PMI-ACP : PMI Agile Certified Practitioner : Part 31
-
A project is starting and the type of work is complex and suitable for agile. In assessing the team members, it appears that co-location would be a challenge.
What should the agile practitioner do?
- Select and implement collaboration tools to augment team interactions
- Provide each geographical area with their own product owner and divide the work between the teams
- Increase the number of requirements documents and ensure they are clearly communicated
- After several sprints, calculate velocity based on primary team location and use secondary team as reserve
-
During a retrospective meeting, a team develops a large list of initiatives. All will have a positive impact and improve team performance.
What should the agile coach do next?
- Positively acknowledge the list and share it with management
- Immediately have the team implement the initiatives
- Help the team choose one or two initiatives for immediate implementation
- Ask the team to choose and implement the most complex initiative
-
The team is refining user stories during the backlog grooming session and confused on the acceptance criteria and level of details.
What should the agile practitioner do?
- Complete the test cases before creating the story in the backlog
- Define the detailed business requirements so that the team can continue with development
- Define the user stories with just enough details so the team can collaborate continuously
- Ensure the acceptance criteria includes testing scenarios, so the team can do thorough testing
-
How should an agile project leader interact with the product owner?
- Conduct regular one-on-one meetings to review development features and trace them back to the product roadmap
- Ensure that they attend regular sprint meetings to provide product-feature feedback
- Share any new versions of the project plan with them, including updated statuses for tasks and project milestones
- Schedule meetings where they can provide team direction regarding new-feature priorities and upcoming sprints
-
A company is moving into a new space and is determining the best configuration for offices. The management team is also considering moving to an agile process.
What advice should an agilist give?
- Arrange the office space to allow co-location of development teams and centrally located information radiators
- Isolate each development team to reduce all outside distractions
- Ensure management understands the need for isolation to allow for concentration
- Define the agile method the company will be using, and implement the office configuration based upon that method
-
During planning sessions, an agile practitioner notices that some team members do not share common ideas.
What should the agile practitioner do?
- Ask the team if they would like to adopt alternative techniques
- Create a team norms document to set participation guidelines
- Ask the scrum master to resolve the issue at the stand up meeting
- Capture feedback during lessons learned at the end of the iteration
-
A product owner concludes that the majority of a project’s value can be delivered by completing only the first half of the prioritized backlog.
What should the product owner do next?
- Remove the second half of the backlog, and communicate their decision in the next backlog grooming meeting
- Reprioritize backlog items to future iterations
- Work with the team to deploy the first half of the backlog to ensure that value is realized
- Meet with project stakeholders to review the backlog and determine if the scope should be adjusted
-
A project team identifies a number of technical challenges with features in the next sprint.
What should they do?
- Request direction from the technical manager
- Encourage the product owner to reallocate the features to another sprint
- Determine who is best qualified to address the challenges
- Ask the product owner to assign the tasks to the most appropriately skilled resources
-
An agile team is planning the next iteration for a product release that has accumulated technical debt.
What should the team do?
- Add code cleanup activities to the product backlog and request prioritization by the product owner
- Add code cleanup activities to the next iteration and request clarification from the product owner
- Add code cleanup activities to the next iteration and ask the product owner to end the current iteration
- Add code cleanup activities to the next release backlog and request documentation from the product owner
-
How can an agile team working on a new product ensure alignment with external stakeholders?
- Ask the product owner to provide a detailed product specification document
- Conduct story-mapping exercises to clarify deliverables and release priorities
- Hold a kick-off meeting to assign roles and responsibilities
- Work with the scrum master and stakeholders to ensure agile principles are followed
-
A product owner complains that some of the requirements identified several iterations ago have not been implemented. The product owner wants to know why the status of these requirements was not communicated.
What should the Scrum Master do?
- Point out that the team chose to work on other requirements to speed up the project
- Ensure that the product owner reviews the contents of the information radiator
- Ensure that the next sprint planning meeting reviews the satisfaction histogram
- Point out that it is the responsibility of the product owner to clarify requirements
-
Team A is working on the second sprint of a product release. Team B, which is an interdependent team located on the same floor, requires extensive and frequent information to complete its sprint goal.
What should the agile team lead do?
- Create a central repository for information, and provide access to team B
- Use an information board that will be visible to all passing through the workspace
- Email all stakeholders with status updates
- Provide team B with the information on an “as needed” basis
-
What should an agile practitioner do to ensure that the end product meets business requirements?
- Invite the team to iteration review meetings
- Obtain agreement from the product owner on business requirements
- Request that regular reports are sent to stakeholders
- Confirm managers and stakeholders are invited to product review meetings
-
A new product owner needs to manage the backlog of a high-visibility, fast-moving project that is consuming a considerable amount of time.
What should the product owner do?
- Schedule regular meetings with the scrum team to write, groom, and size user stories
- Focus on stories based on the highest number of story points to first address those items with the highest value
- Seek regular input from project stakeholders, and reflect this input in the backlog’s priorities
- Schedule in-person, monthly meetings with key stakeholders to review the project’s progress
-
Based on the backlog metrics in the chart, what can explain the jump in points at the end of iteration 4?
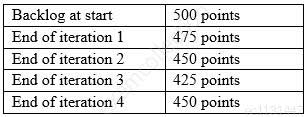
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 31 Q15 043 - The team neglected to account for support and maintenance costs associated with other supported products
- The team discovered that previously accepted work could be greatly improved and added story points associated with that work
- The team realized that some stories were underestimated relative to other stories and reestimated as needed
- The team learned that the product owner needed to increase the output in the next release
-
An agile team is preparing a release plan for a project.
What information will the team need to complete this plan?
- Amount of work needed to complete a single user story
- Amount of work that can be accomplished by each team member
- Amount of work that can be accomplished in an iteration
- Amount of work that can be accomplished by the entire team
-
When prioritizing features to be delivered in an iteration, on what features should an agile team defer work?
- High-risk and high-value
- High-risk and low-value
- Low-risk and low-value
- Low-risk and high-value
-
During a review session, an agile team presented done requirements to a group of stakeholders. Stakeholder feedback indicated that the done requirements failed to meet the most pressing needs and provide value.
What should the team have done to prevent this?
- Reprioritized requirements prior to committing to iteration work
- Ensured that requirements remained stable during the iteration cycle
- Had stakeholders focus on items created after the product backlog was initially built
- Worked on features rather than a set of components
-
Toward the end of a project, the product owner discovers that the project has a high probability of failure due to a critical feature not functioning as expected.
What should the product owner do?
- Terminate the project to cut losses
- Review possible options and make an informed decision to cut losses based on delivered business value
- Bring in experts to increase the probability of success
- Continue the project, release the product without the failing feature, and fix the feature in a subsequent release
-
A company is considering developing a new, complex application that will require a large initial investment. However, if successful, the profit potential is high.
When preparing an analysis, what should be used to encourage stakeholders who are concerned about project failure to authorize the initial investment?
- Calculated planned percent complete (PPC)
- Many small minimally marketable features (MMFs)
- Story points rather than cost estimates
- Calculated earned value (EV)
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest