CAPM : Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) : Part 09
-
Through whom do project managers accomplish work?
- Consultants and stakeholders
- Stakeholders and functional managers
- Project team members and consultants
- Project team members and stakeholders
-
Which quality tool may prove useful in understanding and estimating the cost of quality in a process?
- Checksheets
- Histograms
- Flowcharts
- Control charts
-
The following is a network diagram for a project.
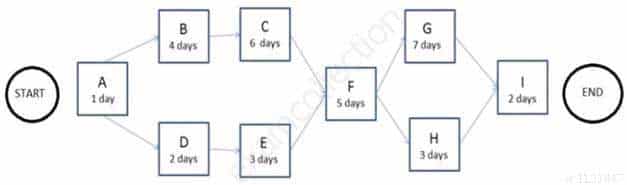
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 09 Q03 003 The total float for the project is how many days?
- 5
- 9
- 12
- 14
-
The following is a network diagram for a project.
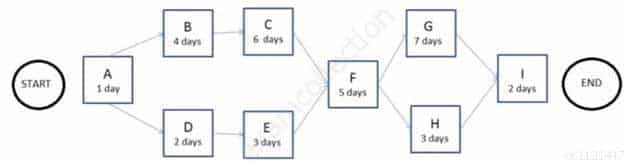
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 09 Q04 004 The free float for Activity E is how many days?
- 2
- 3
- 5
- 8
-
Retreating from an actual or potential conflict or postponing the issue to be better prepared or to be resolved by others describes which of the five general techniques for managing conflict?
- Smooth/accommodate
- Withdraw/avoid
- Compromise/reconcile
- Force/direct
-
Specification of both the deliverables and the processes is the focus of:
- Change control
- Configuration control
- Project monitoring and control
- Issue control
Explanation:
Configuration control is focused on the specification of both the deliverables and the processes; while change control is focused on identifying, documenting, and approving or rejecting changes to the project documents, deliverables, or baselines.
Some of the configuration management activities included in the Perform Integrated Change Control process are as follows:– Configuration identification. Identification and selection of a configuration item to provide the basis for which the product configuration is defined and verified, products and documents are labeled, changes are managed, and accountability is maintained.
– Configuration status accounting. Information is recorded and reported as to when appropriate data about the configuration item should be provided. This information includes a listing of approved configuration identification, status of proposed changes to the configuration, and the implementation status of approved changes.– Configuration verification and audit. Configuration verification and configuration audits ensure the composition of a project’s configuration items is correct and that corresponding changes are registered, assessed, approved, tracked, and correctly implemented. This ensures the functional requirements defined in the configuration documentation have been met.
-
Which output of Project Cost Management consists of quantitative assessments of the probable costs required to complete project work?
- Activity cost estimates
- Earned value management
- Cost management plan
- Cost baseline
Explanation:
7.2.3.1 Activity Cost Estimates
Activity cost estimates are quantitative assessments of the probable costs required to complete project work. Cost estimates can be presented in summary form or in detail. Costs are estimated for all resources that are applied to the activity cost estimate. This includes, but is not limited to, direct labor, materials, equipment, services, facilities, information technology, and special categories such as cost of financing (including interest charges), an inflation allowance, exchange rates, or a cost contingency reserve. Indirect costs, if they are included in the project estimate, can be included at the activity level or at higher levels. -
While processes in the Planning Process Group seek to collect feedback and define project documents to guide project work, organizational procedures dictate when the project planning:
- ends.
- begins.
- delays.
- deviates.
-
A stakeholder expresses a need not known to the project manager. The project manager most likely missed a step in which stakeholder management process?
- Plan Stakeholder Management
- Identify Stakeholders
- Manage Stakeholder Engagement
- Control Stakeholder Engagement
Explanation:13.2 Plan Stakeholder Management
Definition: Stakeholder Management is the process of developing appropriate management strategies to effectively engage stakeholders throughout the project life cycle, based on the analysis of their needs, interests, and potential impact on project success.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it provides a clear, actionable plan to interact with project stakeholders to support the project’s interests.Inputs
1. Project management plan
2. Stakeholder register
3. Enterprise environmental factors
4. Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
1. Expert judgment
2. Meetings
3. Analytical techniques
Outputs
1. Stakeholder management plan
2. Project documents updates -
Skills necessary for project management such as motivating to provide encouragement; listening actively; persuading a team to perform an action; and summarizing, recapping, and identifying next steps are known as:
- organizational skills
- technical skills
- communication skills
- hard skills
Explanation:
Negotiation, influencing and problem-solving skills are all important for a project manager to possess; however, good communication skills are the most important skills a project manager. -
Which tools or techniques are used during the Close Project or Phase process?
- Reserve analysis and expert judgment
- Facilitation techniques and meetings
- Expert judgment and analytical techniques
- Performance reviews and meetings
Explanation:4.1.2.1 Expert Judgment
Expert judgment is often used to assess the inputs used to develop the project charter. Expert judgment is applied to all technical and management details during this process. Such expertise is provided by any group or individual with specialized knowledge or training and is available from many sources, including:
Other units within the organization,
Consultants,
Stakeholders, including customers or sponsors,
Professional and technical associations,
Industry groups,
Subject matter experts (SME), and
Project management office (PMO).Process: 4.6. Close Project or Phase
Definition: The process of finalizing all activities across all of the Project Management Process Groups to formally complete the phase or project.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it provides lessons learned, the formal ending of project work, and the release of organization resources to pursue new endeavors.Inputs
Project management plan
Accepted deliverables
Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
Expert judgment
Analytical techniques
Meetings
Outputs
Final product, service, or result transition
Organizational process assets updates -
When a project is undertaken to reduce defects in a product or service, the objective of the project is to create a/an:
- improvement
- program
- result
- portfolio
-
The degree of uncertainty an entity is willing to take on in anticipation of a reward is known as its risk:
- management
- response
- tolerance
- appetite
Explanation:11 PROJECT RISK MANAGEMENT
[..]
Organizations perceive risk as the effect of uncertainty on projects and organizational objectives. Organizations and stakeholders are willing to accept varying degrees of risk depending on their risk attitude. The risk attitudes of both the organization and the stakeholders may be influenced by a number of factors, which are broadly classifed into three themes:– Risk appetite, which is the degree of uncertainty an entity is willing to take on in anticipation of a reward.
– Risk tolerance, which is the degree, amount, or volume of risk that an organization or individual will withstand.
– Risk threshold, which refers to measures along the level of uncertainty or the level of impact at which a stakeholder may have a specific interest. Below that risk threshold, the organization will accept the risk. Above that risk threshold, the organization will not tolerate the risk.
For example, an organization’s risk attitude may include its appetite for uncertainty, its threshold for risk levels that are unacceptable, or its risk tolerance at which point the organization may select a different risk response.
Positive and negative risks are commonly referred to as opportunities and threats. The project may be accepted if the risks are within tolerances and are in balance with the rewards that may be gained by taking the risks. Positive risks that offer opportunities within the limits of risk tolerances may be pursued in order to generate enhanced value. For example, adopting an aggressive resource optimization technique is a risk taken in anticipation of a reward for using fewer resources. -
The zero duration of milestones in project planning occurs because milestones:
- Are unpredictable and challenge the Plan Schedule Management process.
- Occur at random times in the project plans.
- Represent a moment in time such as a significant project point or event.
- Represent both significant and insignificant points in the project and are difficult to anticipate.
-
Which type of graphic is displayed below?
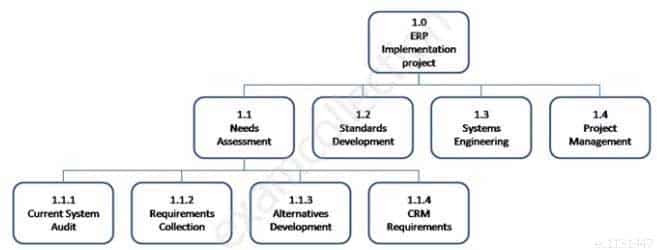
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 09 Q15 005 - Work breakdown structure
- Context diagram
- Control chart
- Pareto diagram
-
An example of a group decision-making technique is:
- nominal group technique
- majority
- affinity diagram
- multi-criteria decision analysis
-
Which tool or technique used in the Control Procurements process can be conducted during the execution of the project to verify compliance with deliverables?
- Procurement documents
- Inspection and audits
- Estimate budget
- Risk register
Explanation:Inspections and Audits. A process to observe performance of contracted work or a promised product against agreed-upon requirements.
Process: 12.3 Control Procurements
Definition: The process of managing procurement relationships, monitoring contract performance, and making changes and corrections as appropriate.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it ensures that both the seller’s and buyer’s performance meets procurement requirements according to the terms of the legal agreement.
Inputs
1. Project management plan
2. Procurement documents
3. Agreements
4. Approved change requests
5. Work performance reports
6. Work performance data
Tools & Techniques
1. Contract change control system
2. Procurement performance reviews
3. Inspections and audits
4. Performance reporting
5. Payment systems
6. Claims administration
7. Records management system
Outputs
1. Work performance information
2. Change requests
3. Project management plan updates
4. Project documents updates
5. Organizational process assets updates -
Job satisfaction, challenging work, and sufficient financial compensation are values related to which interpersonal skill?
- Influencing
- Motivation
- Negotiation
- Trust building
-
The following is a network diagram for a project.
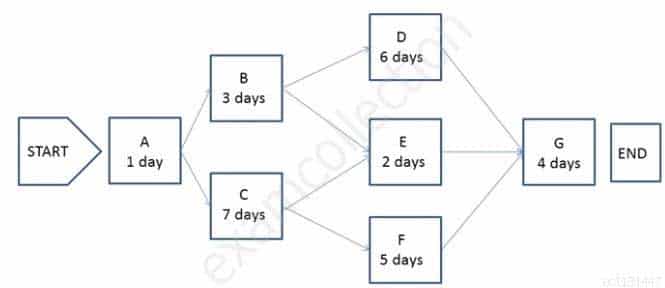
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 09 Q19 006 The shortest non-critical path for the project is how many days in duration?
- 10
- 12
- 14
- 16
-
The following is a network diagram for a project.
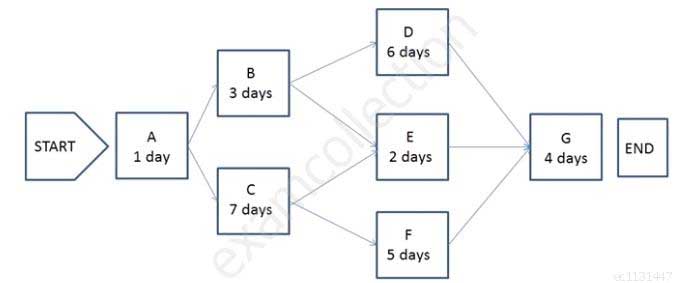
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 09 Q20 007 The critical path for the project is how many days in duration?
- 10
- 12
- 14
- 17