Module 3: Advanced Computer Hardware Exam Answers 2025
IT Essentials 8 Module 3 Exam Answers | ITE 8.0 Module 3 Exam Answers Full 100% 2025
Module 3 of the IT Essentials 8.0 (ITE 8.0) curriculum, titled Advanced Computer Hardware, dives deeper into the functionality, configuration, and troubleshooting of essential computer components. This module covers topics such as motherboard features, storage devices, power supplies, cooling systems, BIOS/UEFI configuration, and peripheral devices. Understanding these concepts is crucial for assembling, upgrading, and maintaining computer systems effectively. If you’re preparing for the 2025 ITE 8.0 Module 3 exam, this guide provides accurate and verified 100% correct answers to help you achieve a perfect score.
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Chapter 3 | |
| Chapter 3 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapter 3 Quiz Answers | Online Test |
| IT Essentials 8 Chapter 4 | |
| Chapter 4 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapter 4 Quiz Answers | Online Test |
IT Essentials 8.01 | ITE 8.01 Chapter 3 Exam Answers Full 100% 2025
-
Which two considerations would be of the greatest importance when building a workstation that will run multiple virtual machines? (Choose two.)
- amount of RAM
- number of CPU cores
- water cooling
- powerful video card
- high-end sound card
Explanation & Hint: Virtual computing requires more powerful hardware configurations because each installation needs its own resources and thus requires a lot of RAM and CPU processing power.
-
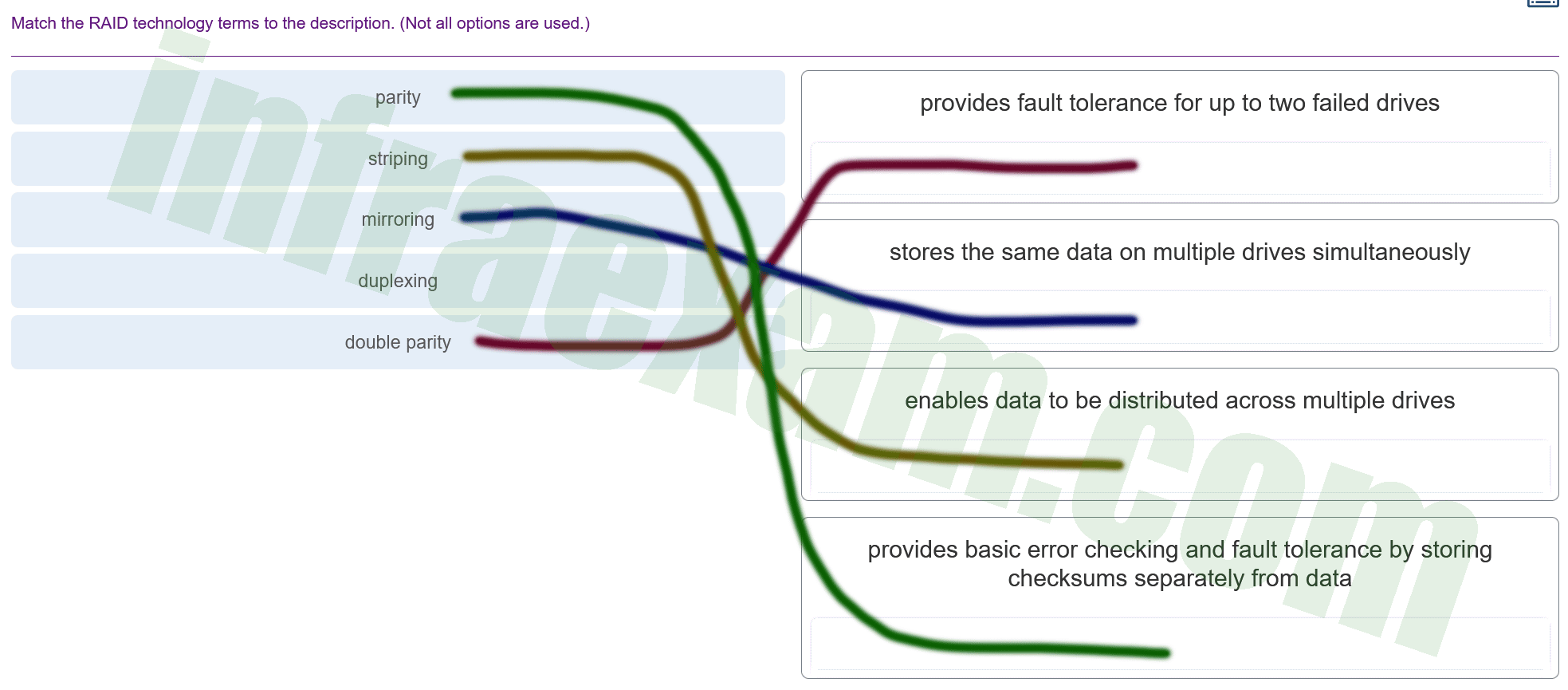
Match the RAID technology terms to the description. (Not all options are used.)
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Chapter 3 Exam Answers 001 Explanation & Hints: - Double parity is connected to “provides fault tolerance for up to two failed drives”. This refers to RAID-6, which can handle two drives failing simultaneously without data loss.
- Mirroring is connected to “stores the same data on multiple drives simultaneously”. This is a description of RAID-1, where data is written identically to two drives, creating a mirrored set.
- Striping is connected to “enables data to be distributed across multiple drives”. This matches RAID-0, where data is split across drives, which can improve speed but does not provide fault tolerance.
- Parity is connected to “provides basic error checking and fault tolerance by storing checksums separately from data”. This is characteristic of RAID-5, which uses parity information to provide fault tolerance for a single drive failure.
-
Which two components are commonly replaced when a computer system with a newer motherboard is being upgraded? (Choose two.)
- RAM
- hard disk drive
- CPU
- optical drive
- CMOS battery
- adapter card
Explanation & Hint: When a motherboard is being upgraded to a newer version, both the CPU and RAM are commonly upgraded to support the motherboard compatibility requirements.
-
What are two reasons for installing a second hard disk drive inside an existing computer? (Choose two.)
- to support a RAID array
- to store BIOS configuration settings
- to store the system swap file
- to increase CPU speed
- to allow access to a secondary display output
Explanation & Hint: The common reasons to install a second hard disk drive in a computer include: 1) increase storage space, 2) increase hard drive speed, 3) install a second operating system, 4) store the system swap file, 5) provide fault tolerance, and 6) backup the original hard drive.
-
A technician has just finished assembling a new computer. When the computer is powered up for the first time, the POST discovers a problem. How does the POST indicate the error?
- It issues a number of short beeps.
- The LED on the front of the computer case flashes a number of times.
- It places an error message in the BIOS.
- It locks the keyboard.
-
Explanation & Hint: The Power-On Self-Test (POST) is a diagnostic process run by the BIOS/UEFI when a computer is powered on. If POST detects a hardware issue, it uses beep codes to indicate the nature of the problem.
- The number and pattern of beeps vary based on the BIOS manufacturer (AMI, Award, Phoenix, etc.).
- Common errors include RAM issues, GPU failures, missing boot devices, or CPU problems.
- If the computer has a speaker connected to the motherboard, these beeps will be heard at startup.
-
What is a function of the BIOS?
- enables a computer to connect to a network
- provides temporary data storage for the CPU
- performs a check on all internal components
- provides graphic capabilities for games and applications
-
Explanation & Hint: The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a firmware that initializes and tests hardware components before loading the operating system. One of its key functions is to perform the Power-On Self-Test (POST), which:
- Checks internal hardware components such as RAM, CPU, GPU, storage drives, and other essential devices.
- Identifies hardware failures and reports them through beep codes or error messages.
- Initializes system settings and prepares the computer for booting the operating system.
-
A technician has assembled a new computer and must now configure the BIOS. At which point must a key be pressed to start the BIOS setup program?
- before the computer is powered on
- during the Windows load process
- during the POST
- after the POST, but before Windows starts to load
Explanation & Hint: To enter the BIOS setup program, you must press the proper key or key sequence during POST. Many motherboards will display graphics while the computer is checking hardware and waiting for the proper key press for the user to enter the BIOS.
-
How does an inline UPS protect computer equipment against electrical power brownouts and blackouts?
- by grounding excess electrical voltage
- by using a battery to supply a constant level of voltage
- by switching from main power to a standby power source
- by stopping the flow of voltage to the computer
Explanation & Hint: Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) contain a battery which is constantly providing a consistent level of voltage to the computer.
-
Which condition refers to a reduced voltage level of AC power that lasts for an extended period of time?
- brownout
- sag
- spike
- surge
Explanation & Hint: Surges and spikes are increased voltage levels. A sag is a short duration reduction in line voltage while a brownout is a reduction in voltage that occurs for an extended period of time.
-
How should a technician dispose of an empty inkjet printer cartridge?
- Refill it.
- Throw it away.
- Follow local regulations for disposal.
- Give it back to the customer.
Explanation & Hint: Refilling used inkjet cartridges is not recommended, as it may void the printer warranty and could leak ink, damaging the printer. Printer cartridges should be recycled, following the procedures established for recycling by the manufacturer. Because they are an environmental hazard, they should never be thrown away.
-
What makes CRT monitor disposal dangerous for a technician who is handling the disposal?
- potential breathing hazards
- potential explosive materials
- potential residual high voltage
- potential health-damaging chemicals
Explanation & Hint: CRT monitors do contain lead, barium, and rare earth metals that can be dangerous to the environment if not disposed of properly, but the danger to the technician is in the high voltage levels that can be stored even after powering occ the monitor and disconnecting the power cord. A technician might be disposing of a CRT monitor that has the cover ajar or removed and be exposed to the high voltage.
-
Which type of interface was originally developed for high-definition televisions and is also popular to use with computers to connect audio and video devices?
- FireWire
- DVI
- HDMI
- USB
- VGA
Explanation & Hint: High definition multimedia interface, or HDMI, was originally a television standard. However, because it has many digital features, it is also a popular interface to connect audio and video devices to computers.
-
What is indicated by the contrast ratio of a monitor?
- the diccerence in the intensity of light between the brightest white and darkest black that can be displayed
- how often the picture image is refreshed
- the total number of pixels that make up the picture
- the ratio of the horizontal and vertical viewing areas of the monitor
Explanation & Hint: Contrast ratio is one of many factors that is used to describe the resolution of a monitor. Contrast ratio is a measure of the diccerence in intensity between white and black areas of the picture. A higher contrast ratio means the monitor can produce pictures with brighter whites and darker blacks.
-
What electrical unit refers to the number of electrons moving through a circuit per second?
- current
- voltage
- resistance
- power
Explanation & Hint: Current refers to the amount of electrons moving through a circuit per second and is measured in amperes or amps.
-
What characteristic of electricity is expressed in watts?
- the amount of work required to move electrons through a circuit
- the resistance to the flow of current in a circuit
- the amount of electrons flowing through a circuit per second
- the work required to move electrons through a circuit multiplied by the number of electrons flowing through a circuit per second
Explanation & Hint: Watts is the unit used to measure the electrical power. Power refers to the work required to move electrons through a circuit multiplied by the number of electrons flowing through a circuit per second.
-
Which is a BIOS security feature that can prevent data from being read from a hard drive even if the hard drive is moved to another computer?
- drive encryption
- RAID
- secure boot
- BIOS passwords
Explanation & Hint: There are several commonly available BIOS security features. Drive encryption is used to encrypt hard drives to prevent data access. Secure boot ensures that devices will only boot a trusted operating system. BIOS passwords allow diccerent levels of BIOS access. RAID is not a BIOS security feature but rather provides redundancy and fault tolerance by using multiple hard drives.
-
What data is stored in the CMOS memory chip?
- BIOS settings
- Windows configuration settings
- user login information
- device drivers
Explanation & Hint: The complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) chip is a small memory chip located on the motherboard that is used to store saved BIOS settings.
-
What is the purpose of LoJack?
- It allows the owner of a device to remotely locate, lock, or delete all files from the device.
- It ensures that a computer will only boot an operating system that is trusted by the motherboard manufacturer.
- It provides passwords for diccerent levels of access to the BIOS.
- It encrypts data on hard drives to prevent access without the correct password.
Explanation & Hint: The LoJack security feature protects against data theft if a device is stolen by allowing the owner to locate, lock, or delete all files on the device.
-
What is one purpose of adjusting the clock speed within the BIOS configuration settings?
- to allow a computer to run multiple operating systems in files or partitions
- to change the order of the bootable partitions
- to disable devices that are not needed or used by the computer
- to allow the computer to run slower and cooler
Explanation & Hint: The CPU clock speed can be adjusted up or down within the BIOS configuration settings. By lowering the clock speed, a CPU can run slower and cooler. Increasing the CPU clock speed makes the computer run faster and hotter.
-
A user playing a game on a gaming PC with a standard EIDE 5400 RPM hard drive finds the performance unsatisfactory. Which hard drive upgrade would improve performance while providing more reliability and more energy ecciciency?
- a 7200 RPM EIDE hard drive
- a 7200 RPM SATA hard drive
- a 10,000 RPM SATA hard drive
- an SSD
Explanation & Hint: Games require a lot of storage. In order for the computer to load and run games quickly, a fast hard drive will need to be installed. To obtain best performance an SSD (Solid-State Drive) will perform faster than an EIDE drive or a SATA drive.
-
Which security feature in modern CPUs protects memory areas that contain part of the operating system from malware attacks?
- encryption
- TPM
- execute disable bit
- LoJack
Explanation & Hint: The execute disable option can be turned on, if the feature is supported by the OS, to prevent malicious code from being executed inside a specific memory area that contains operating system files.
-
A user reports that every morning when a particular computer is turned on, the configuration settings on that computer have to be reset. What action should be taken to remedy this situation?
- Replace the motherboard.
- Replace the CMOS battery.
- Move the jumpers.
- Upgrade the BIOS.
Explanation & Hint: BIOS information is maintained through the use of a CMOS battery. If the CMOS battery no longer provides power, configuration settings may be lost.
-
Which statement describes the capability of an HDMI version 1.4 type A port?
- It can be used for 4K and 8K resolutions.
- It supports high premium speeds of up to 48 Gbps.
- It can change a monitor’s refresh rate to match the source device output rate.
- It uses a 20-pin connector for delivering high-bandwidth video and audio signals.
Explanation & Hint: HDMI version 1.4 type A port is a standard HDMI port. It can change a monitor’s refresh rate to match the source device output rate.
-
What is the advantage of having a redundant power supply?
- It can be used to power high-performance graphic cards.
- It provides a Field Replacement Unit for immediate replacement in the event of a power supply failure.
- It allows for the replacement of the faulty power supply without loss of power to the server.
- It can be linked to increase the wattage required for the newer processors.
Explanation & Hint: A redundant power supply is hot-swappable. This allows the faulty power supply to be replaced without losing power to the computer.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 6?
- 3
- 4
- 6
- 7
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 6 provides fault tolerance for up to two drive failures and requires a minimum of four drives because:
- Uses striping with dual parity – Data and parity are distributed across all drives.
- Can survive two simultaneous drive failures without data loss.
- More storage efficient than mirroring-based RAID levels like RAID 1 or RAID 10.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 10?
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 10 (RAID 1+0) combines mirroring (RAID 1) and striping (RAID 0), requiring a minimum of four drives because:
- Mirroring (RAID 1): Each pair of drives contains identical copies of the data, ensuring redundancy.
- Striping (RAID 0): Data is distributed across mirrored pairs to improve performance.
- Fault Tolerance: The system can survive at least one drive failure per mirrored pair without data loss.
- Performance: RAID 10 provides high-speed read/write performance and strong redundancy.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 10?
- 4
- 6
- 10
- 7
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 10 (RAID 1+0) combines mirroring (RAID 1) and striping (RAID 0) and requires a minimum of four drives because:
- Mirroring (RAID 1) – Each pair of drives contains identical copies of the data, ensuring redundancy.
- Striping (RAID 0) – Data is distributed across mirrored pairs to improve performance.
- Fault Tolerance – The system can survive at least one drive failure per mirrored pair without data loss.
- Performance – RAID 10 offers high-speed read/write performance and strong redundancy.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 1?
- 2
- 6
- 10
- 7
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 1, also known as mirroring, requires a minimum of two drives because:
- Each drive contains an identical copy of the data, ensuring redundancy.
- If one drive fails, the other still has a complete copy, providing fault tolerance.
- No storage efficiency loss for redundancy – only 50% of the total storage is usable.
- Improves read performance, as data can be read from either drive simultaneously.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 5?
- 3
- 7
- 6
- 10
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 5 requires a minimum of three drives and provides fault tolerance for one drive failure by using striping with distributed parity.
- Data and parity are spread across all drives, allowing for redundancy and improved performance.
- If one drive fails, the system can reconstruct lost data using parity information from the remaining drives.
- Efficient use of storage – Only one drive’s worth of space is used for parity, making it more storage-efficient than mirroring-based RAID levels.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 5?
- 3
- 1
- 7
- 10
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 5 provides fault tolerance for one drive failure and requires a minimum of three drives because:
- Uses striping with distributed parity – Data and parity are spread across all drives.
- Can survive the failure of one drive without data loss.
- Efficient use of storage – Only one drive’s worth of space is used for parity, making it more storage-efficient than mirroring-based RAID levels.
- Improves read performance – Since data is striped, reads are faster than single-drive setups.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 6?
- 3
- 4
- 7
- 10
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 6 provides fault tolerance for up to two drive failures and requires a minimum of four drives because:
- Uses striping with dual parity – Data and parity are distributed across all drives.
- Can survive two simultaneous drive failures without data loss.
- More storage efficient than mirroring-based RAID levels like RAID 1 or RAID 10.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 6?
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 6 provides fault tolerance for up to two drive failures and requires a minimum of four drives because:
- Uses striping with dual parity – Data and parity are distributed across all drives.
- Can survive two simultaneous drive failures without losing data.
- More storage efficient than mirroring-based RAID levels like RAID 1 or RAID 10.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 10?
- 4
- 5
- 1
- 6
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 10 (RAID 1+0) combines mirroring (RAID 1) and striping (RAID 0), requiring a minimum of four drives because:
- Mirroring (RAID 1) – Data is duplicated across pairs of drives for redundancy.
- Striping (RAID 0) – Data is split across the mirrored pairs to enhance performance.
- Fault Tolerance – The system can survive at least one drive failure per mirrored pair.
- Improved Speed – Read/write speeds benefit from striping.
-
A data analyst has asked a technician to help protect locally stored data by installing a RAID. What is the minimum number of drives the technician has to install if configuring a RAID level 1?
- 2
- 6
- 1
- 5
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 1, also known as mirroring, requires a minimum of two drives because:
- Each drive contains an identical copy of the data, ensuring redundancy.
- If one drive fails, the other still holds a complete copy, providing fault tolerance.
- Read speeds can improve, but write speeds remain the same since data is written to both drives simultaneously.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer needs protection if one drive fails, fast access, and drive capacity. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 5
- RAID 4
- RAID 2
- RAID 3
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 5 provides a balance of fault tolerance, fast access, and efficient drive capacity by using striping with distributed parity.
- Fault tolerance – Protects against one drive failure by using parity data.
- Fast access – Striping improves read performance, though writes are slightly slower due to parity calculations.
- Efficient drive capacity – Uses only one drive’s worth of storage for parity, meaning more usable space compared to mirroring-based RAID levels.
- Requires at least three drives – Ideal for a setup balancing performance and redundancy.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer needs protection if two drive fails and wants as much drive capacity as possible. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 6
- RAID 7
- RAID 2
- RAID 3
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 6 provides fault tolerance for up to two drive failures while maximizing available storage. It works by using:
- Striping with dual distributed parity – Data is spread across all drives, along with two sets of parity information.
- Protection against two drive failures – Even if two drives fail simultaneously, data remains accessible.
- Better storage efficiency than mirroring-based RAID levels – More usable storage compared to RAID 1 or RAID 10.
- Minimum of four drives required – The more drives used, the better the balance between capacity and redundancy.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer needs protection for one drive failure and only has room in the computer for two drives. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 1
- RAID 7
- RAID 8
- RAID 4
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 1 is the best choice for a system with only two drives that requires protection against one drive failure. It uses mirroring, meaning:
- Each drive contains an identical copy of the data.
- If one drive fails, the other still has a complete copy, ensuring data protection.
- No performance gain for writing, but reading can be improved since data can be read from either drive.
- Requires exactly two drives, making it the only RAID option that meets the customer’s needs.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer wants RAID and full drive capacity, but does not care about a drive failure, because all data is constantly backed up. The computer where the RAID is to be installed only has room for two drives. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 0
- RAID 8
- RAID 7
- RAID 4
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 0 provides maximum drive capacity and performance by striping data across both drives without any redundancy. Given the customer’s requirements:
- Uses full drive capacity (no space is taken up by parity or mirroring).
- Maximizes performance by distributing data across both drives, improving read and write speeds.
- No fault tolerance – if one drive fails, all data is lost, but since the customer backs up data constantly, this is not a concern.
- Requires only two drives, making it the ideal choice for this setup.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer wants data to be stored on two drives that are used to maximum capacity and does not care if a single drive fails, because data is backed up hourly. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 0
- RAID 8
- RAID 7
- RAID 4
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 0 uses striping without parity or mirroring, meaning:
- All available storage capacity is used, with no space taken up by redundancy.
- Performance is maximized since data is split across both drives, increasing read/write speeds.
- No fault tolerance – if one drive fails, all data is lost.
Since the customer does not care about drive failure because data is backed up hourly, RAID 0 is the best choice to maximize storage capacity and performance.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer wants data to be stored on three drives and protection for one drive failure. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 5
- RAID 2
- RAID 8
- RAID 7
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 5 is the best option when using three drives while ensuring fault tolerance in case one drive fails. It provides a balance of performance, storage efficiency, and redundancy through striping with distributed parity.
- Requires a minimum of three drives.
- Data and parity are spread across all drives, meaning no single drive is dedicated to parity (unlike RAID 4).
- If one drive fails, the lost data can be rebuilt using parity information from the remaining drives.
- Good read performance due to striping, though write performance may be slightly slower due to parity calculations.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer wants three drives to be used and protection if one drive fails. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 5
- RAID 2
- RAID 4
- RAID 3
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 5 is the best choice when using three drives while ensuring fault tolerance if one drive fails. It uses striping with distributed parity, which means:
- Data is distributed across all drives, improving read performance.
- Parity information is also distributed, allowing for data recovery if one drive fails.
- Minimum of three drives required, making it the best fit for this scenario.
- If a single drive fails, the RAID array can reconstruct the lost data using parity information.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer wants to incorporate mirroring and striping as part of the RAID. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 10
- RAID 3
- RAID 4
- RAID 2
-
Explanation & Hint: RAID 10 (also known as RAID 1+0) combines mirroring (RAID 1) and striping (RAID 0) to provide both fault tolerance and performance improvement.
- Mirroring (RAID 1): Ensures data redundancy by duplicating data across multiple drives.
- Striping (RAID 0): Distributes data across multiple drives for increased read/write speed.
- RAID 10 requires a minimum of four drives (pairs of mirrored drives that are striped).
- If a drive fails, the system can still function as long as at least one mirrored drive remains intact.
-
A technician has been asked to configure several computers with RAID. The customer wants the best RAID possible with three drives used. Which RAID should the technician install?
- RAID 6
- RAID 3
- RAID 4
- RAID 2
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
A technician is selecting a PC that will be used by a user as a thin client. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- network connection to a server
- multiple SCSI drives
- optical drive
- multiple touch screens
-
Explanation & Hint: A thin client is a lightweight computer that relies on a server for processing power, storage, and applications. Since thin clients do not perform heavy computing tasks locally, a strong network connection to a server is essential to ensure smooth performance, fast data access, and seamless remote computing. Thin clients typically use Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) or cloud-based solutions, making network connectivity the primary consideration.
-
A technician is selecting a web server that will be used to host multiple gaming applications. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- powerful processor
- multiple SCSI drives
- optical drive
- multiple touch screens
-
Explanation & Hint: A web server hosting multiple gaming applications requires a high-performance processor (CPU) to handle multithreading, game logic processing, and high concurrent user loads. Gaming servers demand a high core count and clock speed to manage real-time interactions, physics calculations, and multiplayer connections efficiently. Processors like Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC are ideal choices for such demanding workloads, ensuring smooth gameplay experiences for users.
-
A technician is selecting a web server that will be used to host multiple gaming applications. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- powerful processor
- read-only memory modules
- multiple touch screens
- multiple SCSI drives
-
Explanation & Hint: A web server hosting multiple gaming applications requires a powerful processor (CPU) to handle high-performance tasks such as game logic processing, concurrent user requests, and data transactions. Gaming applications demand significant computational power to manage multiplayer connections, process game physics, and ensure smooth performance. A high-core-count CPU (such as Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC) with a high clock speed is crucial for handling multiple gaming instances efficiently.
-
A technician is selecting a PC that will be used by a songwriter to mix tracks. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- specialized audio card
- dual-fan power supply
- smart card reader
- Thunderbolt connector
-
Explanation & Hint: For a songwriter mixing tracks, a specialized audio card (sound card) is essential. High-quality sound cards provide better audio processing, lower latency, and higher fidelity compared to integrated sound solutions. They support ASIO drivers, multiple input/output channels, and professional-grade audio conversion, which are crucial for music production and mixing. A dedicated external audio interface may also be used for even better sound quality and connectivity with studio equipment like microphones and instruments.
-
A technician is selecting a laptop that will be used by a teleworker for connecting to the internet while traveling anywhere. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- cellular card
- Thunderbolt connector
- smart card reader
- dual-fan power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: A cellular card (also known as a mobile broadband card or WWAN module) allows a laptop to connect to the internet using a cellular network (4G LTE or 5G). This is essential for a teleworker who needs reliable internet access while traveling, especially in locations where Wi-Fi may not be available. A built-in or external cellular card enables seamless connectivity without relying on public or hotel Wi-Fi, ensuring secure and uninterrupted remote work.
-
A technician is selecting a server that will be used by a cloud provider for data storage. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- multiple large hard drives
- smart card reader
- Thunderbolt connector
- dual-fan power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: For a cloud provider that focuses on data storage, having multiple large-capacity hard drives is essential. Cloud storage requires a significant amount of disk space to store and manage user data efficiently. Additionally, using multiple drives allows for RAID configurations, which enhance data redundancy, fault tolerance, and performance. High-capacity SSDs or HDDs ensure that the server can handle large amounts of data while maintaining reliability and scalability.
-
A technician is selecting a server that will be used by a cloud provider to provide fault tolerance for large quantities of stored data. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- RAID
- smart card reader
- Thunderbolt connector
- dual-fan power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: For a cloud provider that requires fault tolerance for large-scale data storage, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a crucial consideration. RAID configurations (such as RAID 1, RAID 5, or RAID 10) provide data redundancy and protection against hardware failures by distributing data across multiple drives. This ensures that if one drive fails, the data remains accessible, minimizing downtime and data loss.
-
A technician is selecting a server that will be used by a cloud provider to provide fault tolerance for large quantities of stored data. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- RAID
- motherboard that supports dual-channeling
- smart card reader
- Thunderbolt connector
-
Explanation & Hint: For a cloud provider that needs fault tolerance for large quantities of stored data, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a critical consideration. RAID provides data redundancy and improves reliability by distributing data across multiple drives. Common RAID configurations such as RAID 1 (mirroring), RAID 5 (striping with parity), and RAID 10 (striping and mirroring) help prevent data loss in case of disk failure, ensuring high availability and fault tolerance.
-
A technician is selecting a PC that will be used by an employee who wants to share a keyboard and mouse among three devices. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- KVM switch
- motherboard that supports dual-channeling
- smart card reader
- Thunderbolt connector
-
Explanation & Hint: A KVM (Keyboard, Video, Mouse) switch allows a user to control multiple computers using a single keyboard and mouse. Since the employee wants to share these peripherals among three devices, a KVM switch is the most important consideration. It enables seamless switching between different systems without requiring multiple keyboards and mice, improving efficiency and reducing desk clutter.
-
A technician is selecting a PC that will be used by an employee who wants to share a keyboard and mouse among three devices. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- KVM switch
- motherboard that supports dual-channeling
- smart card reader
- Thunderbolt connector
-
Explanation & Hint: A KVM (Keyboard, Video, Mouse) switch allows a user to control multiple computers using a single keyboard and mouse. Since the employee wants to share these peripherals among three devices, a KVM switch is the most important consideration, enabling seamless switching between different systems without needing multiple keyboards and mice.
-
A technician is selecting a PC that will be used by an employee who wants to share a keyboard and mouse among three devices. What is a major consideration that needs to be taken into account?
- KVM switch
- UEFI BIOS
- dual-fan power supply
- read-only memory modules
-
Explanation & Hint: A KVM (Keyboard, Video, Mouse) switch allows a user to control multiple computers using a single keyboard, monitor, and mouse. Since the employee wants to share a keyboard and mouse among three devices, a KVM switch is the ideal solution, enabling easy switching between devices without needing multiple input peripherals.
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Chapter 3 | |
| Chapter 3 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapter 3 Quiz Answers | Online Test |
| IT Essentials 8 Chapter 4 | |
| Chapter 4 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Chapter 4 Quiz Answers | Online Test |