PMI-ACP : PMI Agile Certified Practitioner : Part 16
-
Which of the following is NOT one of the 12 core practices of XP?
- Visualize the flow
- On-site Customer
- Coding Standards
- System Metaphor
-
Which of the following is NOT a reason to use a Feature Breakdown Structure (FBS) instead of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)?
- It allows communication between the customer and the development team in terms both can understand.
- It allows you to baseline your project plan due to absence of change.
- It allows tracking of work against the actual business value produced.
- It allows the customer to prioritize the team’s work based on business value.
-
Team members who are part-time on your project will see at least a 15% reduction in their productivity per hour. The type of resource model in Agile is called:
- Collocated
- Fractional assignments
- Distributed resources
- Over-allocated resources
-
Frequent verification and validation is key in Agile but each approach produces a very different result. Verification determines ________________ whereas validation determines _____________.
- if the product is “done” | if the product is “done-done”
- if I am I building the product right | if I am I building the right product
- if I am I building the right product | if I am I building the product right
- if the product has passed unit testing | if the product has passed acceptance testing
-
What type of time estimation excludes non-programming time?
- Ideal Time
- Calendar time
- Duration
- Real Time
-
Which of the following is an example of an information radiator?
- An email of a status report
- A text of a quick question to the Product Owner
- A whiteboard showing the state of work
- A face-to-face conversation
-
Assuming all projects require the same amount of up-front investment, the project with the highest ______________ would be considered the best and undertaken first.
- Earned Value Management (EVM)
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
- Net Present Value (NPV)
- Budget at Completion (BAC)
-
DRAG DROP
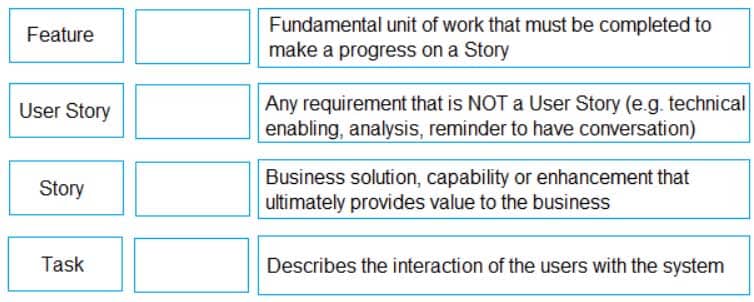
Match each Agile requirement type (on the left) to its definition (on the right).
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q08 014 Question 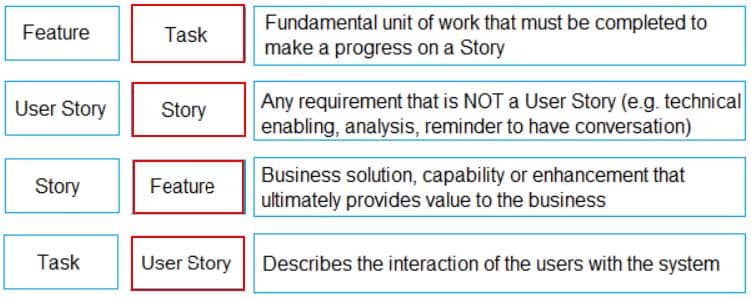
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q08 014 Answer Explanation:
Feature – Business solution, capability, or enhancement that ultimately provides value to the business.
User Story – Describes the interaction of the users with the system.
Story – Any requirement that is NOT a User Story (e.g. technical enabling, analysis, reminder to have conversation)
Task – Fundamental unit of work that must be completed to make a progress on a Story -
80% of the value comes from 20% of the work. Which law is this referring to?
- Parkinson’s Law
- Moore’s Law
- Pareto’s Law
- Jevon’s Paradox
-
Based on the following information, determine the number weeks until the next release.

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q10 015 - 8 weeks
- 12 weeks
- 16 weeks
- 9 weeks
-
DRAG DROP
What is the correct sequence of activities in release planning?

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q11 016 Question 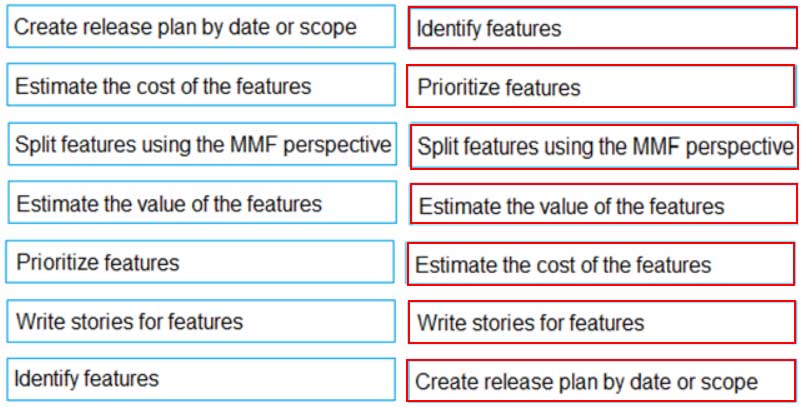
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q11 016 Answer Explanation:
1 – Identity features
2 – Prioritize features
3 – Split features using the MMF perspective
4 – Estimate the value of the features
5 – Estimate the cost of the features
6 – Write stories for features
7 – Create release plan by date or scope -
DRAG DROP
Sequence the following concepts to create the popular acronym for creating good User Stories.

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q12 017 Question 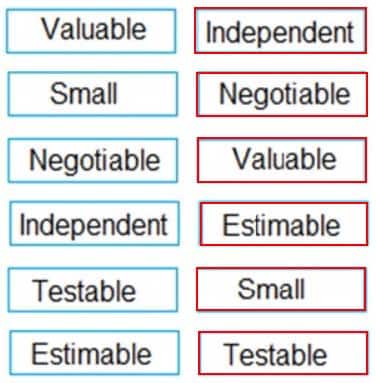
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q12 017 Answer Explanation:
1 – Independent
2 – Negotiable
3 – Valuable
4 – Estimable
5 – Small
6 – Testable -
DRAG DROP
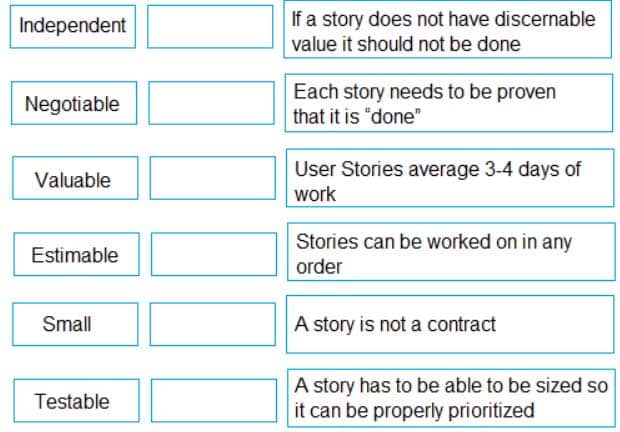
Match the definitions (on the right) to each of the characteristics of a good User Story (on the left).
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q13 018 Question 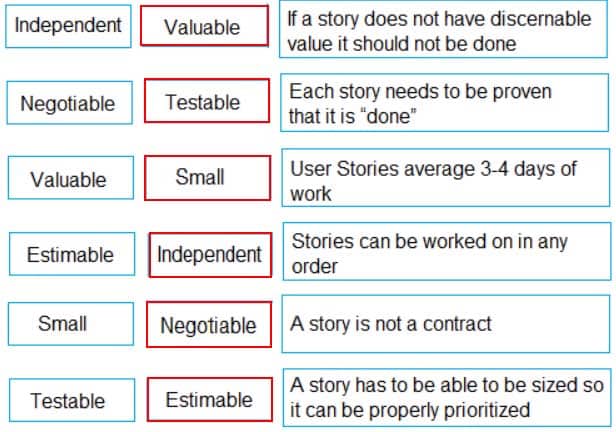
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q13 018 Answer Explanation:
Independent – Stories can be worked on in any order
Negotiable – A story is not a contract
Valuable – If a story does not have discernable value it should not be done
Estimable- A story has to be able to be sized so it can be properly prioritized
Small- User Stories average 3-4 days of work
Testable- Each story needs to be proven that it is “done” -
At minimum, all Kanban boards should have the following columns:
- To-Do, Doing, Done
- Analysis, Design, Develop, Test, Deploy
- Backlog, Design, Develop, Unit Test, Acceptance Test, Ready-to-ship
- The Kanban columns are determined by the team
-
The Kano Model supports what Agile planning activity?
- Estimation
- Prioritization
- Sizing
- Continuous Integration
-
Which one is NOT a level of need in the Kano Model?
- Basic Needs
- Performance Needs
- Enabling Needs
- Excitement Needs
-
DRAG DROP
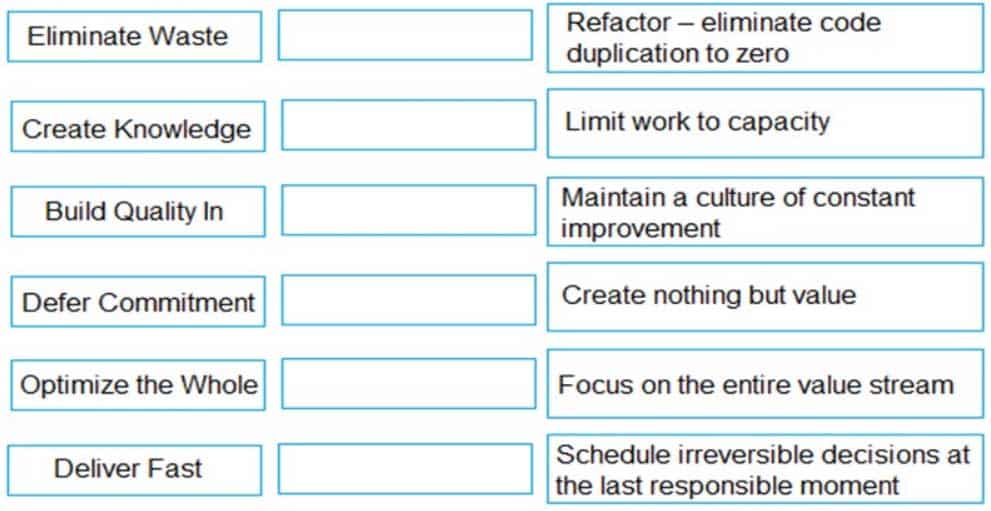
Match a definition (on the right) to a Lean principle (on the left).
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q17 019 Question 
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 16 Q17 019 Answer Explanation:
Eliminate waste- Create nothing but value
Create knowledge- Maintain a culture of constant improvement
Build quality in – Refactor – eliminate code duplication to zero
Defer commitment- Schedule irreversible decisions at the last responsible moment
Optimize the whole- Focus on the entire value stream
Deliver fast- Limit work to capacity -
Net present value (NPV) is a ratio that compares the value of a dollar today to the value of that same dollar in the future. An NPV that is negative suggests what?
- The project should be rejected
- I don’t have enough information
- The project should be deferred
- The project should be put on hold until the value is 0
-
What is the Agile Open Space concept?
- When cubicles walls are removed for an Agile team.
- It is a meeting designed to allow Agile practitioners to meet in self-organizing groups where they can share their latest ideas and challenges.
- The choice to collocate all team members for the beginning of a project.
- It is a core principle of ADSM
-
Osmotic communication is when team members obtain information from overhead conversations.
- True
- False
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest