MD-100 : Windows 10 : Part 05
-
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10 Current branch. Computer1 belongs to a workgroup.
You run the following commands on Computer1.
New-LocalUser –Name User1 –NoPassword Add-LocalGroupMember Users –Member User1
What is the effect of the configurations?
- User1 is prevented from signing in until the user is assigned additional user rights.
- User1 appears on the sign-in screen and can sign in without a password.
- User1 is prevented from signing in until an administrator manually sets a password for the user.
- User1 appears on the sign-in screen and must set a new password on the first sign-in attempt.
Explanation:
User1 will be prompted to change the password at first login. The message will say, “You must change your password”. You do have to set a password, even if it is a blank password before you can log in. -
You have a computer that runs Windows 10 and is joined to Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
You attempt to open Control Panel and receive the error message shown on the following exhibit.
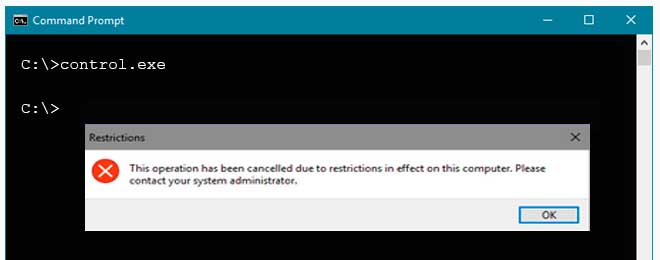
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q02 086 You need to be able to access Control Panel.
What should you modify?
- the PowerShell execution policy
- the local Group Policy
- the Settings app
- a Group Policy preference
-
HOTSPOT
Your domain contains a Computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 does not have a TPM.
You need to be able to encrypt the C drive by using BitLocker Drive Encryption (BitLocker). The solution must ensure that the recovery key is stored in Active Directory.
Which two Group Policy settings should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate settings in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q03 087 -
You have a public computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 contains a folder named Folder1.
You need to provide a user named User1 with the ability to modify the permissions of Folder1. The solution must use the principle of least privilege.
Which NTFS permission should you assign to User1?
- Full control
- Modify
- Write
- Read & execute
Explanation:
The NTFS Full control permission is required to change permissions. -
You have 10 computers that run Windows 10 and have BitLocker Drive Encryption (BitLocker) enabled.
You plan to update the firmware of the computers.
You need to ensure that you are not prompted for the BitLocker recovery key on the next restart. The drive must be protected by BitLocker on subsequent restarts.
Which cmdlet should you run?
- Unlock-BitLocker
- Disable-BitLocker
- Add-BitLockerKeyProtector
- Suspend-BitLocker
-
HOTSPOT
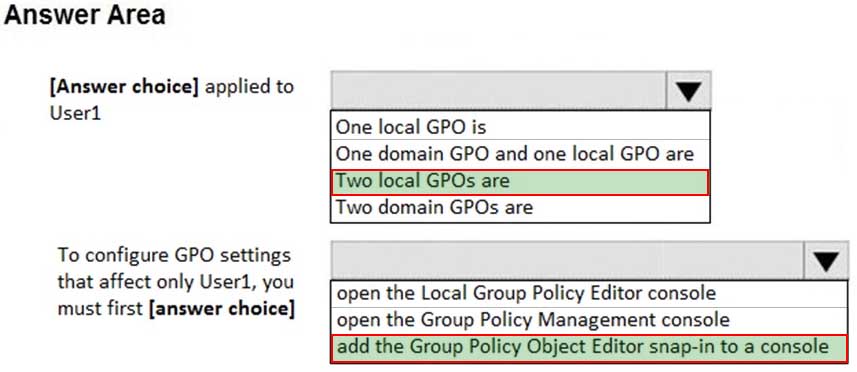
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10.
You are troubleshooting Group Policy objects (GPOs) on Computer1.
You run gpresult /user user1 /v and receive the output shown in the following exhibit.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q06 089 Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q06 090 -
HOTSPOT
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 is in a workgroup.
Computer1 contains the local users shown in the following table.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q07 092 You create a folder named Folder1 that has the permissions shown in the following table.
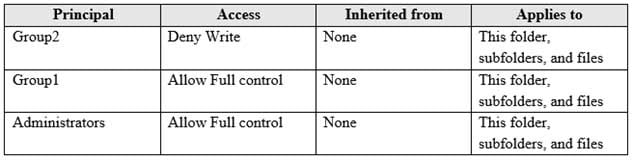
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q07 093 You create a file named File1.txt in Folder1 and allow Group2 Full control permissions to File1.txt.
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
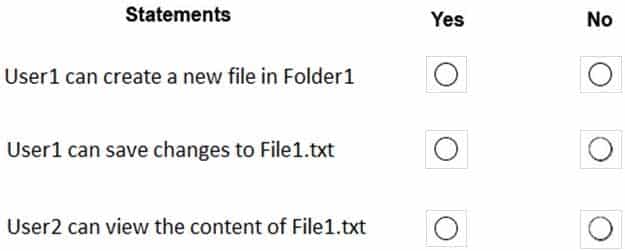
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q07 094 Question -
HOTSPOT
You have a workgroup computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 has the users accounts shown in the following table:

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q08 095 Computer1 has the local Group Policy shown in the following table.
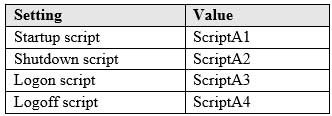
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q08 096 You create the Local Computer\Administrators policy shown in the following table.
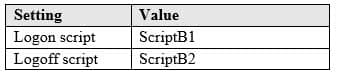
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q08 097 You create the Local Computer\Non-Administrators policy shown in the following table.
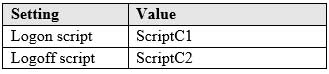
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q08 098 For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q08 099 Question -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
A user named User1 has a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 is joined to an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named contoso.com. User1 joins Computer1 to contoso.com by using [email protected].
Computer1 contains a folder named Folder1. Folder1 is in drive C and is shared as Share1. Share1 has the permission shown in the following table.
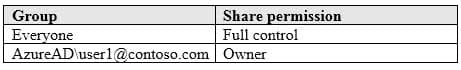
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q09 100 A user named User2 has a computer named Computer2 that runs Windows 10. User2 joins Computer2 to contoso.com by using [email protected].
User2 attempts to access Share1 and receives the following error message: “The username or password is incorrect.”
You need to ensure that User2 can connect to Share1.
Solution: You create a local group on Computer1 and add the Guest account to the group. You grant the group Modify access to Share1.
Does this meet the goal?
- Yes
- No
-
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains 1,000 computers that run Windows 10.
You need to prevent the computers of the research department from appearing in Network in File Explorer.
What should you do?
- Configure DNS to use an external provider
- Modify the %systemroot%\system32\drivers\etc\Networks file.
- Turn off network discovery.
- Disable the Network List Service.
-
HOTSPOT
You have two computers named Computer1 and Computer2 that run Windows 10. The computers are in a workgroup.
You perform the following configurations on Computer1:
– Create a user named User1.
– Add User1 to the Remote Desktop Users group.You perform the following configurations on Computer2:
– Create a user named User1 and specify the same user password as the one set on Computer1.
– Create a share named Share2 and grant User1 Full control access to Share2.
– Enable Remote Desktop.What are the effects of the configurations? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
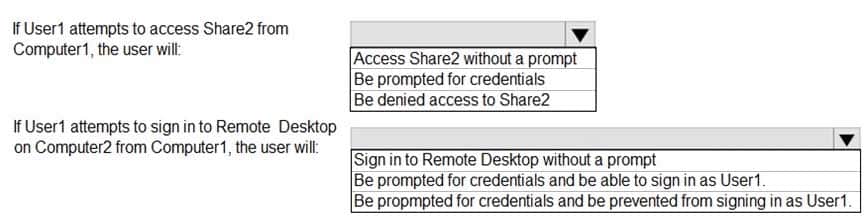
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q11 101 Question -
HOTSPOT
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains a group named Group1.
All the computers in the domain run Windows 10. Each computer contains a folder named C:\Documents that has the default NTFS permissions set.
You add a folder named C:\Documents\Templates to each computer.
You need to configure the NTFS permissions to meet the following requirements:
– All domain users must be able to open the files in the Templates folder.
– Only the members of Group1 must be allowed to edit the files in the Templates folder.How should you configure the NTFS settings on the Templates folder? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
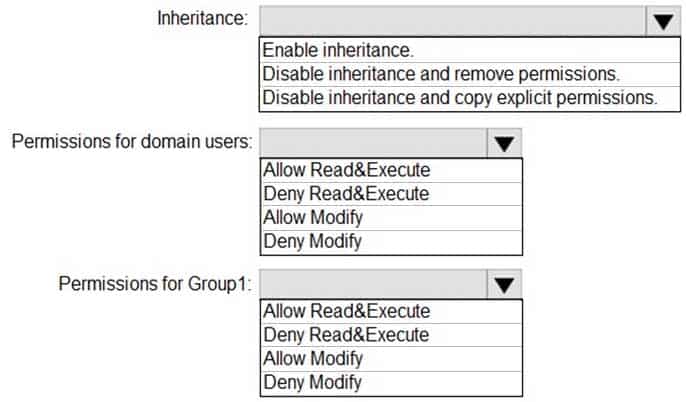
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q12 102 Question -
You deploy Windows 10 to 20 new laptops.
The laptops will be used by users who work at customer sites. Each user will be assigned one laptop and one Android device.
You need to recommend a solution to lock the laptop when the users leave their laptop for an extended period.
Which two actions should you include in the recommendation? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
- Enable Bluetooth discovery.
- From the Settings app, configure the Dynamic lock settings.
- From Sign-in options, configure the Windows Hello settings.
- From the Settings app, configure the Lock screen settings.
- Pair the Android device and the laptop.
- From the Settings app, configure the Screen timeout settings.
-
You have a workgroup computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 has the user accounts shown in the following table.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q14 103 User3, User4, and Administrator sign in and sign out on Computer1. User1 and User2 have never signed in to Computer1.
You are troubleshooting policy issues on Computer1. You sign in to Computer1 as Administrator.
You add the Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) snap-in to an MMC console.
Which users can you select in the RSoP wizard?
- User1, User3, and User4 only
- Administrator only
- User1, User2, User3, User4, and Administrator
- User3, User4, and Administrator only
Explanation:
When selecting users in RSoP, you can only select users who have previously logged on to the system. -
HOTSPOT
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 is in a workgroup.
Computer1 contains the local users shown in the following table.
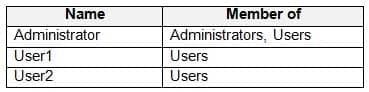
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q15 104 Computer1 contains the folders shown in the following table.
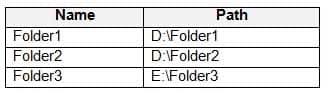
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q15 105 The Users group has Full control permissions to Folder1, Folder2, and Folder3.
User1 encrypts two files named File1.docx and File2.docx in Folder1 by using EFS.
Which users can move each file? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q15 106 Question 
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q15 106 Answer Explanation:EFS works by encrypting a file with a bulk symmetric key. The symmetric key that is used to encrypt the file is then encrypted with a public key that is associated with the user who encrypted the file. Because the encryption & decryption operations are performed at a layer below NTFS, it is transparent to the user and all their applications.
Box 1: User1, User2, and Administrator
Box 2: User1 only
-
HOTSPOT
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 is in a workgroup.
Computer1 contains the local users shown in the following table.
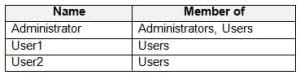
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q16 107 Computer1 contains the folders shown in the following table.
The Users group has Full control permissions to Folder1, Folder2, and Folder3.
User1 encrypts two files named File1.docx and File2.docx in Folder1 by using EFS.
Which users can move each file? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q16 109 
MD-100 Windows 10 Part 05 Q16 110 Explanation:EFS works by encrypting a file with a bulk symmetric key. The symmetric key that is used to encrypt the file is then encrypted with a public key that is associated with the user who encrypted the file. Because the encryption & decryption operations are performed at a layer below NTFS, it is transparent to the user and all their applications.
Box 1: User1, User2, and Administrator
Box 2: User1 only
-
Your network contains an Active Directory domain. The domain contains a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10. Computer1 contains a folder named Folder1.
You plan to share Folder1. Everyone will have Read share permissions, and administrators will have Full control share permission.
You need to prevent the share from appearing when users browse the network.
What should you do?
- Enable access-based enumeration.
- Deny the List NTFS permissions on Folder1.
- Add Folder1 to a domain-based DFS namespace.
- Name the share Folder1$.
Explanation:Appending a dollar sign to share name prevents a share from appearing when users browse the network.
Incorrect Answers:
Access-based enumeration will hide the share from anyone who doesn’t have permission to access the share. However, as ‘Everyone’ has Read access to the share, the share would appear for everyone when they browse the network. -
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a computer that runs Windows 10. The computer contains a folder. The folder contains sensitive data.
You need to log which user reads the contents of the folder and modifies and deletes files in the folder.
Solution: From the properties of the folder, you configure the Auditing settings and from Audit Policy in the local Group Policy, you configure Audit object access.
Does this meet the goal?
- Yes
- No
Explanation:Files and folders are objects and are audited through object access.
-
You have a computer named Computer1 that runs Windows 10.
On Computer1, you turn on File History.
You need to protect a folder named D:\Folder1 by using File History.
What should you do?
- From File Explorer, modify the Security settings of D:\Folder1
- From Backup and Restore (Windows 7), modify the backup settings
- From the Settings app, configure the Backup settings
- From File History in Control Panel, configure the Advanced settingsa
Explanation:To configure File History, click More options on the Backup screen. The Backup options screen allows you to set how often File History backs up your files and how long versions are saved.
-
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a computer that runs Windows 10. The computer contains a folder. The folder contains sensitive data.
You need to log which user reads the contents of the folder and modifies and deletes files in the folder.
Solution: From the properties of the folder, you configure the Auditing settings and from the Audit Policy in the local Group Policy, you configure Audit system events.
Does this meet the goal?
- Yes
- No
Explanation:Files and folders are objects and are audited through object access, not though system events.