Refer to the exhibit. An ACL was configured on R1 with the intention of denying traffic from subnet 172.16.4.0/24 into subnet 172.16.3.0/24. All other traffic into subnet 172.16.3.0/24 should be permitted. This standard ACL was then applied outbound on interface Fa0/0. Which conclusion can be drawn from this configuration?
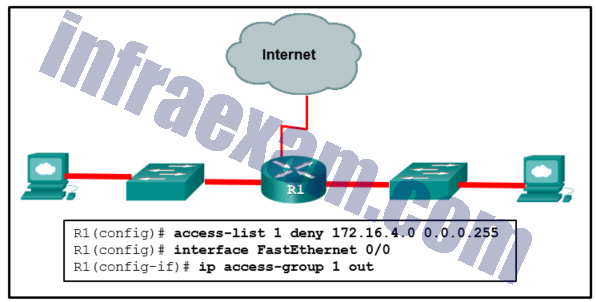
- Only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked, and all other traffic is allowed.
- An extended ACL must be used in this situation.
- The ACL should be applied to the FastEthernet 0/0 interface of R1 inbound to accomplish the requirements.
- All traffic will be blocked, not just traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet.
- The ACL should be applied outbound on all interfaces of R1.
| Answers Explanation & Hints:
Because of the implicit deny at the end of all ACLs, the access-list 1 permit any command must be included to ensure that only traffic from the 172.16.4.0/24 subnet is blocked and that all other traffic is allowed. |