web server is able to ping local workstations. Which component is incorrectly configured?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 02 - subnet mask
- DNS address
- host IP address
- default gateway address
-
A law firm uses DHCPv4 to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses for staff workstations. The DHCP policy specifies that the lease period is 7 days. A staff member returns to the office after 2 weeks of vacation. When the employee turns on the workstation, which DHCPv4 message is sent by the workstation to obtain a valid IPv4 address?
- DHCPACK broadcast message
- DHCPDISCOVER broadcast message
- DHCPOFFER unicast message
- DHCPREQUEST unicast message
-
A company uses DHCP servers to dynamically assign IPv4 addresses to employee workstations. The address lease duration is set as 5 days. An employee returns to the office after an absence of one week. When the employee boots the workstation, it sends a message to obtain an IP address. Which Layer 2 and Layer 3 destination addresses will the message contain?
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and IPv4 address of the DHCP server
- both MAC and IPv4 addresses of the DHCP server
- MAC address of the DHCP server and 255.255.255.255
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255
Answers Explanation & Hints: When the lease of a dynamically assigned IPv4 address has expired, a workstation will send a DHCPDISCOVER message to start the process of obtaining a valid IP address. Because the workstation does not know the addresses of DHCP servers, it sends the message via broadcast, with destination addresses of FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF and 255.255.255.255.
-
The global configuration command ip default-gateway 172.16.100.1 is applied to a switch. What is the effect of this command?
- The switch can communicate with other hosts on the 172.16.100.0 network.
- The switch is limited to sending and receiving frames to and from the gateway 172.16.100.1.
- The switch will have a management interface with the address 172.16.100.1.
- The switch can be remotely managed from a host on another network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A default gateway address is typically configured on all devices to allow them to communicate beyond just their local network.In a switch this is achieved using the command ip default-gateway <ip address>.
-
Which two steps are required before SSH can be enabled on a Cisco router? (Choose two.)
- Give the router a host name and domain name.
- Create a banner that will be displayed to users when they connect.
- Enable SSH on the physical interfaces where the incoming connection requests will be received.
- Generate a set of secret keys to be used for encryption and decryption.
- Set up an authentication server to handle incoming connection requests.
Explanation: There are four steps to configure SSH on a Cisco router. First, set the host name and domain name. Second, generate a set of RSA keys to be used for encrypting and decrypting the traffic. Third, create the user IDs and passwords of the users who will be connecting. Lastly, enable SSH on the vty lines on the router. SSH does not need to be set up on any physical interfaces, nor does an external authentication server need to be used. While it is a good idea to configure a banner to display legal information for connecting users, it is not required to enable SSH.
-
Match the command with the device mode at which the command is entered. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 005 Answers Explanation & Hints: The enable command is entered in R1> mode. The login command is entered in R1(config-line)# mode. The copy running-config startup-config command is entered in R1# mode. The ip address 192.168.4.4 255.255.255.0 command is entered in R1(config-if)# mode. The service password-encryption command is entered in global configuration mode.
-
Which three acronyms/initialisms represent standards organizations? (Choose three.)
- MAC
- IEEE
- IANA
- OSI
- IETF
- TCP/IP
Answers Explanation & Hints: TCP/IP is a protocol stack that contains a lot of other protocols such as HTTP, FTP, and DNS. The TCP/IP protocol stack is required to be used when communicating on the Internet. A MAC address is an address that is burned into an Ethernet network card. OSI is the 7 layer model that is used to explain how networking works.
-
Which three layers of the OSI model make up the application layer of the TCP/IP model? (Choose three.)
- presentation
- transport
- application
- network
- session
- data link
Answers Explanation & Hints: The TCP/IP model consists of four layers: application, transport, internet, and network access. The OSI model consists of seven layers: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link, and physical. The top three layers of the OSI model: application, presentation, and session map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model.
-
A user is attempting to access http://www.cisco.com/ without success. Which two configuration values must be set on the host to allow this access? (Choose two.)
- DNS server
- default gateway
- source port number
- source MAC address
- HTTP server
-
What are two characteristics of 802.11 wireless networks? (Choose two.)
- Stations can transmit at any time.
- They use CSMA/CA technology.
- They are collision-free networks.
- They use CSMA/CD technology.
- Collisions can exist in the networks.
-
A message is sent to all hosts on a remote network. Which type of message is it?
- limited broadcast
- multicast
- directed broadcast
- unicast
Answers Explanation & Hints: A directed broadcast is a message sent to all hosts on a specific network. It is useful for sending a broadcast to all hosts on a nonlocal network. A multicast message is a message sent to a selected group of hosts that are part of a subscribing multicast group. A limited broadcast is used for a communication that is limited to the hosts on the local network. A unicast message is a message sent from one host to another.
-
When a computer assembles a frame to be sent over the network, what is the maximum size of an Ethernet frame?
- 1024 bytes
- 1518 bytes
- 128 bytes
- 64 bytes
Answers Explanation & Hints: Ethernet standards define a frame size with a minimum of 64 bytes and a maximum of 1518 bytes including fields of destination MAC address, source MAC, Length/Type, data payload, and FCS
-
Which function is supplied by the access layer in a three-layer network design?
- application of policies
- backbone connectivity
- routing
- network access
- high-speed connectivity
Answers Explanation & Hints: The main purpose of devices in the access layer is to supply network access to end users. Distribution layer devices provide services such as routing and policy functions. The core layer provides high-speed backbone connectivity.
-
Refer to the exhibit. Match the packets with their destination IP address to the exiting interfaces on the router. (Not all targets are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 05 Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 006 Answers Explanation & Hints: Packets with a destination of 172.17.6.15 are forwarded through Fa0/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.10.5 are forwarded through Fa1/1. Packets with a destination of 172.17.12.10 are forwarded through Fa1/0. Packets with a destination of 172.17.14.8 are forwarded through Fa0/1. Because network 172.17.8.0 has no entry in the routing table, it will take the gateway of last resort, which means that packets with a destination of 172.17.8.20 are forwarded through Serial0/0/0. Because a gateway of last resort exists, no packets will be dropped.
-
When a router receives a packet, what information must be examined in order for the packet to be forwarded to a remote destination?
- destination MAC address
- source IP address
- destination IP address
- source MAC address
Explanation: When a router receives a packet, it examines the destination address of the packet and uses the routing table to search for the best path to that network.
-
A user is setting up a home wireless network. A global address is to be used in NAT translations for traffic flowing through the wireless router. How is this global address assigned?
- The host devices will select an unused IP address on the LAN for performing NAT through the wireless router.
- The default gateway IP address of the LAN device is used as the global address for NAT translations through the wireless router.
- The network administrator will choose an available IP address from the LAN and configure the global addressing of the wireless router.
- The wireless router will act as a DHCP client in order to receive global addressing from the ISP.
-
When a LAN is connected to the internet using a wireless router, how do devices on the LAN communicate on the internet using NAT?
- Each LAN must select a single client device from the wireless router settings that can communicate to the internet via NAT.
- Only a small group of high priority client devices can be chosen by the wireless router to communicate to the internet using NAT.
- Each device must wait to receive a token from the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
- All devices must share the single public IPv4 address assigned to the wireless router in order to communicate to the internet via NAT.
-
What two default wireless router settings can affect network security? (Choose two.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 06 - The SSID is broadcast.
- MAC address filtering is enabled.
- WEP encryption is enabled.
- The wireless channel is automatically selected.
- A well-known administrator password is set.
Explanation: Default settings on wireless routers often include broadcasting the SSID and using a well-known administrative password. Both of these pose a security risk to wireless networks. WEP encryption and MAC address filtering are not set by default. The automatic selection of the wireless channel poses no security risks.
-
Which security function is provided by a firewall?
- passively monitors network traffic and logs intrusion attacks for security analysis
- passively monitors network traffic and automatically blocks intrusion attacks
- aggregates and correlates threat events, contextual information, and network device performance data
- allows or blocks traffic based on IP address, port number, or application
-
In what situation would a Layer 2 switch have an IP address configured?
- when the Layer 2 switch is the default gateway of user traffic
- when the Layer 2 switch is using a routed port
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to forward user traffic to another device
- when the Layer 2 switch needs to be remotely managed
Explanation: Layer 2 switches can be configured with an IP address so that they can be remotely managed by an administrator. Layer 3 switches can use an IP address on routed ports. Layer 2 switches do not need a configured IP address to forward user traffic or act as a default gateway.
-
When would the Cisco IOS image held in ROM be used to boot the router?
- when the full IOS cannot be found
- during a normal boot process
- when the running configuration directs the router to do this
- during a file transfer operation
-
A technician has been asked to troubleshoot a simple network problem that seems to be caused by software. Which troubleshooting approach should be used?
- divide and conquer
- bottom-up
- top-down
- substitution
-
A router with a valid operating system contains a configuration file stored in NVRAM. The configuration file has an enable secret password but no console password. When the router boots up, which mode will display?
- user EXEC mode
- privileged EXEC mode
- setup mode
- global configuration mode
Explanation: If a Cisco IOS device has a valid IOS and a valid configuration file, it will boot into user EXEC mode. A password will be required to enter privileged EXEC mode.
-
What action does a DNS server take if it does not have an entry for a requested URL?
- The server checks with another DNS server to see if it has an entry.
- The server drops the request.
- The server assigns a temporary IP address to the name and sends this IP address to the client.
- The server returns a “page not found” response to the client.
-
A new employee is attempting to configure a cell phone to connect to the email server of the company. What is the source port number when sending an email from a mobile device?
- The source port number is 110.
- The source port number is dynamically generated.
- The source port number is 25.
- The source port number is 143.
-
What is the purpose of the startup configuration file on a Cisco router?
- to facilitate the basic operation of the hardware components of a device
- to contain the configuration commands that the router IOS is currently using
- to provide a limited backup version of the IOS, in case the router cannot load the full featured IOS
- to contain the commands that are used to initially configure a router on startup
Explanation: The startup configuration file is stored in NVRAM and contains the commands needed to initially configure a router. It also creates the running configuration file that is stored in in RAM.
-
Which statement describes the ping and tracert commands?
- Tracert shows each hop, while ping shows a destination reply only.
- Tracert uses IP addresses; ping does not.
- Both ping and tracert can show results in a graphical display.
- Ping shows whether the transmission is successful; tracert does not.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The ping utility tests end-to-end connectivity between the two hosts. However, if the message does not reach the destination, there is no way to determine where the problem is located. On the other hand, the traceroute utility ( tracert in Windows) traces the route a message takes from its source to the destination. Traceroute displays each hop along the way and the time it takes for the message to get to that network and back.
-
Which three features represent benefits of virtualization? (Choose three.)
- fewer security requirements
- less power consumption
- improved disaster recovery
- less equipment
- less device monitoring
- less employee technical training
-
Which three features represent benefits of virtualization? (Choose three.)
- fewer security requirements
- less power consumption
- improved disaster recovery
- less equipment
- less device monitoring
- less employee technical training
-
What is a difference between the functions of Cloud computing and virtualization?
- Cloud computing utilizes data center technology whereas virtualization is not used in data centers.
- Cloud computing provides services on web-based access whereas virtualization provides services on data access through virtualized
- Internet connections.
- Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware whereas virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware.
- Cloud computing requires hypervisor technology whereas virtualization is a fault tolerance technology.
Explanation: Cloud computing separates the application from the hardware. Virtualization separates the OS from the underlying hardware. Virtualization is a typical component within cloud computing. Virtualization is also widely used in data centers. Although the implementation of virtualization facilitates an easy server fault tolerance setup, it is not a fault tolerance technology by design. The Internet connection from a data center or service provider needs redundant physical WAN connections to ISPs.
-
Why does HTTP use TCP as the transport layer protocol?
- to ensure the fastest possible download speed
- because transmission errors can be tolerated easily
- because HTTP requires reliable delivery
- because HTTP is a best-effort protocol
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a host requests a web page, transmission reliability and completeness must be guaranteed. Therefore, HTTP uses TCP as its transport layer protocol.
-
Which two types of devices provide dynamic IPv4 addressing for internal hosts on a local network? (Choose two.)
- ISP DHCP server
- PC-based DHCP client
- wireless router
- PC-based DHCP server
- ISP router
-
When designing an IP address scheme, what is a benefit of using DHCP to assign host addresses?
- A gateway address is not required for hosts on one subnet to communicate with hosts on another subnet.
- Hosts are permanently assigned an address by the DHCP server so that they are easier to manage
- Changing the subnetting scheme does not require manually reassigning individual host addresses.
- Devices on the Internet can easily locate the hosts and send data to them.
-
A technician uses an application to capture packets on the network. One such capture reveals the password that is used by a person in the classroom to initiate a Telnet session with a school network device. What recommendation could the technician make to the person who is using Telnet?
- If possible, enable the network device to use SSH instead of Telnet.
- If possible, configure the business firewall to filter port 23.
- If possible, encrypt the Telnet password on the classroom computer.
- If possible, use a VPN tunnel from the classroom computer to the network device.
-
What is a benefit of using cloud computing in networking?
- Network capabilities are extended without requiring investment in new infrastructure, personnel, or software.
- End users have the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business network.
- Home networking uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
- Technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated.
Explanation: Cloud computing extends IT’s capabilities without requiring investment in new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software. These services are available on-demand and delivered economically to any device anywhere in the world without compromising security or function. BYOD is about end users having the freedom to use personal tools to access information and communicate across a business or campus network. Smart home technology is integrated into every-day appliances allowing them to interconnect with other devices, making them more ‘smart’ or automated. Powerline networking is a trend for home networking that uses existing electrical wiring to connect devices to the network wherever there is an electrical outlet, saving the cost of installing data cables.
-
A technician is tasked with connecting a printer directly to the network and making it accessible to all staff in the general vicinity. What type of network cable is most likely used to connect the printer?
- RJ-11
- fiber-optic
- coaxial
- twisted-pair
-
What benefit does DHCP provide to a network?
- DHCP allows users to refer to locations by a name rather than an IP address.
- Hosts always have the same IP address and are therefore always reachable.
- Hosts can connect to the network and get an IP address without manual configuration.
- Duplicate addresses cannot occur on a network that issues dynamic addresses using DHCP and has static assignments.
-
A medium-sized company uses APs, WLCs, and laptops for employee workstations. An employee reports the inability to connect to the Internet. A technician verifies that other workstations can successfully connect to the Internet. What are two possible reasons for the problem? (Choose two.)
- A default gateway is improperly configured on the AP.
- A bad cable exists between the client and the WLC.
- The workstation is out of range.
- The AP does not have power.
- The wireless client is not configured for DHCP.
-
What is the first step that a switch performs during the bootup sequence?
- Low-level CPU initialization begins.
- POST is initiated.
- The default IOS image is loaded.
- The boot loader is loaded.
-
Which scenario describes a peer-to-peer network?
- Users access shared files from a file server.
- A user visits a webpage on the company web site.
- A user has shared a printer attached to the workstation.
- Users print documents from a network printer that has a built-in NIC.
Explanation: In a peer-to-peer network there is no centralized or dedicated server. A user computer can be a client to request service from another user computer and a server to share a network resource (such as a printer) to other users.
-
What is the difference between the terms bandwidth and throughput?
- Bandwidth represents the data transfer rate in a local network and throughput represents the data transfer rate over the Internet.
- Bandwidth is the capacity of data transfer in a network and throughput is the actual data transfer rate.
- Bandwidth measures data transfer of web applications and throughput measures data transfer of video applications.
- Bandwidth is measured with Mb/s and throughput is measured in Kbps.
-
A network engineer working at a community building that provides free WiFi is holding an IT conference tomorrow evening. A previous conference with over 100 attendees just ended less than 24 hours ago and the network engineer is concerned about the availability of dynamic addressing. How will the network engineer ensure that there are enough IP addresses for the attendees arriving at the IT conference tomorrow?
- The network engineer will create a new pool of IP addresses and provide a new network subnet and router configuration for the conference.
- The network engineer will manually release each lease created by the conference attendees yesterday and statically assign the incoming devices at the conference.
- The network engineer will disconnect all devices using an IP address from the DHCP server in preparation for the conference.
- The network engineer will verify that the DHCP leasing time is set for a couple of hours.
-
A student is sending files from a phone to a computer across a network. Which layer of the TCP/IP model is responsible for reassembling these messages as they are received on the computer?
- application
- transport
- Internet
- network access
-
When a wireless router is being configured for the first time, what type of wired connection is used?
- Ethernet patch cable
- telephone cable
- console cable
- modem cable
Explanation: A straight-through Ethernet cable, or patch cable, is commonly used to connect to a wireless router for initial configuration.
-
Which advanced wireless security measure allows a network administrator to keep sensitive data secure as it travels over the air in a wireless network?
- MAC address filtering
- encryption
- authentication
- traffic filtering
Explanation: Encryption is used to secure plaintext data that would be viewable traveling over a wireless network.
-
Which logical binary operation is used by a network device to determine the network portion of an IPv4 address with a specified subnet mask?
- AND
- OR
- EQUAL
- NOT
-
Match the type of attack with the description. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 007 -
A router receives an incoming packet and cannot determine where to forward it. What will the router do?
- save it until a usable path is installed
- send it back to the source host
- drop it
- broadcast it to directly attached networks
-
Refer to the exhibit. A TCP segment was sent by PC1 to the web server via port 80. Because of an unexpected network failure, the data was forwarded by R1 but was not received by R2. Which statement is correct about this scenario?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 07 - The timer on R1 will expire and R1 will resend the segment to R2.
- R1 will request that PC1 resend the segment.
- The web server will not acknowledge this segment. The PC1 timer will expire and PC1 will resend the segment.
- R1 forwarded the data to R2 but R2 did not receive it. R2 will send a request to R1 to resend the segment.
Explanation: The TCP protocol works between end devices, not between each device on the network. Routers, switches, etc. do not participate in the packet recovery process. For each TCP segment (or group of segments) sent by a host, there is an acknowledgment. If the sender does not receive an acknowledgment within a period of time, the sender resends the segment.
-
A network technician is extending the network from the main office building over several hundred meters to a new security station. The security station needs a high speed connection to support video surveillance of the main building. What type of cable is best suited to connect the security station to the rest of the main office network?
- unshielded twisted pair
- fiber optic
- shielded twisted pair
- coax
-
A network administrator needs to monitor network traffic to and from servers in a data center. Which features of an IP addressing scheme should be applied to these devices?
- addresses from different subnets for redundancy
- random static addresses to improve security
- predictable static IP addresses for easier identification
- dynamic addresses to reduce the probability of duplicate addresses
Explanation: When monitoring servers, a network administrator needs to be able to quickly identify them. Using a predictable static addressing scheme for these devices makes them easier to identify. Server security, redundancy, and duplication of addresses are not features of an IP addressing scheme.
-
What data representation is used when a computer or network device is processing data?
- binary
- readable
- text
- inferred
-
Match the client operation to the network service.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 008 -
Match the description with the associated IOS mode. (Not all options are used.)
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 009 -
Which memory location on a Cisco router or switch stores the startup configuration file?
- ROM
- RAM
- flash
- NVRAM
-
What command will prevent all unencrypted passwords from displaying in plain text in a configuration file?
- (config)# enable password secret
- (config)# enable secret Encrypted_Password
- (config-line)# password secret
- (config)# enable secret Secret_Password
- (config)# service password-encryption
Answers Explanation & Hints: To prevent all configured passwords from appearing in plain text in configuration files, an administrator can execute the service password-encryption command. This command encrypts all configured passwords in the configuration file.
-
Which memory location on a Cisco router or switch will lose all content when the device is restarted?
- ROM
- NVRAM
- RAM
- flash
Answers Explanation & Hints: RAM is volatile memory and will lose all contents if the router or switch is restarted or shutdown.
-
Match the command to the function.
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 010 -
Which statement is correct about network protocols?
- They define how messages are exchanged between the source and the destination.
- Network protocols define the type of hardware that is used and how it is mounted in racks.
- They all function in the network access layer of TCP/IP.
- They are only required for exchange of messages between devices on remote networks.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Network protocols are implemented in hardware, or software, or both. They interact with each other within different layers of a protocol stack. Protocols have nothing to do with the installation of the network equipment. Network protocols are required to exchange information between source and destination devices in both local and remote networks.
-
Refer to the exhibit. PC1 needs to resolve the host name of the web server into an IP address by using DNS. What destination IP address and destination port number will PC1 assign to the DNS query packet?
Networking Essentials (Version 2) – Networking Essentials 2.0 Final Exam Answers 08 - 192.168.10.1 port 53
- 192.168.20.3 port 80
- 192.168.20.3 port 53
- 192.168.20.2 port 80
- 192.168.20.2 port 53
-
Which statement describes the relationship of a physical network and logical IPv4 addressed networks?
- All devices connected to a physical network need to belong to the same IPv4 logical network.
- A physical network can connect multiple devices of different IPv4 logical networks.
- End devices on different IPv4 logical networks can communicate with each other if they all connect to the same switch.
- A local physical network supports one IPv4 logical network.
-
A DHCP configured PC boots up. What is the order of the messages that are sent and received by this PC in order to obtain an appropriate IP address?
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPACK
- DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPOFFER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPREQUEST, DHCPACK
- DHCPREQUEST, DHCPOFFER, DHCPDISCOVER, DHCPACK
-
What are two ways to protect a computer from malware? (Choose two.)
- Empty the browser cache.
- Defragment the hard disk.
- Delete unused software.
- Use antivirus software.
- Keep software up to date.