CAPM : Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) : Part 40
-
Which of the following is a complete set of indexed contract documentation, including the closed contract?
- Procurement package
- Negotiated settlements
- Procurement file
- Procurement management plan
Explanation:
12.4.3.2 Organizational Process Assets Updates
Elements of the organizational process assets that may be updated include, but are not limited to:
– Procurement file. A complete set of indexed contract documentation, including the closed contract, is prepared for inclusion with the final project fles.
– Deliverable acceptance. Documentation of formal acceptance of seller-provided deliverables may be required to be retained by the organization. The Close Procurement process ensures this documentation requirement is satisfed. Requirements for formal deliverable acceptance and how to address nonconforming deliverables are usually defined in the agreement.
– Lessons learned documentation. Lessons learned, what has been experienced, and process improvement recommendations, should be developed for the project fle to improve future procurements. -
Which of the following is a component of three-point estimates?
- Probabilistic
- Most likely
- Expected
- Anticipated
-
Which of the following is a means of reaching a group decision in which everyone agrees on a single course of action?
- Dictatorship
- Majority
- Plurality
- Unanimity
-
Which of the following is a schedule network analysis technique that takes limited resources into account?
- Network reserve analysis
- Critical chain method
- Lead and lag adjustment
- Critical path method
Explanation:
6.6.2.3 Critical Chain Method
The critical chain method (CCM) is a schedule method that allows the project team to place buffers on any project schedule path to account for limited resources and project uncertainties. It is developed from the critical path method approach and considers the effects of resource allocation, resource optimization, resource leveling, and activity duration uncertainty on the critical path determined using the critical path method. To do so, the critical chain method introduces the concept of buffers and buffer management. The critical chain method uses activities with durations that do not include safety margins, logical relationships, and resource availability with statistically determined buffers composed of the aggregated safety margins of activities at specified points on the project schedule path to account for limited resources and project uncertainties. The resource-constrained critical path is known as the critical chain. -
Which of the following is a schematic display of the project’s schedule activities and the logical relationships among them?
- Gantt chart
- Project schedule network diagram
- Project milestone list
- Activity list
-
Which of the following is a tool and technique used in all processes within Project Integration Management?
- Records management system
- Expert judgment
- Project management software
- Issue log
Explanation:
4.1.2.1 Expert Judgment
Expert judgment is often used to assess the inputs used to develop the project charter. Expert judgment is applied to all technical and management details during this process. Such expertise is provided by any group or individual with specialized knowledge or training and is available from many sources, including:
– Other units within the organization,
– Consultants,
– Stakeholders, including customers or sponsors,
– Professional and technical associations,
– Industry groups,
– Subject matter experts (SME), and
– Project management office (PMO). -
Which of the following is an example of a risk symptom?
- Failure to meet intermediate milestones
- Force of nature, such as a flood
- Risk threshold target
- Crashing, front loading, or fast tracking
-
Which of the following is an example of a technique used in quantitative risk analysis?
- Sensitivity analysis
- Probability and impact matrix
- Risk data quality assessment
- Risk categorization
-
Which of the following is an example of contract administration?
- Negotiating the contract
- Authorizing contractor work
- Developing the statement of work
- Establishing evaluation criteria
-
Which of the following is an example of push communication?
- Intranet sites
- Video conferencing
- Knowledge repositories
- Press releases
Explanation:
10.1.2.4 Communication Methods
There are several communication methods that are used to share information among project stakeholders.
These methods are broadly classifed as follows:
– Interactive communication. Between two or more parties performing a multidirectional exchange of information. It is the most effcient way to ensure a common understanding by all participants on specified topics, and includes meetings, phone calls, instant messaging, video conferencing, etc.
– Push communication. Sent to specific recipients who need to receive the information. This ensures that the information is distributed but does not ensure that it actually reached or was understood by the intended audience. Push communications include letters, memos, reports, emails, faxes, voice mails, blogs, press releases, etc.
– Pull communication. Used for very large volumes of information, or for very large audiences, and requires the recipients to access the communication content at their own discretion. These methods include intranet sites, e-learning, lessons learned databases, knowledge repositories, etc.
The choices of communication methods that are used for a project may need to be discussed and agreed upon by the project stakeholders based on communication requirements; cost and time constraints; and familiarity and availability of the required tools and resources that may be applicable to the communications process. -
Which of the following is an input into the Develop Project Team process?
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
- Project staff assignments
- Performance reports
Explanation:9.3 Develop Project Team
Definition: The process of improving competencies, team member interaction, and overall team environment to enhance project performance.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it results in improved teamwork, enhanced people skills and competencies, motivated employees, reduced staff turnover rates, and improved overall project performance.Inputs
1. Human resource management plan
2. Project staff assignments
3. Resource calendars
Tools & Techniques
1. Interpersonal skills
2. Training
3. Team-building activities
4. Ground rules
5. Colocation
6. Recognition and rewards
7. Personnel assessment tools
Outputs
1. Team performance assessments
2. Enterprise environmental factors updates -
Which of the following is an input to the Plan Risk Responses process?
- Risk urgency assessment
- Organizational process assets
- Risk register
- Schedule management plan
Explanation:11.2.3.1 Risk Register
The primary output from Identify Risks is the initial entry into the risk register. The risk register is a document in which the results of risk analysis and risk response planning are recorded. It contains the outcomes of the other risk management processes as they are conducted, resulting in an increase in the level and type of information contained in the risk register over time. The preparation of the risk register begins in the Identify Risks process with the following information, and then becomes available to other project management and risk management processes:
– List of identified risks. The identified risks are described in as much detail as is reasonable. A structure for describing risks using risk statements may be applied, for example, EVENT may occur causing IMPACT, or If CAUSE exists, EVENT may occur leading to EFFECT. In addition to the list of identified risks, the root causes of those risks may become more evident. These are the fundamental conditions or events that may give rise to one or more identified risks. They should be recorded and used to support future risk identification for this and other projects.
– List of potential responses. Potential responses to a risk may sometimes be identified during the Identify Risks process. These responses, if identified in this process, should be used as inputs to the Plan Risk Responses process.Process: 11.5 Plan Risk Responses
Definition: The process of developing options and actions to enhance opportunities and to reduce threats to project objectives.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it addresses the risks by their priority, inserting resources and activities into the budget, schedule and project management plan as needed.Inputs
1. Risk management plan
2. Risk register
Tools & Techniques
1. Strategies for negative risks or threats
2. Strategies for positive risks or opportunities
3. Contingent response strategies
4. Expert judgment
Outputs
1. Project management plan updates
2. Project documents updates -
Which of the following is an output of the Plan Quality process?
- Project document update
- Control chart
- Cost performance baseline
- Organizational process asset update
-
Which of the following is the correct network diagram for the table?
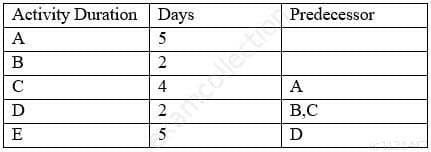
CAPM Certified Associate in Project Management (PMI-100) Part 40 Q14 026 - Begin-A-C-D-E-End-B-D
- Begin-A-B-C-D-E-End
- Begin-A-B-D-E-End A-C-D
- Begin-A-C-D-E-End-B-C
-
Which of the following is the process of identifying the specific actions to be performed to produce the project deliverables?
- Estimate Activity Durations
- Sequence Activities
- Define Activities
- Activity Attributes
Explanation:Process: 6.2 Define Activities
Definition: The process of identifying and documenting the specific actions to be performed to produce the project deliverables.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is to break down work packages into activities that provide a basis for estimating, scheduling, executing, monitoring, and controlling the project work.Inputs
1. Schedule management plan
2. Scope baseline
3. Enterprise environmental factors
4. Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
1. Decomposition
2. Rolling wave planning
3. Expert judgment
Outputs
1. Activity list
2. Activity attributes
3. Milestone list -
Which of the following methods is a project selection technique?
- Flowcharting
- Earned value
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Pareto analysis
Explanation:
8.1.2.1 Cost-Benefit Analysis
The primary benefits of meeting quality requirements include less rework, higher productivity, lower costs, increased stakeholder satisfaction, and increased profitability. A cost-benefit analysis for each quality activity compares the cost of the quality step to the expected benefit. -
Which of the following methods of performance review examines project performance over time to determine if performance is improving or deteriorating?
- Earned value performance
- Trend analysis
- Cost-benefit analysis
- Variance analysis
-
Which of the following processes are within the Initiating Process Group?
- Develop Project Management Plan and Identify Stakeholders
- Develop Project Management Plan and Plan Communications
- Develop Project Charter and Identify Stakeholders
- Develop Project Charter and Develop Project Scope Statement
Explanation:
Initiating Process Group
4.1 Develop Project Charter
13.1 Identify Stakeholders -
Which of the following tools and techniques is used in the Develop Project Team process?
- Acquisitions
- Organizational theories
- Team-building activities
- Virtual teams
Explanation:9.3.2.3 Team-Building Activities
Team-building activities can vary from a 5-minute agenda item in a status review meeting to an off-site, professionally facilitated experience designed to improve interpersonal relationships. The objective of team-building activities is to help individual team members work together effectively. Team-building strategies are particularly valuable when team members operate from remote locations without the beneft of face-to-face contact. Informal communication and activities can help in building trust and establishing good working relationships.
As an ongoing process, team building is crucial to project success. While team building is essential during the initial stages of a project, it is a never-ending process. Changes in a project environment are inevitable, and to manage them effectively, a continued or a renewed team-building effort should be applied. The project manager should continually monitor team functionality and performance to determine if any actions are needed to prevent or correct various team problems.
One of the models used to describe team development is the Tuckman ladder (Tuckman, 1965; Tuckman & Jensen, 1977), which includes fve stages of development that teams may go through. Although it’s common for these stages to occur in order, it’s not uncommon for a team to get stuck in a particular stage or slip to an earlier stage. Projects with team members who worked together in the past may skip a stage.
– Forming. This phase is where the team meets and learns about the project and their formal roles and responsibilities. Team members tend to be independent and not as open in this phase.
– Storming. During this phase, the team begins to address the project work, technical decisions, and the project management approach. If team members are not collaborative and open to differing ideas and perspectives, the environment can become counterproductive.
– Norming. In the norming phase, team members begin to work together and adjust their work habits and behaviors to support the team. The team learns to trust each other.
– Performing. Teams that reach the performing stage function as a well-organized unit. They are interdependent and work through issues smoothly and effectively.
– Adjourning. In the adjourning phase, the team completes the work and moves on from the project. This typically occurs when staff is released from the project as deliverables are completed or as part of carrying out the Close Project or Phase process (Section 4.6). The duration of a particular stage depends upon team dynamics, team size, and team leadership. Project managers should have a good understanding of team dynamics in order to move their team members through all stages in an effective manner.9.3 Develop Project Team
Definition: The process of improving competencies, team member interaction, and overall team environment to enhance project performance.
Key Benefit: The key benefit of this process is that it results in improved teamwork, enhanced people skills and competencies, motivated employees, reduced staff turnover rates, and improved overall project performance.
Inputs
1. Human resource management plan
2. Project staff assignments
3. Resource calendars
Tools & Techniques
1. Interpersonal skills
2. Training
3. Team-building activities
4. Ground rules
5. Colocation
6. Recognition and rewards
7. Personnel assessment tools
Outputs
1. Team performance assessments
2. Enterprise environmental factors updates -
Which of the following tools and techniques is used to estimate cost?
- Budget forecast
- Variance analysis
- Activity cost estimate
- Three-point estimate
Explanation:
Three-Point Estimate. A technique used to estimate cost or duration by applying an average of optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimates when there is uncertainty with the individual activity estimates.