PMI-ACP : PMI Agile Certified Practitioner : Part 07
-
The process of reviewing, testing, and accepting implemented features is called:
- Retrospective.
- Stakeholder review.
- Scope verification.
- Iteration planning.
-
During which activity is the sequence of numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 often used?
- Denoting development sequence
- Estimating development hours
- Indicating priority of a story
- Estimating points of a story
-
Which technique is used by a project team to estimate the amount of work that can be done per iteration?
- Velocity measurement
- Relative prioritization
- Planning Poker
- Release planning
-
Which three criteria should be looked at when setting iteration length?
- Time needed to complete a user story, time needed to build and test the stories, and product team acceptance of the stories
- Timeframe in which the stories must be released, the cost to deliver the features to market, and product team acceptance of the stories
- Delivering chunks of user-valued functionality, time needed to build and test the stories, and product team acceptance of the stories
- Features that categorize the product, the time needed to complete the features, and the cost to deliver the features to market
-
Team velocity is used to:
- Measure the percentage of features completed.
- Judge productivity within the iteration.
- Predict schedules for mature teams.
- Give feedback on delivered value.
-
An Agile team best ensures product quality through:
- The development team’s use of pair programming.
- Quality assurance’s daily collaboration with the development team.
- More frequent inspection after each iteration.
- Feedback gathered during iteration retrospectives.
-
The Kaizen philosophy is change:
- For the better.
- Driven by process improvement.
- Driven by teams.
- For small groups.
-
Following chart lists stories for a release of an Agile project;
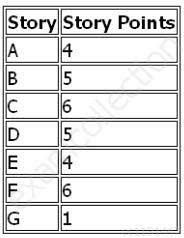
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 07 Q08 002 If the team completes Story A, Story B, and 50% of Story C for the first iteration, what is the team’s velocity?
- 9
- 10
- 12
- 15
-
The following chart lists stories for a release of an Agile project:
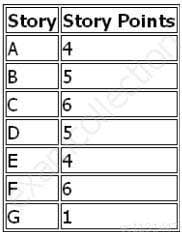
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 07 Q09 003 If the velocity of the team is 10, how many iterations will be needed to complete all of the stories?
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 7
-
Since the last iteration, the team has grown from six members to 14 members. As a result, in the current iteration, the team room is crowded and uncomfortable during the team’s daily standup. It takes the team longer than the ideal amount of time to complete their standup, which creates problems for the team’s current schedule. Based on this information, the project manager should:
- Move the standup to a conference call format so space is not a problem.
- Increase the standup duration and update the team’s calendars.
- Assign each team member a maximum speaking time for future standups.
- Split the team into sub teams and have them schedule separate standups.
-
Which type of estimate refers to estimating a story based on its relationship to one or more other stories?
- Algorithmic
- Computational
- Triangulating
- Rules of Thumb
-
A project team estimates that they should complete 30 story points in the current iteration. Partway through the iteration they realize that they will complete 50 story points at their current rate. The team should:
- Shorten the iteration to meet the estimated velocity.
- Continue to work with the estimated velocity.
- Increase their estimated velocity.
- Release members to meet the estimated velocity.
-
For a critical project, a new team has been formed from various departments. The project manager should start team building by:
- Creating a project charter, documenting roles and responsibilities of each member, and sending it to the team members.
- Taking the team offsite for icebreaker sessions and other activities to ensure team members get to know each other.
- Assembling the team and discussing roles and responsibilities of each member on the team.
- Assembling the team and asking the members to achieve a milestone in a small iteration.
-
When are acceptance tests typically written for a user story?
- After coding the story, but before user acceptance testing begins
- After writing the story, but before coding begins
- At the start of Product Backlog prioritization planning
- After estimating the Product Backlog, but before Sprint planning begins
-
Which of the seven principles of software development is best intended to solve the problem of inventories causing hidden errors in the process?
- Fast-Flexible-Flow
- Optimize the Whole
- Deliver Early and Often
- Eliminate Waste
-
What do project reports show during the Sprint review meeting?
- Estimates compared to the baseline
- Actual results to the plan
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Earned value measurement (EVM)
-
The purpose of “setting the stage” in a project retrospective is to:
- Restate the goal of the meeting and create an open atmosphere.
- Review the scope statement and summarize project results.
- Elevate the team’s morale and ensure that everyone participates.
- Describe the next Iteration and discuss lessons learned.
-
A full cycle of design-code-verifyrelease practiced by extreme Programming (XP) teams is called:
- Story
- Timebox
- Iteration
- Burndown
-
When facilitated and managed well, the primary benefits of a project retrospective should be to:
- Increase empowerment and enjoyment for the team.
- Identify the most important issues for the sponsors.
- Provide an open forum for team member complaints.
- Allow the team to get ahead on release planning.
-
In a Lean project environment, visual controls:
- Can be used by management for communicating specific corrective direction.
- Are easy to use, reflect the team’s progress, and show the team what to do next.
- Are helpful while the team is forming but are less important for more experienced teams.
- Should be kept to a minimum to avoid distracting the team from high-value activities.
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest