15.6.2 Lab – Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default Routes Answers Full 100% 2024
This is Cisco 15.6.2 Lab – Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default Routes Answers Full 100% 2024 for Cisco CCNA 2 v7 SRWE v7.02.
| CCNA 2 v7 & 7.02 | |
| This Modules 14 - 16 | |
| Modules 14 - 16 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Final Exam & PT Skills | |
| ITN Practice Skills Assessment - PT Answers | NA |
| SRWE Practice Skills Assessment – PT Part 1 Answers | NA |
| SRWE Practice Skills Assessment – PT Part 2 Answers | NA |
| SRWE Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Answers | NA |
| SRWE Hands On Skills Exam Answers | NA |
| SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| SRWE Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
Lab – Configure IPv4 and IPv6 Static and Default Routes (Answers Version)
Answers Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the Answers copy only.
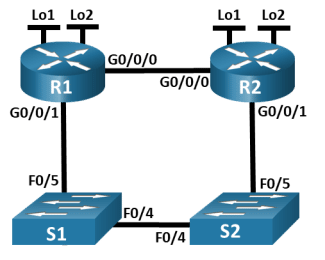
Topology
Addressing Table
|
Device |
Interface |
IP Address / Prefix |
|
R1 |
G0/0/0 |
172.16.1.1 /24 |
|
R1 |
G0/0/0 |
2001:db8:acad:2::1 /64 |
|
R1 |
G0/0/0 |
fe80::1 |
|
R1 |
G0/0/1 |
192.168.1.1 /24 |
|
R1 |
G0/0/1 |
2001:db8:acad:1::1 /64 |
|
R1 |
G0/0/1 |
fe80::1 |
|
R1 |
Loopback1 |
10.1.0.1 /24 |
|
R1 |
Loopback1 |
2001:db8:acad:10::1 /64 |
|
R1 |
Loopback1 |
fe80::1 |
|
R1 |
Loopback2 |
209.165.200.225 /27 |
|
R1 |
Loopback2 |
2001:db8:acad:209::1 /64 |
|
R1 |
Loopback2 |
fe80::1 |
|
R2 |
G0/0/0 |
172.16.1.2 /24 |
|
R2 |
G0/0/0 |
2001:db8:acad:2::2 /64 |
|
R2 |
G0/0/0 |
fe80::2 |
|
R2 |
G0/0/1 |
192.168.1.2 /24 |
|
R2 |
G0/0/1 |
2001:db8:acad:1::2 /64 |
|
R2 |
G0/0/1 |
fe80::2 |
|
R2 |
Loopback1 |
10.2.0.1 /24 |
|
R2 |
Loopback1 |
2001:db8:acad:11::2 /64 |
|
R2 |
Loopback1 |
fe80::2 |
|
R2 |
Loopback2 |
209.165.200.193 /27 |
|
R2 |
Loopback2 |
2001:db8:acad:210::1 /64 |
|
R2 |
Loopback2 |
fe80::2 |
Objectives
Part 1: Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
Part 2: Configure and verify IP and IPv6 addressing on R1 and R2
Part 3: Configure and verify static and default routing for IPv4 on R1 and R2
Part 4: Configure and verify static and default routing for IPv6 on R1 and R2
Background / Scenario
Static and Default routing are the simplest forms of network routing and configured manually. They are fixed, meaning that they do not change dynamically to meet changing network conditions. They are either valid and made available to the routing table or invalid and not made available to the routing table. Static routes have an administrative distance of one by default. However, static and default routes can be configured with an administrator-defined administrative distance. This capability allows the administrator to put the static or default route in reserve, and only make it available to the routing table when routes with lower administrative distances (usually generated by dynamic routing protocols) are no longer valid.
Note:In this lab you will configure static, default, and floating default routes for both IPv4 and IPv6 which may not reflect networking best practices.
Note: The routers used with CCNA hands-on labs are Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 (universalk9 image). The switches used in the labs are Cisco Catalyst 2960s with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) (lanbasek9 image). Other routers, switches, and Cisco IOS versions can be used. Depending on the model and Cisco IOS version, the commands available and the output produced might vary from what is shown in the labs. Refer to the Router Interface Summary Table at the end of the lab for the correct interface identifiers.
Note: Ensure that the routers and switches have been erased and have no startup configurations. If you are unsure contact your Answers.
Answers Note: Refer to the Answers Lab Manual for the procedures to initialize and reload devices
Required Resources
- 2 Routers (Cisco 4221 with Cisco IOS XE Release 16.9.4 universal image or comparable)
- 2 Switches (Cisco 2960 with Cisco IOS Release 15.2(2) lanbasek9 image or comparable)
- 1 PC (Windows with a terminal emulation program, such as Tera Term)
- Console cables to configure the Cisco IOS devices via the console ports
- Ethernet cables as shown in the topology
Instructions
Part 1:Build the Network and Configure Basic Device Settings
In Part 1, you will set up the network topology and configure basic settings on the PC hosts and switches.
Step 1:Cable the network as shown in the topology.
Attach the devices as shown in the topology diagram, and cable as necessary.
Step 2:Configure basic settings for each router.
- Assign a device name to the router.
Open configuration window
router(config)# hostname R1
router(config)# hostname R2
- Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
R1(config)# no ip domain lookup
R2(config)# no ip domain lookup
- Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
R1(config)# enable secret class
R2(config)# enable secret class
- Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
R1(config)# line console 0
R1(config-line)# password cisco
R1(config-line)# login
R2(config)# line console 0
R2(config-line)# password cisco
R2(config-line)# login
- Assign cisco as the VTY password and enable login.
R1(config)# line vty 0 4
R1(config-line)# password cisco
R1(config-line)# login
R2(config)# line vty 0 4
R2(config-line)# password cisco
R2(config-line)# login
- Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
R1(config)# service password-encryption
R2(config)# service password-encryption
- Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
R1(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
R2(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
- Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
R1(config)# exit
R1# copy running-config startup-config
R2(config)# exit
R2# copy running-config startup-config
Close configuration window
Step 3:Configure basic settings for each switch.
Open configuration window
- Assign a device name to the switch.
switch(config)# hostname S1
switch(config)# hostname S2
- Disable DNS lookup to prevent the router from attempting to translate incorrectly entered commands as though they were host names.
S1(config)# no ip domain-lookup
S2(config)# no ip domain-lookup
- Assign class as the privileged EXEC encrypted password.
S1(config)# enable secret class
S2(config)# enable secret class
- Assign cisco as the console password and enable login.
S1(config)# line console 0
S1(config-line)# password cisco
S1(config-line)# login
S2(config)# line console 0
S2(config-line)# password cisco
S2(config-line)# login
- Assign cisco as the VTY password and enable login.
S1(config)# line vty 0 15
S1(config-line)# password cisco
S1(config-line)# login
S2(config)# line vty 0 15
S2(config-line)# password cisco
S2(config-line)# login
- Encrypt the plaintext passwords.
S1(config)# service password-encryption
S2(config)# service password-encryption
- Create a banner that warns anyone accessing the device that unauthorized access is prohibited.
S1(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
S2(config)# banner motd $ Authorized Users Only! $
- Shutdown all interfaces that will not be used.
S1(config)# interface range f0/1–3, f0/6-24, g0/1-2
S1(config-if-range)# shutdown
S2(config)# interface range f0/1–3, f0/6-24, g0/1-2
S2(config-if-range)# shutdown
- Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file.
S1(config-if-range)# exit
S1# copy running-config startup-config
S2(config-if-range)# exit
S2# copy running-config startup-config
Question:
Issuing the command show cdp neighbors at this point on R1 or R2 results in an empty list. Explain.
Because the router interfaces are shut down by default.
Close configuration window
Part 2:Configure and verify IPv4 and IPv6 addressing on R1 and R2
In Part 2, you will configure and verify the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on R1 and R2. Use the table above for the information necessary to complete this part.
Step 1:Configure IP addresses for both routers.
Open configuration window
- Enable IPv6 Unicast Routing on both routers.
R1(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
R2(config)# ipv6 unicast-routing
- Configure the IP address for all the interfaces according to the Addressing Table.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:2::1/64
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config–if)# interface g0/0/1
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1::1/64
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config–if)# interface lo1
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:10::1/64
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config–if)# interface lo2
R1(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1 link-local
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:209::1/64
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config)# interface g0/0/0
R2(config-if)# ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:2::2/64
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config–if)# interface g0/0/1
R2(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1::2/64
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config–if)# interface lo1
R2(config-if)# ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:11::2/64
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
R2(config–if)# interface lo2
R2(config-if)# ip address 209.165.200.193 255.255.255.224
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::2 link-local
R2(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:210::1/64
R2(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 2:Verify addressing
- Issue the command to verify IPv4 assignments to the interfaces.
R1# show ip interface brief
InterfaceIP-AddressOK? Method StatusProtocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0172.16.1.1YES unsetupup
GigabitEthernet0/0/1192.168.1.1YES manual upup
Serial0/1/0unassignedYES unsetupup
Serial0/1/1unassignedYES manual upup
Loopback110.1.0.1YES manual upup
Loopback2209.165.200.225 YES manual upup
f
R2# show ip interface brie
InterfaceIP-AddressOK? Method StatusProtocol
GigabitEthernet0/0/0172.16.1.2YES manual upup
GigabitEthernet0/0/1192.168.1.2YES manual upup
GigabitEthernet0unassignedYES unsetdowndown
Loopback110.2.0.1YES manual upup
Loopback2209.165.200.193 YES manual upup
- Issue the command to verify IPv6 assignments to the interfaces.
R1# show ipv6 interface brief
GigabitEthernet0/0/0[up/up]
FE80::1
2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1
GigabitEthernet0/0/1[up/up]
FE80::1
2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1
Loopback1[up/up]
FE80::1
2001:DB8:ACAD:10::1
Loopback2[up/up]
FE80::1
2001:DB8:ACAD:209::1
R2# show ipv6 interface brief
GigabitEthernet0/0/0[up/up]
FE80::2
2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2
GigabitEthernet0/0/1[up/up]
FE80::2
2001:DB8:ACAD:1::2
Loopback1[up/up]
FE80::2
2001:DB8:ACAD:11::2
Loopback2[up/up]
FE80::2
2001:DB8:ACAD:210::1
Step 3:Save your configuration
Save the running configuration to the startup configuration file on both routers.
R1# copy running-config startup-config
R2# copy running-config startup-config
Close configuration window
Part 3:Configure and verify static and default routing for IPv4 on R1 and R2
In Part 3, you will configure static and default routing on R1 and R2 to enable full connectivity between the routers using IPv4. Once again, the static routing being used here is not meant to represent best practice, but to assess your ability to complete the required configurations.
Step 1:On R1, configure a static route to R2’s Loopback1 network, using R2’s G0/0/1 address as the next hop.
open configuration window
- Use the ping command to ensure that R2’s G0/0/1 interface is reachable.
- Configure a static route for R2’s Loopback1 network via R2’s G0/0/1 address.
R1(config)# ip route 10.2.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2
Step 2:On R1, configure a static default route via R2’s G0/0/0 address.
- Use the ping command to ensure that R2’s G0/0/0 interface is reachable.
- Configure a static default route via R2’s G0/0/0 address.
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.2
Step 3:On R1, configure a floating static default route via R2’s G0/0/1 address.
Configure a floating static default route with an AD of 80 via R2’s G0/0/1 address.
R1(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2 80
Step 4:On R2, configure a static default route via R1’s G0/0/0 address
- Use the ping command to ensure that R1’s G0/0/0 interface is reachable.
- Configure a static default route via R1’s G0/0/0 address.
R2(config)# ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.1
Step 5:Verify that the routes are operational.
- Use the show ip route command to ensure that R1’s routing table shows the static and default routes.
R1# show ip route
Codes: L – local, C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route, H – NHRP, l – LISP
a – application route
+ – replicated route, % – next hop override, p – overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is 172.16.1.2 to network 0.0.0.0
S*0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.2
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C10.1.0.0/24 is directly connected, Loopback1
L10.1.0.1/32 is directly connected, Loopback1
S10.2.0.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.1.2
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C172.16.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
L172.16.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
192.168.1.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L192.168.1.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
209.165.200.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C209.165.200.224/27 is directly connected, Loopback2
L209.165.200.225/32 is directly connected, Loopback2
- On R1, issue the command traceroute 10.2.0.1. The output should show that the next hop is 192.168.1.2.
R1# traceroute 10.2.0.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.2.0.1
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.1.2 1 msec *2 msec
- On R1, issue the command traceroute 209.165.200.193. The output should show that the next hop is 172.16.1.2.
R1# traceroute 209.165.200.193
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 209.165.200.193
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 172.16.1.2 2 msec *3 msec
- Issue the shutdown command on R1 G0/0/0.
R1# config terminal
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0
R1(config-if)# shutdown
R1(config-if)# end
- Demonstrate that the floating static route is working. First, issue the show ip route static command. You should see two static routes. A default static route with an AD of 80 and a static route to the 10.2.0.0/24 network with an AD of 1.
R1# show ip route static
Codes: L – local, C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2
i – IS-IS, su – IS-IS summary, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2
ia – IS-IS inter area, * – candidate default, U – per-user static route
o – ODR, P – periodic downloaded static route, H – NHRP, l – LISP
S*0.0.0.0/0 [80/0] via 192.168.1.2
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
S10.2.0.0/24 [1/0] via 192.168.1.2
- Demonstrate the floating static route is working by issuing the traceroute 209.165.200.193 command. The traceroute will show the next hop as 192.168.1.2.
R1# traceroute 209.165.200.193
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 209.165.200.193
VRF info: (vrf in name/id, vrf out name/id)
1 192.168.1.2 1 msec *1 msec
- Issue the no shutdown command on R1 G0/0/0.
R1# config terminal
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# end
Close configuration window
Part 4:Configure and verify static and default routing for IPv6 on R1 and R2
In Part 4, you will configure static and default routing on R1 and R2 to enable full connectivity between the routers using IPv6. Once again, the static routing being used here is not meant to represent best practice, but to assess your ability to complete the required configurations.
Step 1:On R2, configure a static route to R1’s Loopback1 network, using R1’s G0/0/1 address as the next hop.
Open configuration window
- Use the ping command to ensure that R1’s G0/0/1 interface is reachable.
- Configure a static route for R1’s Loopback1 network via R1’s G0/0/1 address.
R2(config)# ipv6 route 2001:db8:acad:10::/64 2001:db8:acad:1::1
Step 2:On R2, configure a static default route via R1’s G0/0/0 address.
- Use the ping command to ensure that R1’s G0/0/0 interface is reachable.
- Configure a static default route via R1’s G0/0/0 address.
R2(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:2::1
Step 3:On R2, configure a floating static default route via R1’s G0/0/1 address.
Configure a floating static default route with an AD of 80 via R2’s G0/0/1 address.
R2(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:1::1 80
Step 4:On R1, configure a static default route via R1’s G0/0/0 address.
- Use the ping command to ensure that R2’s G0/0/0 interface is reachable.
- Configure a static default route via R2’s G0/0/0 address.
R1(config)# ipv6 route ::/0 2001:db8:acad:2::2
Step 5:Verify that the routes are operational.
- Use the show ipv6 route command to ensure that R2’s routing table shows the static and default routes.
R2# show ipv6 route
IPv6 Routing Table – default – 11 entries
Codes: C – Connected, L – Local, S – Static, U – Per-user Static route
B – BGP, R – RIP, H – NHRP, I1 – ISIS L1
I2 – ISIS L2, IA – ISIS interarea, IS – ISIS summary, D – EIGRP
EX – EIGRP external, ND – ND Default, NDp – ND Prefix, DCE – Destination
NDr – Redirect, RL – RPL, O – OSPF Intra, OI – OSPF Inter
OE1 – OSPF ext 1, OE2 – OSPF ext 2, ON1 – OSPF NSSA ext 1
ON2 – OSPF NSSA ext 2, a – Application
S ::/0 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1
C2001:DB8:ACAD:1::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/1, directly connected
L2001:DB8:ACAD:1::2/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/1, receive
C2001:DB8:ACAD:2::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/0, directly connected
L2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/0, receive
S2001:DB8:ACAD:10::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1
C2001:DB8:ACAD:11::/64 [0/0]
via Loopback1, directly connected
L2001:DB8:ACAD:11::1/128 [0/0]
via Loopback1, receive
C2001:DB8:ACAD:210::/64 [0/0]
via Loopback2, directly connected
L2001:DB8:ACAD:210::1/128 [0/0]
via Loopback2, receive
LFF00::/8 [0/0]
via Null0, receive
- On R2, issue the command traceroute 2001:db8:acad:10::1. The output should show that the next hop is 2001:db8:acad:1::1.
R2# traceroute 2001:db8:acad:10::1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 2001:DB8:ACAD:10::1
1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 6 msec 1 msec 1 msec
- On R2, issue the command traceroute 2001:db8:acad:209::1. The output should show that the next hop is 2001:db8:acad:2::1.
R2# traceroute 2001:db8:acad:209::1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 2001:DB8:ACAD:209::1
1 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1 1 msec 2 msec 1 msec
- Issue the shutdown command on R2 G0/0/0.
R2# config terminal
R2(config)# interface g0/0/0
R2(config-if)# shutdown
R2(config-if)# end
- Demonstrate the floating static route is working. First issue the show ipv6 route static command. You should see two static routes. A default static route with an AD of 80 and a static route to the 2001:db8:acad:10::/64 network with an AD of 1.
R2# show ipv6 route static
Codes: C – Connected, L – Local, S – Static, U – Per-user Static route
B – BGP, R – RIP, H – NHRP, I1 – ISIS L1
I2 – ISIS L2, IA – ISIS interarea, IS – ISIS summary, D – EIGRP
NDr – Redirect, RL – RPL, O – OSPF Intra, OI – OSPF Inter
OE1 – OSPF ext 1, OE2 – OSPF ext 2, ON1 – OSPF NSSA ext 1
ON2 – OSPF NSSA ext 2, a – Application
S ::/0 [80/0]
via 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1
S2001:DB8:ACAD:10::/64 [1/0]
via 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1
- Lastly, demonstrate that the floating static route is working by issuing the traceroute 2001:db8:acad:209::1 command. The traceroute will show the next hop as 2001:db8:acad:1::1.
R2# traceroute 2001:db8:acad:209::1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 2001:DB8:ACAD:209::1
1 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 2 msec 1 msec 1 msec
Close configuration window
Router Interface Summary Table
|
Router Model |
Ethernet Interface #1 |
Ethernet Interface #2 |
Serial Interface #1 |
Serial Interface #2 |
|
1800 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
1900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2801 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
2811 |
Fast Ethernet 0/0 (F0/0) |
Fast Ethernet 0/1 (F0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
2900 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0 (G0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/1 (G0/1) |
Serial 0/0/0 (S0/0/0) |
Serial 0/0/1 (S0/0/1) |
|
4221 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
|
4300 |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/0 (G0/0/0) |
Gigabit Ethernet 0/0/1 (G0/0/1) |
Serial 0/1/0 (S0/1/0) |
Serial 0/1/1 (S0/1/1) |
Note: To find out how the router is configured, look at the interfaces to identify the type of router and how many interfaces the router has. There is no way to effectively list all the combinations of configurations for each router class. This table includes identifiers for the possible combinations of Ethernet and Serial interfaces in the device. The table does not include any other type of interface, even though a specific router may contain one. An example of this might be an ISDN BRI interface. The string in parenthesis is the legal abbreviation that can be used in Cisco IOS commands to represent the interface.
End of document
Device Configs – Final
Router R1
R1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 1877 bytes
!
version 16.9
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname R1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$RYDJ$t/c7oO27si0aj8ubUL4Zm0
!
no aaa new-model
!
no ip domain lookup
!
login on-success log
!
subscriber templating
!
ipv6 unicast-routing
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
redundancy
mode none
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 10.1.0.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:10::1/64
!
interface Loopback2
ip address 209.165.200.225 255.255.255.224
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:209::1/64
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1/64
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
ipv6 address FE80::1 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1/64
!
interface Serial0/1/0
no ip address
!
interface Serial0/1/1
no ip address
!
ip forward-protocol nd
no ip http server
ip http secure-server
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.2
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.2 80
ip route 10.2.0.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.2
!
ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C
!
line con 0
password 7 02050D480809
login
transport input none
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
password 7 0822455D0A16
login
!
end
Router R2
R2# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 1881 bytes
!
version 16.9
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
platform qfp utilization monitor load 80
no platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname R2
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$UiZY$inHX.hTsQ1oHjw81NXiLb/
!
no aaa new-model
!
no ip domain lookup
!
login on-success log
!
subscriber templating
!
ipv6 unicast-routing
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
redundancy
mode none
!
interface Loopback1
ip address 10.2.0.1 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:11::2/64
!
interface Loopback2
ip address 209.165.200.193 255.255.255.224
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:210::1/64
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0
ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0
shutdown
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::2/64
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/1
ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
ipv6 address FE80::2 link-local
ipv6 address 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::2/64
!
interface Serial0/1/0
no ip address
!
interface Serial0/1/1
no ip address
!
ip forward-protocol nd
no ip http server
ip http secure-server
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.1
!
ipv6 route 2001:DB8:ACAD:10::/64 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1
ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:1::1 80
ipv6 route ::/0 2001:DB8:ACAD:2::1
!
!
control-plane
!
banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C
!
line con 0
password 7 045802150C2E
login
transport input none
stopbits 1
line aux 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
password 7 14141B180F0B
login
!
end
Switch S1
S1# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 1707 bytes
!
version 15.2
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname S1
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$.IEP$MS5z.mITakTYTwLWyXHxI0
!
no aaa new-model
system mtu routing 1500
!
!
no ip domain-lookup
!
!
spanning-tree mode pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
!
interface FastEthernet0/6
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/7
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/8
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/9
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/10
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/11
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/12
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/13
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/14
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/15
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/16
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/17
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/18
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/19
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/20
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/21
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/22
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/23
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
shutdown
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
ip http server
ip http secure-server
!
banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C
!
line con 0
password 7 121A0C041104
login
line vty 0 4
password 7 121A0C041104
login
line vty 5 15
login
!
end
Switch S2
S2# show run
Building configuration…
Current configuration : 1707 bytes
!
version 15.2
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
service password-encryption
!
hostname S2
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
enable secret 5 $1$IYmC$UST.4nznlABNG3REPrLc7/
!
no aaa new-model
system mtu routing 1500
!
!
no ip domain-lookup
!
!
spanning-tree mode pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/2
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/3
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/4
!
interface FastEthernet0/5
!
interface FastEthernet0/6
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/7
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/8
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/9
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/10
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/11
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/12
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/13
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/14
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/15
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/16
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/17
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/18
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/19
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/20
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/21
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/22
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/23
shutdown
!
interface FastEthernet0/24
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
shutdown
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
shutdown
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
ip http server
ip http secure-server
!
banner motd ^C Authorized Users Only! ^C
!
line con 0
password 7 00071A150754
login
line vty 0 4
password 7 00071A150754
login
line vty 5 15
login
!
end
| CCNA 2 v7 & 7.02 | |
| This Modules 14 - 16 | |
| Modules 14 - 16 Exam Answers | Online Test |
| Final Exam & PT Skills | |
| ITN Practice Skills Assessment - PT Answers | NA |
| SRWE Practice Skills Assessment – PT Part 1 Answers | NA |
| SRWE Practice Skills Assessment – PT Part 2 Answers | NA |
| SRWE Final PT Skills Assessment (PTSA) Answers | NA |
| SRWE Hands On Skills Exam Answers | NA |
| SRWE Practice Final Exam Answers | Online Test |
| SRWE Final Exam Answers | Online Test |