PMI-ACP : PMI Agile Certified Practitioner : Part 24
-
Similar to inspect and adapt in Scrum, this can be represented as Build, Measure, Learn.
- Six Sigma
- Kaizen
- DMAIC
- Agile Learning Cycle
-
What Scrum event or artifact supports daily inspection and adaptation?
- Product Backlog
- Sprint Backlog
- Sprint
- Scrum
- Working Product Increment
-
What Scrum event or artifact is the single source of requirements for any changes to be made to the product?
- Product Backlog
- Sprint Backlog
- Sprint
- Scrum
- Working Product Increment
-
What Scrum event or artifact is the set of items selected for the Sprint, plus a plan for delivering the product Increment and realizing the Sprint Goal?
- Product Backlog
- Sprint Backlog
- Sprint
- Scrum
- Working Product Increment
-
The Scrum Master’s job is to work with the Scrum Team and the organization to increase the awareness of the artifacts. Which pillar of Scrum does this represent?
- Transparency
- Inspection
- Adaption
-
Scrum users must frequently review Scrum artifacts and progress toward a Sprint Goal to detect undesirable variances. Which pillar of Scrum does this represent?
- Transparency
- Inspection
- Adaptation
-
Based upon this Burndown chart, is this project ahead of schedule or behind schedule?
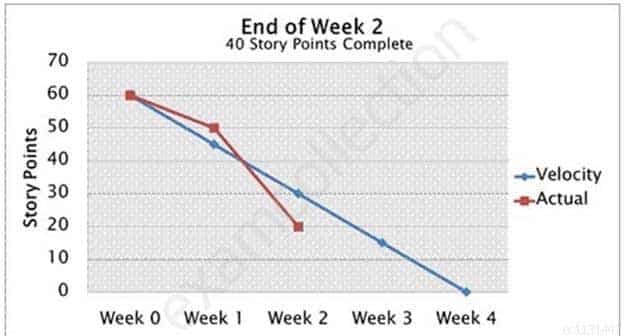
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q07 032 - Ahead of schedule
- Behind schedule
-
Pick the two PMLC models that are based upon the Agile Project Management (APM) approach:
- Linear
- Adaptive
- Incremental
- Iterative
-
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of an Adaptive PMLC Model?
- Iterative Structure
- Clear up front requirements
- Mission Critical Projects
- JIT Planning
-
This management approach is based on knowing well defined goals but not the means for a solution.
- Traditional Project Management
- Emertxe Project Management
- Extreme Project Management
- Agile Project Management
-
This Emertxe Project Management (MPx) approach is when neither a goal nor solution is clearly defined.
- True
- False
-
Every Project Management Life Cycle (PMLC) has a sequence of processes that include these phases:

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q12 033 - True
- False
-
Which of the following is a weakness of an Adaptive PMLC Model?
- Does not waste time on non-value-added work
- Does not waste time planning uncertainty
- Cannot identify what will be delivered at the end of the project
- Avoids all management issues processing scope change requests
-
DRAG DROP
Sequence the core practices of Kanban in order of execution.

PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q14 034 Question 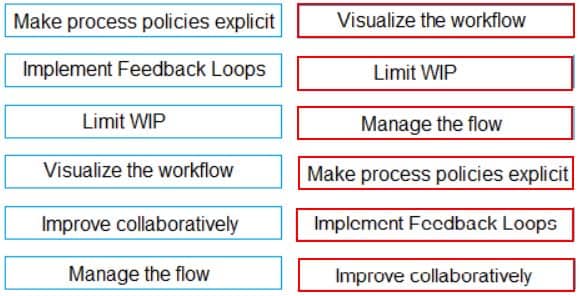
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q14 034 Answer Explanation:
1. Visualize the workflow
2. Limit WIP
3. Manage the flow
4. Make the process policies explicit
5. Implement Feedback Loops
6. Improve collaboratively -
Classes of Services in Kanban are used to:
- Support estimation for Kanban Cards
- Prioritize the queue by risk
- All of the above
- Ensure WIP limits are realistic
-
The following is a picture of which of the following Information Radiators?
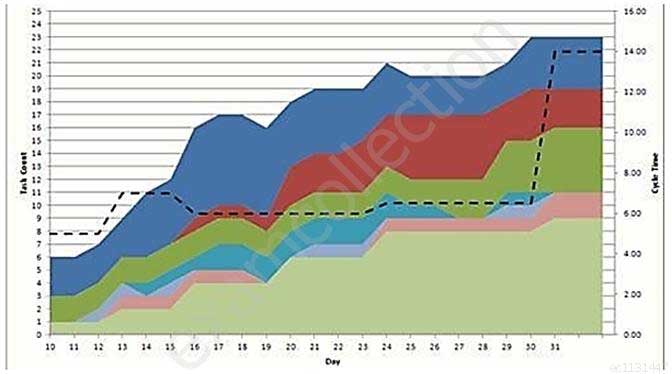
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q16 035 - Burndown Chart
- Kanban Tracking System
- Cumulative Flow Diagram
- Burnup Chart
-
The measure of productivity of a Kanban team is:
- Cycle time
- Lead Time
- Work in Progress
- Velocity
- Throughput
-
Kanban cards should always be written using User Stories.
- True
- False
-
A term used to describe the work that can be delivered which meets the business requirements without exceeding them. (Choose two.)
- Epic
- Minimum Viable Product
- Theme
- User Story
- Minimum Marketable Features
-
DRAG DROP
Order the 5 focusing steps of the Theory of Constraints.
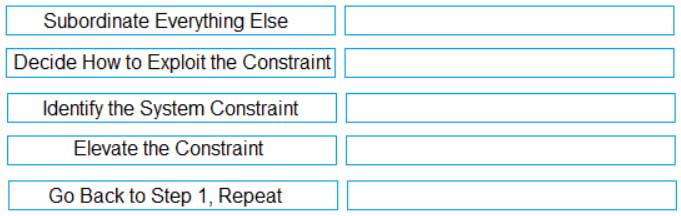
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q20 036 Question 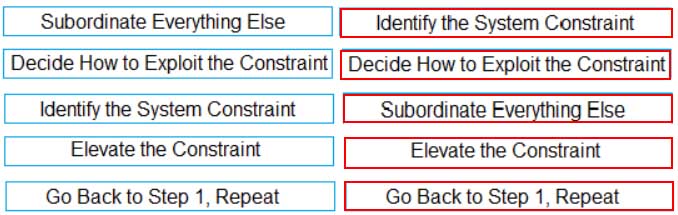
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 24 Q20 036 Answer Explanation:
1. Identify the System Constraint
2 Decide How to Exploit the Constraint
3. Subordinate Everything Else
4. Elevate the Constraint
5. Go back to Step 1, Repeat
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest