PMI-ACP : PMI Agile Certified Practitioner : Part 14
-
Which of the following are 2 attributes of Exploratory testing? (Choose two.)
- It involves minimum planning and maximum test execution
- It is typically automated
- It is unscripted testing
- It is often the sole testing technique
-
A change made to the internal structure of software that makes it easier to understand and cheaper to modify but does not change its observable behavior is referred to as:
- A Spike
- Technical debt
- A User Story
- Refactoring
-
An iteration takes place in a time frame with specific start and end dates, called a time-box. Which of the following is NOT an advantage of time-boxing?
- Establishes a WIP limit
- Forces prioritization
- Demonstrates progress
- Helps control technical debt
-
DRAG DROP
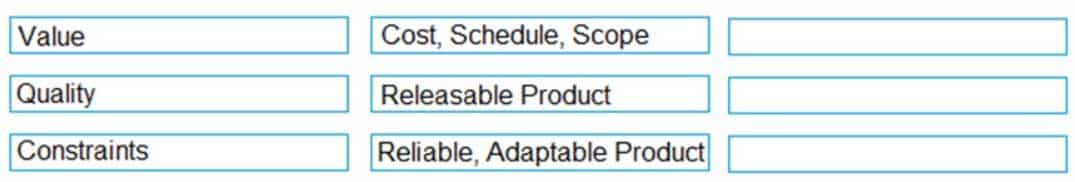
Match each component of the Agile Triangle (on the left) to its associated description (on the right)
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q04 007 Question 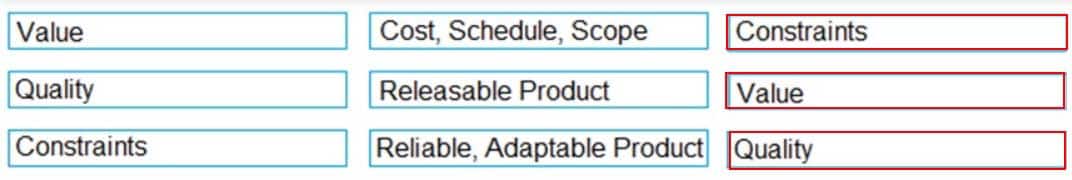
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q04 007 Answer Explanation:
Value – Releasable Product
Quality – Reliable, Adaptable, Product
Constraints – Cost, Schedule, Scope -
Identify the three components of the Agile Triangle. (Choose three.)
- Quality
- Value
- Cost
- Constraints
- Scope
- Leadership
-
There are four critical actions that should be embraced by an adaptive leader: improving speed-to-value, having a passion for quality, doing less, and ________________.
- Inspiring staff
- Managing conflict
- Facilitating meetings
- Ensuring effective communication
-
The 3 items are required for an Agile, adaptive environment: (Choose three.)
- People
- Process
- Product
- Tools
- Technology
-
What is the name of this facilitated process? One or more team members sequence the product backlog from smallest to largest User Story. The rest of the team validates the sequence. The whole team uses a sizing method such as T-shirt size or Fibonacci sequence to group the user stories.
- Relative estimation
- Pairwise comparison
- Planning Poker
- Affinity estimating
-
DRAG DROP
While managing the Agile Product Lifecycle, Match the frequency with which you update the five Agile plans.

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q09 008 Question 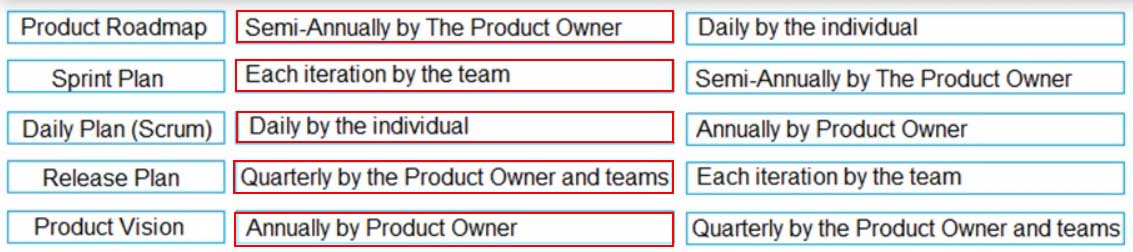
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q09 008 Answer Explanation:
Product Roadmap- Semi-Annually by The Product Owner
Sprint Plan – Each iteration by the team
Daily Plan (Scrum) – Daily by the individual
Release Plan – Quarterly by the Product Owner and teams
Product Vision – Annually by Product Owner -
What are the 5 values of Agile Modeling?
- Communication, Simplicity, Feedback, Courage, Humility
- Communication, Efficiency, Transparency, Courage, Humility
- Communication, Simplicity, Feedback, Adaption, Continuous Improvement
-
Pick the one factor that is NOT part of the Agile Scaling Model.
- Team size
- Geographical distribution
- Domain complexity
- Leadership Style
- Organizational distribution
- Technical complexity
- Organizational complexity
-
What are the 5 phases of the Agile Project Management (APM) delivery framework?
- Envision, Speculate, Explore, Adapt, Close
- Elaborate, Speculate, Examine, Adapt, Close
- Envision, Enable, Explore, Enhance, Close
-
The ultimate goal of __________ is to deploy all but the last few hours of work at any time.
- Continuous Integration
- Collective Code Ownership
- Synchronous Builds
- Asynchronous Builds
-
DRAG DROP
When reading a burn-down chart, what does each status measurement say about project performance? Match the items below.
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q14 009 Question 
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q14 009 Answer Explanation:
Actual Work Line is Above the Ideal Work Line – Behind Schedule
Actual Work Line is Below the ideal Work Line – Ahead of Schedule
Actual Work Line is On the Ideal Work Line – On Schedule -
DRAG DROP
How do you read a burndown bar chart? Match the phrases below to create instructions.

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q15 010 Question 
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q15 010 Answer Explanation:
As tasks are completed – The top of the bar is lowered
When tasks are added to the original set – The bottom of the bar is lowered
When tasks are removed from the original set – The bottom of the bar is raised.
When the amount of work Involved in a task changes – The top of the bar moves up or down -
What are the three components of an Agile Project Charter? (Choose three.)
- Success Criteria
- Vision
- Objectives
- Scope
- Mission
- Risks
-
DRAG DROP
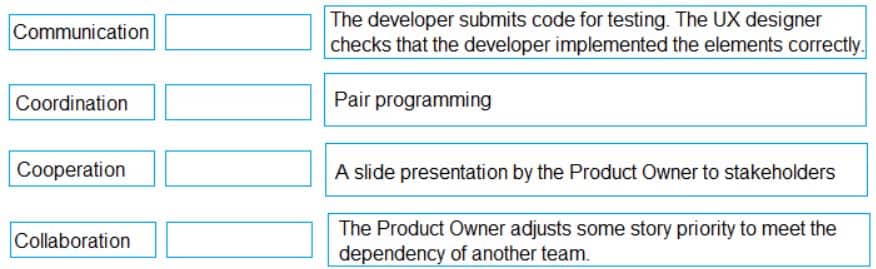
Match each activity (on the left) to its definition (on the right).
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q17 011 Question 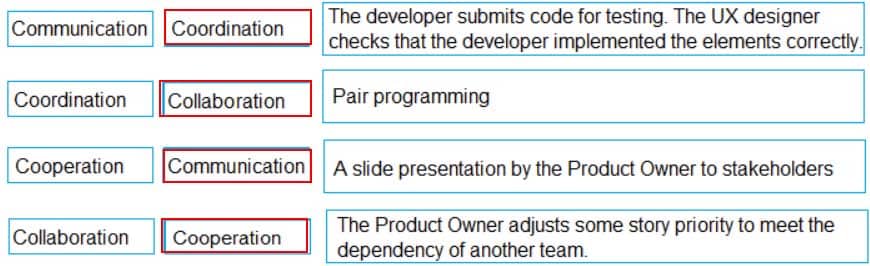
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 14 Q17 011 Answer Explanation:
Communication – A slide presentation by the Product Owner to stakeholders
Coordination – The developer submits code for testing. The UX designer checks that the developer implemented the elements correctly.
Cooperation – The Product Owner adjusts some story priority to meet the dependency of another team.
Collaboration – Pair programming. -
In XP, the practice that any developer can change any line of code to add functionality, fix bugs, improve designs, or refactor demonstrates:
- Collective Code Ownership
- Source Code Control
- Pair Programming
- Continuous Integration
-
When the Agile team works in a single location, the team is said to be ________.
- Co-located
- Distributed
- Outsourced
- Functional
-
Teams of members working in different physical locations are called:
- Co-located Teams
- Distributed Teams
- Outsourced Teams
- Global Teams
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest