IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1101 Certification Practice Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
ITE 8 | IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1101 Certification Practice Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This is Cisco IT Essentials (Version 8.0) – IT Essentials A+ 220-1101 Certification Practice Exam Answer 2023 2024 Full 100% and Cisco NetAcad ITE v7 – IT Essentials (Version 7.00) – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 2023 2024
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Final - Mid-term - Cert | |
| Chapter 1 -9 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Chapter 10 - 14 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1001 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1002 | Online Test |
IT Essentials (Version 8.0) – IT Essentials A+ 220-1101 Certification Practice Exam Answers 2023 2024
-
What characteristic best describes a touch screen?
- an input device that recognizes touch and pressure as instructions
- an output device used to present information from a laptop onto a screen
- an output device that uses LED, LCD, or OLED technology
- a head-mounted device that provides head-motion and eye-tracking sensors and displays three-dimensional images
-
Explanation & Hint: - An input device that recognizes touch and pressure as instructions: This is the most accurate description of a touch screen. Touch screens are primarily input devices that allow users to interact with a device (like a smartphone, tablet, or information kiosk) through touch or pressure. This interaction can include tapping, swiping, pinching, or pressing on the screen’s surface. The technology detects the presence and location of a touch, translating these actions into commands or inputs for the device.
- An output device used to present information from a laptop onto a screen: This description is more suitable for a monitor or display screen, not specifically a touch screen. While touch screens do display information (hence they also function as output devices), their defining characteristic is not just the presentation of information, but their ability to register and respond to touch. Traditional monitors or display screens without touch capabilities would fit this description better.
- An output device that uses LED, LCD, or OLED technology: This description refers to the technology used for the visual display aspect of screens, including touch screens. LED (Light Emitting Diode), LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), and OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) are types of display technologies that can be found in both touch and non-touch screens. While this description is relevant to the display part of a touch screen, it does not encompass the touch-responsive aspect, which is essential to defining a touch screen.
- A head-mounted device that provides head-motion and eye-tracking sensors and displays three-dimensional images: This description fits virtual reality (VR) headsets or augmented reality (AR) headsets rather than touch screens. VR and AR headsets are worn on the head and often include sensors to track head motion and sometimes eye movement, providing an immersive experience with three-dimensional images. This technology is distinct from touch screens, as it focuses on virtual or augmented environments and typically does not involve direct touch interaction.
In summary, while some of these descriptions touch on aspects related to display technology or other types of interactive devices, the first option is the most accurate and specific in describing a touch screen’s primary function as an input device that recognizes touch and pressure.
-
What characteristic best describes a projector?
- an output device used to present information from a laptop onto a screen
- an output device that uses LED, LCD, or OLED technology
- a head-mounted device that provides head-motion and eye-tracking sensors and displays three-dimensional images
- an input device often used to provide secure access to locations or devices by using voice, facial, or fingerprint recognition
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a projector is:
An output device used to present information from a laptop onto a screen: A projector is fundamentally an output device that takes input from various sources like laptops, media players, or other electronic devices and projects the visual content onto a screen or surface. This makes it ideal for presentations, movies, or educational purposes, where a larger viewable area is required. It translates digital signals into visual content that is then enlarged and displayed.
Now, let’s briefly explain why the other options are not suitable for a projector:
- An output device that uses LED, LCD, or OLED technology: This description is more suitable for describing types of display screens or televisions. While modern projectors can use technologies like LED (Light Emitting Diode) or LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) for image projection, this description alone does not encapsulate the primary function of a projector, which is to project images onto a separate surface.
- A head-mounted device that provides head-motion and eye-tracking sensors and displays three-dimensional images: This description corresponds to virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) headsets, not projectors. VR and AR headsets are worn on the head and typically involve immersive experiences with three-dimensional images, often with interactive elements like head-motion and eye-tracking sensors.
- An input device often used to provide secure access to locations or devices by using voice, facial, or fingerprint recognition: This option describes biometric security systems, which are input devices used for security purposes. They are designed to recognize unique physical characteristics like voice, face, or fingerprints to grant access. This is unrelated to the function of a projector, which is to display visual content on a larger scale.
Therefore, the most accurate description of a projector is as an output device used for displaying or presenting visual content from various sources onto a larger surface.
-
What characteristic best describes a stylus?
- a pen-like tool that allows input by touching the surface of the screen
- an input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath
- an input device for playing games and flight simulation applications
- a device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a stylus is:
A pen-like tool that allows input by touching the surface of the screen: A stylus is essentially a small tool resembling a pen, designed to interact with the touch-sensitive surface of devices like tablets, smartphones, or touchscreen laptops. It allows for precise control when using the device, making it ideal for drawing, writing, or selecting items on the screen. The stylus translates the user’s input into digital signals that the device can interpret.
Now, let’s clarify why the other options do not describe a stylus:
- An input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath: This description is more fitting for a scanner. Scanners are used to digitize physical documents or images by scanning them with a light source and converting them into digital data. This is distinctly different from the function of a stylus, which is intended for direct interaction with a touchscreen.
- An input device for playing games and flight simulation applications: This describes gaming controllers or specialized joysticks, which are used to provide input for video games, including flight simulation applications. These devices offer various controls like buttons, triggers, and joysticks to enhance the gaming experience. They are different from a stylus, which is not specifically designed for gaming purposes.
- A device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers: This is a description of a KVM switch (Keyboard, Video, Mouse switch). A KVM switch enables the control of multiple computers using a single keyboard, mouse, and monitor setup. It is unrelated to the functionality of a stylus, which is used as an input device for touchscreen interactions.
In summary, a stylus is best characterized as a pen-like tool that enables precise input on the surface of a touchscreen device.
-
What characteristic best describes an AR headset?
- a head-mounted device that superimposes images and audio over a real world image and can provide users immediate access to information about their real surroundings
- an input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath
- an input device for playing games and flight simulation applications
- a device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes an AR (Augmented Reality) headset is:
A head-mounted device that superimposes images and audio over a real-world image and can provide users immediate access to information about their real surroundings: AR headsets are designed to overlay digital content (like images, audio, or other sensory enhancements) onto the real world. This technology enhances the user’s perception of reality by adding virtual elements to their physical environment, often in real-time. AR headsets are used in various applications, including gaming, education, and professional fields, to provide an interactive experience that combines the virtual with the real world.
Now, let’s look at why the other options do not describe an AR headset:
- An input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath: This describes a scanner. Scanners are used to convert physical documents or images into digital form by scanning them. This is fundamentally different from AR headsets, which do not digitize physical objects but rather augment the user’s view of the real world with digital information.
- An input device for playing games and flight simulation applications: While this could partially apply to AR headsets in the context of gaming, it’s more specifically a description of gaming controllers or simulation equipment. AR headsets do facilitate gaming experiences by augmenting reality, but they are not limited to this function and are used for a broader range of applications.
- A device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers: This describes a KVM switch (Keyboard, Video, Mouse switch). A KVM switch enables the use of a single set of input and output devices to control multiple computers, which is unrelated to the functionality of an AR headset.
In summary, an AR headset’s defining characteristic is its ability to augment the real world with digital content, enhancing the user’s environment with overlaid images, audio, and potentially other sensory data.
-
What characteristic best describes a signature pad?
- an input device that provides verification of package delivery by digitizing a written name
- an input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath
- an input device for playing games and flight simulation applications
- a device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a signature pad is:
An input device that provides verification of package delivery by digitizing a written name: A signature pad is a specialized input device designed to capture and digitize handwritten signatures. It is commonly used in situations where a physical signature is required for verification or authorization purposes, such as in package delivery, point-of-sale transactions, or document signing. The signature pad converts the motion and pressure of a pen or stylus into a digital image that represents the handwritten signature.
Now, let’s explain why the other options do not describe a signature pad:
- An input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath: This description fits a scanner, specifically a flatbed scanner. Scanners are used to digitize physical documents or images, but they do not specialize in capturing handwritten signatures like signature pads.
- An input device for playing games and flight simulation applications: This describes gaming controllers or specialized joysticks used in gaming and simulation contexts. These devices provide interactive control for video games and simulators but are unrelated to the function of a signature pad, which is focused on capturing handwritten signatures.
- A device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers: This is a description of a KVM switch (Keyboard, Video, Mouse switch). A KVM switch allows a single set of input and output devices to control multiple computers. It is a device for managing computer inputs and outputs, not related to the signature capturing function of a signature pad.
In summary, a signature pad is accurately described as an input device that captures and digitizes handwritten signatures, commonly used for verification purposes in various transactions and document-signing scenarios.
-
What characteristic best describes a magstripe reader?
- an input device that reads encoded information from the back of plastic cards
- an input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath
- an input device for playing games and flight simulation applications
- a device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers1
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a magstripe reader is:
An input device that reads encoded information from the back of plastic cards: A magstripe reader, short for magnetic stripe reader, is specifically designed to read the encoded information stored in the magnetic stripe found on the back of plastic cards like credit cards, debit cards, identification cards, and key cards. When a card is swiped through the reader, it decodes the information contained in the magnetic stripe, which is typically used for processing transactions, verifying identity, or granting access.
Now, let’s look at why the other options do not describe a magstripe reader:
- An input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath: This describes a scanner, particularly a flatbed scanner. Such scanners are used for digitizing physical documents or images by scanning them, which is different from the function of a magstripe reader that reads data from magnetic stripes.
- An input device for playing games and flight simulation applications: This refers to gaming controllers or flight simulators’ joysticks. These devices are used to interact with and control video games or simulation software. They are not related to the functionality of magstripe readers, which are used for reading encoded data on cards.
- A device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers: This describes a KVM switch (Keyboard, Video, Mouse switch). A KVM switch is used to control multiple computers using a single set of peripherals (keyboard, mouse, and monitor). This technology is unrelated to magstripe readers, which are focused on reading data from magnetic stripes on cards.
In summary, a magstripe reader is best characterized as an input device designed to read and decode information from the magnetic stripes on plastic cards.
-
What characteristic best describes a barcode scanner?
- an input device that reads barcodes affixed to most retail products
- an input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath
- an input device for playing games and flight simulation applications
- a device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a barcode scanner is:
An input device that reads barcodes affixed to most retail products: A barcode scanner is a device specifically designed to read and interpret barcodes, which are typically found on retail products, inventory items, and various other objects. The scanner uses light sensors to translate the barcode’s patterns of lines (or other geometric patterns in the case of 2D barcodes) into digital data. This data is then used for various purposes like tracking inventory, processing sales transactions, or managing product information.
Now, let’s clarify why the other options do not describe a barcode scanner:
- An input device that digitizes an image by placing the document on a flat glass surface and scanning from underneath: This describes a flatbed scanner, which is used for digitizing physical documents or images. Flatbed scanners capture the entire surface of a document, unlike barcode scanners that specifically read the encoded information in barcodes.
- An input device for playing games and flight simulation applications: This refers to gaming controllers or specialized joysticks used for interactive control in video games, including flight simulators. These devices are unrelated to the function of barcode scanners, which are used in retail and inventory management contexts.
- A device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers: This is a description of a KVM switch (Keyboard, Video, Mouse switch). KVM switches enable a single set of input and output devices (keyboard, mouse, monitor) to control multiple computers, which is distinct from the purpose of barcode scanners.
In summary, a barcode scanner is accurately characterized as an input device that reads and decodes barcodes typically found on retail products and other items for data capture and processing.
-
What characteristic best describes a keyboard?
- the first type of input device used for creating documents and emails
- an input device for playing games and flight simulation applications
- a device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers
- an input device that recognizes touch and pressure as instructions
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a keyboard is:
The first type of input device used for creating documents and emails: A keyboard is a fundamental input device primarily used for typing text into computers and various digital devices. It is essential for creating documents, composing emails, and entering commands or data. Keyboards feature a set of keys representing letters, numbers, symbols, and function commands, facilitating a wide range of typing and input tasks.
Now, let’s explain why the other options do not describe a keyboard:
- An input device for playing games and flight simulation applications: While keyboards can be used for gaming, including playing games and flight simulation applications, this is not their primary or defining characteristic. Gaming keyboards are a specialized subset, but the general purpose of keyboards extends well beyond gaming.
- A device that allows the use of one set of keyboard, mouse, and monitor to control multiple computers: This describes a KVM switch (Keyboard, Video, Mouse switch), not a keyboard. A KVM switch allows a single set of input and output devices (keyboard, mouse, and monitor) to control multiple computers, which is different from the inherent function of a keyboard.
- An input device that recognizes touch and pressure as instructions: This description is more apt for touchscreens or touchpad devices. While a keyboard does require pressure on the keys to register input, this characteristic is not as distinctive as it is for devices like touchscreens, where touch and pressure are the primary modes of interaction.
In summary, a keyboard is best characterized as a primary input device used for typing and entering data, which is integral for tasks like creating documents and composing emails.
-
What characteristic best describes an NFC device?
- an input device allowing users to pay for a product by tapping their credit card or smartphone on another device
- an input device that reads barcodes affixed to most retail products
- an input device that reads encoded information from the back of plastic cards
- a pen-like tool that allows input by touching the surface of the screen
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes an NFC (Near Field Communication) device is:
An input device allowing users to pay for a product by tapping their credit card or smartphone on another device: NFC devices enable wireless communication over short distances, typically a few centimeters. They are commonly used for contactless payment systems, where a user can make a payment by tapping an NFC-enabled credit card, smartphone, or other devices against an NFC reader. The technology allows for quick and secure data exchange, facilitating transactions in retail settings, access control, and various other applications that require close-range wireless communication.
Now, let’s clarify why the other options do not describe an NFC device:
- An input device that reads barcodes affixed to most retail products: This describes a barcode scanner, which reads the visual patterns of lines or shapes on barcodes to obtain information. While barcode scanners are also used in retail, they function differently from NFC devices, relying on optical scanning rather than wireless communication.
- An input device that reads encoded information from the back of plastic cards: This is a description of a magstripe (magnetic stripe) reader. Magstripe readers decode the information stored in the magnetic stripe on the back of credit cards and other types of cards. Unlike NFC devices, they require physical swiping of the card through the reader.
- A pen-like tool that allows input by touching the surface of the screen: This describes a stylus, a tool used for precise input on touchscreen devices. A stylus is used for writing or drawing on a touchscreen and is unrelated to the wireless communication capabilities of NFC devices.
In summary, an NFC device is best characterized as a technology that enables contactless communication and data transfer, often used for facilitating contactless payments by tapping a compatible card or smartphone on the NFC reader.
-
What characteristic best describes a mouse?
- the first type of input device used to navigate the graphical user interface
- an input device allowing users to pay for a product by tapping their credit card or smartphone on another device
- an input device that reads barcodes affixed to most retail products
- an input device that reads encoded information from the back of plastic cards
-
Explanation & Hint: The characteristic that best describes a mouse is:
The first type of input device used to navigate the graphical user interface: A mouse is a peripheral input device primarily designed to interact with a computer’s graphical user interface (GUI). It allows users to point, click, drag, and scroll with ease, facilitating navigation and selection within the GUI. The mouse has been a fundamental component of personal computing since the popularization of graphical interfaces, providing an intuitive way to interact with computers.
Now, let’s explain why the other options do not describe a mouse:
- An input device allowing users to pay for a product by tapping their credit card or smartphone on another device: This describes Near Field Communication (NFC) devices used in contactless payment systems. Users can make payments by tapping an NFC-enabled credit card or smartphone against an NFC reader. This function is not related to the capabilities of a computer mouse.
- An input device that reads barcodes affixed to most retail products: This is a description of a barcode scanner. Barcode scanners are used to read the information encoded in the barcodes found on retail products and other items. This technology is distinct from that of a mouse, which is used for navigating and interacting with a computer’s GUI.
- An input device that reads encoded information from the back of plastic cards: This refers to magstripe (magnetic stripe) readers. These devices read the data stored in the magnetic stripes on the back of cards like credit cards and key cards. Unlike a mouse, which is used for GUI navigation, magstripe readers are used for processing card-based transactions and access control.
In summary, a mouse is best characterized as a pioneering input device for computer GUI navigation, offering precise control for pointing, clicking, and executing commands within a graphical environment.
-
A technician is building a thick client workstation that would be used to run a database and wants to ensure the best protection against errors. What type of memory would be best suited for this?
- ECC
- RDRAM
- DDR3
- DDR2
Answers Explanation & Hints: RDRAM, DDR2, and DDR3 RAM do not offer any error correction abilities for data within the memory module. ECC RAM allows for the detection of multiple bit errors and correction of single bit errors within the memory modules.
-
A user has just upgraded a gaming system with 8GB of DDR3 800 MHz RAM and still finds that the system lags during gameplay. The system has a high end graphics card, liquid cooling, and a 7,200 rpm EIDE drive. What can the user do to improve system performance?
- Change the voltage setting for the RAM.
- Replace the EIDE drive with an SSD.
- Replace the liquid cooling system with a high speed ball bearing fan cooling system.
- Add two more case fans.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because the system has already has a high end graphics card and a liquid cooling system, it is already optimized for the gaming environment and the introduction of the new additional RAM would add to its performance. The only hardware component that could result in the lag in performance in this scenario is the hard drive, which would perform much faster when replaced with an SSD.
-
A network administrator would like to use one keyboard, mouse, and display to monitor and control multiple servers in the server room. Which device should the administrator purchase to accomplish this?
- joystick
- digitizer
- KVM switch
- VR headset
Answers Explanation & Hints: A keyboard, video, mouse (KVM) switch is a hardware device that can be used to control more than one computer from a single set of devices, often called a console, consisting of a keyboard, video monitor, and mouse.
-
A user wants to purchase a monitor that will be light, consume the least amount of power, and provide deep dark levels in the display. Which display type would best meet these requirements?
- plasma
- LCD
- LED
- OLED
Answers Explanation & Hints: For monitors of the same Plasma monitors consume the highest amount of power followed by LCD monitors and than LED monitors. Of the different types of LED monitors, OLED monitors will offer the deeper dark levels in the display.
-
An art appreciation college professor wants to apply for a technology grant to allow students to have a virtual tour of the Louvre Museum in Paris, France. Which mobile technology should the professor request to accomplish this goal?
- e-reader
- GPS
- smart watch
- VR headset
Answers Explanation & Hints: A virtual reality (VR) headset can be used in a training situation for educational purposes such as touring a remote location, military training, or medical training. Gaming applications are also popular. A person wears a special headset that projects a slightly different image to each eye, allowing the image to be viewed in 3D. The person may also wear headphones and a microphone depending on the application.
-
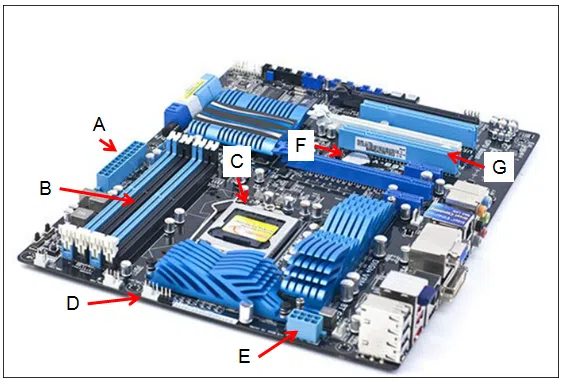
Refer to the exhibit. Match the letter found in the exhibit with the description. (Not all options are used.)
ITE 8 IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 002 ITE 8 IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 01 Explanation & Hint: A ==> Main motherboard power socket: If ‘A’ is pointing to the primary power connector, it is where the main power cable from the power supply unit (PSU) connects to the motherboard. This power socket typically accepts a 20-pin or 24-pin connector that supplies power to the entire board.
B ==> Memory slot: Memory slots are where the RAM modules are installed and they usually come in pairs to support dual-channel configurations. They are long, thin connectors with clips on either side to hold the RAM in place.
C ==> CPU socket: The CPU socket is specifically designed to house the processor and has multiple pin configurations, or contact points, that match the CPU’s design—whether that’s LGA (Land Grid Array), PGA (Pin Grid Array), or BGA (Ball Grid Array) for different types of processors.
E ==> Auxiliary power socket: The auxiliary power socket provides additional power directly to the CPU, especially for those that have high power requirements. It’s usually an 8-pin or 4-pin connector.
F ==> Powers CMOS when computer is off: The CMOS battery is a small, round battery on the motherboard that provides power to the BIOS/UEFI firmware’s CMOS settings, preserving them when the computer is turned off or unplugged from the mains.
For ‘D’ and ‘G’, since there are no corresponding matches, I cannot provide a description. However, typically on a motherboard:
- ‘D’ could be related to various components, such as a PCI slot, SATA connectors, USB headers, or other interfaces.
- ‘G’ could be pointing to anything from expansion card slots, additional chipset heatsinks, onboard audio, or network controllers, among others.
If these descriptions do not seem to fit what you’re seeing, please ensure that the correct labels correspond to the appropriate components on the motherboard. If you can view the image and verify the components each letter is pointing to, I can provide more precise explanations.
-
Which sequence of steps is required to correctly install a heat sink and fan assembly onto a CPU in a desktop PC?
- 1. Apply a small amount of thermal compound to the CPU.
2. Align the heat sink and fan assembly retainers with the holes on the motherboard.
3. Place the fan and heat sink assembly onto the CPU socket.
4. Tighten the fan and heat sink assembly retainers to secure the assembly in place.
5. Connect the assembly power cable to the CPU fan connector on the motherboard. - 1. Connect the assembly power cable to the CPU fan connector on the motherboard.
2. Align the heat sink and fan assembly retainers with the holes on the motherboard.
3. Place the fan and heat sink assembly onto the CPU socket.
4. Tighten the fan and heat sink assembly retainers to secure the assembly in place.
5. Place the correctly aligned CPU gently into the socket. - 1. Place the correctly aligned CPU gently into the socket.
2. Align the heat sink and fan assembly retainers with the holes on the motherboard.
3. Place the fan and heat sink assembly onto the CPU socket.
4. Tighten the fan and heat sink assembly retainers to secure the assembly in place.
5. Connect the assembly power cable to the CPU fan connector on the motherboard. - 1. Apply a small amount of thermal compound to the CPU.
2. Align the heat sink and fan assembly retainers with the holes on the motherboard.
3. Place the correctly aligned CPU gently into the socket.
4. Tighten the fan and heat sink assembly retainers to secure the assembly in place.
5. Connect the assembly power cable to the CPU fan connector on the motherboard.Answers Explanation & Hints: The CPU must be securely installed in its socket on the mother board before the thermal paste is applied, the heat sink and fan assembly is installed, and the fan is connected to the CPU fan power connector on the motherboard.
- 1. Apply a small amount of thermal compound to the CPU.
-
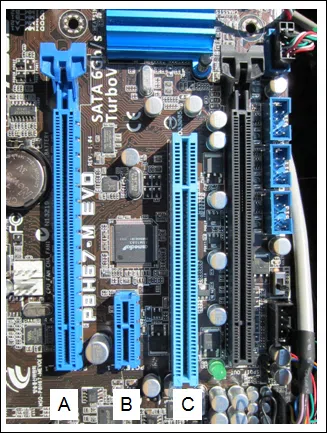
Refer to the exhibit. Match the type of expansion slot to the letter shown in the graphic. (Not all options are used.)
ITE 8 IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 001 ITE 8 IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 02 Explanation & Hint: A ==> PCI: This is the older type of expansion slot, typically used for a variety of expansion cards before the advent of PCIe. It’s larger than the PCIe x1 slot and has been a standard for many years.
B ==> PCIe x1: This is the smaller expansion slot designed for cards that do not require a lot of bandwidth, like network cards, sound cards, or other interface cards.
C ==> PCIe x16: This is the largest slot on the motherboard, typically used for graphics cards (GPUs). It offers the highest bandwidth of these slots, which is necessary for the high data transfer rates required by modern graphics cards.
These slots allow for the addition of various functionalities to the computer system by accommodating compatible expansion cards. Each slot type is designed to provide a certain level of data transfer speed, and they are keyed differently to prevent the insertion of incompatible cards.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port):
- AGP was developed specifically for video cards. It was widely used from the late 1990s until the mid-2000s.
- It provided a direct connection between the card and the memory, which allowed for faster processing of complex graphics.
- AGP slots were designed to deliver faster performance with 3D graphics and video streams.
- Over time, AGP was phased out in favor of the more versatile and faster PCI Express (PCIe) standard for graphics cards.
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture):
- ISA was an early type of expansion slot used from the early 1980s into the late 1990s.
- It was initially a 16-bit system, later expanded to 32-bit in the EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) version.
- ISA slots were used for a wide variety of cards, including modems, sound cards, and network cards.
- As computer technology evolved, ISA slots became less common due to their limited speed and bandwidth compared to newer standards.
MCA (Micro Channel Architecture):
- MCA was introduced by IBM in the mid-1980s with their PS/2 systems.
- It was designed to overcome the limitations of ISA by providing a higher bandwidth and greater expansion capabilities.
- MCA supported plug and play configuration, which allowed the system to automatically configure devices.
- Despite its technical advantages, MCA was not widely adopted outside of IBM’s own systems due to proprietary issues and competition from the more open and widely supported PCI standard.
Each of these architectures was used in different eras of computing and has been largely replaced by newer technologies such as PCI and PCI Express, which offer greater speed, flexibility, and bandwidth.
-
Which connector would be used for a laptop external hard drive?
- DVI
- eSATA
- PATA
- SATA
- S/PDIF
-
Explanation & Hint: For connecting an external hard drive to a laptop, the most suitable connector among those listed would be:
eSATA (External Serial Advanced Technology Attachment):
- eSATA is an extension to the SATA interface, tailored for external storage needs. It allows for the connection of external mass storage devices like hard drives while offering the same performance as internal drives.
- eSATA ports are designed to connect external SATA devices and are capable of fast data transfer rates comparable to internal drives.
The other connectors listed have different primary purposes:
DVI (Digital Visual Interface):
- DVI is used to connect a video source, such as a computer, to a display device, like a monitor. It is not used for hard drives.
PATA (Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment):
- PATA, also known as IDE, is an older disk drive interface that was common in desktop and laptop computers before being largely replaced by SATA. External drives with PATA interfaces typically use USB rather than a direct PATA connection because laptops do not have external PATA connectors.
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment):
- SATA is used for connecting internal hard drives and SSDs in desktop and laptop computers. While SATA itself is for internal connections, the external version is eSATA.
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface Format):
- S/PDIF is an audio interface used to transmit digital audio signals between devices. It is not used for data storage devices like hard drives.
Therefore, for an external hard drive, eSATA is the correct choice if both the hard drive and the laptop have eSATA ports. If they do not, external hard drives often use USB connectors (such as USB 3.0 or USB-C) for universal compatibility and convenience.
-
Which three PC desktop functions are typically provided on the front panel and must be connected to the motherboard? (Choose three.)
- network activity light
- PC power button
- drive activity light
- USB connectors
- CPU temperature indicator
- audio power button
Answers Explanation & Hints: USB connectors, PC power button, and drive activity light are the most common PC front panel functions. If available, the network activity light, CPU temperature indicator, and audio power button are not typically located on the front panel of the computer.
-
Which statement is correct about applying firmware updates?
- Firmware updates are sometimes irreversible.
- It is possible to use the Roll Back feature to reverse the change.
- The firmware updates can be installed automatically using the Windows Service Pack utility.
- Firmware updates should not be included as part of the preventive maintenance program.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Firmware updates can make the hardware unusable if not performed correctly. Sometimes it is not possible to revert to the original firmware once the update has been performed because of how the changes are applied to the EPROM technology.
-
Which RAID level allows for extension of a dynamic volume without any redundancy?
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Answers Explanation & Hints: A RAID array 0 allows for striping over a variety of disks without providing for any redundancy. This allows for faster read and write functions because they are spread over multiple drives and thus adds the benefit of the simultaneous use of multiple actuator arms of the various hard drives.
-
A computer technician has recommended a data storage system that combines data striping and parity. The user has a limited budget and is prepared to forego performance to implement this system. Which RAID system would meet these requirements?
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 0+1
Answers Explanation & Hints: RAID 5 best meets the required storage and cost specifications. RAID 0 provides data striping without redundancy. RAID 1 uses disk mirroring and has a high cost. RAID 0+1 combines data striping and mirroring but also has a high cost.
-
A user has a computer with a single hard drive and a RAID adapter installed. Which additional component is necessary to complete the RAID installation?
- a USB connection
- a floppy disk drive
- one or more additional hard drives
- a DVD drive
Answers Explanation & Hints: RAID installations require two or more hard drives. Floppy drives and DVD drives cannot form part of a RAID array. A USB connector may be used to access external hard drives that are not part of a RAID array.
-
A user is connecting a home entertainment system and wants to use one cable to carry all the digital video and audio signals from the source device to the LCD TV. What type of cable should the user use?
- DVI-D
- HDMI
- VGA
- S-Video
Answers Explanation & Hints: A DVI-D cable will carry video digital signals only, and the S-Video and VGA cable types carry only analog video signals. An HDMI cable will carry both the audio and video digital signals.
-
A user has connected a USB 3.0 device to a computer using a 3 ft (1m) USB 3.0 cable. However, instead of an expected data transfer rate of up to 5 Gb/s, the user notes a data transfer rate of no more than 450 Mb/s. What is the most probable reason for this lower than expected data transfer rate?
- The device was connected to a USB 2.0 port on the computer.
- The cable used exceeds the maximum length that allows USB 3.0 to transfer data at 5Gb/s.
- The device was connected to a USB 1.1 port on the computer.
- The USB 3.0 cable is faulty.
Answers Explanation & Hints: USB 2.0 allows transmission speeds up to 480 Mb/s and USB 1.1 allows transmission rates of up to 12 Mb/s in full-speed mode. A transmission speed of 450 Mb/s would indicate that a USB 2.0 port was used on the computer because USB devices can only transfer data up to the maximum speed allowed by the specific port. The generally accepted maximum length of a USB 3.0 cable is 9.8 ft (3m) which is three times the length of the cable used in this example, so the cable length is acceptable for full USB 3.0 capability. If a USB cable is faulty then no data transfer at all is likely to occur.
-
What transfers heat away from the processor first?
- cooling fins
- thermal compound
- CPU fan
- case fans
Answers Explanation & Hints: Thermal compound is the first item of contact with the CPU, which then dissipates the heat to the cooling fins. The heat is conducted away from the CPU by the CPU fan and finally exhausted through the case fans.
-
Which design specification criterion is most important when designing a computer that will be a thin client whose applications are accessed from a remote virtual server?
- amount of RAM
- amount of local hard drive storage
- number of processor cores
- speed of network card
-
Explanation & Hint: When designing a computer that will be a thin client with applications accessed from a remote virtual server, the most important design specification criterion is the:
Speed of network card:
- Thin clients rely heavily on network connectivity to access applications and resources on a remote server. Therefore, having a fast and reliable network card is crucial to ensure that the thin client can communicate with the server quickly and without interruption.
- The network card’s speed will affect the overall performance of remote applications, as it determines how quickly data can be transmitted between the thin client and the server.
The other components, while important in a general sense, are less critical for a thin client setup:
Amount of RAM:
- While sufficient RAM is necessary for running the local operating system and any client-side processes, thin clients typically require less RAM than standard desktop computers because the heavy processing is done on the server side.
Amount of local hard drive storage:
- Local storage is less important for a thin client because the applications and data are stored on the remote server. Thin clients often use minimal local storage or might even boot from a network location.
Number of processor cores:
- The local processing power in a thin client is generally not as critical, since the processing is done on the server. A thin client needs just enough processing power to run the client operating system and handle the user interface for the remote applications.
In summary, the speed of the network card is typically the most critical specification for a thin client, as it directly impacts the client’s ability to effectively use remote services and applications.
-
A technician is building a workstation that will be used for virtualization. Which two components would the technician use? (Choose two.)
- dual monitors
- high-end graphics card
- liquid cooling
- maximum amount of RAM
- multicore processors
Answers Explanation & Hints: Dual monitors are useful in a video editing station. Liquid cooling assemblies and high-end graphics cards are normally required in high performance gaming systems. A virtualization workstation would need maximum RAM and CPU cores.
-
A small company is setting up a new remote satellite office. Employees in the remote office need to access network resources from the main office of the company. An IT manager is deciding whether to deploy thin or thick clients at the remote office. What is the key technical factor to be considered?
- network sharing requirements
- RAID level required
- requirements for the display screens between thin and thick clients
- internet connection bandwidth between the main and remote office
Answers Explanation & Hints: Thick clients are standard computers that have their own operating system, applications, and local storage. They are stand-alone systems and all of the processing is performed locally on the computer. On the other hand, thin clients are typically low-end network computers that rely on remote servers to perform all data processing. Thin clients in a remote office will require a reliable, high-bandwidth, internet connection to a server. Typically thin clients do not have any internal storage and have limited local resources.
-
Which three components would a technician use in building a CAD workstation? (Choose three.)
- SSD
- maximum RAM
- specialized graphics card
- TV Tuner card
- high-end sound card
- Windows 7 Home edition
Answers Explanation & Hints: A TV Tuner card is normally used for an home entertainment system and a high end sound card is normally used for a gaming system. Windows 7 Home edition would not be the operating system of choice on a CAD station. A CAD station would normally require a specialized graphics card, large amounts of fast RAM, and a high performance storage device, such as SSD.
-
A customer asks for a solution to a printer problem that is beyond the knowledge level of the technician. What should the technician do?
- Try to fix the problem anyway.
- Tell the customer to call the printer manufacturer to fix the problem.
- Gather as much information as possible and escalate the problem.
- Ask the customer to call again when another technician can provide a solution to the problem.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Trying to fix a problem that is beyond the knowledge level of the technician may create additional problems.
-
After consulting the manufacturer manuals, a technician applies a series of recommended solutions that resolve a problem with a workstation computer. What is the next step in the troubleshooting process that the technician should perform?
- Verify the solution and confirm full system functionality.
- Document the findings, actions, and outcomes.
- Test the theory of probable cause.
- Determine the next steps to resolve the problem.
Answers Explanation & Hints: After the recommended solutions have been applied to resolve the problem, full system functionality should be verified and preventive measures implemented if applicable. This would be followed by documenting the solution and actions. Determining the next steps to resolve the problem and testing the theory of probable cause have already been completed in this scenario.
-
After questioning a user about the problems being experienced with a PC operating system, the support technician suspects that a recent service pack installation has failed. Which step of the troubleshooting process has the technician just concluded?
- Test the theory to determine the cause of the problem.
- Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem.
- Establish a theory of probable cause.
- Document findings, actions, and outcomes.
Answers Explanation & Hints: By suspecting that an operating system service pack has failed to install successfully, the technician has established a theory of probable cause of the problem. The next step would be to test the theory to determine the cause of the problem, followed by establishing a plan of action to resolve the problem. Documentation is the final step and would occur after the solution has been verified and the system restored to full functionality.
-
A computer locks up frequently, and no error message can be seen on screen. The problem occurs every time the user attempts to restart the computer. What is the most likely reason for this problem?
- The index service is not running.
- The power supply has failed.
- A startup file has become corrupted.
- The CPU is overheating.
Answers Explanation & Hints: If the power supply has failed the PC would turn off or could display a stop error message if the failure is partial. The index service not running does not cause a PC to lockup. No startup file is likely to be corrupted as the issue appears during normal operation. An overheading CPU would cause the computer to lockup.
-
A technician suspects that a power supply is faulty. How can it be checked?
- by checking the temperature of the power supply
- by using a multimeter
- by taking apart the power supply
- by powering up the PC after disconnecting each connector in turn
Answers Explanation & Hints: The temperature of the power supply does not indicate if it is operational. A PC technician should never open a power supply as dangerous voltages might still be present even when disconnected. Disconnecting the connectors in turn and powering the PC is not a recommended practice. In the absence of a power supply tester, a multimeter can allow to check if voltages are present.
-
What are two possible causes of a computer running slowly? (Choose two.)
- The hard drive has been partitioned.
- The computer is overheating.
- The CPU has been overclocked.
- The RAM is not compatible with the motherboard.
- Not enough RAM is installed in the system.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Not having enough RAM or the computer overheating can cause a computer to run slowly. An overclocked CPU would tend to speed up the computer. If the RAM is not compatible with the motherboard, the computer would not start up. Partitioning a hard drive does not cause the computer to run more slowly.
-
Which type of network consists of several geographically dispersed networks that cover a large area?
- LAN
- WAN
- PAN
- SAN
Answers Explanation & Hints: A Wide Area Network (WAN) is a collection of geographically dispersed networks.
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a network contained in a single floor, building, or campus.
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is a network that reaches at most 10 meters.
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a network specifically constructed to connect storage devices to each other.
-
A user is setting up a home wireless network. Which type of device must the user have in order to establish the wireless network and provide access to the internet for multiple home devices?
- hub
- wireless router
- switch
- patch panel
Answers Explanation & Hints: A wireless router connects multiple wireless devices to the network. It will then aggregate the internet access requests from home devices to the internet.
-
A customer who travels frequently wants to know which technology is the most suitable for being connected to the corporate network at all times at low cost. Which network technology would a network administrator recommend?
- satellite
- ISDN
- cellular
- microwave
Answers Explanation & Hints: Cellular networks can provide access to data networks at any given time. ISDN and microwave networks require a fixed location. Satellite would work, but is very expensive.
-
Which device converts digital signals to analog signals and vice versa?
- hub
- switch
- modem
- router
Answers Explanation & Hints: Modems are used to connect computers to POTS analog lines. Hubs, routers, and switches work using digital signals at all times.
-
A tourist is traveling through the countryside and needs to connect to the internet from a laptop. However, the laptop only has Wi-Fi and Ethernet connections. The tourist has a smartphone with 3G/4G connectivity. What can the tourist do to allow the laptop to connect to the internet?
- Enable tethering and create a hotspot.
- Use an Ethernet cable to connect the smartphone to the laptop.
- Use the smartphone to access web pages and then pass the web pages to the laptop.
- Use the smartphone to access the internet through a satellite connection and then share that connection with the laptop.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Many cell phones have the ability to connect to other devices through a feature called tethering. The connection can be made using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or a USB cable. Once a device is connected, it is able to use the cellular connection of the phone to access the internet. When a cellular phone allows Wi-Fi devices to connect and use the mobile data network, this is called a hotspot.
-
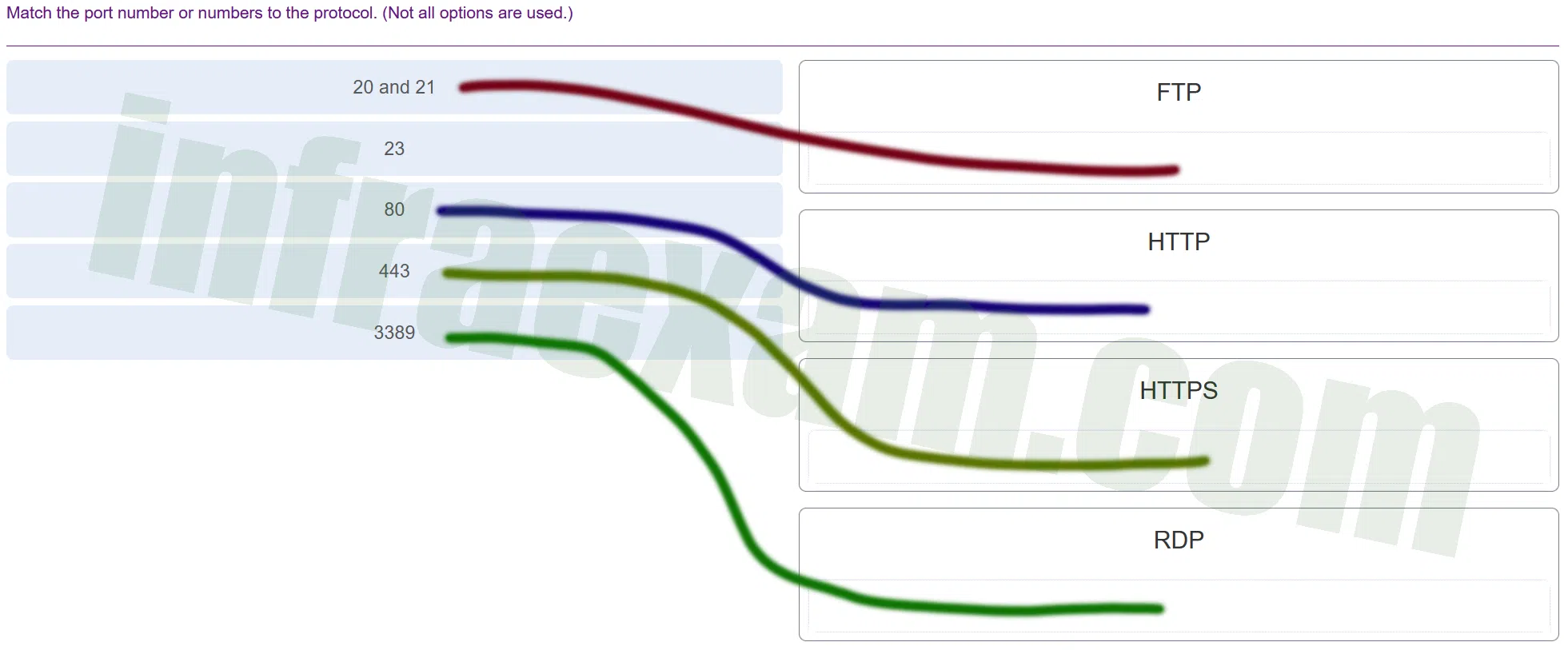
Match the port number or numbers to the protocol. (Not all options are used.)
ITE 8 IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 03 Explanation & Hint: - FTP (File Transfer Protocol) typically uses ports 20 and 21. Port 21 is for control (commands) and port 20 for data transfer.
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) uses port 80 for standard web traffic.
- HTTPS (HTTP Secure) uses port 443 for secure web traffic, which is encrypted using SSL/TLS.
- RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) uses port 3389 for remote desktop connections.
-
Which protocol automates assignment of IP addresses on a network, and which port number does it use? (Choose two.)
- DHCP
- DNS
- SMB
- 53
- 67
- 80
Answers Explanation & Hints: DNS uses port 53 and translates URLs to IP addresses. SMB provides shared access to files and printers and uses port 445. Port 80 is used by HTTP. HTTP is a protocol used to communicate between a web browser and a server.
-
A technician wants to use Remote Desktop to configure another PC. Which firewall port on the remote PC should be open in order for Remote Desktop to work?
- 23
- 115
- 443
- 3389
Answers Explanation & Hints: Port 23 is used for Telnet, port 115 is used by Simple File Transfer Protocol, and port 443 is used by HTTPS. Port 3389 is used by the RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) to connect to other PCs remotely.
-
A network administrator is setting up the wireless network in a small office. The administrator wants to choose a wireless protocol standard that takes advantage of 5 GHz throughput but is also compatible with a few existing devices that operate at 2.4 GHz. Which wireless standard should the administrator deploy?
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- 802.11ac
Answers Explanation & Hints: 802.11n operates at both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz and is backward compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g. 802.11b and 802.11g operate at 2.4 GHz only. 802.11a and 802.11ac operate at 5 GHz only.
-
A network administrator is setting up a device for two objectives. The first objective is to store frequently visited web content on the device so that the local users can access the content quickly. Another objective is to achieve a certain level of network security by hiding the internal IP addresses. Which device should the administrator set up?
- firewall
- web server
- proxy server
- authentication server
Answers Explanation & Hints: A proxy server has the authority to act as another computer. A popular use for a proxy server is to act as storage or cache for web pages that are frequently accessed by devices on the internal network. In addition, a proxy server can effectively hide the IP addresses of internal hosts because all requests going out to the internet are sourced from the IP address of the proxy server.
-
A small company is setting up a web server to promote products on the internet. The company network administrator is searching for an online service that can provide the domain name and name resolution services. Which type of online service can provide such functions to the company?
- web service
- DHCP service
- proxy service
- DNS service
Answers Explanation & Hints: An online DNS service can provide domain name registration and name resolution for the registered domain services. This service eliminates the need for setting up a fully functional DNS server in the small company.
-
Which networking device transmits data to all ports regardless of the destination address?
- router
- switch
- hub
- firewall
Answers Explanation & Hints: The purpose of a hub is to extend the cabling range by regenerating and repeating signals. Switches,routers, and firewalls send data to the destination by examining the header of the packet to determine the exit ports.
-
Which device will prevent data from flooding out of every port with the exception of broadcast traffic and traffic to unknown destination addresses?
- modem
- hub
- router
- switch
Answers Explanation & Hints: A switch will select the outgoing port for every data frame based on the MAC destination address. A hub will flood all ports with any traffic. A router will select the outgoing port based on the IP destination address and the modem is used to connect the LAN to a WAN.
-
What are plenum rated cables used for?
- for cables that are used between buildings
- for cables that are installed inside the floors and ceilings of buildings
- for cables that are used to connect workstations to wall sockets
- for cables that are used to connect computers back-to-back
Answers Explanation & Hints: In case of a fire, a nonplenum rated cable could carry the fire from one part of a building to another. Plenum rated cables contain special plastic material that retards fire and produces less smoke when subjected to high temperature. These make them suitable to install in areas where air is circulating.
-
Which tool is more commonly used to check the wire mapping on a Category 5e UTP cable once it is terminated on both ends?
- cable tester
- tone probe
- multimeter
- osciloscope
Answers Explanation & Hints: The most commonly used tool to check the wire mapping on a UTP cable is a cable tester. The multimeter is more commonly used to check voltages. A tone probe is more commonly used for cable identification. The osciloscope is more commonly used to test signals.
-
A technician is troubleshooting a PC unable to connect to the network. What command should be issued to check the IP address of the device?
- tracert
- ping
- nslookup
- ipconfig
Answers Explanation & Hints: The commands tracert and ping are used to test the connectivity of the PC to the network. The command nslookup initiates a query to an Internet domain name server.
-
Which feature will assign a computer an IP address even if there is no working DHCP server in the network?
- DNS
- ARP
- WINS
- APIPA
Answers Explanation & Hints: APIPA is Automatic Private IP Addressing. If there is no working DHCP server, the computer will use a random IP address from the 169.254.X.X class B range. ARP, WINS, and DNS serve other networking purposes.
-
When a wireless network in a small office is being set up, which type of IP addressing is typically used on the networked devices?
- public
- private
- network
- wireless
Answers Explanation & Hints: In setting up the wireless network in a small office, it is a best practice to use private IP addressing because of the flexibility and easy management it offers.
-
In setting up a small office network, the network administrator decides to assign private IP addresses dynamically to workstations and mobile devices. Which feature must be enabled on the company router in order for office devices to access the internet?
- QoS
- NAT
- UPnP
- MAC filtering
Answers Explanation & Hints: Network Address Translation (NAT) is the process used to convert private addresses to internet-routable addresses that allow office devices to access the internet.
-
A company is deploying a wireless network in the distribution facility in a Boston suburb. The warehouse is quite large and it requires multiple access points to be used. Because some of the company devices still operate at 2.4GHz, the network administrator decides to deploy the 802.11g standard. Which channel assignments on the multiple access points will make sure that the wireless channels are not overlapping?
- channels 1, 5, and 9
- channels 2, 6, and 10
- channels 1, 6, and 11
- channels 1, 7, and 13
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the North America domain, 11 channels are allowed for 2.4GHz wireless networking. Among these 11 channels, the combination of channels 1, 6, and 11 are the only non-overlapping channel combination.
-
A support desk technician is asking a customer a series of questions about a problem connecting to the network. Which step of the troubleshooting process is the technician applying?
- Identify the problem.
- Establish a theory of probable cause.
- Establish a plan of action to resolve the problem.
- Test the theory to determine cause.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Before any solutions can be proposed or tested, the problem must first be identified. This is done by gathering information from the customer by asking questions and clarifying details of the problem.
-
What is a result when the DHCP servers are not operational in a network?
- Workstations are assigned with the IP address 0.0.0.0.
- Workstations are assigned with the IP address 127.0.0.1.
- Workstations are assigned with IP addresses in the 10.0.0.0/8 network.
- Workstations are assigned with IP addresses in the 169.254.0.0/16 network.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When workstations are configured with obtaining IP address automatically but DHCP servers are not available to respond to the requests, a workstation can assign itself an IP addresses from the 169.254.0.0/16 network.
-
A user complains to a technician that none of the apps that use a GPS are working properly. What should the technician do first if the GPS function is suspect?
- Replace the gyroscope.
- Calibrate the gyroscope.
- Replace the GPS antenna.
- Ensure the Location setting is enabled.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A global positioning system (GPS) is used for geographic location, navigation, and specialized search results. Both iOS and Android devices have a Location or Location services setting to control whether the GPS is turned on. The WiFi/GPS antenna may need to be replaced if the location service is turned on but GPS still does not work.
-
A teenager has asked the grandparents for a specific type of mobile technology. The grandparents do not remember the specific name of the device, but remember that the teenager wants to receive a cell phone call on it. Which technology is likely to be the one the teenager wants?
- e-reader
- GPS
- smart watch
- VR headset
Answers Explanation & Hints: A smart watch commonly has many of the same functions of a smart phone such as receiving/placing calls, playing online games, and using applications such as a calculator or geolocator.
-
What are the two widths of internal hard drives in laptops? (Choose two.)
- 1.8 inches
- 2.5 inches
- 3.5 inches
- 5.25 inches
- 3.8 inches
Answers Explanation & Hints: Laptop hard drives are 1.8 inches or 2.5 inches in width. Desktop hard drives are 3.5 inches in width. 5.25 inches is the width of optical drives in desktop computers. No components have a width of 3.8 inches.
-
Where is the integrated Wi-Fi antenna typically located in a laptop?
- on the keyboard
- on the system board
- integrated into the wireless card
- above the screen
Answers Explanation & Hints: The integrated Wi-Fi antenna is typically located above the screen and is connected to the wireless card by an antenna wire which is located along the sides of the screen.
-
Because of limited space on a laptop keyboard, some keys have a dual-purpose. What are these keys called?
- control keys
- alternate keys
- special purpose keys
- function keys
Answers Explanation & Hints: Special function keys allow the user to access a second function on a dual-purpose key by pressing the Function (Fn) key at the same time the dual-purpose key is pressed.
-
On a laptop keyboard, which three functions can typically be accessed through the use of special function keys? (Choose three.)
- volume settings
- wireless functionality
- display brightness
- Windows Start menu
- Task Manager
- Control Panels
Answers Explanation & Hints: Volume settings, wireless functionality, and display brightness usually can each be accessed by pressing the Function (Fn) key along with the appropriate dual-purpose key on the keyboard. The Windows Start menu is accessed by pressing the Windows key. Task Manager is accessed by pressing Ctrl-Shift-Esc. Control Panel is accessed by pressing the Windows key + the letter C.
-
Which three components can a docking station make available to a laptop that a port replicator does not? (Choose three.)
- PS/2 ports
- additional hard drive
- additional optical drive
- USB ports
- PCI cards
- networking ports
Answers Explanation & Hints: USB ports, PS/2 ports, and networking ports are found on both port replicators and docking stations. Only docking stations have the ability to connect a laptop to PCI cards, additional hard drives, and optical drives.
-
Which laptop component is required to be replaced or upgraded by a technician rather than by a computer user?
- inverter
- RAM
- hard drive
- battery
Answers Explanation & Hints: RAM, a hard drive, and a battery are all CRUs and can be replaced by the customer. A power inverter is a FRU and requires specialized expertise to replace and should be done by a technician.
-
For mobile devices, what are two advantages of using flash memory storage technology that is the equivalent of solid state drives? (Choose two.)
- light weight components
- power efficiency
- ease of upgrading
- high capacity
- flash memory storage is field-serviceable
Answers Explanation & Hints: The light weight and power efficiency of flash memory components are advantages of using the equivalent of a solid state drive for storage in mobile devices. Flash memory typically does not have the capacity of magnetic storage devices such as hard disk drives. To reduce weight, mobile devices typically do not contain discrete SSD units and the individual flash memory components that are used are not field-serviceable and cannot be upgraded.
-
A teenager is using a remote control unit to control a TV set. Which wireless technology is most likely being used?
- IR
- NFC
- hotspot
- Bluetooth
Answers Explanation & Hints: Infrared (IR) is a wireless connection technology. It can be used to control other IR-enabled devices remotely, such as a TV, set-top box, or audio equipment.
-
Which two mobile device components are field replaceable? (Choose two.)
- touch screen
- SIM card
- internal SSD
- battery
- accelerometer sensors
Answers Explanation & Hints: Mobile devices do not typically have any field serviceable components. Field replaceable components are usually limited to the battery, the SIM card, and a memory card.
-
Which two methods are used to directly connect mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones to a data network? (Choose two.)
- WiMax
- cellular communications
- Bluetooth
- wired Ethernet
- Wi-Fi
Answers Explanation & Hints: Mobile devices connect wirelessly to data networks using either Wi-Fi or a telecommunication provider cellular network. Bluetooth is used to connect to peripherals or other local devices over very short distances. Ethernet is a wired network access technology and is not used by mobile devices. Mobile devices do not typically implement WiMAX technology.
-
A computer technician has successfully returned a laptop to full operation and verified system functionality. Actions the technician performed included modifying the registry and applying patches to the operating systems. What is the next step in the troubleshooting process that the technician should do?
- Reboot the computer.
- Document the solution.
- Consult manufacturer manuals and repair logs.
- Re-attach and test all peripherals.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The technician is ready to conclude the troubleshooting process by documenting the solution. The manufacturer manuals and repair logs would be consulted to establish a plan of action and resolve the problem before the solution has been applied. Rebooting the computer, and re-attaching and testing all peripherals, would occur during the testing and verification stage after the solution has been implemented.
-
A user notices that there is intermittent wireless connectivity on a laptop that is running a wireless PCI Express Micro card using the wireless 802.11n standard. What should the user do to fix the problem?
- Replace the PCI Express Micro card with a Mini-PCIe card.
- Replace the PCI Express Micro card with a Mini-PCI card.
- Move the laptop to a new location.
- Replace the OS on the laptop.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In this situation the intermittent loss of wireless connectivity could be due to the distance from the access point or some obstruction in the signal path. Moving to a new location would remedy the problem. Replacing the wireless PCI Express Micro card or replacing the OS will not resolve the problem.
-
A technician connects a new LCD monitor for the first time and finds the display very pixilated. What is a possible solution to this problem?
- Set the screen to native resolution.
- Change the monitor video connector from DVI to HDMI.
- Power cycle the monitor.
- Set the screen resolution to VGA.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The native screen resolution is the optimum design resolution for the monitor and using this should resolve any display issues. Changing the type of video connector and power cycling the monitor is unlikely to resolve this problem. If the display is pixilated, it is most likely at VGA resolution.
-
A sales representative returns to the office and connects the laptop to an external display device. The display device is powered on, but the laptop image is not showing on the display device. What are two things that should be checked? (Choose two.)
- The laptop is not in sleep mode.
- The video cable is firmly connected.
- The screen refresh rate is set correctly.
- The LCD backlight is properly adjusted.
- The laptop is sending the video signal to the external device.
Answers Explanation & Hints: For an external display device to display a laptop screen, the video cable should be connected firmly on both ends. In addition, the laptop needs to send the video signal to the display device.
-
Which mode would be best suited for a laptop that is displaying oversized images and icons?
- native
- XGA
- VGA
- SVGA
Answers Explanation & Hints: Native resolution will provide the optimal resolution supported by the display on a laptop.
-
A user complains that the image on a laptop looks dull and pale. What is the most likely cause of the problem?
- The screen refresh rate is set incorrectly.
- The display properties are set incorrectly.
- The inverter is damaged or malfunctioning.
- The LCD backlight is not properly adjusted.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The problem of a laptop screen that looks dull and pale is most likely caused by an improper LCD backlight setting.
-
A user complains that the laptop display is flickering. Which two problems could cause this situation? (Choose two.)
- The track pad is dirty.
- Power to the pixels has been cutoff.
- The screen refresh rate is set incorrectly.
- The inverter is damaged or malfunctioning.
- The LCD backlight is not properly adjusted.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The problem of a flickering laptop display is most likely caused by the image not refreshing fast enough or by a malfunctioning/damaged inverter.
-
There is a shared laptop in the conference room of a company. One day an employee turns on the laptop to prepare for joining a videoconference. However, the image on the laptop display is pixilated. What should the user do first to correct the problem?
- Calibrate the LCD backlight.
- Adjust the screen refresh rate.
- Set the display to native resolution.
- Set the display to the lowest resolution.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The native resolution would provide the best image display. In this scenario, the user should try the native resolution first and then adjust to other resolution options if needed.
-
What process takes place in a laser printer after the drum is conditioned for the new latent image?
- charging
- exposing
- developing
- fusing
- transferring
Answers Explanation & Hints: The drum is conditioned for the new latent image during the charging step.
The printing process involves seven steps for a laser printer:- processing
- charging
- exposing
- developing
- transferring
- fusing
- cleaning
-
What type of printer requires the ribbon to be changed when producing faded and light characters?
- inkjet
- impact
- laser
- thermal
Answers Explanation & Hints: Inkjet, laser, or thermal printers do not use ribbons.
-
What is an advantage of using a printer that is connected to a hardware print server compared with a computer-shared printer?
- A computer that shares a printer always allows for faster printing of documents.
- A hardware print server is always available to all users.
- A computer that shares a printer always prioritizes the printing tasks.
- A hardware print server will have more memory to store the print job than a computer will have that shares a printer.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A PC sharing a printer is usually running multiple tasks simultaneously besides printing and is therefore slower to process and send documents to the printer. A disadvantage of hardware print servers is that they frequently contain less storage space for the print queue compared with a dedicated print server or a computer-shared printer.
-
A technician wants to allow many computers to print to the same printer, but does not want to affect the performance of the computers. What will the technician do to achieve this?
- Use a software print server.
- Use a computer-shared printer.
- Use a hardware print server.
- Install a second printer.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A hardware print server allows many users to print to the same printer without using the resources of any computer. A computer-shared printer uses a computer to manage all of the print jobs. There is no software print server. Installing a second printer would reduce the print jobs on any one computer, but would still use computer resources.
-
A user is reporting that an inkjet printer is printing colors different from what the printer should be printing. The printer has separate cartridges for each color and the user changed the cyan cartridge recently. What is the action that could fix the problem?
- Perform a printer head cleaning.
- Check for loose printer cables.
- Use a different type of paper.
- Purchase a maintenance kit.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A head cleaning routine is needed if the cartridges get clogged or if they are new. Typically, inkjet printers print different colors if one of the cartridges is not able to function properly.
-
Which two field replaceable units could be found in a laser printer maintenance kit? (Choose two.)
- fuser assembly
- pickup rollers
- power supply
- paper trays
- drum
- toner cartridge
Answers Explanation & Hints: Usually, manufacturers include in the maintenance kits the parts that are subject to wear. Such parts could be a fuser assembly, transfer rollers, separation pads, and pickup rollers. Power supplies, and drum and paper trays are considered replacement parts that are changed at the time of failure, whereas the toner cartridge is considered a consumable.
-
What is best used to clean the heating element on a thermal printer?
- mild solvent
- soap foam
- isopropyl alcohol
- distilled water
Answers Explanation & Hints: Cleaning the heating element regularly with isopropyl alcohol will extend the life of the printer. Using any of the other substances could damage the printer.
-
A user reports that a computer is unable to print on an inkjet printer. The technician has determined that there is no paper in the paper bin. What is the next step in the troubleshooting process?
- Establish a plan of action.
- Determine the exact cause.
- Verify system functionality.
- Document the findings.
Answers Explanation & Hints: What the technician just did was to determine the exact cause. What is next in the troubleshooting process is to establish a plan of action.
-
A user reports that a laser printer is printing shadow images and letters. Which part should the technician replace to correct this problem?
- network cable
- pick up roller
- drum
- fuser
Answers Explanation & Hints: The drum is a metal cylinder that holds an electrostatic charge to pick up the toner powder. If the drum is defective, then the charge on the cylinder will not hold the correct latent image to attract the toner.
-
A technician is called to work on a laser printer that prints vertical lines on every printed page. Which laser printer part should be checked first?
- pickup rollers
- RAM
- toner cartridge
- wiper blade
Answers Explanation & Hints: A vertical line could be a sign of a faulty drum or a problem with the toner cartridge. The toner cartridge is the easiest one to test if it is faulty and can be reused later if it turns out to not be the problem.
-
A technician is called to troubleshoot a problem where a user claims that none of the print jobs from this morning have printed. The technician sees that there is only one printer installed in the device list and it is a network printer shared with other users. What should the technician check?
- the print queue
- the IP address of the printer
- the fuser assembly
- the user rights to the printer
Answers Explanation & Hints: A networked printer might have a backed up print queue caused by the printer being offline, out of paper, or a paper jam. There might also be a document stuck in the print queue causing all of the others after it to not print. Check the printer for any issues first then check the print queue and see if sending a different document to the top of the queue or canceling the document at the top of the queue frees up the printer.
-
A user reports that a “Document failed to print” message appears every time the network printer is restarted. What could be a cause of the problem?
- The fuser is faulty.
- The IP address on the printer is statically assigned.
- The user rights to the printer have been configured incorrectly.
- The IP address assigned to the printer is a duplicate IP address.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Networked printers are commonly assigned a static IP address. A DHCP reservation can be made and the MAC address of the printer can be entered at the DHCP server so that the printer receives the same IP address each time, or a technician can just manually enter an IP address into the printer. Each device must have a unique IP address, and a duplicate one would cause a network printer to not function.
-
What are two functions of hypervisors? (Choose two.)
- to partition the hard drive to run virtual machines
- to protect the host from malware infection from the virtual machines
- to manage virtual machines
- to allocate physical system resources to virtual machines
- to share the antivirus software across the virtual machines
Answers Explanation & Hints: The hypervisor does not protect the hosting OS from malware. Neither does it allow sharing software across virtual machines. The hard drive of the supporting computer does not need to be partitioned to run virtual machines. The hypervisor creates and manages virtual machines on a host computer and allocates physical system resources to them.
-
A computer technician is asked to configure a workstation with two virtual machines. What would be the purpose of the configuration?
- to have redundancy in case of hard drive failure
- to increase the performance of the computer
- to have two separate operating systems running at the same time on one computer
- to allow multiple applications, that require more RAM than is installed, to be active simultaneously
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the process of virtualization, virtual machines are created. Different operating systems can be installed on each virtual machine without interfering with one another.
-
A computer technician creates a virtual environment. Which security measure should the technician take for the virtual machine running Windows 10, if any?
- Each virtual machine should have antivirus software installed.
- Because each virtual machine contains an operating system that is different from what is on the host computer, no security software is needed.
- A hardware firewall should be placed between each virtual machine and the internet or it will be necessary to ensure that the Windows firewall is enabled on each virtual machine.
- The virtual machine must use the same secure passwords as the host computer uses.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Virtual machines are susceptible to the same security threats that a host computer is. All security measures that are recommended for a computer in a home or business environment should also be taken within the virtual environment.
-
Which two minimum requirements should be met for a technician to enable Hyper-V on a Windows 10 computer? (Choose two.)
- 4 GB RAM
- 8 GB RAM
- 16 GB RAM
- 32-bit operating system
- 32- or 64-bit operating system
- 64-bit operating system
Answers Explanation & Hints: Windows Hyper-V in Windows 10 has the following minimum requirements:64-bit operating system
BIOS virtualization support and hardware enforced data execution prevention
4 GB RAM
Windows 10 Enterprise, Pro, or Education editions
CPU support for VM Monitor Mode Extension (VT-c on Intel CPUs)
-
A technician is setting up a new VM. How will internet connectivity be provided to the VM?
- through an IPsec tunnel
- through a virtual private network
- through a virtual NIC that connects through the host computer NIC
- through port forwarding configuration on the firewall of the operating system used within the VM
Answers Explanation & Hints: In creating a virtualized environment, the hypervisor creates a virtual NIC that works with the host physical NIC. It virtualizes the network resource to be shared with all VM virtual NICs in providing network connectivity.
-
Which component would be required when deploying a virtual desktop to a corporate user?
- metered service
- minimum of 6 GB of RAM
- SSD
- virtual NIC
Answers Explanation & Hints: A virtual desktop is one where the desktop and all applications are run from a server. A virtual desktop uses a virtual NIC.
-
What would a technician require in order to install a hypervisor on a client machine?
- an SSD
- multiple storage drives
- a server housed by a cloud service provider
- virtualization software
Answers Explanation & Hints: A hypervisor is used to create a virtual machine (VM). The hypervisor can be part of an operating system such as Windows Hyper-V or it can be downloaded from a virtualization vendor such as VMWare or Oracle.
-
Which character of the Cloud model provides easy monitoring, controlling, reporting, and billing for both the provider and customers?
- rapid elasticity
- resource pooling
- measured service
- broad network access
- on-demand self-service
Answers Explanation & Hints: With measured service of the Cloud model, the resource usage can be easily monitored, controlled, reported, and billed to provide full visibility to both the Cloud service provider and customers.
-
A company uses cloud services and is setting up a new switch supplied by the cloud provider. Which cloud model is used by the company?
- DaaS
- IaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Whenever a company has an infrastructure device like a router or switch in the company cloud solution, the cloud model being used is IaaS.
-
A company owns servers for a particular corporate application. The servers are housed in an external data center. The company has an agreement with a cloud provider to spin up additional servers for the same application during peak usage. Which cloud model is the company using?
- community
- hybrid
- private
- public
Answers Explanation & Hints: A private cloud is a cloud-based service where the company manages the devices or applications within the cloud. They are just located away from the business at a provider site. If a company is using a public cloud, a provider manages the devices or the applications or both for the company. A hybrid cloud is a combination of two types of clouds, and a common practice is a private and public cloud combination.
-
What is meant by a cloud service being metered?
- The company is charged a monthly or annual fee for a specific service.
- The company is charged based on the amount of service used.
- The company is allowed unlimited access to a service during specific periods of time.
- A special device is attached to the demarcation point where the service provider network ends and the company network starts.
Answers Explanation & Hints: An unmetered cloud service is one where the service is free or it is charged on a monthly or annual basis. A metered cloud service has the charge based on how much the service is used. A company can also have an unmetered service up to a particular point and then the company is assessed additional charges based on how much additional services the company used.
-
A company has a few employees that are designers. The designers do not have the CAD application loaded on their local computer. Instead, the designers use a CAD application hosted by the application developer. Which type of virtualization is the company using?
- DaaS
- IaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing type that provides access to one or more applications through a server. This server is not owned or managed by the company using the application.
-
A Windows 10 computer has several printers configured in the Control Panel Devices and Printers window. Which printer will the computer choose to be the first option for printing?
- the printer that is set as the default printer
- the software-based printer that is used to create PDF files
- the software-based printer that is used to create XPS files
- a manual selection, which is always needed
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Default Printer option is set globally and will be the first printer to print a job unless another printer is selected in a Per-Document manner. Software-based printers are just instances of different kinds of printers, but to be chosen to do the job, they will need to be selected as a default or Per-Document printer. Selecting a printer every time a printing job sends is not needed.
-
What problems can be resolved by implementing QoS and traffic engineering protocols in an enterprise VoIP network?
- excessive latency and jitter
- unexpected infrastructure disruptions
- excessive noise and interference
- the inability to transfer calls
Answers Explanation & Hints: Deploying QoS (Quality of Service) and traffic engineering protocols on an enterprise network can resolve problems of excessive latency (data transmission delay) and jitter (excessive variation in delay). Unexpected infrastructure disruptions, excessive noise and interference, and the inability to transfer calls are IP telephony configuration or physical layer problems that the deployment of QoS and traffic engineering protocols cannot resolve.
-
Which two devices commonly make use of Power over Ethernet (PoE)? (Choose two.)
- IP phones
- wireless access points
- network printers
- network storage devices
- wireless speakers
Answers Explanation & Hints: IP phones and wireless access points commonly use Power over Ethernet (PoE). Network printers and storage devices typically use externally connected power sources such as electrical outlets or USBs. Wireless speakers use a battery power source.
-
Which network device is used to ensure that each server, providing the same service on a network, is used as much as the others on that network?
- load balancer
- router
- client
- wireless access point
Answers Explanation & Hints: Specifically, a load balancer is used to ensure that each server providing the same service on a network is used as much as the others on that network. A router routes data between different networks. Client is the term used to describe hosts (end devices) on a network that accesses servers. A wireless access point enables hosts to connect to a wireless network.
-
A technician is building a gaming computer with a PCIex16 graphics card. The graphics card requires 100 watts of power to run. How will this power be supplied?
- from the PCIe slot on the motherboard
- from the AGP slot on the motherboard
- from the PCIe slot on the motherboard, together with a separate PCIe power connector from the power supply
- from the PCIe power connector from the power supply
Answers Explanation & Hints: PCIe can supply up to 25 watts of power to each slot. A graphics card can supply up to 75 watts. For potent graphics cards, an additional 75 watts can be supplied by a PCIe power connector from the power supply.
-
Match the Wi-Fi standard with the maximum supported speed.
ITE 8 IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials A+ 220-1001 Certification Practice Exam Answers 04 Explanation & Hint: - 802.11n: This standard, also known as Wi-Fi 4, can reach speeds of up to 600 Mbps.
- 802.11ad: This Wi-Fi standard is known for its very high-speed potential, reaching up to 7 Gbps. It operates in the 60 GHz frequency band.
- 802.11ax: Also known as Wi-Fi 6, is the successor to 802.11ac and can achieve higher speeds, often quoted up to 9.608 Gbps under optimal conditions.
- 802.11ac: This standard, also known as Wi-Fi 5, increased the maximum speed over its predecessors to a range that often tops out around 1.3 Gbps, but with advancements and multiple streams, it can theoretically reach over 6.933 Gbps.
- 802.11a: This is an older standard that typically had a maximum throughput of 54 Mbps, but it is not listed among the options you’ve provided.
With the given options, the correct matches would be:
- 802.11n with 600 Mbps
- 802.11ad with 7 Gbps
- 802.11ax with 9.608 Gbps
- 802.11ac likely corresponds to the speed closest to its theoretical maximum, but none of the provided speeds match the typical top speeds of 802.11ac. If we were to choose the closest one, it might be 6.933 Gbps, assuming advanced configurations.
- 802.11a it would align with 40 Mbps if that were an option.
-
While a user is working on a spreadsheet, the computer reboots. What are two components that could cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- ROM
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
- RAID
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer unexpectedly reboots while a user is working on a spreadsheet, the issue could be related to hardware or software problems. However, focusing on the hardware components listed:
- Power Supply: A failing or inadequate power supply can cause the computer to restart without warning. If the power supply is unable to provide a steady and sufficient amount of power to the system components, it can lead to sudden reboots.
- CPU: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is less likely to be the cause of random reboots compared to the power supply. However, if the CPU is overheating due to a malfunctioning fan or poor thermal paste application, it could trigger the system’s protective measure to reboot to prevent damage.
The other components listed are less likely to cause a computer to reboot:
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): ROM is non-volatile memory that is typically used to store firmware. While ROM errors can cause a system to fail to boot, they are less likely to cause a system to reboot unexpectedly.
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): The BIOS firmware initializes and tests hardware at startup. A BIOS issue might prevent the computer from booting, but it’s not a common cause of random reboots once the system is running.
- Wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller): While driver issues with a wireless NIC can potentially cause system instability, they are unlikely to cause the system to reboot entirely. It’s more likely to lead to connectivity issues.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): Problems with RAID could potentially cause data access issues or system instability, but random reboots are not a typical symptom unless there is a major fault with the RAID controller hardware.
Thus, the most likely culprits for the computer rebooting unexpectedly would be the power supply and potentially the CPU, especially if it’s related to overheating.
-
While a user is working on a spreadsheet, the computer reboots. What are two components that could cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- motherboard
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
- RAID
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer reboots unexpectedly while a user is working on a spreadsheet, the two components from the list that could be the cause of such an issue are indeed:
- CPU: If the CPU is overheating, it may cause the computer to reboot in an attempt to prevent damage. Overheating can occur due to a malfunctioning fan, degraded thermal paste, blocked airways, or a heavy processing load that exceeds the cooling system’s capabilities.
- Power Supply: An unstable or failing power supply can also cause the computer to reboot. If the power supply is unable to provide consistent power due to internal faults, degradation, or external power fluctuations, the computer may restart unexpectedly.
These components are critical to the system’s operation, and issues with either can result in the computer restarting to protect itself from potential damage. When diagnosing such issues, it is common to check the system’s temperature and power supply health, among other things.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- hard drive
- wireless NIC
- ROM
- BIOS
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer suddenly reboots without user intervention, especially after being used for a continuous period, it often suggests an issue with hardware components that are prone to overheating or power issues. The two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem are:
- CPU: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) can overheat due to sustained use, especially if there is insufficient cooling, such as a malfunctioning fan, clogged heatsink, or degraded thermal paste. Overheating can trigger safety mechanisms that reboot the computer to prevent damage to the processor.
- Power Supply: The Power Supply Unit (PSU) can cause reboots if it becomes unstable or fails. This could be due to overheating, a fault within the PSU, or inadequate power being delivered to the system’s components.
While other listed components might cause system issues, they are less likely to cause a computer to reboot:
- Hard Drive: A failing hard drive would typically cause data access issues, system freezes, or crashes rather than a reboot.
- Wireless NIC: Network Interface Cards, even if they fail or encounter issues, are more likely to cause loss of network connectivity, not a system reboot.
- ROM: Read-Only Memory in the context of computer hardware usually refers to the memory that stores the BIOS/UEFI firmware. Problems with ROM could potentially prevent booting but are less likely to cause mid-use reboots.
- BIOS: The Basic Input/Output System is firmware that initializes the computer hardware during the boot process. A BIOS error could prevent a computer from starting up or cause instability, but it’s a less common cause of spontaneous reboots during operation.
Given the scenario described, issues with the CPU and power supply are the more probable causes of the unexpected reboot.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- display port or display
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
- RAID
-
Explanation & Hint: When a computer reboots on its own after being used for a while, it typically points to issues related to overheating or power supply problems. Based on the hardware parts listed, the two most likely to cause such a problem are:
- CPU: The CPU is susceptible to overheating, especially after continuous use. If the cooling system is not functioning properly or if the CPU is under a heavy load, it may overheat. Modern CPUs have built-in thermal protection that will shut down or reboot the computer to prevent damage when they reach a critical temperature.
- Power Supply: The power supply unit (PSU) provides power to all the components of the computer. If the PSU is failing or if it’s not providing a consistent power supply due to issues like overheating, voltage fluctuations, or defects, it can cause the computer to reboot.
The other components listed are less likely to cause a computer to reboot:
- Display Port or Display: While a malfunctioning display or port can cause screen issues, they typically do not trigger a system reboot.
- BIOS: The BIOS firmware is responsible for booting up the computer. Although a corrupt BIOS can cause boot issues, it’s not usually the cause of a spontaneous reboot during normal operation.
- Wireless NIC: A network interface controller is unlikely to cause a system reboot. At most, a defective NIC might lead to network connectivity issues.
- RAID: A Redundant Array of Independent Disks is used for data storage and redundancy. Faults in RAID may lead to data access issues or system crashes, but spontaneous reboots are not commonly directly caused by RAID issues.
Therefore, the CPU and the power supply are the most likely culprits in this scenario.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- surge strip
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
- RAID
-
Explanation & Hint: In the scenario where a computer reboots suddenly after being used for a continuous period in the morning, the two most likely hardware causes are:
- CPU: The CPU is central to the computer’s operations and is susceptible to overheating, particularly if it’s been under a sustained heavy load or if there is a problem with its cooling system (like a failed fan or degraded thermal compound). Overheating can cause the system to shut down or reboot unexpectedly to prevent damage.
- Power Supply: The power supply unit (PSU) is critical for providing stable power to the computer. If the PSU is faulty, overheating, or failing, it can lead to irregular power delivery, which may cause the system to reboot. Additionally, if the PSU cannot cope with the energy demands of the system, this might also lead to sudden reboots.
While a surge strip could also be a factor if it’s faulty or if there was a power surge, it is less of a component of the computer and more of an accessory for power management. However, if the surge strip fails or triggers due to a surge, it could cut off power to the computer, causing it to reboot.
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is less likely to cause reboots once the system has successfully started up. Problems with the BIOS more typically prevent the computer from booting at all or cause issues during the boot process.
A wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller) generally wouldn’t cause the system to reboot. Issues with a wireless NIC would typically lead to network connectivity problems.
Problems with RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations usually result in data access issues or storage-related errors, not typically in sudden system reboots.
Given the options, the CPU and power supply are the most probable hardware parts that could cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly. If including external factors, a surge strip could also be considered, especially if the reboot coincides with power fluctuations.
-
A technician has been called in to investigate a problem with the computer rebooting randomly throughout the day. What two pieces of hardware could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- surge strip
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
- RAID
-
Explanation & Hint: Random reboots can be caused by a few different hardware issues. If a technician is investigating random reboots, they would likely consider the following two hardware components as potential causes:
- Power Supply: A failing power supply can cause random reboots. This could be due to it overheating, having inconsistent power output, or experiencing power surges that disrupt the normal flow of electricity to the computer’s components.
- CPU: Overheating or malfunctioning of the CPU can lead to random reboots. The CPU has a thermal protection feature that will shut down the system to prevent damage if it gets too hot. This could be due to a cooling system that isn’t working properly (e.g., a failed fan or dried-out thermal paste).
The other pieces of hardware listed are generally less likely to cause random reboots:
- Surge Strip: While a faulty surge strip can cause power interruptions, it would typically cut power entirely rather than just reboot the computer. However, it’s still a possibility if the surge strip is poorly regulating the power or if it’s faulty and causes brief interruptions in power.
- BIOS: Issues with the BIOS can cause boot problems or system instability, but they are less likely to cause random reboots once the system has successfully started up.
- Wireless NIC: A network interface card, unless it’s causing a system-level conflict or has a severe driver issue, typically doesn’t cause reboots. Network problems usually manifest as connectivity issues.
- RAID: While RAID controller issues can lead to data loss or corruption, they generally do not cause the system to reboot. If there is a major fault with the RAID controller hardware, it could potentially lead to system instability, but this is less common.
Therefore, the two most likely suspects in such a situation would be the power supply and the CPU, especially in the context of hardware-related problems.
-
For two days in a row, a user has noticed that the computer reboots several times before it eventually starts. What are two suspect components? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- BIOS
- motherboard
- ROM
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer is rebooting several times before starting up, and considering the CPU and power supply as the two suspect components:
- CPU: If the CPU is malfunctioning or overheating, it can cause the system to reboot multiple times. Overheating can happen if the CPU’s cooling system (heatsink and fan) is not functioning properly, if there is a build-up of dust blocking airflow, or if the thermal paste between the CPU and heatsink has degraded and is not conducting heat effectively. Additionally, if there is an issue with the CPU’s power delivery or with the CPU itself, it could cause instability that leads to multiple reboots.
- Power Supply: The power supply is a critical component that, if failing, can cause the computer to reboot. This might be due to power fluctuations, overheating within the PSU itself, or problems with the electrical supply from the outlet. A PSU that’s on the verge of failure may struggle to provide the consistent power required to keep the system running, especially during the power-intensive boot-up phase.
When diagnosing such issues, a technician would likely start by checking these two components. They might monitor the CPU temperature, check the condition of the thermal paste, ensure that the cooling system is working correctly, and test the power supply unit’s output to ensure it’s providing stable and sufficient power. If either the CPU or the power supply is found to be faulty, it would need to be repaired or replaced to resolve the rebooting issue.
-
While a user is working on a spreadsheet, the computer reboots. What are two components that could cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- ROM
- motherboard
- wireless NIC
- BIOS
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer reboots unexpectedly while a user is working on a spreadsheet, the two components from the list that could be the cause of such an issue are indeed:
- CPU: If the CPU is overheating, it may cause the computer to reboot in an attempt to prevent damage. Overheating can occur due to a malfunctioning fan, degraded thermal paste, blocked airways, or a heavy processing load that exceeds the cooling system’s capabilities.
- Power Supply: An unstable or failing power supply can also cause the computer to reboot. If the power supply is unable to provide consistent power due to internal faults, degradation, or external power fluctuations, the computer may restart unexpectedly.
These components are critical to the system’s operation, and issues with either can result in the computer restarting to protect itself from potential damage. When diagnosing such issues, it is common to check the system’s temperature and power supply health, among other things.
-
While a user is working on a spreadsheet, the computer reboots. What are two components that could cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- motherboard
- display port or display
- surge strip
- hard drive
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer reboots unexpectedly while a user is working on a spreadsheet, the two components from the list that could be the cause of such an issue are indeed:
- CPU: If the CPU is overheating, it may cause the computer to reboot in an attempt to prevent damage. Overheating can occur due to a malfunctioning fan, degraded thermal paste, blocked airways, or a heavy processing load that exceeds the cooling system’s capabilities.
- Power Supply: An unstable or failing power supply can also cause the computer to reboot. If the power supply is unable to provide consistent power due to internal faults, degradation, or external power fluctuations, the computer may restart unexpectedly.
These components are critical to the system’s operation, and issues with either can result in the computer restarting to protect itself from potential damage. When diagnosing such issues, it is common to check the system’s temperature and power supply health, among other things.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- hard drive
- surge strip
- RAID
- display port or display
-
Explanation & Hint: In the scenario where a computer suddenly reboots after continuous use in the morning, the two most likely hardware causes are:
- CPU: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is a critical component, and if it overheats, it can cause the computer to reboot. Overheating may occur due to a malfunctioning cooling system (like a failed fan or degraded thermal paste), blocked airways, or a heavy processing load. Modern CPUs have built-in thermal protection that will shut down or reboot the computer to prevent damage when reaching critical temperatures.
- Power Supply: The Power Supply Unit (PSU) provides electrical power to the computer. If it’s failing or not providing stable power due to issues like overheating, internal component failure, or inadequate wattage, it can lead to irregular power delivery, causing the computer to reboot.
The other components listed are generally less likely to cause random reboots:
- Hard Drive: A failing hard drive can cause data access issues, system freezes, or crashes, but it’s less likely to cause the system to reboot on its own.
- Surge Strip: If a surge strip is failing or if there’s a power surge, it might cut off power to the computer. However, this usually results in a power loss rather than a reboot.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): Issues with RAID can lead to data loss or system crashes but are not typically associated with causing random reboots.
- Display Port or Display: Display issues can cause screen errors or loss of visual output but do not usually result in a system reboot.
Considering these options, the CPU and the power supply are the most probable hardware parts that could cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly.
-
A technician is setting up a server that requires two connections between the client and the server, one for commands and replies, the other for the actual transfer of files. What type of server will accomplish this task?
- FTP server
- print server
- DNS server
- web server
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of server that requires two connections between the client and the server, one for commands and replies and the other for the actual transfer of files, is an FTP server (File Transfer Protocol server).
Here’s a brief overview of why the other server types don’t fit this description:
- Print Server: A print server manages print requests and network-connected printers. It typically does not use two separate connections for commands and data transfer as described.
- DNS Server (Domain Name System server): A DNS server translates domain names into IP addresses. It does not require two separate connections for command and data transfer.
- Web Server: A web server hosts and serves web pages. It primarily uses HTTP or HTTPS protocols, which do not inherently require two separate connections for commands and file transfers.
FTP, on the other hand, specifically uses two distinct network connections in its standard mode of operation: one for sending control commands (like login credentials and commands to change directories or list files) and another for the actual transfer of files. This is a distinctive feature of the FTP protocol.
-
A network analyst is setting up a server that uses a store-and-forward method of sending, storing, and retrieving electronic messages across a network. What type of server is the analyst setting up?
- email server
- FTP server
- print server
- web server
-
Explanation & Hint: The network analyst is setting up an Email Server. An email server uses a store-and-forward method to handle electronic messages. This process involves receiving emails, storing them, and then forwarding them to the intended recipient when they are available to receive the email. This type of server manages the sending, receiving, and storing of email messages over a network.
To clarify why the other options do not fit this description:
- FTP Server (File Transfer Protocol server): An FTP server is used for the storage and transfer of files between systems, but it does not use a store-and-forward method. It is primarily for direct file transfers.
- Print Server: A print server manages the printing process within a network, handling print jobs sent to networked printers. It does not use store-and-forward for emails or messages.
- Web Server: A web server hosts and serves web content (like websites). It does not handle emails or use a store-and-forward method for messages.
Email servers uniquely fit the description of using a store-and-forward method for handling electronic messages.
-
A manager works remotely and needs to access classified information on the web servers within the company head office. What type of server uses the secure HTTP (HTTPS) for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web.
- web server
- print server
- DNS server
- FTP server
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of server that the manager would need to access classified information securely, using HTTPS (Secure HTTP) for exchanging text, graphic images, sound, and video on the web, is a Web Server.
HTTPS is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) with added security capabilities. It is used for secure communication over a computer network within a web browser, ensuring that the data exchanged between the browser and the server is encrypted and secure. This is particularly important for transferring sensitive or classified information, as in the scenario you described.
Here’s a brief overview of the other server types:
- Print Server: A print server manages print requests within a network, handling the connections to printers. It does not use HTTPS as it is not involved in web-based data exchange.
- DNS Server (Domain Name System server): A DNS server translates domain names into IP addresses. While it is a crucial component of web browsing, it does not itself host or serve web content and does not use HTTPS for secure transactions.
- FTP Server (File Transfer Protocol server): An FTP server is used for storing and transferring files. While there is a secure version known as FTPS (FTP Secure), this is different from HTTPS and is typically used for file transfers rather than viewing web content.
In the context of your scenario, a web server using HTTPS is the appropriate choice for securely accessing and exchanging various types of web content, including classified information.
-
A network administrator in a corporate headquarters office is setting up a new laptop for a new employee. What type of service will provide an IP address for the new device?
- DHCP
- FTP server
- print server
- web server
-
Explanation & Hint: The service that will provide an IP address for the new laptop in a corporate environment is DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
DHCP is a network management protocol used on IP networks whereby a DHCP server dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to each device on a network, so they can communicate with other IP networks. This automates and centrally manages the assignment of IP addresses, subnet masks, gateway, and other network settings.
The other services mentioned serve different purposes:
- FTP Server (File Transfer Protocol server): An FTP server is used for the storage and transfer of files. It does not assign IP addresses.
- Print Server: A print server manages networked printers and print jobs but does not handle the assignment of IP addresses.
- Web Server: A web server hosts and serves web content and also does not play a role in assigning IP addresses to devices on the network.
Therefore, for the task of automatically assigning an IP address to a new device on the network, DHCP is the correct service.
-
A technician is setting up an environment where popular and frequently accessed web pages are stored locally on the internal network. What type of server will accomplish this task?
- proxy server
- print server
- DNS server
- FTP server
-
Explanation & Hint: The technician is setting up a Proxy Server to accomplish the task of storing popular and frequently accessed web pages locally on the internal network.
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between end users and the internet. It can cache (store) frequently accessed web pages and resources. When a user requests a web page that has been previously accessed, the proxy server can provide the cached version quickly, without needing to retrieve it from the internet again. This can improve access speed and reduce bandwidth usage.
The other server types serve different purposes:
- Print Server: Manages networked printers and print jobs. It is not involved in caching or serving web content.
- DNS Server (Domain Name System server): Translates domain names into IP addresses, facilitating the finding of websites on the internet. It does not cache web content.
- FTP Server (File Transfer Protocol server): Used for the transfer and storage of files between systems, typically not used for caching web content.
Therefore, for caching and serving frequently accessed web content locally, a proxy server is the appropriate choice.
-
A technician is setting up an environment where popular and frequently accessed web pages are stored locally on the internal network. What type of server will accomplish this task?
- proxy server
- DHCP
- DNS server
- print server
-
Explanation & Hint: In this scenario, the technician is setting up a server environment to store popular and frequently accessed web pages locally on the internal network. The type of server that will accomplish this task is a Proxy Server.
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between users and the internet. It can cache (store) web pages and other online content locally. When a user requests a web page, the proxy server first checks if it has a stored (cached) version of this page. If it does, the proxy server provides the page from its cache, speeding up the access time and reducing bandwidth usage. This is particularly useful for frequently accessed websites in an organization, as it improves efficiency and load times.
The other options serve different purposes:
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): DHCP servers assign IP addresses to devices on a network. They do not store or cache web content.
- DNS Server (Domain Name System server): A DNS server translates domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses. It does not cache web content but helps in resolving domain names to their respective IP addresses.
- Print Server: A print server manages print requests within a network and controls networked printers. It has no functionality related to storing or caching web content.
Hence, for the described requirement, a proxy server is the most suitable type of server.
-
A user needs to connect to Cisco.com but does not know the IP address for this website. What type of server will translate the website name into an IP address?
- DNS server
- DHCP
- print server
- FTP server
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of server that translates a website name, like “Cisco.com,” into an IP address is a DNS (Domain Name System) server. DNS servers are responsible for converting human-readable domain names into the numerical IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network.
Here’s a brief overview of the other server types mentioned:
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server: This server automatically assigns IP addresses and other network configurations to devices on a network, but it doesn’t translate domain names to IP addresses.
- Print Server: A print server manages one or more printers in a network, allowing multiple computers to share these printers. It doesn’t have a role in translating domain names.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Server: An FTP server is used for the storage and transfer of files over a network. Like a print server, it does not translate domain names to IP addresses.
-
An administrator is setting up a framework to support access control on a network device. What type of server is able to control those who are permitted to access a network and track what actions they perform while accessing the network?
- authentication server
- DHCP
- DNS server
- print server
-
Explanation & Hint: For setting up a framework to control who is permitted to access a network and to track their actions while accessing the network, an Authentication Server would be the most appropriate choice.
An authentication server is a type of server used to verify the identity of users by validating their credentials before they access a network resource. It can also keep track of user activities, providing an audit trail of their actions while on the network. This is essential for maintaining network security and for compliance with various regulatory standards.
To briefly describe the other server types:
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server: Assigns IP addresses and other network configurations to devices on a network. It doesn’t handle user authentication or activity tracking.
- DNS (Domain Name System) Server: Translates domain names into IP addresses. It doesn’t involve user authentication or monitoring their activities.
- Print Server: Manages printers and print jobs in a network environment. It has no role in network access control or user activity tracking.
-
A company is setting up one new laser printer on every floor. What type of server will store the print jobs in a queue and then spool them to the device when it is ready?
- print server
- DHCP
- DNS server
- FTP server
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of server that will store the print jobs in a queue and then spool them to the device when it’s ready is a Print Server.
A print server’s primary function is to manage one or more printers in a network. It receives print jobs from client computers and sends these jobs to the appropriate printer, managing the print queue to ensure that documents are printed in the order they were received. This is particularly useful in an environment like a company with multiple printers, as it helps in efficient management and distribution of print jobs.
The other server types mentioned have different functions:
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) Server: Assigns IP addresses and other network configurations to devices on a network, but doesn’t manage print jobs.
- DNS (Domain Name System) Server: Translates domain names into IP addresses, and isn’t involved in managing printers or print jobs.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol) Server: Used for the transfer of files over a network but does not handle print jobs or printer management.
-
What network service controls those who are permitted to access a network, what they can do while they are there, and track what actions they perform while accessing the network?
- AAA
- DHCP
- DNS server
- print server
-
Explanation & Hint: The network service that controls who is permitted to access a network, what they can do while they are there, and tracks what actions they perform while accessing the network is AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting).
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of a user or device attempting to access the network.
- Authorization: Determines what an authenticated user or device is permitted to do on the network.
- Accounting: Keeps track of what actions the user or device performs while on the network.
The other services mentioned have different functions:
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol): Assigns IP addresses and other network configurations to devices on a network, but doesn’t manage user access or track activities.
- DNS (Domain Name System) Server: Translates domain names into IP addresses, and is not involved in user access control or activity tracking.
- Print Server: Manages printers and print jobs in a network, unrelated to network access control or user activity monitoring.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds an access point. What is the purpose of this device?
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
- It is an all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS functionality as well as stateful firewall services.
- It is placed between two or more networks and protects data and equipment from unauthorized access.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of an access point found by the technician is to use radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices. An access point is a device that creates a wireless local area network, or WLAN, usually in an office or large building. It connects to a router (via a wired network) and projects a Wi-Fi signal to a designated area. This allows wireless devices to connect to the network without needing a physical cable.
The other options described different types of network devices:
- An all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS functionality as well as stateful firewall services is typically a security device, often referred to as a Unified Threat Management (UTM) appliance or a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW). It provides multiple security features but is not primarily used for creating wireless networks.
- A device placed between two or more networks that protects data and equipment from unauthorized access is typically a firewall. Its primary role is to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- A device that connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information is a router. Routers are used to forward data packets between computer networks, creating an overlay internetwork.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a cloud-based network controller. What is the purpose of this device?
- It is a device that allows a network administrator to manage many remote networking devices from a central location.
- It is placed between two or more networks and protects data and equipment from unauthorized access.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a cloud-based network controller, which the technician found, is to allow a network administrator to manage many remote networking devices from a central location. Cloud-based network controllers are part of a cloud-managed networking architecture. They enable administrators to oversee, configure, and troubleshoot network devices such as routers, switches, and access points through a cloud interface. This approach simplifies network management, especially for distributed networks across multiple locations, by providing centralized control and visibility without the need for physical access to each device.
The other options describe different network components or functions:
- A device placed between two or more networks that protects data and equipment from unauthorized access is typically a firewall. Its primary function is network security, controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
- A device that connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks using IP addressing information is a router. Routers direct traffic on the internet or between different networks.
- A device that uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices is a wireless access point. It connects wireless devices to a wired network, creating a wireless local area network (WLAN).
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a router. What is the purpose of this device?
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
- It is an all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS functionality as well as stateful firewall services.
- It is placed between two or more networks and protects data and equipment from unauthorized access.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a router, like the one found by the technician in the storage locker, is to connect networks and forward traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information. A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. It manages traffic between your local network (like your home or office network) and the internet, routing data to its destination based on IP addresses. Routers are essential for determining the best path for traffic to travel across multiple networks.
The other options refer to different devices or functions:
- A device that is an all-in-one security appliance with IDS/IPS functionality and stateful firewall services is typically a Unified Threat Management (UTM) appliance or a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW). These devices provide comprehensive security features but are distinct from routers.
- A device placed between two or more networks that protects data and equipment from unauthorized access is a firewall. Firewalls monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on security rules.
- A device that uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices is a wireless access point. It creates a wireless local area network (WLAN), usually connecting to a router to provide internet access to nearby wireless devices.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a firewall. What is the purpose of this device?
- It is placed between two or more networks and protects data and equipment from unauthorized access.
- It is an all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS functionality as well as stateful firewall services.
- It connects multiple end devices and can be configured for VLANs and port security.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a firewall, like the one found by the technician in the storage locker, is to be placed between two or more networks and protect data and equipment from unauthorized access. A firewall is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and decides whether to allow or block specific traffic based on a defined set of security rules. Its primary function is to establish a barrier between your internal network and external sources (such as the internet) to block malicious traffic like viruses and hackers.
The other options describe different types of network devices or functionalities:
- An all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS functionality as well as stateful firewall services typically refers to a more advanced type of firewall or a Unified Threat Management (UTM) system, which combines multiple security features in one device. While some firewalls have these capabilities, not all do.
- A device that connects multiple end devices and can be configured for VLANs and port security is typically a network switch. Switches are used to connect various devices on a local area network (LAN), like computers, and can segment traffic using VLANs.
- A device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN is also a description of a network switch, particularly focusing on its role in managing traffic within a LAN.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds an Ethernet NIC. What is the purpose of this device?
- It is needed to connect a computer to a wired local-area network.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of an Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card) found by the technician is to connect a computer to a wired local-area network. An Ethernet NIC is a hardware component that provides a computer with the ability to access and communicate over a network via Ethernet, which is a common wired networking standard. It typically has a port for an Ethernet cable and allows a computer to connect to a network such as a home network, office network, or the internet.
The other options describe different devices or technologies:
- A device that uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices is typically a wireless access point or a wireless network adapter. These are used for wireless networking, as opposed to an Ethernet NIC which is for wired networking.
- A device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN is a network switch. Switches are used to connect various devices within a local area network and manage the flow of data between them.
- A device that connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information is a router. Routers are used to connect multiple networks and route data between them, such as between a local network and the internet.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a Cisco ASA 5505-X (UTM). What is the purpose of this device?
- It is an all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS functionality as well as stateful firewall services.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
- It connects multiple end devices and can be configured for VLANs and port security.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a Cisco ASA 5505-X (UTM), found by the technician, is to be an all-in-one security appliance that includes IDS/IPS (Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System) functionality as well as stateful firewall services. The Cisco ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) 5505-X is a part of Cisco’s range of network security devices and is designed to provide comprehensive, enterprise-class security. It combines several security functions including:
- Stateful Firewall Services: Monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS): Identifying and managing potential threats, including unauthorized access attempts and vulnerabilities.
- It may also include other features like VPN (Virtual Private Network) capabilities, content security, and more, making it a versatile tool for network security.
The other options describe different types of network devices or functionalities:
- A device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN is typically a network switch. It’s used to connect various devices within a LAN.
- A device that connects multiple end devices and can be configured for VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) and port security is a network switch. This is mainly used for managing network traffic and securing network segments.
- A device that uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices is a wireless access point or a wireless router. This is used in wireless networking environments.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a wireless NIC. What is the purpose of this device?
- It is needed to connect a computer or smart device to an 802.11 network.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a wireless NIC (Network Interface Card) found by the technician is to connect a computer or smart device to an 802.11 network. A wireless NIC is a hardware component that enables a computer or other device to connect to a wireless local area network (WLAN). It uses the 802.11 networking standard, which is the basis for Wi-Fi, and allows the device to communicate over radio waves with a wireless access point or router to access the network and, in turn, the internet.
The other options describe different functionalities:
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices: While this is true for a wireless NIC, the statement is more generally applicable to devices like wireless access points or routers, which broadcast the Wi-Fi signal.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN: This describes a network switch, used within wired networks to connect and manage devices.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information: This is a description of a router, which routes data between different networks, such as a local network and the internet.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a repeater. What is the purpose of this device?
- It is used to regenerate weak signals to extend the distance a signal can travel.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a repeater, like the one found by the technician, is to regenerate weak signals to extend the distance a signal can travel. A repeater is a network device used to extend the reach of a network signal. It works by receiving a weak or low-level signal, amplifying it, and then transmitting the boosted signal further. Repeaters are used in both wired and wireless networks to ensure that the signal can cover longer distances without degradation.
The other options describe different network devices or functionalities:
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices: This describes a wireless access point or router, which allows wireless devices to connect to a network.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN: This is a description of a network switch, which is used to connect various devices within a local area network (LAN) and manage the traffic between them.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information: This describes a router’s function, which is to route data between different networks, such as between a home or office network and the internet.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a patch panel. What is the purpose of this device?
- It provides a wired or wireless connection between end devices, switches, and routers and in some cases, can regenerate weak signals.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
- It connects multiple end devices and can be configured for VLANs and port security.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a patch panel, like the one found by the technician, is to provide a wired connection between end devices, switches, and routers. A patch panel is a hardware device that centralizes cables from various network devices in a single location. It is primarily used in structured cabling systems and data centers. By organizing and managing network cables, a patch panel simplifies the connectivity and maintenance of the network infrastructure. It does not regenerate weak signals, configure VLANs, or provide wireless connectivity.
The other options describe different devices or functionalities:
- It provides a wired or wireless connection and can regenerate weak signals: This is more characteristic of devices like repeaters or network switches with specific functionalities, not a patch panel.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN: This describes a network switch, which connects devices within a LAN and can be used to segment traffic for efficiency and security.
- It connects multiple end devices and can be configured for VLANs and port security: This also refers to a network switch, particularly focusing on its capabilities to manage network traffic and security.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices: This is a function of wireless access points or wireless routers, which allow for the connection of wireless devices to a network.
-
A technician is searching through a storage locker and finds a hub. What is the purpose of this device?
- It is a legacy device that connects end devices and where traffic from one connected device floods out to every other connected device.
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information.
-
Explanation & Hint: The purpose of a hub, like the one found by the technician, is to be a legacy device that connects end devices and where traffic from one connected device floods out to every other connected device. A hub is a basic networking device used in early network designs, functioning at the physical layer of the OSI model. When it receives a packet of data at one of its ports, it broadcasts that data to all other ports, regardless of which device the data is intended for. This can lead to inefficiencies and security concerns, as every device on the network receives all the data, and only the intended recipient processes it further. Due to these limitations, hubs have largely been replaced by more advanced network switches.
The other options describe different network devices or functions:
- It uses radio waves to provide network access to wireless devices: This describes wireless access points or routers, which are used for creating wireless networks.
- It is a device whose sole purpose is to connect end devices and to microsegment a LAN: This is a description of a network switch. Switches are more advanced than hubs and can intelligently direct traffic to specific devices, reducing network congestion and improving security.
- It connects networks and forwards traffic to remote networks by using IP addressing information: This is a function of a router, which routes data packets between different networks.
-
A school is installing a new shared printer but the printer is not showing up on the list of available printers. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Manually add the printer IP address.
- Reset the page counter.
- Replace the pickup roller.
- Configure the printer for duplex printing.
- Power cycle the printer.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of the new shared printer not showing up on the list of available printers at a school, the technician can take the following steps:
- Manually Add the Printer IP Address: The technician should first check if the printer has been properly configured on the network and has a valid IP address. If the printer is connected to the network but not appearing automatically, manually adding the printer by its IP address can often resolve the issue.
- Power Cycle the Printer: Turning the printer off and then on again can resolve many connectivity issues. This simple step can help reset the printer’s network connection.
The other suggestions are less likely to address the problem of the printer not showing up on the network:
- Reset the Page Counter: This is typically done for maintenance or accounting purposes and is not related to network connectivity issues.
- Replace the Pickup Roller: This would be necessary if the printer was experiencing paper feed issues, but it’s not relevant to a printer not appearing on the network.
- Configure the Printer for Duplex Printing: This setting adjusts how the printer handles double-sided printing and won’t affect network visibility.
If these steps do not resolve the issue, the technician may need to check the network settings, printer sharing settings, and ensure that the correct drivers are installed on the computers that need to access the printer.
-
A school is installing a new shared printer but the printer is not showing up on the list of available printers. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Manually add the printer IP address.
- Reset the page counter.
- Install a USB hub.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of a new shared printer not showing up on the list of available printers at a school, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Manually Add the Printer IP Address: If the printer is correctly configured on the network and has a valid IP address, manually adding the printer using its IP address can be an effective solution. This involves accessing the printer settings on the computers that need to use the printer and entering the printer’s IP address to establish a direct connection.
- Connect the Printer Using Wireless: If the printer supports wireless connectivity and it’s not appearing on the network, setting up or reconfiguring its wireless connection could help. This includes ensuring the printer is connected to the correct Wi-Fi network and that there are no issues with the wireless signal.
The other suggestions are unlikely to be helpful in this scenario:
- Reset the Page Counter: Resetting the page counter is generally done for maintenance or tracking purposes and has no impact on network visibility or connectivity.
- Install a USB Hub: This is useful if you need more USB ports on a device, but it’s not relevant to a network connectivity issue unless the printer is intended to be shared via a direct USB connection to a single computer, which then shares it over the network.
- Check the Vibration of the Crystals: This suggestion does not apply to standard printer troubleshooting or setup. It doesn’t relate to any known method of resolving printer connectivity issues.
If the problem persists after trying these steps, the technician should check other factors such as network settings, printer sharing configurations, firewall settings, and ensure that the printer drivers are correctly installed on the computers.
-
Employees are complaining that they send print jobs to a newly installed printer but the print jobs never print. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- The printer is connected to the wrong port. Modify the port.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Install a USB hub.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Reset the page counter.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of employees sending print jobs to a newly installed printer but the jobs not printing, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Modify the Port Settings: The technician should check if the printer is connected to the correct port on the network. Incorrect port settings can prevent print jobs from reaching the printer. This involves verifying and adjusting the printer’s port settings in the printer properties on the server or on individual computers.
- Connect the Printer Using Wireless: If the printer is wireless-capable and the issues persist with a wired connection, trying a wireless connection might help. This involves ensuring the printer is properly connected to the Wi-Fi network.
The other suggestions are less likely to address the specific issue at hand:
- Check the Vibration of the Crystals: This suggestion is not relevant to printer troubleshooting and does not correspond to any recognized method of resolving printer connectivity or functionality issues.
- Install a USB Hub: Installing a USB hub is beneficial when additional USB ports are needed, but it’s unlikely to resolve a network printer issue, especially if the problem is related to multiple users.
- Reset the Page Counter: Resetting the page counter is generally for maintenance or tracking purposes and is not related to solving connectivity or printing issues.
Additionally, the technician should ensure that the printer is online and check for any error messages on the printer itself. They should also verify that the correct drivers are installed and that the printer is set as the default printer if necessary. If the print queue is backed up, clearing it and restarting the printer might also help.
-
Users have noticed that the colors on their printed documents are different from the colors that they see on their computer screens. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Calibrate the printer.
- Install a USB hub.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Reset the page counter.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of the colors on printed documents being different from those seen on computer screens, the technician should:
- Calibrate the Printer: This is the most relevant step for addressing color discrepancies between the screen and the printed output. Printer calibration involves adjusting the printer’s color settings to ensure that the output matches what is seen on the screen as closely as possible. This can sometimes involve using specific calibration tools or software provided by the printer manufacturer.
The other suggestions are not directly related to resolving color discrepancies in printing:
- Install a USB Hub: This would be useful for expanding the number of USB ports on a computer, but it won’t impact the color accuracy of printed documents.
- Check the Vibration of the Crystals: This suggestion does not apply to standard printer troubleshooting or setup and does not relate to resolving printing color issues.
- Connect the Printer Using Wireless: While this might be necessary if there are connectivity issues, changing the connection method from wired to wireless (or vice versa) will not typically affect the color accuracy of printouts.
- Reset the Page Counter: Resetting the page counter is generally for maintenance or tracking purposes and is not related to color calibration or print quality.
Additionally, it might be beneficial to check the color settings on the users’ computer screens. Sometimes, the issue might also involve monitor calibration, ensuring that the display itself is accurately representing colors.
-
A technician has just completed a preventive maintenance on the department printer. Users are now complaining that the printer is no longer available. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Check that the printer is plugged into a power source.
- Install a USB hub.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Reset the page counter.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of the department printer being unavailable to users after preventive maintenance, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Check that the Printer is Plugged into a Power Source: First, ensure that the printer is properly plugged in and turned on. Sometimes during maintenance, devices can become unplugged or powered off, and this simple check can often resolve the issue.
- Connect the Printer Using Wireless: If the printer is wireless-capable and was previously using a wireless connection, ensure that it is still connected to the correct Wi-Fi network. Sometimes settings may be reset or lost during maintenance.
The other suggestions are less likely to be relevant in this context:
- Install a USB Hub: This would be useful if more USB ports are needed, but it’s unlikely to be related to the printer being unavailable to users, especially in a networked environment.
- Check the Vibration of the Crystals: This is not a relevant step in standard printer troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Reset the Page Counter: This is typically done for maintenance records or accounting purposes and is not related to the availability or connectivity of the printer.
Additionally, the technician should check any network connections (if it’s a network printer) to ensure the printer is properly connected to the network. Verifying the printer’s status on the network and ensuring that the correct drivers are installed and configured on user computers are also important steps. If the printer was physically moved during maintenance, checking all cable connections (Ethernet or USB, depending on the setup) is also crucial.
-
A technician has just completed a preventive maintenance on the department printer. Users are now complaining that the printer is no longer available. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Check that the printer is plugged into a power source.
- Update the OS.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Install a USB hub.
- Reset the page counter.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of the department printer being unavailable to users after preventive maintenance, the technician should:
- Check that the Printer is Plugged into a Power Source: The first step should be to ensure that the printer is properly connected to a power source and turned on. It’s not uncommon for devices to be accidentally unplugged or powered off during maintenance.
- Update the OS: While not the most immediate step for a printer issue, ensuring that the operating system on the server or computers connecting to the printer is up to date can sometimes resolve compatibility or driver-related issues. However, this is more of a secondary step after checking physical connections and power.
The other suggestions are unlikely to address the issue:
- Check the Vibration of the Crystals: This is not a relevant or recognized method in standard printer troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Install a USB Hub: Installing a USB hub would be beneficial if additional USB ports are needed, but this doesn’t directly relate to a network printer being unavailable post-maintenance.
- Reset the Page Counter: This is typically done for maintenance records or accounting purposes and would not affect the availability or connectivity of the printer.
Additionally, the technician should check network connections if it’s a network printer, ensure the printer is correctly connected to the network, and that any required printer services are running. Verifying the printer’s status in the printer settings on user computers and ensuring the printer is set as the default printer might also help. If the printer is shared through a server, checking the server’s printer sharing settings is also important.
-
Students who use the same printer are complaining that recently printed documents contain unknown characters. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Re-install the printer driver.
- Power cycle the printer.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Install a USB hub.
- Reset the page counter.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of recently printed documents containing unknown characters, the technician should:
- Re-install the Printer Driver: This issue often arises due to a problem with the printer driver. Re-installing or updating the printer driver on the computers sending print jobs can often resolve this kind of issue. Corrupted or outdated drivers can cause incorrect or garbled printing.
- Power Cycle the Printer: Turn the printer off, wait for a few moments, and then turn it back on. Power cycling can clear any errors or glitches that the printer may have encountered, which could be causing the issue with the unknown characters.
The other suggestions are less likely to be effective in this scenario:
- Check the Vibration of the Crystals: This is not a recognized method in standard printer troubleshooting or maintenance.
- Install a USB Hub: Installing a USB hub is useful for expanding USB port availability but won’t address issues related to print quality or characters being printed incorrectly.
- Reset the Page Counter: Resetting the page counter is typically done for maintenance tracking purposes and would not have an impact on the quality or accuracy of the printing.
Additionally, it might be useful to check if the problem occurs from all computers or only specific ones, as this can help isolate the issue. If the problem is isolated to specific documents or applications, ensuring those documents and applications are functioning correctly is also important.
-
All documents printed by the laser printer in the branch office have ghost or shadow images appearing on the paper. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Replace the drum.
- Configure the printer for duplex printing.
- Update the BIOS.
- Update the OS.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
-
Explanation & Hint: To resolve the issue of ghost or shadow images appearing on the paper when using a laser printer, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Replace the Drum: Ghosting or shadowing on printed documents is often a sign of a problem with the printer’s drum unit. Over time, the drum can wear out or become damaged, leading to poor quality prints. Replacing the drum unit in the laser printer is likely to resolve this issue.
The other suggestions are less likely to address this specific problem:
- Configure the Printer for Duplex Printing: This setting adjusts how the printer handles double-sided printing and is not related to the quality of the images being printed, such as ghosting.
- Update the BIOS: Updating the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is related to the computer’s firmware and is unlikely to have any impact on a printer’s output quality.
- Update the OS (Operating System): While keeping the OS updated is generally good practice, it’s unlikely to directly resolve a hardware-related print quality issue like ghosting.
- Connect the Printer Using Wireless: Changing the printer’s connection method from wired to wireless (or vice versa) will not affect the print quality or resolve issues like ghosting.
Additionally, it may be helpful to perform a general maintenance check on the printer, including cleaning and ensuring all other consumable parts (like toner cartridges) are in good condition.
-
An office assistant in a law firm is trying to print many large legal documents but is getting “memory overload” error messages from the printer. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Add more memory to the printer.
- Replace the pickup roller.
- Update the BIOS.
- Update the OS.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
-
Explanation & Hint: When an office assistant in a law firm encounters “memory overload” error messages while printing large legal documents, the most appropriate steps to resolve this issue include:
- Add More Memory to the Printer: This is likely the most direct solution to a memory overload issue. Printers have their own RAM to process documents for printing. When a document is too large for the printer’s current memory capacity, it can result in a memory overload error. Increasing the printer’s memory can allow it to handle larger documents more effectively.
- Update the Printer’s Firmware: While not listed in these options, this is often a relevant step. Firmware updates can sometimes improve the efficiency of how a printer uses its memory, potentially resolving memory overload issues.
- Reduce the Document’s Size or Print in Smaller Batches: If adding memory is not an option, another workaround is to reduce the size of the document being printed, or to print the document in smaller batches. This can be less demanding on the printer’s memory.
- Connect the Printer Using Wireless: This might not directly solve a memory issue, but if the memory overload is related to a data transmission bottleneck when connected via a cable (which is less common), switching to a wireless connection might help. However, this is less likely to be effective if the issue is truly due to insufficient memory in the printer itself.
The other options you mentioned, such as replacing the pickup roller, updating the BIOS, and updating the OS, are less likely to be relevant for a memory overload issue in a printer. The pickup roller is related to the physical picking and feeding of paper, not memory. BIOS and OS updates are more related to the computer or server that is sending the print job, not the printer’s ability to handle large documents.
-
A reporter is trying to print several high resolution photographs but the color laser printer is going extremely slowly. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Add more RAM to the printer.
- Replace the pickup roller.
- Update the BIOS.
- Update the OS.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a reporter is experiencing extremely slow printing with high-resolution photographs on a color laser printer, there are several potential solutions to consider:
- Add More RAM to the Printer: This is a viable solution if the slowness is due to the printer’s inability to process large files quickly. High-resolution photos require more memory to process than standard documents. Upgrading the printer’s RAM can significantly improve its ability to handle these large files more efficiently.
- Update the Printer’s Firmware or Driver: While not listed in these options, updating the printer’s firmware or the driver on the computer can often resolve performance issues. Manufacturers frequently release updates to improve the functionality and efficiency of their printers.
- Optimize the Print Settings: Before considering hardware changes, it’s wise to check the print settings. Printing high-resolution photos in the highest quality mode can be very slow. Adjusting the settings to a slightly lower quality or opting for draft mode can speed up the process without significantly impacting the output quality for certain uses.
- Check the Network Connection: If the printer is networked, a slow or unstable network connection can cause delays. Switching from a wired to a wireless connection, or vice versa, can sometimes improve the situation, especially if the current connection is problematic. However, this is more of a trial-and-error approach.
- Inspect for Hardware Issues: While replacing the pickup roller won’t typically resolve issues with slow printing of high-resolution photos, it’s a good practice to ensure that all hardware components of the printer are functioning correctly. A general maintenance check can sometimes uncover hidden issues that affect performance.
The other options you mentioned, such as updating the BIOS and updating the OS, are less directly related to the printer’s performance issues. The BIOS and OS updates pertain more to the computer or server sending the print jobs, and are unlikely to impact the speed of the printer itself unless there are specific compatibility issues or driver problems.
-
A receptionist is complaining about the following printer issue: The print queue seems to be functioning properly, but the printer does not print. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- There is a bad cable connection.
- The printer has an error such as out of paper, out of toner, or paper jam.
- The print queue is overloaded.
- The printer does not have enough RAM.
- The printer lid has not been closed securely.
-
Explanation & Hint: For the issue described where the print queue seems to be functioning properly, but the printer does not print, two possible causes could be:
- There is a Bad Cable Connection: This is a common issue that can disrupt communication between the computer and the printer. If the cable connection is loose, damaged, or not properly connected, the printer might appear ready in the print queue but fail to receive or process the print command. Checking and securing the cable connections, or replacing a faulty cable, can resolve this issue.
- The Printer has an Error such as Out of Paper, Out of Toner, or Paper Jam: Printers often fail to start printing if there are operational issues like being out of paper, out of toner, or having a paper jam. These errors might not always be communicated back to the print queue on the computer, leading to a situation where the job appears ready to print but the printer remains inactive. Checking the printer for these common issues and resolving them (by adding paper, replacing toner, or clearing a jam) can solve the problem.
The other options, such as an overloaded print queue or the printer not having enough RAM, are less likely in this scenario given the symptoms described. An overloaded print queue would generally slow down printing rather than completely stop it. Insufficient RAM in the printer typically affects the printer’s ability to handle large or complex documents, not its ability to start a print job. The printer lid not being closed securely could be a potential issue, but it’s generally less common and would typically trigger an error or warning message on the printer itself.
-
A photographer is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer issues a “Document failed to print” message. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- A cable is loose or disconnected.
- The printer is no longer shared.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
- The print queue is overloaded.
- The printer lid has not been closed securely.
-
Explanation & Hint: - A cable is loose or disconnected: This is a common and straightforward issue. If the connection between the printer and the computer (or network) is not secure due to a loose or disconnected cable, it can prevent the printer from receiving print jobs. Ensuring all cables are properly connected is an essential step in troubleshooting printer issues.
- The printer is no longer shared: In a network environment, especially in offices or shared spaces, printers are often set up as shared devices. If the printer sharing settings are altered or if the printer is somehow removed from the network sharing options, it could lead to an inability to print, especially from other computers on the network. Restoring the printer’s shared status or ensuring that network sharing settings are correctly configured can resolve this issue.
These two causes are indeed plausible and can be relatively common in different printing environments. Checking and addressing both can help in resolving the printing issue.
-
A reporter is complaining about the following printer issue: The paper jams when the printer is printing. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The printer could be dirty.
- The humidity could be high and that causes the paper to stick together.
- The laser printer is emitting too much radiation.
- The printer does not have enough RAM.
- The print queue is overloaded.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a reporter experiences paper jams while printing, two possible causes for this issue could be:
- The Printer Could Be Dirty: Over time, dust and debris can accumulate inside a printer, leading to paper jams. The presence of dirt or foreign objects can obstruct the paper’s path, causing it to jam as it moves through the printer. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the printer can help prevent such issues.
- The Humidity Could Be High and That Causes the Paper to Stick Together: High levels of humidity can affect the condition of the paper. In humid conditions, paper can absorb moisture from the air, causing sheets to stick together. This makes it more likely for multiple sheets to be fed through the printer at once, leading to jams. Using a dehumidifier in the room or storing paper in a dry, cool place can mitigate this problem.
The other options listed are less likely to be the cause of paper jams. Radiation from a laser printer is not a factor in causing paper jams. Similarly, insufficient RAM in the printer or an overloaded print queue typically affects the printer’s ability to process and handle print jobs efficiently, but these factors do not directly cause physical paper jams.
-
A manager is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer is printing incorrect colors. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The print heads might need to be cleaned and calibrated.
- An incorrect cartridge could be installed.
- The printer is using the wrong cable.
- The print queue is overloaded.
- The printer lid has not been closed securely.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a manager encounters an issue with their printer printing incorrect colors, two possible causes could be:
- The Print Heads Might Need to Be Cleaned and Calibrated: This is a common issue in printers, especially those that use inkjet technology. Over time, print heads can become clogged with ink or dust, leading to poor color output. Additionally, if the print heads are misaligned, it can also result in inaccurate color reproduction. Cleaning and calibrating the print heads can often resolve these issues and improve color accuracy.
- An Incorrect Cartridge Could Be Installed: Using the wrong type of ink or toner cartridge can lead to incorrect colors being printed. This can happen if a cartridge is incompatible with the printer model or if a color cartridge is placed in the wrong slot. Ensuring that the correct cartridges are installed and properly seated can solve this problem.
The other options, such as using the wrong cable, the print queue being overloaded, or the printer lid not being closed securely, are less likely to cause an issue with incorrect colors. The type of cable used generally does not affect color output, and an overloaded print queue would typically lead to delays in printing rather than color inaccuracies. Similarly, an unsecured printer lid might cause other operational issues but is unlikely to directly result in incorrect color printing.
-
A technician is complaining about the following printer issue: The print appears faded on the paper. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The toner cartridge is low.
- The paper might be incompatible with the printer.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
- The printer does not have enough RAM.
- The print queue is overloaded.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician encounters an issue with print appearing faded on paper, two likely causes could be:
- The Toner Cartridge is Low: This is a common reason for faded prints, especially in laser printers. When toner levels are low, the printer can’t apply enough toner to the paper, resulting in a faded appearance. Replacing or refilling the toner cartridge is a straightforward solution to this problem.
- The Paper Might be Incompatible with the Printer: Using the wrong type of paper for the specific printer can affect print quality. Some printers are optimized for certain types of paper, and using a different kind might not absorb or hold the ink or toner properly, leading to faded prints. Switching to a compatible paper type as recommended by the printer manufacturer can improve print quality.
The other options, such as the wrong printer type being selected, the printer not having enough RAM, or the print queue being overloaded, are less likely to cause faded prints. Selecting the wrong printer type might affect print layout or formatting but typically does not result in faded prints. Insufficient printer RAM and an overloaded print queue generally affect the printer’s ability to process and manage print jobs efficiently, but they do not directly impact the intensity of the print on the paper.
-
A librarian is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer control panel displays no image. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The contrast of the screen may be set too low.
- The printer is not turned on.
- The room temperature is above normal.
- The print queue is overloaded.
- The printer lid has not been closed securely.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a librarian is facing an issue where the printer control panel displays no image, two possible causes could be:
- The Contrast of the Screen May Be Set Too Low: If the contrast setting on the printer’s control panel is too low, it might make the display appear blank or very faint. Adjusting the contrast settings to increase visibility can resolve this issue if the display is otherwise functioning properly.
- The Printer is Not Turned On: This may seem basic, but it’s a common oversight. If the printer is not properly powered on, the control panel will not display any image. Ensuring that the printer is connected to a power source and turned on is a fundamental step to resolve this issue.
The other options, such as the room temperature being above normal, the print queue being overloaded, or the printer lid not being closed securely, are less likely to cause an issue with the printer control panel display. Room temperature typically affects the printer’s internal mechanics rather than its electronic display. An overloaded print queue might delay printing or cause operational errors, but it wouldn’t impact the display on the control panel. Similarly, an unsecured printer lid might trigger an error message or halt printer operations, but it’s unlikely to affect the control panel display directly.
-
A teacher is complaining about the following printer issue: The paper is creased after printing. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The paper-feed tray might not be firmly adjusted against the edges of the printer.
- The paper might be loaded incorrectly.
- Print jobs are being sent to the wrong printer.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
- The laser printer is emitting too much radiation.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a teacher experiences the issue of paper being creased after printing, two possible causes could be:
- The Paper-Feed Tray Might Not Be Firmly Adjusted Against the Edges of the Printer: If the paper-feed tray is not properly aligned or adjusted, it can cause the paper to feed into the printer at an angle or inconsistently. This misalignment can lead to the paper being creased as it moves through the printer. Adjusting the tray to ensure it is snug against the edges of the printer and that paper is aligned correctly can help prevent this issue.
- The Paper Might Be Loaded Incorrectly: Loading paper improperly into the printer’s tray can also cause creasing. This includes overfilling the tray, using paper that is bent or curled, or not aligning the paper correctly in the tray. Ensuring that the paper is loaded properly, without any pre-existing creases or curls, and in accordance with the printer’s guidelines, can reduce the occurrence of this issue.
The other options, such as print jobs being sent to the wrong printer, the wrong printer type being selected, or the laser printer emitting too much radiation, are not likely to be relevant to the issue of paper creasing. Sending jobs to the wrong printer or selecting the wrong printer type would typically affect where and how the document is printed, but not the physical condition of the paper. The concept of a laser printer emitting “too much radiation” is a misconception and is not associated with paper creasing. Laser printers use laser technology to transfer toner to paper, which does not involve harmful levels of radiation.
-
A receptionist is complaining about the following printer issue: The print queue seems to be functioning properly, but the printer does not print. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- There is a bad cable connection.
- The printer has an error such as out of paper, out of toner, or paper jam.
- The print queue is overloaded.
- A test page was never printed.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a receptionist encounters an issue where the print queue seems to be functioning properly, but the printer does not print, two possible causes could be:
- There is a Bad Cable Connection: A faulty or disconnected cable can disrupt the communication between the computer and the printer. Even if the print queue on the computer appears to be functioning normally, a bad cable connection can prevent the printer from receiving the print commands. Checking and ensuring a secure and functional cable connection or replacing a damaged cable can resolve this issue.
- The Printer has an Error such as Out of Paper, Out of Toner, or Paper Jam: These are common printer errors that can halt printing operations. The printer might display these errors on its control panel or through indicator lights. If the printer is out of paper or toner, or if there is a paper jam, it will not be able to complete the print job despite the queue appearing normal. Resolving these issues (by adding paper, replacing toner, or clearing a jam) can enable the printer to start printing again.
The other options, such as the print queue being overloaded, a test page never being printed, or the wrong printer type being selected, are less likely to be the direct cause of the printer not printing in this scenario. An overloaded print queue might slow down printing but typically doesn’t stop it completely. A test page not being printed would not affect subsequent print jobs. Selecting the wrong printer type could cause format or compatibility issues, but it wouldn’t usually result in the printer not printing at all if it’s correctly connected and operational.
-
A photographer is complaining about the following printer issue: The paper is not being fed into the printer. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The paper may be wrinkled.
- The printer could be set to print to a different paper size than is currently loaded.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
- A test page was never printed.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a photographer experiences an issue with paper not being fed into the printer, two possible causes could be:
- The Paper May Be Wrinkled: Wrinkled or curled paper can cause feed issues in printers. If the paper is not flat or has any physical deformities, it might not be picked up properly by the printer’s rollers. Using smooth, flat paper that is free from wrinkles can help prevent this issue.
- The Printer Could Be Set to Print to a Different Paper Size Than Is Currently Loaded: If the printer settings specify a different paper size than the size actually loaded in the tray, it can lead to feeding problems. The printer might attempt to feed paper from a tray or a slot that isn’t loaded with the correct size, resulting in no paper being fed for printing. Ensuring that the printer settings match the actual paper size loaded in the printer can resolve this problem.
The other options, such as the paper tray being flimsy, a test page never being printed, or the wrong printer type being selected, are less likely to directly cause the issue of paper not being fed into the printer. A flimsy paper tray might affect the stability of the paper but generally does not prevent it from being fed into the printer. The absence of a test page printout would not impact the printer’s ability to feed paper. Selecting the wrong printer type in the printer settings might cause formatting issues or print errors but typically doesn’t result in a failure to feed paper.
-
A reporter is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer is printing unknown characters. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The wrong or an outdated printer driver is installed.
- The printer has a loose connection.
- The laser printer is emitting too much radiation.
- A test page was never printed.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
-
Explanation & Hint: In the scenario where a printer is producing unknown characters, the two most plausible causes are:
- The Wrong or an Outdated Printer Driver is Installed: This is a common cause of printing issues. Printer drivers facilitate communication between the computer and the printer. If the driver is incorrect or outdated, it can lead to miscommunication, resulting in the printer outputting unknown or garbled characters. Updating or reinstalling the correct printer driver can often resolve this issue.
- The Printer has a Loose Connection: A loose or faulty connection between the printer and the computer can lead to intermittent or incorrect data transmission. This can manifest as the printer printing unknown characters because it is not receiving the correct information from the computer. Checking and securing all cables, or even replacing them if they are damaged, can help fix this problem.
It’s important to address both software (driver) and hardware (connection) aspects when troubleshooting printer issues like this.
-
While a technician is installing a printer, the technician hears a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- RAM
- optical drive
- monitor
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician hears a loud clicking noise while installing a printer, the first device to check would typically be the hard drive. Clicking noises are often associated with hard drives, especially when they encounter read/write errors or mechanical failures. This is commonly referred to as the “click of death” and can be a sign of a failing hard drive.
The other components listed (RAM, optical drive, monitor) are less likely to produce a clicking noise. RAM does not have moving parts, so it wouldn’t make a clicking sound. An optical drive could make a noise when reading a disc, but it’s usually more of a whirring or spinning sound rather than clicking. Monitors do not have moving parts either and are unlikely to produce such noises.
Therefore, investigating the hard drive should be the initial step when addressing the clicking noise issue during printer installation.
-
While a technician is installing a printer, the technician hears a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- sound card
- optical drive
- monitor
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician hears a loud clicking noise while installing a printer, the device they should check first is the optical drive. This recommendation is based on the context of the situation – installing a printer. It’s possible that the installation involves the use of a CD or DVD for printer drivers or software, and if the optical drive is in use during this process, it could make clicking noises if there is an issue with the disc (like scratches or dirt) or a mechanical problem with the drive itself.
While hard drives can also make clicking noises, these are usually associated with more serious issues like the “click of death,” indicating hard drive failure. However, in the context of printer installation, the hard drive is less likely to suddenly exhibit this kind of problem.
The sound card and monitor are unlikely to be sources of a clicking noise. Sound cards typically produce electronic sounds or noise, not mechanical clicking, and monitors don’t have moving parts that would cause such a noise.
-
While working in a computer training room, the technician notices that one computer emits a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- sound card
- optical drive
- monitor
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician notices a loud clicking noise coming from a computer in a training room, the first device to check should be the hard drive. Clicking noises coming from a computer are often associated with hard drives, especially when they encounter read/write errors or mechanical failures. This is commonly referred to as the “click of death” and can be a sign of a failing hard drive.
Hard drives have moving parts (like the read/write head and spinning platters), and a clicking sound could indicate that these parts are malfunctioning. This issue should be addressed promptly, as it could lead to data loss.
The other devices listed are less likely to produce a clicking noise:
- Sound Card: A sound card typically wouldn’t produce a mechanical clicking noise. Issues with sound cards usually manifest as problems with audio output, like distortion or no sound at all.
- Optical Drive: While an optical drive could potentially make a clicking noise when reading a disc, this would only occur if a disc is in use. If the noise is constant and not related to disc usage, the optical drive is less likely to be the cause.
- Monitor: Monitors, especially modern LCD/LED types, do not have moving parts and are unlikely to produce a clicking noise. Noise from monitors would be unusual and more likely electronic in nature if it occurs.
Given these considerations, investigating the hard drive should be the initial step in resolving the issue of the clicking noise in the computer.
-
While working in a computer training room, the technician notices that one computer emits a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- internal speaker
- optical drive
- monitor
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician notices a loud clicking noise coming from a computer in a training room, the first device to check should be the hard drive. Clicking noises from a computer are commonly associated with hard drive issues. These noises can indicate mechanical failures or read/write errors, often referred to as the “click of death,” which could be a sign of a failing hard drive. Hard drives have mechanical components like read/write heads and spinning platters, and problems with these parts can produce clicking sounds.
While the other components listed might also produce sounds, they are less likely to produce a clicking noise:
- Internal Speaker: While the internal speaker can produce various sounds, a consistent clicking noise is unlikely to originate from it unless specifically produced by the system’s audio output, which is rare in normal operation.
- Optical Drive: An optical drive might make clicking noises, but this is typically only when reading or writing to a disc. If no disc is being used, or if the noise is continuous and not obviously tied to disc activity, the optical drive is less likely to be the cause.
- Monitor: Monitors, especially newer ones, do not have moving parts and thus are unlikely to produce mechanical clicking noises. Any noise from a monitor would be unusual and more likely to be electronic in nature if it occurs.
Therefore, the hard drive is the most likely culprit for a clicking noise in a computer and should be the first component to check.
-
While working in a computer training room, the technician notices that one computer emits a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- internal speaker
- motherboard
- CPU fan
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician hears a loud clicking noise from a computer in a training room, the first device to check should be the hard drive. This is because clicking noises are commonly associated with hard drive issues, such as mechanical failures or read/write errors. These noises can indicate significant problems, often referred to as the “click of death,” suggesting a potential failure of the hard drive.
Other components listed are less likely to produce a clicking noise:
- Internal Speaker: The internal speaker in a computer usually doesn’t produce a clicking sound unless it’s being driven by a specific audio signal. It’s not a common source of mechanical noises.
- Motherboard: While the motherboard is a central component, it doesn’t have moving parts that would produce a clicking sound. Issues with the motherboard typically manifest as system errors or failures to boot, not as audible clicking.
- CPU Fan: Although fans can make noises, these are usually more of a whirring or buzzing sound rather than a distinct clicking. However, if the fan is hitting something or is severely unbalanced, it might produce a clicking noise. After checking the hard drive, if no issue is found, the CPU fan could be a secondary item to inspect.
Considering these possibilities, the hard drive is the most likely source of a loud clicking noise in a computer and should be examined first.
-
Every time a user turns on the computer in the morning, the user hears a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- internal speaker
- motherboard
- CPU fan
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user hears a loud clicking noise every time they turn on their computer, the first device a technician should check is the hard drive. Clicking noises from a computer are commonly associated with hard drive issues, particularly mechanical failures or read/write errors. This type of noise, often referred to as the “click of death,” can indicate a significant problem with the hard drive, such as the failure of the read/write head or spindle motor.
The other components listed are less likely to be the source of a clicking noise:
- Internal Speaker: It’s unlikely for the internal speaker to produce a clicking noise unless it’s being driven by specific audio signals, which is uncommon during the startup process.
- Motherboard: The motherboard itself doesn’t have moving parts that would produce a mechanical clicking sound. Issues with motherboards typically manifest in other ways, such as failure to boot or system errors.
- CPU Fan: While fans can sometimes make noises, these are usually more of a whirring or buzzing sound rather than a distinct clicking. However, if a fan blade is hitting an obstruction or if there’s a bearing issue, it could produce a clicking sound. This is less common compared to hard drive issues but could be a secondary check if the hard drive is not the culprit.
Given these considerations, the hard drive should be the primary focus of the technician’s initial investigation.
-
Every time a user turns on the computer in the morning, the user hears a loud clicking noise. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- optical drive
- CPU fan
- CPU
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user reports hearing a loud clicking noise every time they turn on their computer, the first device a technician should check is the hard drive. Clicking noises emanating from a computer are often associated with hard drive issues, especially mechanical failures or read/write errors. This kind of noise, sometimes referred to as the “click of death,” can indicate a significant problem with the hard drive’s mechanical components, like the read/write head or the spindle motor.
The other components listed, while they can produce noises, have characteristics that are different from a clicking sound:
- Optical Drive: An optical drive can make clicking noises, but this is typically only when a disc is being read or written to. If the noise occurs every time the computer is turned on, regardless of whether a disc is in the drive, it’s less likely to be the cause.
- CPU Fan: CPU fans can make a variety of noises, especially if they are malfunctioning or if something is obstructing the fan blades. While a fan issue can sometimes sound like clicking, it’s usually more of a whirring or buzzing sound.
- CPU: The CPU itself does not make noise, as it lacks moving parts. Any noise directly associated with the CPU would more likely be related to its cooling system, such as the CPU fan.
Given these points, the hard drive is the most probable source of the clicking noise and should be examined first.
-
When a co-worker steps into another office, the co-worker notices that the computer is making a loud clicking noise and asks about it. The technician is contacted to investigate. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- monitor
- CPU fan
- CPU
-
Explanation & Hint: When a computer emits a loud clicking noise, the first device a technician should check is the hard drive. This is because a clicking sound often indicates a problem with the hard drive, commonly known as the “click of death.” This noise can be a sign of mechanical failure within the hard drive, which might lead to data loss.
While other components like the CPU fan or the CPU itself could potentially make unusual noises, these are usually more like whirring or buzzing sounds rather than clicking. The monitor is unlikely to make such a noise unless it’s related to its internal electronics, which is less common compared to hard drive issues.
Therefore, the technician should start by examining the hard drive to diagnose the issue accurately and take appropriate action.
-
When a user turns on a workstation, the screen displays an “Invalid Boot Disk” error. The user calls the help desk. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- power supply
- CPU fan
- CPU
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user encounters an “Invalid Boot Disk” error upon turning on a workstation, the first device a technician should check is the hard drive. This error typically indicates that the system is unable to find a bootable operating system, which is usually stored on the hard drive. The problem could be due to various issues with the hard drive, such as a failure, disconnection, corruption of system files, or incorrect boot order in the BIOS settings.
The power supply is less likely to be the cause of this specific error. While a failing power supply can cause a range of issues, it wouldn’t typically result in an “Invalid Boot Disk” message.
Similarly, the CPU fan and the CPU are not the primary suspects for this error. Issues with the CPU or its cooling fan might prevent the computer from booting, but they wouldn’t usually cause an “Invalid Boot Disk” message to appear.
Therefore, the technician should start by checking the hard drive to ensure it is properly connected, functioning, and configured as the primary boot device in the system’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
-
When a user turns on a workstation, the screen displays an “Invalid Boot Disk” error. The user calls the help desk. Which device should the technician check first?
- hard drive
- motherboard
- CPU fan
- CPU
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user encounters an “Invalid Boot Disk” error upon turning on a workstation, the first device a technician should check is the hard drive. This error typically indicates that the system is unable to find a bootable operating system, which is usually stored on the hard drive. The problem could be due to various issues with the hard drive, such as a failure, disconnection, corruption of system files, or incorrect boot order in the BIOS settings.
The motherboard could be a secondary point of investigation, particularly if there are reasons to suspect a broader hardware failure or issues with the BIOS settings. However, motherboard issues would typically manifest in more generalized boot failures or system instability, not specifically an “Invalid Boot Disk” error.
The CPU fan and the CPU are less likely to be the cause of this specific error. While problems with the CPU or its cooling fan might prevent the computer from booting entirely, they generally wouldn’t cause an “Invalid Boot Disk” message to appear.
Therefore, the technician should start by checking the hard drive to ensure it is properly connected, functioning, and configured as the primary boot device in the system’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Check the Startup folder.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the drive is recognized by the operating system, the technician should use Device Manager. Device Manager in Windows is a system utility that lists all the hardware devices installed on the computer. It can be used to check if the drive is being detected by the operating system and if there are any issues with the drivers or the device itself.
Here’s why the other options are less appropriate:
- Check the Startup folder: This action is not relevant to the problem. The Startup folder contains programs that run on system startup, and it wouldn’t provide information about the presence or status of a drive.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used to display network configuration details and is not related to checking the status of storage drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: While this could be a step in troubleshooting hardware connection issues, it’s more invasive and should be considered only after confirming that the drive is not recognized by the operating system through less intrusive methods like checking Device Manager.
Therefore, the first step should be to open Device Manager and look under the “Disk drives” section to see if the missing drive is listed. If it is not listed, the technician might then consider physical troubleshooting steps like checking connections or swapping cables.
-
A computer has two mechanical hard drives. The second drive (D:) is used for data storage. When trying to save an email attachment to the local hard drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To check if the D: drive (the second mechanical hard drive) is recognized by the operating system, the technician should use File Explorer. File Explorer in Windows is a user-friendly tool that allows users to view and manage files and drives on their computer. By using File Explorer, the technician can quickly verify whether the D: drive is visible to the operating system and accessible.
Here’s why the other options are less appropriate:
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used for displaying network configuration details and has no relevance to checking the status of storage drives.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1: This address is a loopback address for the local machine, typically used for network testing. It would not provide information about the local storage drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: This hardware troubleshooting step should be considered only after confirming through software means (like using File Explorer) that the drive is not recognized. Swapping cables is more invasive and should be a later step in the troubleshooting process.
Therefore, the technician should start by opening File Explorer to see if the D: drive is listed under “This PC” or “Computer.” If the drive is not visible there, further troubleshooting steps, including checking disk management, examining physical connections, or swapping cables, may be necessary.
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Boot into UEFI/BIOS and see if the drive appears.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the drive is recognized by the operating system after a user reports that it is no longer visible in the save options of an application, the technician should take the following steps:
- Use Device Manager: This is a good initial step. Device Manager shows all the hardware components of the system, including storage drives. If the drive is not listed in Device Manager, it suggests that the operating system is not recognizing it, which could be due to a hardware issue or a driver problem.
- Boot into UEFI/BIOS and see if the drive appears: This is another important step if the drive is not visible in Device Manager. Checking the UEFI/BIOS will determine if the drive is recognized at the hardware level. If the drive is not detected in the UEFI/BIOS, it suggests a more fundamental hardware issue, such as a disconnected or failed drive.
The other options are not relevant to the problem:
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1: This action would not provide any useful information regarding the status of local storage drives. The address 127.0.0.1 is the loopback address used for network testing and does not relate to local drive configuration.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used to display network configuration and is not relevant to checking the status of storage drives.
Therefore, the technician should start with Device Manager to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system, and if not, proceed to check the UEFI/BIOS settings.
-
A laptop has an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive (D:). When the user tries to save a spreadsheet to the D: drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not there. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the D: drive (mechanical hard drive) is recognized by the operating system on a laptop with both an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive, the technician should use the Disk Management Control Panel. Disk Management is a Windows utility that provides a detailed view of all connected storage devices, their partitions, and statuses. It can be used to verify whether the D: drive is visible to the operating system and to manage drive partitions.
Here’s why the other options are less appropriate:
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1: This action is not useful for this issue. The address 127.0.0.1 is a loopback address for network testing and is not related to local storage drive configuration.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used for displaying network configuration information and is irrelevant to checking the status of storage drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: This is not typically applicable to laptops, as their internal drives often use different connectors (NVMe drives use a dedicated slot, while mechanical drives use a SATA connection) and are not as easily swappable as in desktops. Moreover, physical troubleshooting like this should only be considered after confirming the drive’s status through software diagnostics.
Therefore, the technician should open the Disk Management tool (which can be accessed by right-clicking on “This PC” or “My Computer” and selecting “Manage,” then navigating to “Disk Management”) to see if the D: drive is listed and in a healthy state. If the drive is not visible in Disk Management, further hardware diagnostics or a physical inspection might be necessary.
-
A computer has an SSD for the operating system and applications and uses another mechanical hard drive for data storage. The user reports that data can no longer be saved to the mechanical hard drive. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
-
Explanation & Hint: To check if the mechanical hard drive is recognized by the operating system in a computer that uses an SSD for the operating system and applications, and a mechanical hard drive for data storage, the technician should:
- Use Device Manager: This is the first step to take. Device Manager in Windows provides a comprehensive list of all hardware devices installed, including storage drives. By opening Device Manager, the technician can quickly see if the mechanical hard drive is recognized by the operating system. If the drive is not listed, it may indicate a problem with the drive’s connection, failure, or an issue with the drivers.
The other options provided are less suitable for the initial diagnosis:
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD: This is a more advanced troubleshooting step that involves physically handling the hardware. It should only be considered if other software-based diagnostic methods (like using Device Manager) do not reveal the cause of the problem. Additionally, this method assumes that the user has the technical skill and tools to safely perform such an operation, which might not be the case.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1: This method is not relevant to the issue. The address 127.0.0.1 is a loopback address used in network testing and does not provide information about local storage drives.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used to display network configuration details and is not relevant to checking the status of storage drives.
Therefore, starting with Device Manager to check if the mechanical hard drive is recognized by the operating system is the most appropriate first step. If the drive is not visible there, further investigation, possibly involving physical checks or swapping SATA ports, may be necessary.
-
A laptop has an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive (D:). When the user tries to save a spreadsheet to the D: drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not there. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel.
- Determine if the hard drive service is set to start automatically.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To check if the mechanical hard drive (D:) is recognized by the operating system on a laptop with an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive, the technician should:
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: This is the most appropriate first step. Disk Management is a Windows utility that shows a detailed view of all the storage devices connected to the computer, including their format, partition style, and health status. By using Disk Management, the technician can see if the D: drive is visible to the operating system and whether it has any issues such as being unformatted or having a lost partition.
The other options are less suitable for this situation:
- Determine if the hard drive service is set to start automatically: There isn’t a specific “hard drive service” that would need to be set to start automatically in Windows for a drive to be recognized. This option does not apply to the scenario described.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used for displaying network configuration information and is not relevant for checking the status of storage drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: In a laptop, swapping data cables isn’t usually feasible or relevant, as laptops typically have dedicated connectors for NVMe and SATA drives and do not use standard data cables like desktops. Additionally, physical manipulation of internal components should only be considered after confirming the drive’s status through software diagnostics.
Therefore, the technician should start by opening the Disk Management tool to check if the D: drive is listed and to diagnose any visible issues. If the drive is not visible in Disk Management, further investigation may be necessary, potentially including hardware diagnostics.
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user reports that a drive, which was previously available, is no longer visible within an application, the technician should first use File Explorer to check if the drive is recognized by the operating system. Here’s why:
- Use File Explorer: This is the simplest and most direct method to check if the drive is visible in the operating system. File Explorer shows all the drives and partitions that are currently recognized and accessible by Windows. If the drive is not visible in File Explorer, it indicates that the operating system is not recognizing it, which could be due to several reasons like a disconnected drive, a drive failure, or a software issue.
The other options are not as appropriate for an initial assessment:
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD: This is a more advanced and invasive troubleshooting step. It should only be considered if other methods fail to recognize the drive. Moreover, this assumes the user has the technical skill and appropriate tools, which might not be the case.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1: This step is not relevant to the issue. The address 127.0.0.1 is a loopback address for network testing and does not relate to local drive configuration or troubleshooting.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used to display network configuration details and is not relevant for checking the status of storage drives.
Therefore, the first and most straightforward step is to use File Explorer to see if the drive is listed. If the drive is not visible there, then further investigation, possibly including the use of Disk Management or physical checks, may be necessary.
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel.
- Use the Msconfig utility.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user reports that a drive previously available is no longer visible within an application, the technician should first use the Disk Management Control Panel to determine if the drive is recognized by the operating system. Here’s why:
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: Disk Management is a Windows utility that provides a comprehensive view of all storage devices connected to the computer, including their status, partitions, and formatting. If the drive is not visible in Disk Management, it suggests a problem with the drive being recognized by the system, possibly due to disconnection, failure, or a configuration issue.
The other options are less suitable for this scenario:
- Use the Msconfig utility: The System Configuration utility (msconfig) is primarily used to troubleshoot startup processes and services. It is not used for managing or diagnosing issues with storage drives.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: The ‘ipconfig’ command is used to display network configuration information and is irrelevant for checking the status of storage drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: Swapping data cables is a more advanced and invasive hardware troubleshooting step. It should be considered only after confirming through software means (like using Disk Management) that the drive is not recognized. Additionally, this approach assumes a desktop environment where cables can be easily swapped, which may not be applicable in all cases, especially with laptops.
Therefore, the technician should start by opening the Disk Management tool to check if the drive is listed and to diagnose any visible issues. If the drive is not visible in Disk Management, further investigation may be required, potentially including hardware diagnostics.
-
A computer has two mechanical hard drives. The second drive (D:) is used for data storage. When trying to save an email attachment to the local hard drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user is unable to see the second mechanical hard drive (D:) as an option for saving an email attachment, the technician should follow these steps to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system:
- Use File Explorer: The first and simplest step is to use File Explorer. This will show all the drives and partitions currently recognized by Windows. If the D: drive is not visible in File Explorer, it suggests that the operating system is not recognizing it. This could be due to a variety of reasons, such as a disconnection, drive failure, or a software issue.
The other options are less suitable for an initial diagnosis:
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: This command is used for network configuration and is not relevant for checking the status of storage drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: Swapping cables is a more advanced troubleshooting step. It should be considered only after simpler software-based methods have been tried. This step assumes that the user has the technical skills and necessary tools, which might not always be the case.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD: This is another advanced step and involves physically handling the hardware. Like swapping cables, it should only be considered if simpler methods fail to detect the drive. This step also assumes the user has the technical ability and tools to safely perform such an operation.
Therefore, the technician should start with File Explorer to check if the D: drive is listed. If the drive is not visible there, further investigation may be necessary, potentially including the use of Disk Management or physical checks of the drive’s connections.
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Check the Startup folder.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user reports that a previously visible drive is no longer appearing in the save options of an application, the technician should take the following steps to determine if the drive is recognized by the operating system:
- Use Device Manager: The technician should first check Device Manager. Device Manager in Windows provides a list of all hardware devices installed, including storage drives. If the drive is not listed in Device Manager, it suggests that the operating system is not recognizing it, which could be due to various reasons like a disconnected drive, a drive failure, or an issue with the drivers.
The other options provided are less suitable for the initial assessment:
- Check the Startup folder: This folder contains programs that run on system startup and is not relevant to detecting hardware drives. Checking the Startup folder won’t provide information about the presence or status of a hard drive.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: This is a more advanced and invasive step. It involves physically handling the hardware and should be considered only after software-based methods (like checking Device Manager) have been exhausted. Moreover, this assumes a desktop environment where such swapping is feasible, which may not be applicable in all cases, especially with laptops.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD: Like swapping cables, this is a more advanced hardware troubleshooting step. It should be considered only after confirming through software diagnostics that the drive is not recognized. This step also assumes a level of technical skill and appropriate tools, which might not be available in all situations.
Therefore, the technician should start with Device Manager to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system. If the drive is not visible there, further investigation may be required, potentially involving Disk Management or physical checks of the drive’s connections.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an error message about decryption appears when opening an email. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Install an appropriate certificate.
- Check the display settings.
- Check the fan on the GPU.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician encounters an error message about decryption while opening an email on a laptop, the most likely solution is to:
Install an appropriate certificate: Encryption and decryption issues in emails often relate to digital certificates. If the email is encrypted, the recipient needs the correct certificate and associated private key to decrypt it. Installing the appropriate certificate, which could be provided by the sender or an internal IT department in a corporate environment, would likely resolve the decryption error.
The other options are less likely to be relevant:
- Check the display settings: This is unlikely to help with a decryption error. Display settings affect the visual output of the laptop but do not influence the decryption process of emails.
- Check the fan on the GPU: The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) fan and its functionality are not related to email decryption issues. The GPU fan is involved in cooling the graphics processing unit and wouldn’t impact the ability to decrypt emails.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off: Turning off Wi-Fi would not solve a decryption issue. In fact, it could prevent further troubleshooting steps that require internet access, such as downloading the necessary certificates or getting support from online resources.
Therefore, the recommended action is to install the appropriate certificate to address the decryption error with the email.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an error message about decryption appears when opening an email. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Install an appropriate certificate.
- Check the screen refresh rate.
- Check the fan on the GPU.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: When encountering an error message about decryption while opening an email on a laptop, the most likely solution is to:
Install an appropriate certificate: This is the most relevant solution to address an email decryption issue. If the email is encrypted, the recipient needs the correct digital certificate and the associated private key to decrypt it. Installing the appropriate certificate, which might be provided by the sender, the IT department in a corporate environment, or a trusted certificate authority, should resolve the decryption error.
The other options are less relevant to the issue:
- Check the screen refresh rate: The screen refresh rate pertains to the display properties and has no impact on the decryption of emails. It is unrelated to issues involving the opening or reading of encrypted emails.
- Check the fan on the GPU: The fan on the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is responsible for cooling the graphics card and has no bearing on the decryption of emails. GPU issues typically manifest as graphical errors or overheating problems, not decryption errors.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off: Turning off Wi-Fi is not a relevant step for solving decryption issues. In fact, disconnecting from the internet might prevent necessary steps that require online access, like downloading the needed certificates or seeking online assistance.
Given these options, the appropriate action to address the decryption error is to install the correct digital certificate on the laptop.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an error message about decryption appears when opening an email. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Install an appropriate certificate.
- Replace the digitizer.
- Check the fan on the GPU.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician encounters an error message about decryption while opening an email on a laptop, the most likely solution is to:
Install an appropriate certificate: This is the most relevant approach for resolving a decryption error in an email. Encrypted emails require specific digital certificates for decryption. The recipient needs the correct certificate and associated private key to decrypt the email. Installing or updating the appropriate certificate, which might be provided by the sender, an internal IT department, or a certificate authority, is usually necessary to resolve such decryption issues.
The other options are not relevant to the decryption issue:
- Replace the digitizer: The digitizer is a component related to the touch screen functionality of a laptop. It has no connection to email decryption issues. Replacing it would not address a problem related to decrypting emails.
- Check the fan on the GPU: The fan on the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is responsible for cooling the graphics card. It’s not related to the decryption of emails. Issues with the GPU or its fan would typically manifest as overheating problems or graphical errors, not as decryption errors in emails.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off: Turning off Wi-Fi would not help with a decryption issue and would actually hinder the process if the laptop needs internet access to download the necessary certificates or to receive support.
Therefore, the appropriate action in this case is to install the correct digital certificate needed for decrypting the email.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an error message about decryption appears when opening an email. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Install an appropriate certificate.
- Update all security apps.
- Check the fan on the GPU.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: When encountering an error message about decryption while opening an email on a laptop, the most likely solution is to:
Install an appropriate certificate: Decryption issues in emails often stem from problems related to digital certificates. If the email is encrypted, the recipient requires the correct digital certificate and associated private key to decrypt it. Installing the appropriate certificate, which could be provided by the sender, an IT department in a corporate setting, or a trusted certificate authority, is the most direct way to resolve the decryption error.
The other options are less relevant to the decryption issue:
- Update all security apps: While keeping security applications updated is generally good practice, it may not directly resolve an email decryption issue. However, in some cases, if a security application is involved in managing digital certificates or encryption, updating it could potentially help, especially if there’s a known bug or compatibility issue in the current version.
- Check the fan on the GPU: The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) fan’s function is to cool the graphics processor and has no impact on the decryption of emails. GPU issues usually manifest as visual display problems or overheating, not decryption errors.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off: Turning off Wi-Fi is unlikely to solve a decryption issue. In fact, if the laptop needs to download a necessary certificate or access online resources for troubleshooting, being connected to the internet would be beneficial.
Given these options, the most appropriate initial step is to install the correct digital certificate needed to decrypt the email.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and a key on the keyboard is not responding as it should. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Clean with compressed air.
- Update all security apps.
- Check the fan on the GPU.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: When dealing with a key on a laptop keyboard that is not responding as it should, the most effective solution is to:
Clean with compressed air: Dust, debris, or other small particles can often get lodged under the keys of a keyboard, causing them to become unresponsive or to behave erratically. Using compressed air can help to dislodge and remove this debris, potentially resolving the issue with the non-responsive key.
The other options are not relevant to the issue of a malfunctioning key:
- Update all security apps: Updating security applications is important for overall computer security, but it is not related to the functionality of a physical keyboard.
- Check the fan on the GPU: The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) fan is responsible for cooling the graphics card and is unrelated to issues with keyboard keys.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off: Turning off Wi-Fi has no relevance to a problem with a keyboard key and would not contribute to resolving such an issue.
Therefore, the recommended first step is to clean the affected key using compressed air. If this does not resolve the problem, further troubleshooting might include checking for hardware damage or considering a keyboard replacement.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and a key on the keyboard is not responding as it should. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Clean with compressed air.
- Ensure that Bluetooth is not activated.
- Recharge the battery.
- Check the display settings.
-
Explanation & Hint: For a key on a laptop keyboard that is not responding correctly, the most appropriate solution is to:
Clean with compressed air: When keys on a laptop keyboard are unresponsive or malfunctioning, it’s often due to dust, crumbs, or other debris lodged under the keys. Using compressed air to blow out the debris can often resolve the issue. It’s a non-invasive and effective first step in troubleshooting keyboard problems.
The other options are less likely to address the issue with the keyboard:
- Ensure that Bluetooth is not activated: Bluetooth settings are generally unrelated to the functionality of a wired or built-in laptop keyboard. Bluetooth would be more relevant for issues with external, wireless Bluetooth keyboards.
- Recharge the battery: The battery’s charge level typically affects the overall power of the laptop but is unlikely to cause specific keys on the keyboard to malfunction.
- Check the display settings: The display settings control the visual output on the laptop’s screen and have no impact on the functionality of the keyboard.
Given these options, using compressed air to clean under and around the problematic key is the most relevant and practical solution to try first. If the issue persists, further investigation might be needed, possibly looking into hardware damage or considering a professional repair or replacement of the keyboard.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and GPS is not functioning. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Verify that airplane mode is not activated.
- Ensure that Bluetooth is not activated.
- Recharge the battery.
- Check the display settings.
-
Explanation & Hint: When dealing with an issue where GPS is not functioning on a laptop, the most appropriate solution is to:
Verify that airplane mode is not activated: Airplane mode disables all wireless communications on a device, which includes Wi-Fi, cellular connectivity, and often GPS. Ensuring that airplane mode is turned off is a crucial step in troubleshooting GPS issues, as it would re-enable the necessary wireless connections for GPS functionality.
The other options are less likely to directly address the GPS issue:
- Ensure that Bluetooth is not activated: While Bluetooth is a wireless technology, it is generally independent of GPS functionality. Disabling or enabling Bluetooth is unlikely to affect the GPS.
- Recharge the battery: While it’s important to have sufficient battery power for all functions, a low battery typically does not specifically disable GPS functionality. However, if the battery is extremely low, the device might limit certain functions to save power, but this is less common.
- Check the display settings: Display settings affect the visual output of the laptop’s screen and are not related to GPS functionality.
Therefore, the first step should be to verify that airplane mode is not activated, ensuring that all wireless communications necessary for GPS are enabled. If this does not resolve the issue, further troubleshooting might involve checking GPS settings in the operating system, updating drivers, or investigating any specific software that the laptop uses for GPS functionality.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and GPS is not functioning. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Verify that airplane mode is not activated.
- Check the fan on the GPU.
- Recharge the battery.
- Check the display settings.
-
Explanation & Hint: When dealing with an issue where GPS is not functioning on a laptop, a suitable solution to try is:
Verify that airplane mode is not activated: Airplane mode disables wireless communications on a device, which can include Wi-Fi, mobile data, and often GPS. If airplane mode is activated, it could prevent the GPS from functioning properly. Ensuring that airplane mode is off is a necessary step in troubleshooting GPS issues.
The other options are less likely to be related to the GPS issue:
- Check the fan on the GPU: The fan on the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is responsible for cooling the graphics processor. This is unrelated to the functionality of the GPS system in a laptop.
- Recharge the battery: While it’s important to maintain a good battery level for overall device operation, a low battery is not typically a direct cause of GPS malfunction. However, in some cases, extremely low battery levels might lead to limited functionality to conserve power.
- Check the display settings: Display settings affect the visual output on the laptop screen and do not have a direct impact on the GPS functionality.
Therefore, the first and most relevant action is to check and ensure that airplane mode is not activated, allowing all wireless communication necessary for GPS to operate correctly. If the GPS issue persists even after ensuring that airplane mode is off, further investigation might be needed into the laptop’s hardware, drivers, or specific GPS software settings.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and GPS is not functioning. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Verify the status of service.
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off.
- Recharge the battery.
- Check the display settings.
-
Explanation & Hint: When dealing with a GPS functionality issue on a laptop, the most appropriate solution is to:
Verify the status of service: This means checking whether the GPS service is enabled and functioning correctly within the operating system or the specific application that requires GPS. Some laptops may have settings or software that control the use of GPS. Ensuring that these services are active and properly configured is important for troubleshooting GPS issues.
The other options are less likely to address the GPS problem:
- Ensure that Wi-Fi is turned off: Turning off Wi-Fi is generally not necessary for GPS functionality. In fact, some devices use Wi-Fi to assist in location services, although this is more common in smartphones than laptops.
- Recharge the battery: While a sufficiently charged battery is important for overall device operation, a low battery level does not specifically target GPS functionality. However, it’s worth noting that some devices might limit certain functions to save power when the battery is very low.
- Check the display settings: Display settings affect the visual output of the laptop’s screen and are unrelated to GPS functionality.
Given these options, the most relevant first step is to verify the status of the GPS service or settings on the laptop. This includes checking any dedicated GPS software, location services settings in the operating system, and ensuring that no system settings are disabling the GPS functionality. If this does not resolve the issue, further investigation into hardware, driver compatibility, or specific application settings might be required.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and GPS is not functioning. What is a possible solution for this situation?
- Verify the status of service.
- Ensure that only one app is open at a time.
- Recharge the battery.
- Check the display settings.
-
Explanation & Hint: When troubleshooting a non-functioning GPS on a laptop, the most appropriate solution is to:
Verify the status of service: This involves checking if the GPS service or feature is enabled and functioning correctly within the operating system or the specific application that requires GPS. In some laptops, GPS functionalities are managed through settings or dedicated software. Making sure these services are active and properly configured is crucial for resolving GPS issues.
The other options are less likely to directly address the GPS problem:
- Ensure that only one app is open at a time: Having multiple apps open simultaneously is generally not a cause of GPS malfunction. Modern laptops are designed to multitask effectively. Unless there is a specific conflict between apps that is known to affect GPS functionality, this is unlikely to be a solution.
- Recharge the battery: While maintaining a good battery level is important for the overall operation of a laptop, a low battery level typically does not selectively impair GPS functions. However, if the battery is extremely low, the device may limit certain functionalities to conserve power.
- Check the display settings: Display settings are related to the visual output of the laptop and do not have a direct impact on GPS functionality.
Therefore, the first and most relevant step is to verify the status of the GPS service or settings on the laptop. This could involve checking any location services settings in the operating system, ensuring that no system settings are disabling GPS, and verifying that any GPS-specific software is properly configured. If the issue persists after these checks, further investigation into hardware capabilities, driver issues, or specific application settings might be necessary.
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Final - Mid-term - Cert | |
| Chapter 1 -9 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Chapter 10 - 14 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1001 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1002 | Online Test |