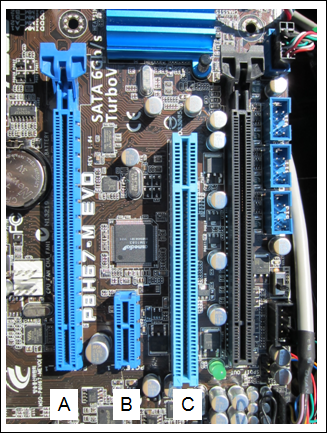
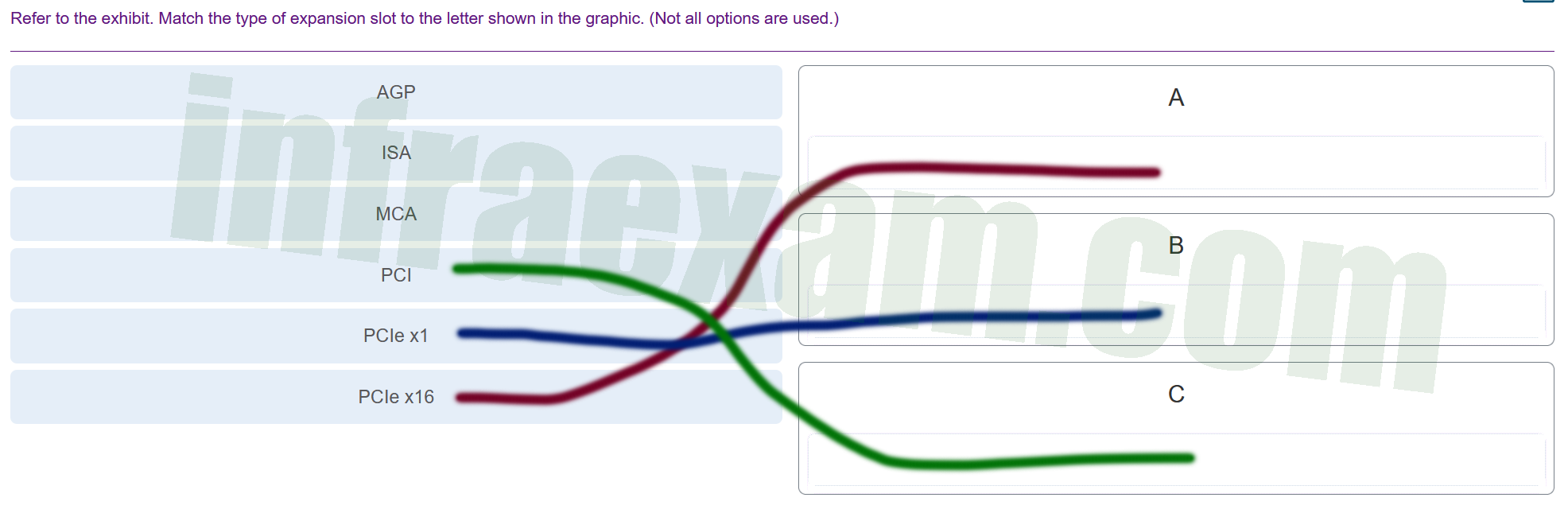
Refer to the exhibit. Match the type of expansion slot to the letter shown in the graphic. (Not all options are used.)
| Explanation & Hint:
A ==> PCI: This is the older type of expansion slot, typically used for a variety of expansion cards before the advent of PCIe. It’s larger than the PCIe x1 slot and has been a standard for many years. B ==> PCIe x1: This is the smaller expansion slot designed for cards that do not require a lot of bandwidth, like network cards, sound cards, or other interface cards. C ==> PCIe x16: This is the largest slot on the motherboard, typically used for graphics cards (GPUs). It offers the highest bandwidth of these slots, which is necessary for the high data transfer rates required by modern graphics cards. These slots allow for the addition of various functionalities to the computer system by accommodating compatible expansion cards. Each slot type is designed to provide a certain level of data transfer speed, and they are keyed differently to prevent the insertion of incompatible cards. AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port):
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture):
MCA (Micro Channel Architecture):
Each of these architectures was used in different eras of computing and has been largely replaced by newer technologies such as PCI and PCI Express, which offer greater speed, flexibility, and bandwidth. |