PMI-ACP : PMI Agile Certified Practitioner : Part 36
-
Agile team A struggles to deliver committed stories due to technical dependencies with team B, which continuously fails to meet its delivery commitments.
What should the agile team lead do?
- Create a new team to deliver the dependencies, and bring team B under performance management.
- Conduct a vision-sharing session with the teams to communicate the project’s overall goals.
- Swap team members from both teams so that deliveries are better supported.
- Discuss negotiating the delivery timelines with team A.
-
During a Kanban team’s daily stand up, an agile coach observes that the team seems disinterested in the work status. While it appears that there are no issues with flow, there is a marked lack of attention to team effort. When the agile coach queries the team for reasons, members explain that work continues to be scheduled with no end in sight.
What should the agile coach do?
- Work with the team to determine points at which to celebrate its work.
- Provide the team with a break by scheduling a team event.
- Have the team increase work in progress (WIP) levels to more quickly complete the flow.
- Rejuvenate the team by temporarily reducing WIP levels.
-
A globally distributed project team is using email and phone calls as the only way to share information. Delays in resolving issues often occur due to misinterpreted communications, leading to a lower team velocity.
What steps should the project leader take to improve knowledge sharing?
- Meet individually with each team member to identify the issues and relay information to the remaining members through status reports.
- Establish a live video feed between the dispersed teams to enable spontaneous engagement and collaboration on issues.
- Request that the customer co-locate the team to overcome the communication issues, as this is the only method to ensure agility.
- Inform the customer of the challenges and lower velocity of the project to accommodate for the slower delivery pace.
-
An agile project has three more iterations before the release. There is a lot of report functionality to be created and defects to be cleared. During a daily scrum, a team member suggests a timebox spike to find a more efficient way to deliver reports.
What should the project leader do?
- Encourage the team to self-organize and determine how to best complete their existing work and this spike.
- Encourage the team to complete their just existing work since the team velocity indicates they are already struggling to meet the release goal.
- Direct the team to defer the spike until the next release and add the action on the backlog for prioritization.
- Direct the team to work on the spike immediately given the importance of reporting functionality to complete the iteration.
-
A scrum team has eight developers, but only two are database engineers. During the last few retrospectives, the team identified that most sprint stories are dependent upon database engineers. This has created a bottleneck in completing stories.
What should be proposed to the team?
- Have other team developers attend training to learn database skills.
- Monitor the retrospectives of two additional sprints before taking action.
- Plan fewer stories for the sprint to reduce the database engineers’ workload.
- Ask the scrum master to work with the product owner to remove backlog stories that have database dependency.
-
The executive leadership wants to understand ways to better deliver on time and on budget.
What can the project team do to assist in achieving the organizational goal?
- Maintain and review a lessons learned repository to improve delivery of future projects.
- Ask each team member to post corrective action to the backlog.
- Engage the project management office (PMO) to take responsibility identifying lessons learned on projects.
- Perform a root cause analysis to identify alternative approaches for performing the next project.
-
An agile team discovers a new risk and identifies that its impact may be severe.
What should an agile practitioner recommend?
- Add a goal to the current iteration to fully mitigate or control the risk.
- Balance risk reduction and value adding activities in the next iteration.
- Continue with the current plan to maintain team velocity.
- Update the risk register and seek direction from a risk specialist.
-
A new agile team member notices that the team’s current process involves excessive documentation.
What should the new team member do?
- Teach the team the appropriate agile principle, obtain consensus, and drive adoption.
- Allow another team member to prepare those documents that do not appear to bring value.
- Notify the project manager about other documentation techniques, and identify which documents bring value and which do not.
- Follow the existing process to avoid conflicts.
-
After seeing the planned features for an upcoming release, a customer notes that a vitally important and complex one is missing. The team estimates that this feature significantly exceeds its average velocity.
How can this issue be resolved?
- Break down the feature into smaller parts, and commit to completing the minimum viable product.
- Complete the iteration to which they have already committed, and include the feature in the next release.
- Change the planned features to include only the vitally important one.
- Extend the iteration to complete the feature.
-
A company president is concerned about the impact of a natural disaster on the company.
How should management identify areas to apply its resources and mitigate potential impacts?
- Establish and keep an active risk register that includes mitigation strategies and a cost-benefit analysis.
- Establish and keep an active risk register based on qualitative risk analysis and expected losses.
- Have each development team post the highest risk development items on the information radiator.
- Avoid risk by splitting development teams into two locations to ensure knowledge continuity.
-
A scrum master is part of a project team using technologies overseen by the IT department. The IT director oversees several company initiatives and is unfamiliar with the details of each one.
As an active project stakeholder, to which meeting should the IT director be invited?
- Planning
- Daily scrum
- Sprint demo
- Retrospective
-
During backlog refinement meeting, the new developer on the team asks the product owner to discuss a new performance threshold requirement and how it impacts the stories in the backlog.
What should the team do?
- Add this threshold requirement request as acceptance criteria in all impacted stories
- Create a spike story to analyze the impact of the threshold requirement on current stories
- Conduct design planning session to review the performance threshold requirement
- Identify the tasks for the new performance threshold requirement
-
During a daily stand up meeting, a developer expresses concerns that the selected technology limits the number of concurrent users.
What should the agile team lead do?
- Ask the team to conduct research to find a viable solution.
- Select a better technology for team implementation.
- Obtain customer input on their technology requirements.
- Consult the product owner about their non-functional requirements.
-
Based on the chart, what is the current status of the iteration when comparing story points planned versus completed?
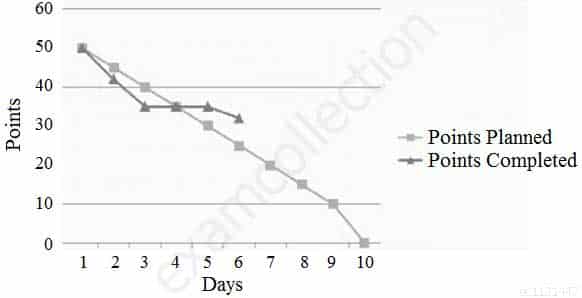
PMI-ACP PMI Agile Certified Practitioner Part 36 Q14 044 - The iteration is in jeopardy.
- The team has removed scope.
- The iteration is ahead of schedule.
- The team’s velocity is constant.
-
A product’s scope and acceptance criteria have been defined, and the product is planned for release at the end of the next quarter.
What should the project team do next?
- Estimate the project team’s capacity.
- Determine how much work can be delivered.
- Calculate how much work will fit into the next iteration.
- Estimate items in the product backlog.
-
During sprint retrospectives, some team members are very vocal and tend to dominate the conversation, while others are more reserved and less likely to participate.
What should the scrum master do?
- Encourage all team members to participate, and have them type their retrospective feedback into the agile lifecycle management tool.
- Ask more specific questions during the retrospectives.
- Use retrospective techniques, such as silent writing, clustering, and dot voting to field feedback prior to discussion by the team.
- Ask team members to email feedback that can be summarized in a spreadsheet for the team.
-
An agile practitioner notices that team members are disengaged. As a result, the team’s velocity has decreased.
What should the agile practitioner do to get the team back on track?
- Escalate the issue to the project sponsor.
- Remove stories to increase velocity.
- Hold a standup to address the issue.
- Facilitate a team retrospective.
Subscribe
0 Comments
Newest