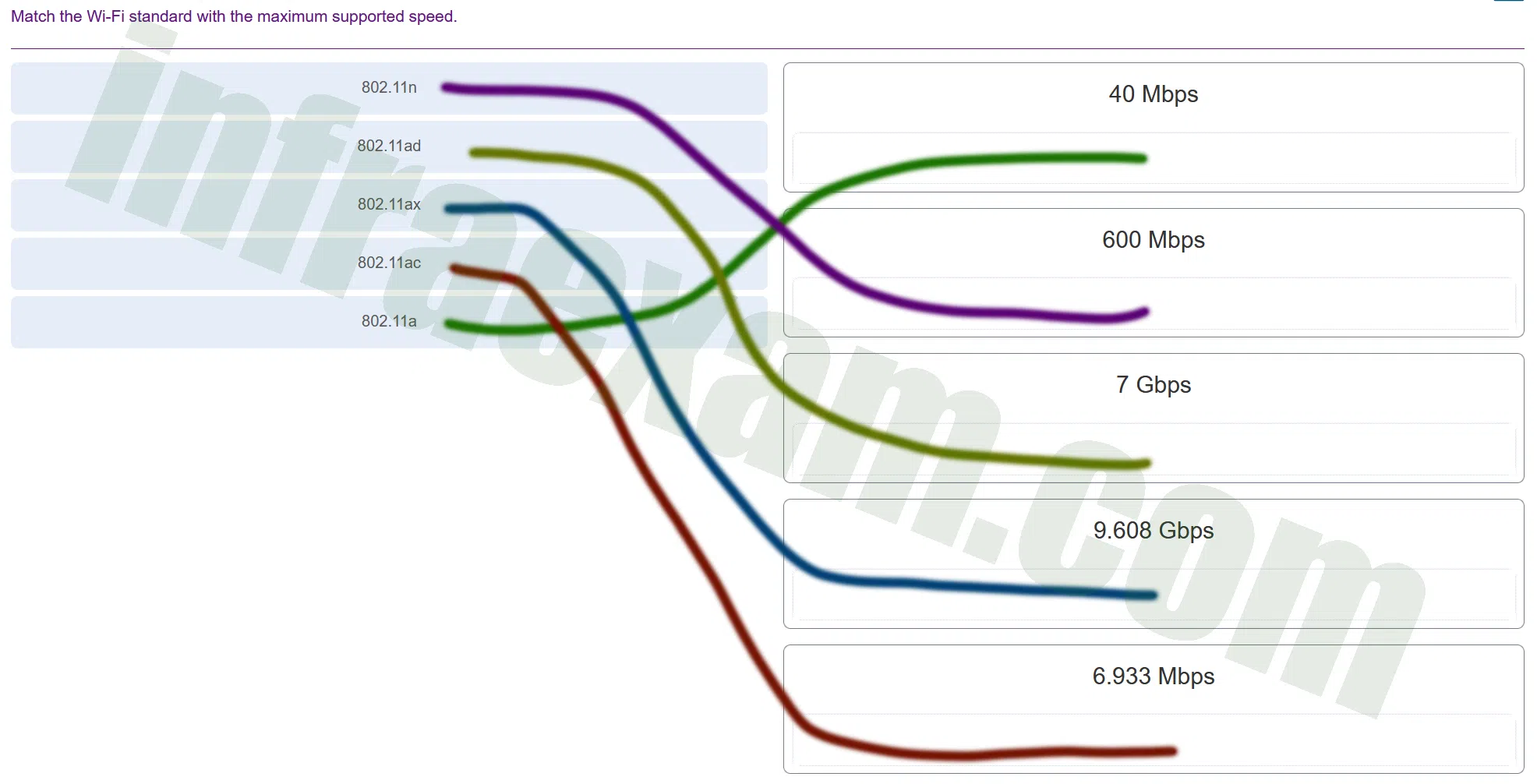
Explanation & Hint:
- 802.11n: This standard, also known as Wi-Fi 4, can reach speeds of up to 600 Mbps.
- 802.11ad: This Wi-Fi standard is known for its very high-speed potential, reaching up to 7 Gbps. It operates in the 60 GHz frequency band.
- 802.11ax: Also known as Wi-Fi 6, is the successor to 802.11ac and can achieve higher speeds, often quoted up to 9.608 Gbps under optimal conditions.
- 802.11ac: This standard, also known as Wi-Fi 5, increased the maximum speed over its predecessors to a range that often tops out around 1.3 Gbps, but with advancements and multiple streams, it can theoretically reach over 6.933 Gbps.
- 802.11a: This is an older standard that typically had a maximum throughput of 54 Mbps, but it is not listed among the options you’ve provided.
With the given options, the correct matches would be:
- 802.11n with 600 Mbps
- 802.11ad with 7 Gbps
- 802.11ax with 9.608 Gbps
- 802.11ac likely corresponds to the speed closest to its theoretical maximum, but none of the provided speeds match the typical top speeds of 802.11ac. If we were to choose the closest one, it might be 6.933 Gbps, assuming advanced configurations.
- 802.11a it would align with 40 Mbps if that were an option.
|