PCNSE : Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer : Part 05
-
Which processing order will be enabled when a Panorama administrator selects the setting “Objects defined in ancestors will take higher precedence?”
- Descendant objects will take precedence over other descendant objects.
- Descendant objects will take precedence over ancestor objects.
- Ancestor objects will have precedence over descendant objects.
- Ancestor objects will have precedence over other ancestor objects.
Explanation:
Reference:
https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/web-interface-help/device/device-setup-management
-
An administrator using an enterprise PKI needs to establish a unique chain of trust to ensure mutual authentication between Panorama and the managed firewalls and Log Collectors.
How would the administrator establish the chain of trust?
- Use custom certificates
- Enable LDAP or RADIUS integration
- Set up multi-factor authentication
- Configure strong password authentication
Explanation:Reference: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/panorama/panorama_adminguide/panorama-overview/plan-your-panorama-deployment -
What will be the egress interface if the traffic’s ingress interface is ethernet1/6 sourcing from 192.168.111.3 and to the destination 10.46.41.113 during the time shown in the image?
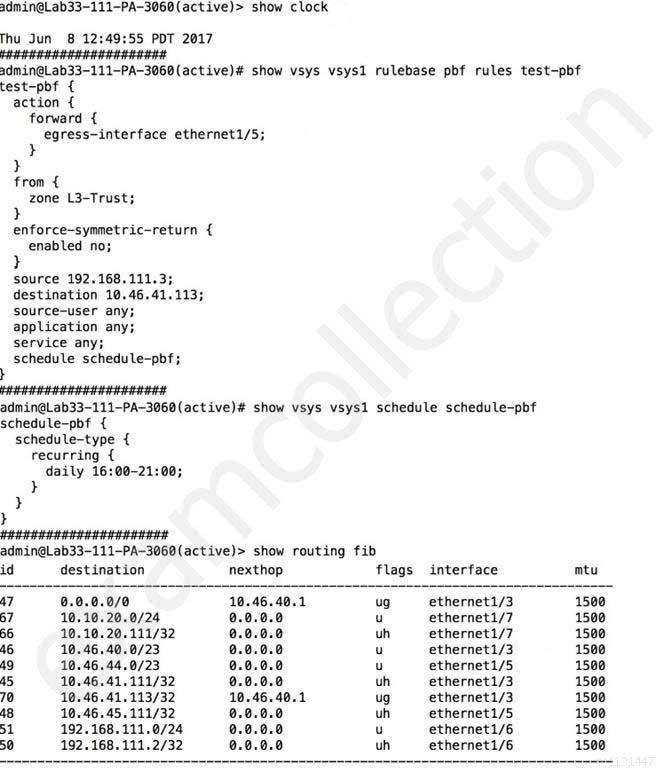
PCNSE Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer Part 05 Q03 022 - ethernet1/7
- ethernet1/5
- ethernet1/6
- ethernet1/3
-
Refer to the exhibit. A web server in the DMZ is being mapped to a public address through DNAT.
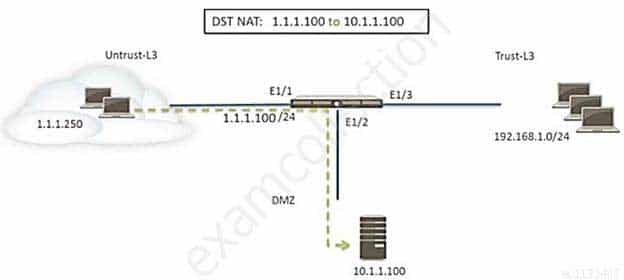
PCNSE Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer Part 05 Q04 023 Which Security policy rule will allow traffic to flow to the web server?
- Untrust (any) to Untrust (10.1.1.100), web browsing – Allow
- Untrust (any) to Untrust (1.1.1.100), web browsing – Allow
- Untrust (any) to DMZ (1.1.1.100), web browsing – Allow
- Untrust (any) to DMZ (10.1.1.100), web browsing – Allow
-
A web server is hosted in the DMZ and the server is configured to listen for incoming connections on TCP port 443. A Security policies rules allowing access from the Trust zone to the DMZ zone needs to be configured to allow web-browsing access. The web server hosts its contents over HTTP(S). Traffic from Trust to DMZ is being decrypted with a Forward Proxy rule.
Which combination of service and application, and order of Security policy rules, needs to be configured to allow cleartext web-browsing traffic to this server on tcp/443?
- Rule #1: application: web-browsing; service: application-default; action: allow
Rule #2: application: ssl; service: application-default; action: allow - Rule #1: application: web-browsing; service: service-http; action: allow
Rule #2: application: ssl; service: application-default; action: allow - Rule # 1: application: ssl; service: application-default; action: allow
Rule #2: application: web-browsing; service: application-default; action: allow - Rule #1: application: web-browsing; service: service-https; action: allow
Rule #2: application: ssl; service: application-default; action: allow
- Rule #1: application: web-browsing; service: application-default; action: allow
-
Which two options prevent the firewall from capturing traffic passing through it? (Choose two.)
- The firewall is in multi-vsys mode.
- The traffic is offloaded.
- The traffic does not match the packet capture filter.
- The firewall’s DP CPU is higher than 50%.
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/monitoring/take-packet-captures/disable-hardware-offload -
A global corporate office has a large-scale network with only one User-ID agent, which creates a bottleneck near the User-ID agent server.
Which solution in PAN-OS® software would help in this case?
- application override
- Virtual Wire mode
- content inspection
- redistribution of user mappings
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/user-id/deploy-user-id-in-a-large-scale-network -
An administrator has been asked to create 100 virtual firewalls in a local, on-premise lab environment (not in “the cloud”). Bootstrapping is the most expedient way to perform this task.
Which option describes deployment of a bootstrap package in an on-premise virtual environment?
- Use config-drive on a USB stick.
- Use an S3 bucket with an ISO.
- Create and attach a virtual hard disk (VHD).
- Use a virtual CD-ROM with an ISO.
Explanation:Reference: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/virtualization/virtualization/set-up-the-vm-series-firewall-on-kvm/install-the-vm-series-firewall-on-kvm/use-an-iso-file-to-deploy-the-vm-series-firewall -
Which two benefits come from assigning a Decryption Profile to a Decryption policy rule with a “No Decrypt” action? (Choose two.)
- Block sessions with expired certificates
- Block sessions with client authentication
- Block sessions with unsupported cipher suites
- Block sessions with untrusted issuers
- Block credential phishing
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/decryption/define-traffic-to-decrypt/create-a-decryption-profile -
Which User-ID method should be configured to map IP addresses to usernames for users connected through a terminal server?
- port mapping
- server monitoring
- client probing
- XFF headers
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/71/pan-os/pan-os/user-id/configure-user-mapping-for-terminal-server-users -
Which feature can be configured on VM-Series firewalls?
- aggregate interfaces
- machine learning
- multiple virtual systems
- GlobalProtect
-
In High Availability, which information is transferred via the HA data link?
- session information
- heartbeats
- HA state information
- User-ID information
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/high-availability/ha-concepts/ha-links-and-backup-links -
The firewall identifies a popular application as an unknown-tcp.
Which two options are available to identify the application? (Choose two.)
- Create a custom application.
- Create a custom object for the custom application server to identify the custom application.
- Submit an App-ID request to Palo Alto Networks.
- Create a Security policy to identify the custom application.
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/app-id/use-application-objects-in-policy/create-a-custom-application -
If an administrator wants to decrypt SMTP traffic and possesses the server’s certificate, which SSL decryption mode will allow the Palo Alto Networks NGFW to inspect traffic to the server?
- TLS Bidirectional Inspection
- SSL Inbound Inspection
- SSH Forward Proxy
- SMTP Inbound Decryption
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/decryption/configure-ssl-inbound-inspection -
A client has a sensitive application server in their data center and is particularly concerned about resource exhaustion because of distributed denial-of-service attacks.
How can the Palo Alto Networks NGFW be configured to specifically protect this server against resource exhaustion originating from multiple IP addresses (DDoS attack)?
- Define a custom App-ID to ensure that only legitimate application traffic reaches the server.
- Add a Vulnerability Protection Profile to block the attack.
- Add QoS Profiles to throttle incoming requests.
- Add a DoS Protection Profile with defined session count.
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/zone-protection-and-dos-protection/zone-defense/dos-protection-profiles-and-policy-rules/dos-protection-profiles -
Which two methods can be used to verify firewall connectivity to AutoFocus? (Choose two.)
- Verify AutoFocus status using the CLI “test” command.
- Check the WebUI Dashboard AutoFocus widget.
- Check for WildFire forwarding logs.
- Check the license.
- Verify AutoFocus is enabled below Device Management tab.
Explanation:Reference:https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/getting-started/enable-autofocus-threat-intelligence -
Which CLI command enables an administrator to check the CPU utilization of the dataplane?
-
show running resource-monitor -
debug data-plane dp-cpu
-
show system resources
-
debug running resources
-
-
Which DoS protection mechanism detects and prevents session exhaustion attacks?
- Packet Based Attack Protection
- Flood Protection
- Resource Protection
- TCP Port Scan Protection
Explanation:Reference: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/pan-os/zone-protection-and-dos-protection/zone-defense/dos-protection-profiles-and-policy-rules/dos-protection-profiles -
Which two subscriptions are available when configuring Panorama to push dynamic updates to connected devices? (Choose two.)
- Content-ID
- User-ID
- Applications and Threats
- Antivirus
Explanation:Reference: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/pan-os/web-interface-help/device/device-dynamic-updates -
View the GlobalProtect configuration screen capture.
What is the purpose of this configuration?
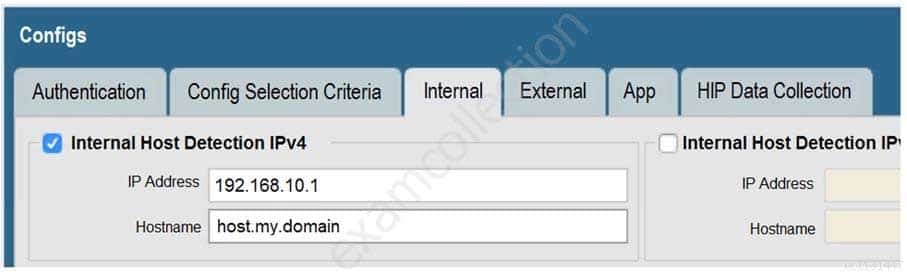
PCNSE Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer Part 05 Q20 024 - It configures the tunnel address of all internal clients to an IP address range starting at 192.168.10.1.
- It forces an internal client to connect to an internal gateway at IP address 192.168.10.1.
- It enables a client to perform a reverse DNS lookup on 192.168.10.1 to detect that it is an internal client.
- It forces the firewall to perform a dynamic DNS update, which adds the internal gateway’s hostname and IP address to the DNS server.
Explanation:Reference: https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/documentation/80/globalprotect/globalprotect-admin-guide/globalprotect-portals/define-the-globalprotect-client-authentication-configurations/define-the-globalprotect-agent-configurations
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest