ITE 8 – IT Essentials ( Version 7.0) – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam 1 – 9 Answers | ITE v7.02 Final Exam 1 – 9
ITE 8 | IT Essentials 8 – IT Essentials 8 Final Chapter Ch 1 – 9 Exam Answers Full 100% 2023 2024
This is Cisco IT Essentials (Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam Ch 1 – 9 Exam answers 2023 2024 Full 100% and Cisco Netacad ITE v7 | ITE v7.02 Final Exam 1 – 9 | – IT Essentials (Version 7.00) – IT Essentials 7.0 Final Exam 1 – 9 Exam Answers 2023 2024.
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Final - Mid-term - Cert | |
| Chapter 1 -9 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Chapter 10 - 14 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1001 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1002 | Online Test |
ITE 8.01 – IT Essentials (Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam Ch 1 – 9 Exam Answers 2023 2024
-
In which situation would an ESD strike potentially cause harm to the PC?
- when replacing a mechanical hard drive with an M.2 SSD
- when installing an additional display in a workplace cubicle
- when using a grounded mat and working on a computer on an ungrounded workbench
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: The highest risk of ESD damage to a PC occurs when replacing a mechanical hard drive with an M.2 SSD. This process involves direct handling of highly sensitive electronic components, making them particularly susceptible to damage from electrostatic discharge. It’s crucial to follow proper ESD safety protocols, like using grounding wristbands and working on anti-static surfaces, during this procedure to prevent potential harm to the PC.
-
A person has started a new technical job. In which situation would ESD be an issue?
- when installing a processor
- when using a grounded mat and working on a computer on an ungrounded workbench
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
- while exchanging one laptop AC adapter with one that is not from the original equipment manufacturer
-
Explanation & Hint: When installing a processor, the risk of ESD damage is exceptionally high. This task involves direct contact with one of the most sensitive components in a computer, requiring strict adherence to ESD safety protocols to prevent potentially catastrophic damage to the processor.
-
A technician is about to begin preventive maintenance on a company PC. In which situation would ESD be an issue?
- when replacing a motherboard
- while attaching speakers to a surround sound card
- when using a grounded mat and working on a computer on an ungrounded workbench
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: For a technician performing preventive maintenance on a company PC, ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) concerns are paramount, especially when handling internal components. Here’s an assessment of ESD risks in each situation:
- When Replacing a Motherboard: This is a high-risk situation for ESD. The motherboard is the central hub of the computer with numerous sensitive electronic components. Static electricity can easily damage these components, so it’s crucial to use proper ESD protection like grounding wristbands and anti-static mats.
- While Attaching Speakers to a Surround Sound Card: This presents a lower risk of ESD damage compared to handling the motherboard. Speakers and sound cards are less sensitive to static discharge, but basic ESD precautions are still advisable.
- When Using a Grounded Mat and Working on a Computer on an Ungrounded Workbench: This situation poses a moderate ESD risk. While the grounded mat provides some protection, the ungrounded workbench can still contribute to a buildup of static electricity. Ensuring full grounding of both the technician and the work area is important.
- When Installing a Dual-Voltage Power Supply: This is another high-risk situation for ESD. Power supplies, though robust, are connected to various sensitive parts of the PC, and improper handling can cause static electricity to damage these components. Proper ESD precautions should be observed.
In summary, the highest ESD risks are encountered when replacing a motherboard and installing a dual-voltage power supply, due to the direct handling of sensitive internal components. Using a grounded mat on an ungrounded workbench still presents a risk, albeit reduced. Attaching external peripherals like speakers carries the lowest risk, but ESD precautions are always recommended in any technical maintenance setting.
-
A technician is about to begin preventive maintenance on a company PC. In which situation would ESD be an issue?
- when installing RAM
- when walking across a carpeted area and then touching a keyboard that is attached to a tower PC
- when using a grounded mat and working on a computer on an ungrounded workbench
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: When installing RAM, ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) is a significant issue. RAM modules are highly sensitive to static electricity, and even a small static discharge can cause damage to these components. It’s crucial to follow strict ESD precautions, such as using grounding wristbands and working on anti-static surfaces, to prevent damaging the RAM during installation.
-
In which situation would an ESD strike potentially cause harm to the PC?
- when replacing a mechanical hard drive with an M.2 SSD
- when replacing high voltage laser printer parts
- when using a grounded mat and working on a computer on an ungrounded workbench
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: When replacing a mechanical hard drive with an M.2 SSD, there is a substantial risk of ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) causing harm to the PC. This is because both types of storage devices contain sensitive electronic components that are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity. Proper ESD protection measures, such as using grounding wristbands and anti-static mats, are crucial to prevent static discharge that can damage these components during the replacement process.
-
An instructor has given a student an assignment to assemble a PC. In which situation should the student be aware that ESD is an issue?
- when installing RAM
- when working in a corporate environment that has carpet installed under tower PCs
- when using a grounded mat and working on a computer on an ungrounded workbench
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
-
Explanation & Hint: When installing RAM, the student should be acutely aware that ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) is an issue. RAM modules are highly sensitive to static electricity, and an ESD event can easily damage these components. The student must employ proper ESD protection measures, such as grounding wristbands and anti-static mats, to ensure the safe handling and installation of RAM in the PC assembly process.
-
A technician is about to begin preventive maintenance on a company PC. In which situation would ESD be an issue?
- when replacing a motherboard
- while attaching speakers to a surround sound card
- when working in a corporate environment that has carpet installed under tower PCs
- when walking across a carpeted area and then touching a keyboard that is attached to a tower PC
-
Explanation & Hint: When replacing a motherboard, ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) is a significant issue. The motherboard contains numerous sensitive electronic components and circuits that are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity. During preventive maintenance, the technician must take stringent ESD precautions, such as using grounding wristbands and working on anti-static surfaces, to prevent damaging the motherboard with static discharge.
-
A person has started a new technical job. In which situation would ESD be an issue?
- when installing a processor
- when installing a dual-voltage power supply
- when working in a corporate environment that has carpet installed under tower PCs
- when walking across a carpeted area and then touching a keyboard that is attached to a tower PC
-
Explanation & Hint: When installing a processor, ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) is a critical issue to consider. Processors are highly sensitive to static electricity, and an ESD event can cause irreversible damage to these components. Therefore, it’s essential for anyone in a technical job to use proper ESD protection methods, such as grounding wristbands and anti-static mats, when handling and installing processors to prevent any potential damage.
-
A technician is about to begin preventive maintenance on a company PC. In which situation would ESD be an issue?
- when replacing a motherboard
- when installing a UPS
- when working in a corporate environment that has carpet installed under tower PCs
- when walking across a carpeted area and then touching a keyboard that is attached to a tower PC
-
Explanation & Hint: When replacing a motherboard, ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) is a significant issue. The motherboard contains numerous sensitive electronic components and circuits that are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity. During preventive maintenance, the technician must take stringent ESD precautions, such as using grounding wristbands and working on anti-static surfaces, to prevent damaging the motherboard with static discharge.
-
In which situation would an ESD strike potentially cause harm to the PC?
- when replacing a mechanical hard drive with an M.2 SSD
- while exchanging one laptop AC adapter with one that is not from the original equipment manufacturer
- when working in a corporate environment that has carpet installed under tower PCs
- when walking across a carpeted area and then touching a keyboard that is attached to a tower PC
-
Explanation & Hint: When replacing a mechanical hard drive with an M.2 SSD, there is a substantial risk of ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) causing harm to the PC. This is because both types of storage devices contain sensitive electronic components that are highly susceptible to damage from static electricity. Proper ESD protection measures, such as using grounding wristbands and anti-static mats, are crucial to prevent static discharge that can damage these components during the replacement process.
-
What two motherboard components control the system boot operations? (Choose two.)
- BIOS chip
- UEFI chip
- Northbridge chip
- Southbridge chip
- CPU
Answers Explanation & Hints: System boot services are provided by the motherboard BIOS and UEFI chips.
-
A technician is upgrading an ATX motherboard with another ATX motherboard. Which component might be affected by this and need to be upgraded and bought as an additional purchase?
- BIOS
- chipset
- CMOS battery
- CPU
- PCIe adapter
Answers Explanation & Hints: The motherboard, CPU, and power supply must be compatible.
-
A customer has requested that a PC be built that will support eSATA. Which component should be checked to be sure that this feature is supported?
- CPU
- chipset
- hard disk
- RAM module
Answers Explanation & Hints: The chipset on a motherboard consists of integrated circuits that control how system hardware interacts with the CPU and motherboard. It also provides the capability and features needed, such as the maximum memory supported on the motherboard, multiple USB ports, eSATA connections, surround sound, and video.
-
Which memory module used to hold instructions for booting a PC and loading the OS, but is still used on adapters even though the memory contents cannot be changed?
- RAM
- ROM
- cache
- main memory
Answers Explanation & Hints: ROM stands for read-only memory.
-
What is a characteristic of DDR SDRAM?
- It transfers data twice per clock cycle compared to once per clock cycle for SDRAM.
- DDR SDRAM modules have double the number of pins of SDRAM memory modules.
- It is dynamic memory whereas SDRAM is static memory.
- It operates at double the voltage of SDRAM memory.
Answers Explanation & Hints: DDR SDRAM transfers data twice per clock cycle, whereas SDRAM transfers data once each clock cycle. Both DDR SDRAM and SDRAM are forms of dynamic memory. The difference in data transfer rate between DDR SDRAM and SDRAM is not determined by the number of pins, nor the operating voltage.
-
What are two safety hazards when dealing with laser printers? (Choose two.)
- high voltage
- hot components
- heavy metals
- proprietary power bricks
- unwieldy card cages
Answers Explanation & Hints: Laser printers require high voltage when initially powered on and to charge the drum in preparation for writing data to the drum. This high voltage requirement is why most laser printers are not normally connected to a UPS. A laser printer also has a fuser assembly used to apply heat and pressure to the toner to permanently attach it to the paper. The laser printer must be unplugged and the fuser assembly must be allowed to cool before working inside the printer.
-
Which component requires a technician to install screws externally through the PC case?
- RAM
- CPU
- motherboard
- power supply
Answers Explanation & Hints: The power supply commonly has four screws that attach from outside the case through case holes into screw holes on the power supply.
-
A technician is installing an internal HDD. To which motherboard connector will the technician connect the data cable?
- ATX
- PCI
- PWR_SW
- SATA
Answers Explanation & Hints: Internal hard drives are commonly SATA drives that have a data cable that extends from the drive to a motherboard SATA connector..
-
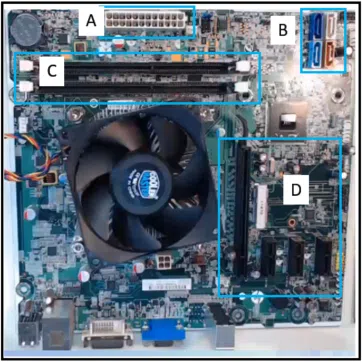
Refer to the exhibit. A technician has been asked to install a video card. Which section of the motherboard will the technician use to install the card?
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 9 Answers 01 - section A
- section B
- section C
- section D
Answers Explanation & Hints: Graphics cards, also known as video cards, are installed into a PCIe x16 expansion slot. The expansion slots on a motherboard are located near the motherboard ports.
-
When a PC is being assembled, what component is connected to the motherboard with a SATA cable?
- the optical drive
- the network interface card
- the video card
- the power supply
Answers Explanation & Hints: SATA cables, or serial ATA cables, are used to carry data from drives to the motherboard.
-
A technician is troubleshooting a computer that is experiencing hardware failure detected by the BIOS. What is one way this failure is indicated?
- The computer automatically boots into Safe Mode and displays a warning on the screen.
- The screen flashes with a red background and displays a warning message.
- The computer emits a pattern of beeps indicating the failing device.
- The computer returns an error message that indicates the I/O address of the failing device.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Beep codes are a result of POST and these vary between computer vendors based on what BIOS is installed.
-
Which three features can be configured in the BIOS settings to secure a computer? (Choose three.)
- MAC filtering
- drive encryption
- TPM
- file encryption
- TKIP key
- passwords
Answers Explanation & Hints: Passwords, drive encryption, and TPM are BIOS configurable security features. File encryption, TKIP key, and MAC filtering are security features not configured within BIOS.
-
What is the purpose of RAID adapters?
- to allow older PCI technology expansion slots to be used
- to provide enhanced audio and graphic capabilities
- to connect multiple storage devices for redundancy or speed
- to connect peripheral devices to a PC to improve performance
Answers Explanation & Hints: RAID 0 allows “striping” or writing data across two hard drives, but provides no redundancy. The other RAID versions provide redundancy.
-
When a new motherboard is being installed, between which two components must thermal compound be applied? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- RAM
- chassis
- heat sink
- chipset
- motherboard
Answers Explanation & Hints: You must apply thermal compound between the new CPU and the heat sink/fan assembly to avoid overheating the CPU. The thermal paste helps to conduct heat from the CPU to the heat sink.
-
What is the purpose of a Safety Data Sheet?
- to specify procedures for dealing with potentially hazardous materials
- to specify procedures in designing and building common computer systems
- to specify procedures for the operation of sensitive components and prevention of electrostatic discharge
- to specify procedures in the use of humidity control and prevention of moisture damage
Answers Explanation & Hints: A Safety Data Sheet is a fact sheet that summarizes information about material identification, including hazardous ingredients that can affect personal health, fire hazards, and first-aid requirements. The SDS explains how to dispose of potentially hazardous materials in the safest manner.
-
Which negative environmental factor does cleaning the inside of a computer reduce?
- dust
- EMI
- rust
- ESD
Answers Explanation & Hints: Accumulated dust inside the computer can prevent the flow of air and can hinder cooling.
-
What is a recommended procedure to follow when cleaning computer components?
- Remove the CPU before cleaning.
- Blow compressed air on cooling fans so that they will spin when dust is being removed.
- Use window cleaner on LCD screens.
- Hold cans of compressed air upright while spraying.
Answers Explanation & Hints: When using compressed air, keep the can upright to prevent the fluid from leaking onto computer components.
-
On the production floor, a furniture plant has laptops for process monitoring and reporting. The production floor environment is around 80 degrees Fahrenheit (27 degrees Celsius). The humidity level is fairly high around 70 percent. Fans are mounted in the ceiling for air circulation. Wood dust is prevalent. Which condition is most likely to adversely affect a laptop that is used in this environment?
- the temperature
- the humidity
- the air flow
- the dust
Answers Explanation & Hints: Most laptops are created to be tolerant of a wide range of humidity levels and room temperatures. Dust, however, can cause overheating and failures.
-
After a technician tests a theory of probable causes, what two actions should the technician take if the testing did not identify an exact cause? (Choose two.)
- Establish a new theory of probable causes.
- Randomly replace components one at a time until the problem is solved.
- Document each test tried that did not correct the problem.
- Verify full system functionality.
- Test all remaining possible causes starting with the most complex.
Answers Explanation & Hints: If the exact cause of the problem has not been determined after you have tested all your theories, establish a new theory of probable causes and test it.
-
What would happen if a PC that contains a power supply that does not automatically adjust for input voltage is set to 230 volts and attaches to an outlet in the United States?
- The power supply would explode.
- The PC would not turn on.
- The PC would display an error code.
- The PC would emit a series of beeps.
Answers Explanation & Hints: In the United States, the wall outlet electrical power is standardized at 120 volts AC.
-
Which type of network spans a single building or campus and provides services and applications to people within a common organizational structure?
- PAN
- WAN
- LAN
- MAN
Answers Explanation & Hints: A LAN is smaller or more contained than a WAN, which can span several cities. A MAN is usually contained in one city. A PAN is a very small network of devices that are located in close proximity to one another, usually within range of a single person.
-
What are two types of wired high-speed Internet connections? (Choose two.)
- cable
- satellite
- cellular
- DSL
- dial-up
Answers Explanation & Hints: Cable and DSL Internet technologies both use physical cabling to provide an Internet connection to a residence or a small business. Although dial-up is a wired technology, it does not provide a high-speed Internet connection. Satellite and cellular connections provide a wireless Internet connection.
-
In what two situations would UDP be better than TCP as the preferred transport protocol? (Choose two.)
- when applications need to guarantee that a packet arrives intact, in sequence, and unduplicated
- when a faster delivery mechanism is needed
- when delivery overhead is not an issue
- when applications do not need to guarantee delivery of the data
- when destination port numbers are dynamic
Answers Explanation & Hints: UDP is a very simple transport layer protocol that does not guarantee delivery. Devices on both ends of the conversation are not required to keep track of the conversation. UDP is used as the transport protocol for applications that need a speedy, best-effort delivery.
-
The current IP configuration of a small company is done manually and is time-consuming. Because of increased network growth, a technician needs a simpler way for IP configuration of workstations. Which service would simplify the workstation IP configuration task?
- APIPA
- DHCP
- DNS
- ICMP
Answers Explanation & Hints: In networks with more than a few hosts, DHCP simplifies the addressing process. A DHCP server automatically assigns host IP addresses.
-
A company is looking for a next-generation firewall that provides VPN functionality, IDS/IPS functionality, and DoS/DDoS protection. Which device would be best suited for this task?
- multipurpose device
- router
- endpoint management server
- UTM
- TPM
Answers Explanation & Hints: A universal threat management (UTM) device is a security device that can provide firewall, IDS/IPS, and proxy server functionality as well as email filtering and DoS/DDoS protection.
-
A student is helping a friend with a home computer that can no longer access the Internet. Upon investigation, the student discovers that the computer has been assigned the IP address 169.254.100.88. What could cause a computer to get such an IP address?
- static IP addressing with incomplete information
- interference from surrounding devices
- reduced computer power supply output
- unreachable DHCP server
Answers Explanation & Hints: When a PC does not have a static IP address or cannot pick one up from a DHCP server, Windows will automatically assign the PC an IP address using APIPA, that uses the range of addresses 169.254.0.0 to 169.254.255.255.
-
What three values must be added to the IPv4 properties of a NIC in order for a computer to have basic connectivity with the network? (Choose three.)
- subnet mask
- DHCP server address
- domain name
- default gateway
- speed and duplex
- IP address
Answers Explanation & Hints: The IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address values should be added to the NIC properties in order for the computer to have basic network connectivity. This can be done either statically or dynamically with DHCP. An additional value that should be present if the computer is to be used to connect to the Internet is the DNS server value. A computer automatically attempts to locate a DHCP server if configured to do so. A DHCP server address is not used. Finally, NAT is configured on a router, not on a computer host, and speed and duplex settings are NIC hardware settings and not IPv4 properties of the NIC.
-
A device has an IPv6 address of 2001:0DB8:75a3:0214:0607:1234:aa10:ba01 /64. What is the host identifier of the device?
- 2001:0DB8:75a3
- 0607:1234:aa10:ba01
- 2001:0DB8
- ba01
Answers Explanation & Hints: An IPv6 address is made up of 128 bits that are represented as eight blocks of four hexadecimal digits that are called hextets. Because each hexadecimal digit represents four bits, each hextet represents 16 bits. The /64 network prefix indicates that the first 64 bits, or first four hextets, represent the network portion of the address. Because there are 128 bits in an IPv6 address, this leaves the last 64 bits, or last four hextets, to represent the host identifier. The value for the last four hextets is 0607:1234:aa10:ba01.
-
How can a user prevent specific applications from accessing a Windows computer over a network?
- Enable MAC address filtering.
- Disable automatic IP address assignment.
- Block specific TCP or UDP ports in Windows Firewall.
- Change default usernames and passwords.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Network applications have specific TCP or UDP ports that can be left open or blocked in Windows Firewall. Disabling automatic IP address assignment may result in the computer not being able to connect to the network at all. Enabling MAC address filtering is not possible in Windows and would only block specific network hosts, not applications. Changing default usernames and passwords will secure the computer from unauthorized users, not from applications.
-
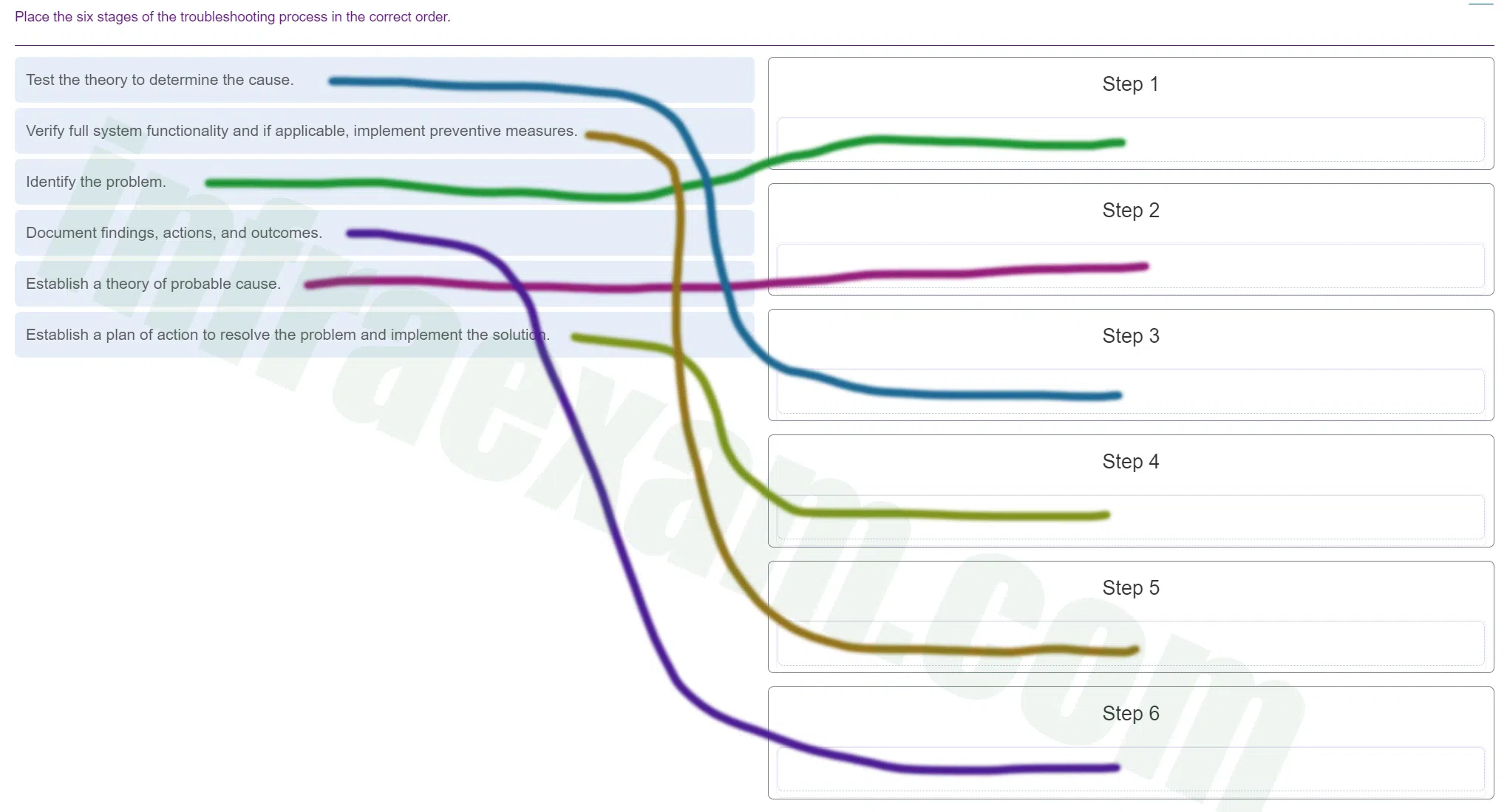
Place the six stages of the troubleshooting process in the correct order.
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 9 Answers 001 Explanation & Hint: - Identify the Problem: Determine the exact nature of the issue.
- Establish a Theory of Probable Cause: List possible reasons for the problem.
- Test the Theory to Determine the Cause: Perform tests to confirm if one of the theories is correct.
- Establish a Plan of Action to Resolve the Problem and Implement the Solution: Create a step-by-step plan to fix the issue and then carry out the solution.
- Verify Full System Functionality and If Applicable, Implement Preventive Measures: Check if the problem is completely resolved and the system is functioning correctly, then take any preventive measures to avoid the problem in the future.
- Document Findings, Actions, and Outcomes: Keep a record of the problem, how it was resolved, and the outcome for future reference.
-
A technician has been asked to configure Wi-Fi calling on a corporate mobile device. In which situation would this feature be most advantageous?
- in an emergency situation and no minutes are left on the phone
- when sending WEA updates
- when in an area with poor cellular coverage
- in a store transaction making a payment using the mobile device
Answers Explanation & Hints: Wi-Fi calling is not supported on all mobile devices, but when enabled, it uses a Wi-Fi network to make voice calls. It is very useful in areas with poor cellular coverage.
-
Which statement is true about laptops?
- Most of the internal components that are designed for laptops cannot be used for desktops.
- Laptop motherboards have standard form factors.
- Laptops use fewer components than desktops use.
- Laptop CPUs do not use cooling devices.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Laptop internal components are designed with a small form factor and are proprietary. Although a laptop CPU uses less power, it needs a cooling device (heat sink and fan).
-
Which standard provides a bridge between laptop hardware and the operating system and a way for technicians to configure power management schemes to get the best performance?
- ACPI
- PCIe
- Bluetooth
- 802.11
Answers Explanation & Hints: The Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) standard has specific sleep states that can be assigned to a device in order to conserve power. PCIe is a motherboard interface. Bluetooth and 802.11 are wireless standards.
-
Which two laptop components are considered replaceable by the customer. (Choose two.)
- battery
- integrated card reader
- mini-PCIe module
- RAM
- display
Answers Explanation & Hints: Customer-replaceable units (CRUs) do not typically require a lot of technical skill to replace. RAM and a battery are two examples of a CRU. In contrast, a field-replaceable unit (FRU), such as a display, motherboard, keyboard, or touchpad, commonly requires a technician to install.
-
A user wants to synchronize some apps, movies, music, and ebooks between mobile devices. What are the two types of connections used to synchronize this type of data? (Choose two.)
- cellular
- Wi-Fi
- USB
- Bluetooth
- NFC
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because of the amount of data transferred during video synchronization, synchronization occurs through either a Wi-Fi connection or a wired USB connection.
-
A technician is explaining the differences between inkjet printers and laser printers to a customer. Which two comparisons should the technician make? (Choose two.)
- Inkjet printers are less expensive as an initial purchase than laser printers.
- A laser printer is significantly slower than an inkjet printer.
- Both laser and inkjet printers produce poor quality images.
- The laser printer output is dry after printing, but an inkjet printer may still have wet ink on the paper after printing.
- Inkjet printers use plain paper to make economical prints, but laser printers require more expensive thermal paper.
-
Explanation & Hint: When explaining the differences between inkjet and laser printers to a customer, the technician should make the following two comparisons:
- Inkjet printers are less expensive as an initial purchase than laser printers. This is generally true; the upfront cost of inkjet printers is typically lower than that of laser printers.
- The laser printer output is dry after printing, but an inkjet printer may still have wet ink on the paper after printing. Laser printers use toner and a heat process to fuse the toner to the paper, which results in a dry print immediately after printing. Inkjet printers, on the other hand, use liquid ink which can sometimes require a short time to dry.
The other statements are incorrect:
- A laser printer is not significantly slower than an inkjet printer. In fact, laser printers are usually faster, especially for text documents.
- Both laser and inkjet printers can produce high-quality images, with modern printers often providing excellent image quality suitable for a variety of professional and home uses.
- Inkjet printers do not exclusively use plain paper to make economical prints, nor do laser printers require thermal paper. Both types of printers can print on a variety of media, and laser printers typically use regular printer paper, not thermal paper.
-
A user chooses the collate option and prints two copies of a three-page document. What is the order in which the pages are printed?
- pages 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3
- pages 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3
- pages 3, 3, 2, 2, 1, 1
- pages 3, 2, 1, 3, 2, 1
Answers Explanation & Hints: The collate feature enables a printer to sort multiple copies of a document with the proper page order for each copy.
-
A color laser printer is used to print documents with graphics and photographs. Users are complaining that printing takes too long. Which component of the printer should be upgraded in order to improve printing performance?
- CPU
- RAM
- hard drive
- toner cartridges
Answers Explanation & Hints: Because documents with graphics and photographs generate much larger print jobs, the printing process will run more efficiently if the printer memory is adequate to store the entire job before the job starts.
-
What service is available for Windows to provide software print server services to MAC OS clients?
- Bonjour Print Server
- Print to XPS
- Apple AirPort Extreme
- Apple AirPrint
Answers Explanation & Hints: Bonjour Printer Server from Apple comes with MAC OS X and is a free download for Windows users to be used as a software print server. Airport Extreme, a dedicated print server, and a PC with a printer attached serving as a print server are all hardware print sharing solutions.
-
Which three components are typically found in laser printer maintenance kits? (Choose three.)
- fuser assembly
- primary corona
- pickup rollers
- transfer rollers
- secondary corona
- paper trays
Answers Explanation & Hints: Laser printer maintenance kits typically contain components that wear and can be installed with minimal disassembly of the printer. Corona wires are internal components that would require a trained technician to replace. Paper trays are components that are not typically replaced during maintenance, but would be replaced any time if damaged.
-
A technician is installing a new printer in a cool, damp environment. After the printer cabling is done, and the software and print driver are installed, the printer test page jams. What is the most likely cause of the print failure?
- incorrect printer driver
- too much humidity
- not enough printer memory
- loose printer cables
Answers Explanation & Hints: Paper jams are commonly caused when the paper being used is dirty, affected by humidity, or is the wrong type of paper for the printer.
-
A data center has recently updated a physical server to host multiple operating systems on a single CPU. The data center can now provide each customer with a separate web server without having to allocate an actual discrete server for each customer. What is the networking trend that is being implemented by the data center in this situation?
- BYOD
- virtualization
- maintaining communication integrity
- online collaboration
Answers Explanation & Hints: Virtualization technology can run several different operating systems in parallel on a single CPU.
-
How does virtualization help with disaster recovery within a data center?
- Power is always provided.
- Less energy is consumed.
- Server provisioning is faster.
- Hardware does not have to be identical.
Answers Explanation & Hints: Disaster recovery is how a company goes about accessing applications, data, and the hardware that might be affected during a disaster. Virtualization provides hardware independence which means the disaster recovery site does not have to have the exact equipment as the equipment in production. Server provisioning is relevant when a server is built for the first time. Although data centers do have backup generators, the entire data center is designed for disaster recovery. One particular data center could never guarantee that the data center itself would never be without power.
-
Which two hypervisors are suitable to support virtual machines in a data center? (Choose two.)
- Virtual PC
- VMware Fusion
- VMware ESX/ESXi
- Oracle VM VirtualBox
- Microsoft Hyper-V 2012
Answers Explanation & Hints: VMware ESX/ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-V 2012 are Type 1 hypervisors that have direct access to the hardware resources. Type 1 hypervisors are more efficient than hosted architectures, and enable greater scalability, performance, and robustness. They are used to support enterprise VMs in data centers. Oracle VM VirtualBox, VMware Fusion, and Microsoft Virtual PC are host based Type 2 hypervisors.
-
A web designer accesses a company Windows 10 computer remotely. The designer often needs to simultaneously open multiple applications, such as a web page editor and a graphics editor. Rather than opening them in multiple windows, the designer opens them in different virtual desktops. What technology is being used by the designer?
- virtual reality
- Windows Virtual Desktop
- cloud-based applications
- virtual desktop infrastructure
Answers Explanation & Hints: Windows 10 has a feature called Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD). A user can create multiple virtual desktops and navigate among them easily. This feature reduces the clutter on a desktop of Windows caused by opening multiple applications. With WVD, a user can have each application open in a separate desktop.
-
Which Cloud computing service would be best for an organization that needs to collaboratively create applications and deliver them over the web?
- PaaS
- IaaS
- SaaS
- ITaaS
Answers Explanation & Hints: Platform as a service (PaaS) provides a collaborative environment where multiple developers can create software and host an application through a Cloud provider.
-
Which statement describes a feature of SDRAM?
- It requires constant power to function.
- Its connector always has 240 pins.
- It can process overlapping instructions in parallel.
- It is able to support two writes and two reads per CPU clock cycle.
Answers Explanation & Hints: SDRAM ( Synchronous Dynamic RAM) works in synchronization with the memory bus and has higher transfer rates because it can process overlapping instructions in parallel.
-
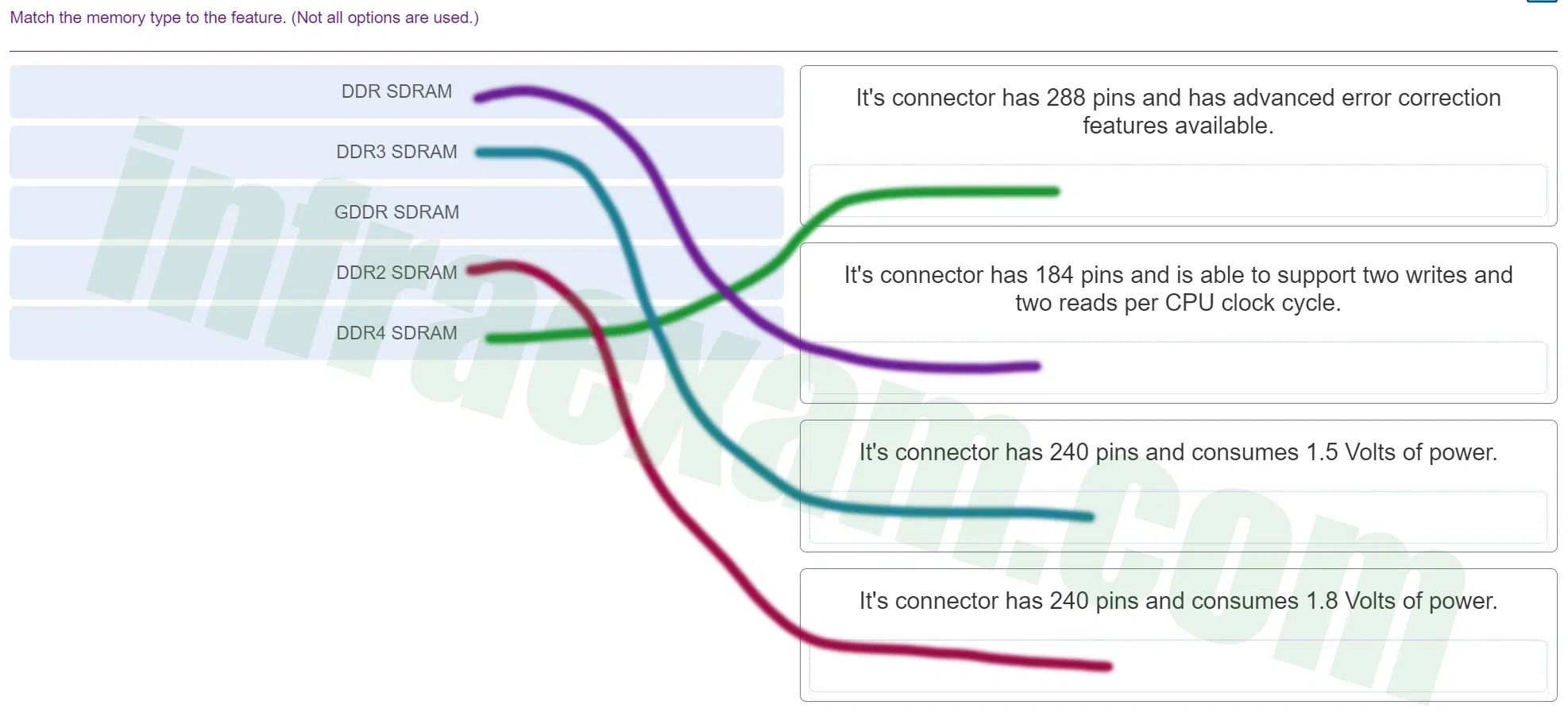
Match the memory type to the feature. (Not all options are used.)
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 9 Answers 002 Explanation & Hint:
- DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic RAM) typically refers to the original DDR memory, which has been superseded by newer generations. It generally has a 184-pin connector for DIMMs and operates at 2.5 volts.
- DDR2 SDRAM improves upon the original DDR by using less power and providing higher speeds. It typically comes with a 240-pin connector and operates at 1.8 volts.
- DDR3 SDRAM further improves upon DDR2 with even higher speed and lower power consumption. It also has a 240-pin connector but operates at 1.5 volts.
- GDDR SDRAM (Graphics Double Data Rate SDRAM) is often used in graphics cards. It is optimized for high bandwidth and is not typically used for general-purpose computing in PCs.
- DDR4 SDRAM is the most recent generation of DDR memory. It has a 288-pin connector and includes features like improved data rates, increased transfer rates, and more efficient power consumption compared to DDR3. It operates at a lower voltage of 1.2 volts but can also be found in variants that use 1.35 volts for low-power operations.
-
A technician is troubleshooting a server that displays the error message “RAID not found” after a power outage over the weekend. What is a possible cause for this
- The BIOS firmware needs updating.
- The FSB settings have changed and are wrong.
- The external RAID controller is not receiving power.
- The CPU multiplier is set too high.
Answers Explanation & Hints: The loss of the RAID controller can be caused by the external RAID controller not receiving power, incorrect BIOS settings, failure of the RAID controller or incorrect drivers for the RAID controller.
-
A customer brings in a laptop with a touch screen that is not working correctly. The touch screen either does not respond at all or provides unusual or inaccurate responses. What is a possible cause for such behavior?
- The battery is not seated properly.
- The DC jack is not grounded or is loose.
- The digitizer is faulty.
- Too many apps are open.
Answers Explanation & Hints: A touch screen that is unresponsive or inaccurate can be caused by dirt or grease on the screen, the screen protector, or apps consuming too many resources.
-
What are two security risks associated with sharing printers in a corporate environment? (Choose two.)
- user authentication
- cached files
- document viewing in the print queue
- dumpster diving
- shoulder surfing
Answers Explanation & Hints: Three security concerns related to shared printers include (1) cached print files could contain sensitive data; (2) user authentication is needed to control access to the printer; and (3) print jobs could be read by others, intercepted, copied, or modified. Although the names of documents can be viewed in the print queue, document viewing is not possible. Dumpster diving and shoulder surfing are security concerns whether the printer is shared or not.
-
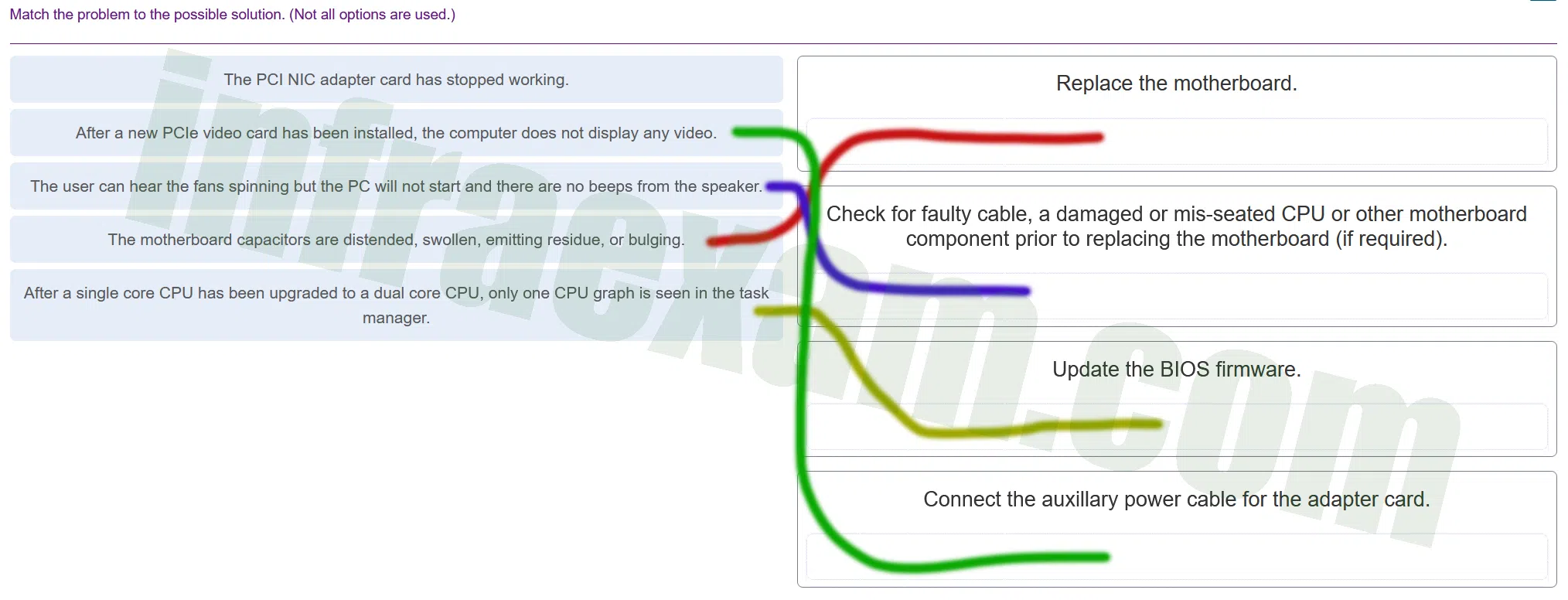
Match the problem to the possible solution. (Not all options are used.)
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 9 Answers 003 Explanation & Hint:
- After a new PCIe video card has been installed, the computer does not display any video.
- Solution: Connect the auxiliary power cable for the adapter card. Many modern video cards require additional power directly from the power supply, and forgetting to connect this can result in no video output.
- The user can hear the fans spinning but the PC will not start, and there are no beeps from the speaker.
- Solution: Check for faulty cable, a damaged or mis-seated CPU, or other motherboard component prior to replacing the motherboard (if required). No beeps typically indicate a fundamental hardware issue that can be due to several factors including power, CPU, or motherboard problems.
- The motherboard capacitors are distended, swollen, emitting residue, or bulging.
- Solution: Replace the motherboard. Distended or bulging capacitors are a clear sign of hardware failure on the motherboard.
- After a single core CPU has been upgraded to a dual core CPU, only one CPU graph is seen in the task manager.
- Solution: Update the BIOS firmware. If the BIOS doesn’t recognize the new multi-core processor, an update may be necessary to ensure the motherboard can properly utilize the new CPU.
- After a new PCIe video card has been installed, the computer does not display any video.
-
A software engineer is involved in the development of an application. For usability tests, the engineer needs to make sure that the application will work in both Windows 10 Enterprise and Windows 11 environments. The features and functions must be verified in the actual OS environment. The engineer is using a Windows 10 Pro workstation. What two technologies can help the engineer achieve the usability tests? (Choose two.)
- dual boot
- two separate CPUs
- storage redundancy
- client-side virtualization
- two separate hard disks
Answers Explanation & Hints: Client-side virtualization enables a host OS to provide a virtual environment within which a guest OS can be installed and be operational as an actual OS. The dual boot configuration will provide an option to run either OS (but not both at the same time). Just using two disks is not a sufficient solution to run two separate OS.
-
Which protocol is used by Windows for file and printer sharing?
- SMB
- SMTP
- HTTPS
- IMAP
Answers Explanation & Hints: SMB (Server Message Block) is the protocol used for file and printer sharing by Windows. SMTP and IMAP are protocols used in email services. HTTPS is the protocol used for secure web browsing.
-
Which laptop LCD technology uses tilting crystals to provide a much higher contrast ratio than other types?
- Vertical alignment (VA)
- In-Plane switching (IPS)
- Twisted Nematic (TN)
- Organic light-emitting diode (OLED)
Answers Explanation & Hints: Vertical alignment (VA) laptop display technology uses tilting crystals to provide a much higher contrast ratio than other types. In-Plane switching (IPS) and Twisted Nematic (TN) do not have this feature. Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays are not used in laptops.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses mirroring and striping, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 10
- 5
- 1
- 8
-
Explanation & Hint: Mirroring is a feature of RAID 1, and striping is a feature of RAID 0. When both mirroring and striping are used together, it is known as RAID 10 (also referred to as RAID 1+0). Therefore, the technician is using RAID level 10.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses mirroring, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 1
- 6
- 5
- 3
-
Explanation & Hint: If the RAID setup uses mirroring without mentioning striping or parity, the technician is installing RAID 1. RAID 1 is known for mirroring data across two or more disks for redundancy.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses striping with parity, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 5
- 6
- 1
- 4
-
Explanation & Hint: If the RAID setup uses striping with parity, the technician is installing RAID 5. RAID 5 is known for striping data across all drives in the array with distributed parity for fault tolerance.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses striping, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 0
- 6
- 5
- 2
-
Explanation & Hint:
If the RAID setup uses striping alone without any form of redundancy or parity, the technician is installing RAID 0. RAID 0 is known for striping data across multiple disks to increase performance but does not provide any fault tolerance.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses striping with double parity, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 6
- 1
- 5
- 7
-
Explanation & Hint: If the RAID setup uses striping with double parity, the technician is installing RAID 6. RAID 6 extends RAID 5 by adding another parity block, thus allowing for two disk failures within the array without loss of data.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses striping with double parity, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 6
- 10
- 5
- 7
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses mirroring, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 1
- 10
- 6
- 3
-
Explanation & Hint: If the RAID setup uses mirroring, the technician is installing RAID 1. RAID 1 creates an exact copy (or mirror) of a set of data on two or more disks. This is a good way to ensure data redundancy.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses mirroring and striping, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 10
- 6
- 5
- 8
-
Explanation & Hint: If the RAID setup uses both mirroring and striping, the technician is installing RAID 10. RAID 10 combines the features of RAID 1 (mirroring) and RAID 0 (striping) to provide redundancy and improved performance.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses striping with parity, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 5
- 10
- 6
- 4
-
Explanation & Hint: If the RAID setup uses striping with parity, the technician is installing RAID 5. RAID 5 is characterized by striping data across multiple disks with parity information distributed among the disks for fault tolerance.
-
A computer technician is installing a RAID. If the RAID uses striping, which RAID level is the technician using?
- 0
- 1
- 5
- 2
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old battery?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Throw it away.
- Take it to the garbage dump.
- Burn it.
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct way to dispose of an old battery is to Recycle following local regulations. Batteries contain materials that can be harmful to the environment and should not be thrown in the regular trash. It’s important to follow local guidelines for recycling batteries to ensure they are handled properly and safely.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of a broken monitor?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Bury it.
- Take it to the garbage dump.
- Burn it.
-
Explanation & Hint: The appropriate way to dispose of a broken monitor is to Recycle following local regulations. Monitors, especially older ones with CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) technology, can contain hazardous materials like lead and mercury. It’s important to follow local environmental regulations and guidelines for electronic waste to ensure these materials are handled and disposed of safely and responsibly. Recycling centers or special e-waste disposal services are usually equipped to process this type of waste correctly.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old power supply?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Burn it.
- Take it to the garbage dump.
- Bury it.
-
Explanation & Hint: When disposing of an old power supply from a PC, it is imperative to recycle it following local regulations. This is not just the most environmentally responsible option, but often a legal requirement. Recycling ensures that hazardous materials are handled properly and that recyclable components are reused, thus minimizing environmental harm.
Here’s a breakdown of the disposal methods:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the optimal choice. Electronic waste contains materials that can be harmful if not disposed of correctly. Proper recycling processes these materials in a safe and responsible manner.
- Burn it: Highly inadvisable. Burning electronic components releases toxic fumes and chemicals, posing severe health risks and environmental damage.
- Take it to the garbage dump: Generally not recommended. Disposing of electronic waste in regular garbage leads to hazardous materials contaminating landfills, which can leach into soil and groundwater.
- Bury it: Like dumping, burying electronic waste is environmentally harmful. It carries the risk of toxic substances contaminating the soil.
In conclusion, responsibly recycling the power supply according to local guidelines is crucial for environmental protection and often for compliance with waste management laws.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of old RAM?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Destroy it with a hammer.
- Burn it.
- Bury it.
-
Explanation & Hint: When disposing of old RAM (Random Access Memory) from PCs, the most appropriate and environmentally responsible method is to recycle it, adhering to local regulations. Like other electronic components, RAM modules contain materials that can be hazardous if not disposed of properly. Recycling ensures that these materials are handled correctly and that any reusable components are salvaged, reducing environmental impact.
Let’s evaluate the suggested disposal methods:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the best option. Recycling electronic components like RAM is essential for handling potentially hazardous materials safely and for conserving resources. It’s important to check with local e-waste recycling facilities or municipal waste management services for specific guidelines on electronic waste recycling.
- Destroy it with a hammer: This method is not advisable. Physically destroying RAM does not address the environmental concerns of disposing of electronic waste. Moreover, it could potentially release harmful substances and is generally not a safe practice.
- Burn it: Burning RAM, or any electronic component, is highly inadvisable. This process can release toxic chemicals into the environment and is harmful to both human health and the ecosystem.
- Bury it: Burying electronic waste, including RAM, is environmentally detrimental. This can lead to the leaching of toxic substances into the soil and groundwater, causing long-term environmental harm.
In summary, the most responsible method for disposing of old RAM is to recycle it in accordance with local regulations. This approach is not only environmentally sound but also often a legal requirement in many regions. It ensures the safe and sustainable management of electronic waste.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of old RAM?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Seal in a plastic bag before putting in the garbage.
- Give it to your neighbor.
- Destroy it with a hammer.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a technician is tasked with disposing of old RAM (Random Access Memory) modules from upgraded PCs, the appropriate method of disposal is crucial for both environmental and data security reasons. Here are the options you listed, along with an assessment of their suitability:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the best and most responsible choice. Recycling electronic components like RAM is essential for the safe handling of potentially hazardous materials and for resource conservation. It is important to check with local e-waste recycling facilities or municipal waste management services for specific guidelines on recycling electronic waste.
- Seal in a plastic bag before putting in the garbage: This method is not recommended. Disposing of RAM in regular garbage does not address the environmental concerns associated with electronic waste. Additionally, RAM modules can contain materials that are harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly.
- Give it to your neighbor: Giving old RAM to someone who can use it is a form of reuse, which is generally positive for sustainability. However, this only makes sense if the RAM is still functional and compatible with the neighbor’s needs. It’s also important to ensure that all sensitive data has been securely erased before handing it over.
- Destroy it with a hammer: Physically destroying RAM might be considered if there are serious concerns about data security, but this should be a last resort. This method can be dangerous and does not address environmental concerns. It’s better to use professional data destruction services that also ensure environmentally responsible disposal.
In conclusion, recycling old RAM in accordance with local regulations is the most environmentally responsible and typically the safest method. If reuse is an option and data security is not a concern, giving it to someone who can make use of it is also a good choice. Physical destruction should only be considered for data security reasons and should be carried out with caution, ideally by professionals.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old motherboard?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Seal in a plastic bag before putting in the garbage.
- Give it to your neighbor.
- Destroy it with a hammer.
-
Explanation & Hint: When disposing of old motherboards from PCs, it’s crucial to consider both environmental impact and data security. Here’s a look at the suggested methods for disposal:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the best and most responsible option. Motherboards, like other electronic components, contain various metals and potentially hazardous materials that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. Recycling ensures that these materials are handled in an environmentally safe manner and that valuable resources are recovered. Check with local e-waste recycling facilities or municipal waste management services for specific guidelines on electronic waste recycling.
- Seal in a plastic bag before putting in the garbage: This method is not advisable. Disposing of electronic components like motherboards in regular garbage is environmentally harmful. It can lead to the release of toxic substances into landfills and the environment. It’s also likely to be against local regulations for disposing of e-waste.
- Give it to your neighbor: If the motherboard is still functional and your neighbor can use it, this is a form of reuse and can be a good option. However, ensure that all sensitive data has been securely erased before giving it away. It’s important to consider compatibility and functionality.
- Destroy it with a hammer: Physically destroying a motherboard might be considered for data security purposes, but it should be a last resort. This approach can be dangerous due to the potential release of hazardous materials, and it doesn’t address environmental concerns. If data security is a significant concern, it’s better to use professional data destruction services that also ensure environmentally responsible disposal.
In conclusion, recycling the motherboard following local regulations is the most environmentally friendly and responsible method. Reuse is a viable option if the motherboard is still functional and data security has been addressed. Physical destruction is not recommended due to safety and environmental concerns and should only be considered for data security in specific circumstances.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old hard drive?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Seal in a cardboard box.
- Give it to your neighbor.
- Destroy it with a hammer.
-
Explanation & Hint: Disposing of old hard drives from PCs, particularly in a business context, requires careful consideration due to both environmental concerns and data security. Here’s a look at the suggested methods for disposal:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is generally the best option for environmental responsibility. Hard drives contain various metals and potentially hazardous materials that should not end up in landfills. Recycling ensures these materials are handled properly. Before recycling, however, it’s crucial to ensure that all data on the hard drives has been securely erased or destroyed to prevent data breaches. Check with local e-waste recycling facilities for specific guidelines.
- Seal in a cardboard box: Simply placing a hard drive in a cardboard box and disposing of it is not advisable. This approach neither addresses the environmental impact of electronic waste nor ensures the security of any data remaining on the drive.
- Give it to your neighbor: This could be an option if the hard drive is still functional and you want to promote reuse. However, before doing so, you must ensure that all sensitive data has been completely and securely erased. Be aware that standard file deletion is not sufficient; use data wiping software or professional services.
- Destroy it with a hammer: Physical destruction of a hard drive can be effective for ensuring data security, especially if there are concerns about sensitive data. However, this method can be dangerous due to the risk of physical injury and the potential release of harmful materials. If you choose this method, take necessary safety precautions. Note that after destruction, the remains should still be recycled appropriately.
In conclusion, the most responsible method for disposing of old hard drives is to securely erase all data and then recycle the drive following local regulations. If data security is a high concern and the data cannot be securely erased, physical destruction is an option, but it must be done safely and followed by proper recycling. Giving away the hard drive is only suitable if you can ensure all data has been securely erased.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old hard drive?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Fix it with duct tape and reuse it.
- Give it to your neighbor.
- Destroy it with a hammer.
-
Explanation & Hint: When disposing of old hard drives from upgraded PCs, it’s important to consider both environmental factors and data security. Here’s an assessment of the suggested disposal methods:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the most responsible and advisable option. Recycling ensures that the materials in the hard drive are handled correctly, and harmful substances are properly dealt with. Before recycling, it’s crucial to ensure that all data on the hard drives has been securely erased to prevent data breaches. Check with local e-waste recycling facilities for specific guidelines.
- Fix it with duct tape and reuse it: This approach is not recommended for hard drives. If a hard drive is damaged to the point where it needs physical repair like duct tape, it’s generally not reliable for further use, especially in a business environment where data integrity and security are paramount. Additionally, this doesn’t address potential long-term failures or data loss.
- Give it to your neighbor: Before considering this option, ensure that all sensitive data has been completely and securely erased from the hard drive. Standard file deletion is not sufficient; data wiping software or professional services should be used. However, if the hard drive is old or potentially unreliable, it might not be advisable to pass it on for use by someone else.
- Destroy it with a hammer: Physically destroying a hard drive can be an effective way to ensure data security, particularly if there are concerns about sensitive information. However, this method should be approached with caution due to safety concerns and the potential release of hazardous materials. If you choose physical destruction, it must be done safely, and the remains of the drive should still be recycled properly.
In summary, the best practice for disposing of old hard drives is to securely erase all data and then recycle them in accordance with local regulations. Physical destruction is a viable option for ensuring data security, but it must be followed by proper recycling. Reusing a hard drive that requires makeshift repairs like duct tape is not recommended, especially in a business setting where data reliability is critical.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old battery?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Fix it with duct tape and reuse it.
- Give it to your neighbor.
- Destroy it with a hammer.
-
Explanation & Hint: When disposing of old batteries from PCs, it’s crucial to handle them appropriately due to their chemical composition and potential environmental impact. Here’s an assessment of the suggested disposal methods:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the best and most responsible option. Batteries, especially those used in computers, contain chemicals that can be harmful to the environment if not disposed of properly. Recycling ensures that these materials are handled safely and responsibly. It’s important to check with local recycling centers or municipal waste management services for specific guidelines on battery disposal.
- Fix it with duct tape and reuse it: This method is not advisable for batteries. If a battery is damaged to the point where it needs repair, it’s generally not safe to continue using it. Damaged batteries can be a safety hazard, potentially leading to leaks or even fires. Therefore, reusing a damaged battery, even after attempted repairs, is not recommended.
- Give it to your neighbor: Handing over an old or used battery is generally not a good idea. If the battery is no longer functioning properly or is nearing the end of its lifespan, it could pose a risk to others. Moreover, there’s the issue of responsible disposal once the battery is no longer usable.
- Destroy it with a hammer: Physically destroying a battery is extremely dangerous and should never be attempted. Batteries contain hazardous materials that can be harmful if released, and physical damage can lead to dangerous leaks or chemical reactions.
In conclusion, the most appropriate way to dispose of old batteries from PCs is to recycle them following local regulations. This method ensures environmental safety and proper handling of potentially hazardous materials. Reusing damaged batteries or giving them away is not recommended due to safety and environmental concerns, and physical destruction is dangerous and should be avoided.
-
A technician is upgrading many PCs used within the company. How should the technician dispose of an old battery?
- Recycle following local regulations.
- Throw it away.
- Take it home.
- Give it to your neighbor.
-
Explanation & Hint: When disposing of old batteries from PCs, it’s important to consider both environmental and safety factors. Here’s a look at the suggested methods for disposal:
- Recycle following local regulations: This is the most responsible and advisable option. Batteries contain various metals and chemicals that can be harmful to the environment and potentially dangerous if not disposed of properly. Recycling ensures that these materials are handled in an environmentally safe manner. Check with local e-waste recycling facilities or municipal waste management services for specific guidelines on battery disposal.
- Throw it away: This method is not recommended. Disposing of batteries in regular trash can lead to environmental contamination and potential safety hazards, as batteries can leak harmful chemicals or cause fires if damaged. Most regions have specific regulations against disposing of batteries in regular trash due to these risks.
- Take it home: Simply taking an old battery home doesn’t address the need for proper disposal. If the intention is to dispose of it responsibly from home, it’s still necessary to follow local recycling regulations.
- Give it to your neighbor: Unless the battery is still in good condition and the neighbor has a use for it, giving away an old battery isn’t advisable. If it’s nearing the end of its lifespan or is no longer functioning properly, it could pose risks. Additionally, the eventual disposal of the battery still needs to be handled responsibly.
In summary, the best practice for disposing of old batteries from PCs is to recycle them in accordance with local regulations. This approach ensures environmental safety and proper handling of potentially hazardous materials. Throwing batteries in the trash is not environmentally safe and is often against local disposal regulations. Passing them on to others doesn’t address the fundamental issue of proper disposal.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- hard drive
- RAID
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint: When a computer reboots suddenly without user intervention, particularly after being used for an extended period, it often points to issues related to hardware stability or overheating. The two hardware components most likely to cause this problem are:
- Power Supply: A faulty or inadequate power supply can cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly. If the power supply is unable to deliver consistent power due to age, damage, or being underpowered for the system’s requirements, it can lead to sudden reboots. This is especially likely if the computer has been under continuous use, placing more demand on the power supply.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is another common culprit in cases of unexpected reboots, often due to overheating. Continuous use can cause the CPU temperature to rise, especially if the cooling system (like fans or heat sinks) is not working effectively or if thermal paste has degraded. When the CPU overheats, most systems are designed to reboot automatically to prevent damage.
While other components like the hard drive, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), and wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller) can potentially cause issues, they are less likely to be the cause of sudden reboots compared to the power supply and CPU. A failing hard drive or RAID issues would more commonly result in system freezes or error messages, BIOS issues would typically prevent the computer from booting up correctly in the first place, and a faulty wireless NIC is more likely to cause network-related problems rather than a system reboot.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- display port or display
- RAID
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint: When a computer reboots suddenly without user intervention, particularly after being used for an extended period, it often points to issues related to hardware stability or overheating. The two hardware components most likely to cause this problem are:
- Power Supply: A faulty or inadequate power supply can cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly. If the power supply is unable to deliver consistent power due to age, damage, or being underpowered for the system’s requirements, it can lead to sudden reboots. This is especially likely if the computer has been under continuous use, placing more demand on the power supply.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is another common culprit in cases of unexpected reboots, often due to overheating. Continuous use can cause the CPU temperature to rise, especially if the cooling system (like fans or heat sinks) is not working effectively or if thermal paste has degraded. When the CPU overheats, most systems are designed to reboot automatically to prevent damage.
While other components like the hard drive, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), and wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller) can potentially cause issues, they are less likely to be the cause of sudden reboots compared to the power supply and CPU. A failing hard drive or RAID issues would more commonly result in system freezes or error messages, BIOS issues would typically prevent the computer from booting up correctly in the first place, and a faulty wireless NIC is more likely to cause network-related problems rather than a system reboot.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- surge strip
- RAID
- BIOS
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint: When a computer reboots suddenly without user intervention, particularly after being used for an extended period, it often points to issues related to hardware stability or overheating. The two hardware components most likely to cause this problem are:
- Power Supply: A faulty or inadequate power supply can cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly. If the power supply is unable to deliver consistent power due to age, damage, or being underpowered for the system’s requirements, it can lead to sudden reboots. This is especially likely if the computer has been under continuous use, placing more demand on the power supply.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is another common culprit in cases of unexpected reboots, often due to overheating. Continuous use can cause the CPU temperature to rise, especially if the cooling system (like fans or heat sinks) is not working effectively or if thermal paste has degraded. When the CPU overheats, most systems are designed to reboot automatically to prevent damage.
While other components like the hard drive, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), and wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller) can potentially cause issues, they are less likely to be the cause of sudden reboots compared to the power supply and CPU. A failing hard drive or RAID issues would more commonly result in system freezes or error messages, BIOS issues would typically prevent the computer from booting up correctly in the first place, and a faulty wireless NIC is more likely to cause network-related problems rather than a system reboot.
-
A technician has been called in to investigate a problem with the computer rebooting randomly throughout the day. What two pieces of hardware could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- surge strip
- ROM
- wireless NIC
- motherboard
-
Explanation & Hint:
CPU and Power Supply are indeed two pieces of hardware that could cause a computer to reboot randomly. Let’s explore why these are correct and why the other options are less likely:- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is the brain of the computer, handling all the instructions it receives from hardware and software. Overheating is a common reason a CPU might cause the computer to reboot. If the CPU gets too hot, it can trigger a safety mechanism that restarts the computer to prevent damage. Additionally, a CPU that is malfunctioning or under extreme stress from processes can also lead to system instability and random reboots.
- Power Supply: As previously mentioned, a faulty or inadequate power supply can lead to instability in the computer’s operation. Inconsistencies in power delivery or a failing power supply unit can cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly. This is one of the most common hardware issues that lead to random reboots.
Now, let’s discuss why the other options are less likely:
- Surge Strip: While a faulty surge strip can cause power issues, it’s more likely to cut off power entirely rather than cause random reboots. Surge strips typically protect against power surges and do not directly interact with the computer’s internal processes.
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): ROM is a type of non-volatile memory used mainly for firmware (a software that is closely tied to specific hardware). Issues with ROM are less likely to cause random reboots and more likely to result in boot failures or errors in executing firmware-related tasks.
- Wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller): A wireless NIC, which handles network connections, is unlikely to cause random reboots. Issues with a wireless NIC would more commonly result in network connectivity problems, not system instability.
- Motherboard: While a faulty motherboard can cause a wide range of issues, including reboots, it’s less common compared to CPU and power supply problems. Motherboard issues can be more complex and varied, affecting various aspects of the computer’s operation.
In summary, the CPU and Power Supply are more directly linked to the common causes of random reboots, such as overheating and power instability, respectively.
-
A technician has been called in to investigate a problem with the computer rebooting randomly throughout the day. What two pieces of hardware could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- RAID
- ROM
- wireless NIC
- motherboard
-
Explanation & Hint:
In this scenario, the two pieces of hardware that could most likely cause a computer to reboot randomly throughout the day are the CPU and Power Supply. Here’s why these are the correct choices, and why the other options are less likely:- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is crucial for processing all computer operations. If the CPU overheats or fails due to other issues like manufacturing defects or age, it can lead to system instability, causing the computer to reboot unexpectedly. Overheating is particularly common and can be triggered by inadequate cooling, dust buildup, or thermal paste degradation.
- Power Supply: The power supply is responsible for providing stable power to the computer. If it’s faulty, provides insufficient power, or fluctuates in power output, it can lead to random reboots. Power supply issues are a common cause of such problems, especially in older or lower-quality units.
Now, let’s explain why the other options are less likely:
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): RAID is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units. While RAID issues can lead to data loss or corruption, they are unlikely to cause the computer to reboot randomly.
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): ROM contains firmware used during the booting process. Problems with ROM would typically prevent a computer from booting up rather than causing it to reboot randomly.
- Wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller): A wireless NIC facilitates wireless networking. Issues with a wireless NIC would more likely lead to network connectivity problems, not random reboots of the entire system.
- Motherboard: The motherboard, while a central component, is less likely to be the cause compared to the CPU and power supply. However, it’s worth noting that a faulty motherboard can also lead to random reboots due to its role in connecting and managing all computer components.
In summary, the CPU and Power Supply are the most likely culprits in this scenario due to their direct involvement in the computer’s power management and processing tasks.
-
For two days in a row, a user has noticed that the computer reboots several times before it eventually starts. What are two suspect components? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- BIOS
- ROM
- wireless NIC
- motherboard
-
Explanation & Hint:
For a computer that reboots several times before eventually starting, two suspect components that could be causing this issue are the Power Supply and the Motherboard. Here’s an explanation for these choices and why the other options are less likely:- Power Supply: If the power supply is failing or not providing consistent power, it can cause the computer to reboot multiple times before it stabilizes and starts properly. Issues like power fluctuations or inadequate power output can lead to such behavior. The power supply is a common culprit in cases where a computer struggles to start up correctly.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the central hub for all computer components. If there are issues with the motherboard, such as faulty capacitors, bad solder joints, or problems with the BIOS firmware that resides on it, it can lead to instability during the boot process. This can manifest as repeated reboots before the system successfully starts.
Now, let’s discuss why the other options are less likely:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): While a faulty CPU can cause a system to be unstable, it’s less likely to cause multiple reboots before a successful start. CPU problems typically result in a failure to boot or system instability after booting.
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): BIOS issues can prevent a computer from starting, but they are less likely to cause multiple reboots before a successful start. BIOS problems usually result in a failure to boot or error messages during the boot process.
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): ROM in this context usually refers to the memory where the BIOS firmware is stored. Like BIOS issues, ROM problems would more likely lead to boot failure or error messages rather than multiple reboots.
- Wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller): A wireless NIC is involved in network connectivity and is unlikely to cause issues with the boot process. Problems with a wireless NIC typically manifest as connectivity issues once the system has booted.
In this scenario, the Power Supply and Motherboard are the most likely candidates due to their integral roles in providing power and facilitating the boot process.
-
For two days in a row, a user has noticed that the computer reboots several times before it eventually starts. What are two suspect components? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- ROM
- BIOS
- RAID
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint:
In the scenario where a computer reboots several times before eventually starting, the two suspect components to consider are the Power Supply and the BIOS. Here’s why these components are likely suspects, along with explanations for why the other options are less likely:- Power Supply: A failing or inadequate power supply can cause instability during the boot process. If the power supply is not delivering consistent and sufficient power, it can lead to the computer rebooting multiple times before it stabilizes enough to start properly. This is a common issue and should be one of the first components to check in such scenarios.
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): BIOS issues can lead to a variety of startup problems. If the BIOS is corrupted, improperly configured, or facing compatibility issues with hardware, it can cause the system to reboot repeatedly during the boot process. This might be due to the BIOS attempting to reset to safe parameters or encountering errors that prevent normal startup.
Now, let’s consider why the other options are less likely:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): While a faulty CPU can cause system instability, it generally leads to a failure to boot or system crashes rather than repeated reboots during the startup process.
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): ROM typically refers to the non-volatile memory where the BIOS is stored. Issues with ROM itself are rare and would more likely prevent the computer from starting at all rather than causing multiple reboots.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): Problems with RAID configurations usually lead to data access or storage issues. While it’s possible for RAID issues to impact the boot process, especially if the system disk is part of a RAID array, it’s less likely to cause repeated reboots compared to power supply or BIOS issues.
- Wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller): A wireless NIC, being primarily responsible for network connectivity, is unlikely to cause issues with the boot process. Problems with a wireless NIC would typically manifest as network-related issues after the system has booted.
In summary, the Power Supply and BIOS are the most likely components to investigate in this case, given their crucial roles in powering the system and initiating the boot process.
-
While a user is working on a spreadsheet, the computer reboots. What are two components that could cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- ROM
- BIOS
- RAID
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint: In the scenario where a computer reboots unexpectedly while a user is working on a spreadsheet, the two components most likely to cause this issue are the CPU and Power Supply. Here’s an explanation for these choices and why the other options are less likely:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is critical for processing all the tasks on a computer. If the CPU is overheating, it could cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly as a protective measure. Additionally, other CPU issues like voltage irregularities or physical damage can also lead to sudden reboots.
- Power Supply: An unstable or failing power supply can cause the computer to reboot without warning. Issues like power surges, inadequate power output, or a failing power supply unit can lead to sudden loss of power or power fluctuations, resulting in the computer rebooting.
Now, let’s discuss why the other options are less likely:
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): ROM, which typically contains firmware like the BIOS, is not usually a direct cause of random reboots. Issues with ROM would more likely lead to boot problems or errors in firmware execution, rather than unexpected reboots during regular operation.
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): While BIOS issues can cause startup problems, they are less likely to cause a computer to reboot randomly during regular operations like working on a spreadsheet.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): RAID is a data storage technology used for redundancy and performance. Problems with RAID arrays generally lead to data access or storage issues and are unlikely to cause sudden reboots unless the system’s primary disk is affected. Even then, it’s a less common cause compared to CPU or power supply issues.
- Wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller): A wireless NIC handles network connections and is unlikely to cause the system to reboot. Issues with a wireless NIC would more commonly result in network connectivity problems.
In summary, the CPU and Power Supply are the most likely culprits behind a computer rebooting unexpectedly while in use, due to their direct roles in processing and power management.
-
While a user is working on a spreadsheet, the computer reboots. What are two components that could cause this issue? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- motherboard
- BIOS
- RAID
- wireless NIC
-
Explanation & Hint: If a computer reboots suddenly while a user is working on a spreadsheet, this can be indicative of issues with specific hardware components. The two components most likely to cause such an issue are:
- Power Supply: A faulty or unstable power supply unit (PSU) is a common cause of unexpected reboots. If the PSU is unable to deliver consistent power, possibly due to age, wear, damage, or being underpowered for the computer’s requirements, it can result in the computer rebooting suddenly. This kind of issue can occur regardless of the specific tasks being performed on the computer.
- Motherboard: The motherboard, being the central hub that connects all components of the computer, could also be a cause of sudden reboots. Issues such as faulty capacitors, poor soldering, electrical short circuits, or other hardware failures on the motherboard can lead to instability and cause the system to reboot.
While other components like the CPU, BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), and wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller) might also be responsible for various computer issues, they are less likely to cause sudden reboots in the scenario described:
- A CPU problem would more commonly lead to system freezes or shutdowns due to overheating, rather than reboots.
- BIOS issues typically prevent the computer from booting correctly or affect system stability in more consistent ways.
- Problems with RAID setups usually manifest in data access or storage issues.
- A malfunctioning wireless NIC would primarily affect network connectivity, not cause the system to reboot.
-
After continuous morning use, a computer suddenly reboots without the intervention of the user. What are the two most likely hardware parts that could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
- CPU
- power supply
- hard drive
- wireless NIC
- BIOS
- ROM
-
Explanation & Hint: When a computer reboots suddenly without user intervention, particularly after being used for an extended period, it often points to issues related to hardware stability or overheating. The two hardware components most likely to cause this problem are:
- Power Supply: A faulty or inadequate power supply can cause the computer to reboot unexpectedly. If the power supply is unable to deliver consistent power due to age, damage, or being underpowered for the system’s requirements, it can lead to sudden reboots. This is especially likely if the computer has been under continuous use, placing more demand on the power supply.
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is another common culprit in cases of unexpected reboots, often due to overheating. Continuous use can cause the CPU temperature to rise, especially if the cooling system (like fans or heat sinks) is not working effectively or if thermal paste has degraded. When the CPU overheats, most systems are designed to reboot automatically to prevent damage.
While other components like the hard drive, RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), and wireless NIC (Network Interface Controller) can potentially cause issues, they are less likely to be the cause of sudden reboots compared to the power supply and CPU. A failing hard drive or RAID issues would more commonly result in system freezes or error messages, BIOS issues would typically prevent the computer from booting up correctly in the first place, and a faulty wireless NIC is more likely to cause network-related problems rather than a system reboot.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 137. What service application is the client requesting?
- NetBIOS (NetBT)
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The destination port number in a packet helps identify the service or protocol intended for the communication. If a client packet is received by a server with a destination port number of 137, it indicates that the client is requesting the NetBIOS (NetBT) service.
Here’s a brief explanation of the services associated with the given port numbers and protocols:
- NetBIOS (NetBT): Port 137 is associated with NetBIOS Name Service. NetBIOS provides services related to the session layer of the OSI model and is used for LAN-based network communication. NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) uses port 137 for name resolution services.
- SMB/CIFS: The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol, often referred to in the context of the Common Internet File System (CIFS), typically uses ports like 445 or 139 (in combination with NetBIOS). Port 137 is not directly associated with SMB/CIFS.
- HTTPS: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) uses port 443. It is the secure version of HTTP, used primarily for secure communication over a computer network within a web browser.
- SLP (Service Location Protocol): SLP uses port 427 for service discovery in local networks. It’s not associated with port 137.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 137 is meant for a NetBIOS service, specifically the NetBIOS Name Service.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 22. What service application is the client requesting?
- SSH
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 22 is requesting the SSH (Secure Shell) service. Port 22 is the standard TCP/IP port assigned for SSH communications. SSH is a cryptographic network protocol used for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. It is commonly used for secure data communication, remote command-line login, remote command execution, and other secure network services between two networked computers.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 143. What service application is the client requesting?
- IMAP
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 143 is requesting the IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) service. Port 143 is the standard port used by IMAP, which is a protocol for accessing email on a remote server from a local client. IMAP allows clients to read emails as if they were stored locally on their device, but actually, the emails are maintained on the server.
As for the other options:
- SMB/CIFS: The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol and the Common Internet File System (CIFS) are used for file sharing, printer sharing, and other network communication tasks. These protocols typically use port 445 or 139, not port 143.
- HTTPS: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is used for secure communication over a computer network within a web browser and typically uses port 443. It is not related to port 143.
- SLP (Service Location Protocol): SLP is used for computers and other devices to find services in a local area network without prior configuration. It typically uses port 427, not port 143.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 143 is specifically requesting IMAP services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 23. What service application is the client requesting?
- Telnet
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 23 is requesting the Telnet service. Telnet is a network protocol used for bidirectional interactive text-based communication over a virtual terminal. It operates on port 23, which is the standard assignment for Telnet services. Telnet is often used for remote administration of devices but is less secure compared to modern protocols like SSH (Secure Shell) because it transmits data, including login credentials, in plaintext.
As for the other options:
- SMB/CIFS: The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol and the Common Internet File System (CIFS) are used for network file sharing and printer services. These protocols typically operate on ports 139 and 445, not port 23.
- HTTPS: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is used for secure web browsing, encrypting the data exchanged between a web browser and a server. It operates on port 443, not port 23.
- SLP (Service Location Protocol): SLP is used for locating services in Local Area Networks (LANs) without prior configuration. This protocol typically uses port 427, not port 23.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 23 specifically indicates a request for Telnet services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 161. What service application is the client requesting?
- SNMP
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 161 is requesting the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) service. SNMP is a widely used protocol for network management and monitoring. Port 161 is the designated port for SNMP agents to listen for SNMP requests from managers. SNMP is primarily used to collect information from, and configure, network devices such as routers, switches, printers, and servers.
Explanation of the incorrect options:
- SMB/CIFS: Server Message Block (SMB) and Common Internet File System (CIFS) are protocols used for network file sharing and printer services. They typically use ports 139 and 445, not port 161.
- HTTPS: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is used for secure communication over a computer network within a web browser. It encrypts the data exchanged between a web browser and a server and operates on port 443, not port 161.
- SLP (Service Location Protocol): SLP is used for locating services in local area networks without prior configuration. It typically uses port 427, not port 161.
Thus, a packet with a destination port number of 161 is specifically indicative of a request for SNMP services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 389. What service application is the client requesting?
- LDAP
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 389 is requesting the LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) service. LDAP is used for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol network. Port 389 is the standard port for LDAP communications, facilitating operations like directory searches and modifications.
Explanation of the incorrect options:
- SMB/CIFS: Server Message Block (SMB) and Common Internet File System (CIFS) are protocols used for network file sharing and printer services. They operate on ports 139 and 445, not port 389.
- HTTPS: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is used for secure web communications and typically operates on port 443. It’s not associated with port 389.
- SLP (Service Location Protocol): SLP is used for locating services in local area networks without prior configuration, typically operating on port 427, not port 389.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 389 is specifically indicative of a request for LDAP services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 25. What service application is the client requesting?
- SMTP
- SMB/CIFS
- HTTPS
- SLP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 25 is requesting the SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service. SMTP is used for sending emails over the Internet. Port 25 is the standard port designated for SMTP communications and is primarily used for email transmission between mail servers or from email clients to mail servers for sending emails.
Explanation of the incorrect options:
- SMB/CIFS: Server Message Block (SMB) and Common Internet File System (CIFS) are protocols used for network file sharing and printer services. They typically use ports 139 and 445, not port 25.
- HTTPS: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is used for secure web communications, operating typically on port 443. It’s not associated with port 25.
- SLP (Service Location Protocol): SLP is used for locating services in local area networks without prior configuration, typically operating on port 427, not port 25.
Thus, a packet with a destination port number of 25 specifically indicates a request for SMTP services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 427. What service application is the client requesting?
- SLP
- SMB/CIFS
- SMTP
- DNS
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 427 is requesting the SLP (Service Location Protocol) service. SLP is used for locating services in local area networks without prior configuration. It typically operates on port 427, facilitating network services to find and use other services within the same network.
Explanation of the incorrect options:
- SMB/CIFS: Server Message Block (SMB) and Common Internet File System (CIFS) are protocols used for network file sharing and printer services. They typically use ports 139 and 445, not port 427.
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), used for sending emails, operates typically on port 25. It’s not associated with port 427.
- DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS), which translates domain names to IP addresses, typically uses port 53, not port 427.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 427 is specifically indicative of a request for SLP services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 53. What service application is the client requesting?
- DNS
- SMTP
- DHCP
- TFTP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 53 is requesting the DNS (Domain Name System) service. DNS is used for translating human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses that computers use to identify each other on the network. Port 53 is the standard port used for both DNS queries and responses.
Explanation of the incorrect options:
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), used for sending emails, typically operates on port 25. It is not associated with port 53.
- DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which is used for dynamically distributing network configuration parameters, such as IP addresses, typically uses ports 67 and 68, not port 53.
- TFTP: Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP), a simplified version of FTP used to transfer files, typically uses port 69. It’s not associated with port 53.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 53 specifically indicates a request for DNS services.
-
A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 427. What service application is the client requesting?
- SLP
- SMTP
- DNS
- DHCP
-
Explanation & Hint: The client packet with a destination port number of 427 is requesting the SLP (Service Location Protocol) service. SLP is used for locating services in local area networks without prior configuration. It typically operates on port 427, facilitating network services to find and use other services within the same network.
Explanation of the incorrect options:
- SMB/CIFS: Server Message Block (SMB) and Common Internet File System (CIFS) are protocols used for network file sharing and printer services. They typically use ports 139 and 445, not port 427.
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), used for sending emails, operates typically on port 25. It’s not associated with port 427.
- DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS), which translates domain names to IP addresses, typically uses port 53, not port 427.
Therefore, a packet with a destination port number of 427 is specifically indicative of a request for SLP services.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1
-
Explanation & Hint: The compressed format of the IPv6 address
2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001can be derived by following the rules for IPv6 address compression. These rules allow for the omission of leading zeros in each 16-bit block and the replacement of one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::). However, the double colon can only be used once in an address to ensure its uniqueness.Given these rules, the correct compressed format for this IPv6 address is:
2001:db8::a0b0:8:1Explanation of the options:
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1: Correct. It omits leading zeros and replaces consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon.
- 2001:db80:0:1::80:1: Incorrect. This changes the value of the original address (the second block is
db80instead ofdb8) and misplaces zeros. - 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000: Incorrect. This changes the value of the original address and does not correctly represent the zero blocks.
- 2001:db80:::1::80:1: Incorrect and invalid. Multiple uses of the double colon (::) are not allowed in a single IPv6 address, and it also changes the value of the original address.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290, the following rules should be applied:- Leading zeros in each 16-bit block can be omitted.
- One or more consecutive blocks of zeros can be replaced with a double colon (::), but this can only be done once in the address.
Applying these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290Explanation of the options:
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290: Correct. It removes leading zeros and collapses the consecutive blocks of zeros into a double colon.
- fe80:9:20::b000:290: Incorrect. This alters the original address’s structure and values.
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290: Incorrect. It changes the address’s structure and values, not accurately reflecting the original address.
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290: Incorrect and invalid. Multiple uses of the double colon (::) are not allowed in a single IPv6 address, and it also changes the original address values.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909?
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
2002:0042:0010:c400:0000:0000:0000:0909, we apply the following rules:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::). This can be done only once in an address.
Using these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
2002:42:10:c400::909Explanation of the options:
- 2002:42:10:c400::909: Correct. It correctly omits leading zeros and replaces the consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon.
- 200:420:110:c4b::910:0:90: Incorrect. This changes the values in the original address, altering its meaning.
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99: Incorrect. This changes the values in the original address and does not accurately represent the original blocks.
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99: Incorrect. This also changes the values in the original address and does not accurately represent the original blocks.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290, we apply the standard rules of IPv6 address compression:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::). This can be done only once in an address.
Using these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290Explanation of the options:
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290: Correct. It correctly omits leading zeros and collapses the consecutive blocks of zeros into a double colon.
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29: Incorrect. This changes the values in the original address, altering its structure and meaning.
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290: Incorrect. It changes the structure and values of the original address and does not accurately represent the original blocks.
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029: Incorrect. This option changes the original address’s structure and values, not accurately reflecting the original address.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990?
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
- 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99
- 2002:42:10:c400::909
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990, we need to apply the standard rules for IPv6 address compression:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::), but only once in an address.
Applying these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
2002:420:c4:1008:25:190:0:990Explanation of the options:
- 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990: Almost correct, but it misses a ‘0’ in the last block before ‘990’. It should be
0:990, not::990. - 2002:4200::25:1090:0:99: Incorrect. This changes the values in the original address and does not accurately represent the original blocks.
- 2002:42:10:c400::909: Incorrect. This does not match the original address’s structure or values.
- 2002:42::25:1090:0:99: Incorrect. This also changes the values in the original address and does not accurately represent the original blocks.
Thus, the first option is the closest, but the correct compressed format is
2002:420:c4:1008:25:190:0:990.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000?
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
2001:0db8:0000:0000:0ab8:0001:0000:1000, we follow the standard rules for IPv6 address compression:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::), but this can only be done once in the address.
Applying these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000Explanation of the options:
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000: Correct. It correctly omits leading zeros and collapses the consecutive blocks of zeros into a double colon.
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1: Incorrect. This changes the values in the original address, which is not a correct representation.
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1: Incorrect. This option alters the structure and values of the original address.
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1: Incorrect. This option also changes the structure and values of the original address.
Therefore, the first option,
2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000, is the correctly compressed format of the given IPv6 address.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029?
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
fe80:0000:0000:0000:0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029, we apply the standard rules for IPv6 address compression:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::). This can be done only once in the address.
Using these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29Explanation of the options:
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29: Correct. This format correctly omits leading zeros and replaces the consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon.
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290: Incorrect. This changes the structure and values of the original address.
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290: Incorrect. This does not accurately represent the original address’s values or structure.
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290: Incorrect and invalid. It has multiple uses of the double colon (::) and does not accurately reflect the original address’s values.
Thus, the first option,
fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29, is the correctly compressed format of the given IPv6 address.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001?
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
2001:0db8:0000:0000:0000:a0b0:0008:0001, we apply the standard rules for IPv6 address compression:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::), but this can only be done once in the address.
Applying these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
2001:db8::a0b0:8:1Explanation of the options:
- 2001:db8::a0b0:8:1: Correct. It correctly omits leading zeros and collapses the consecutive blocks of zeros into a double colon.
- 2001:db8:1::ab8:0:1: Incorrect. This changes the values in the original address, which is not a correct representation.
- 2001:db8::ab8:1:0:1000: Incorrect. This option does not accurately represent the original address’s structure or values.
- 2001:db8:0:1::8:1: Incorrect. This also changes the structure and values of the original address.
Therefore, the first option,
2001:db8::a0b0:8:1, is the correctly compressed format of the given IPv6 address.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290?
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
fe80:09ea:0000:2200:0000:0000:0fe0:0290, we follow the standard rules for IPv6 address compression:- Omit leading zeros in each 16-bit block.
- Replace one or more consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon (::). This can only be done once in the address.
Applying these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290Explanation of the options:
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290: Correct. This format correctly omits leading zeros and replaces the consecutive blocks of zeros with a double colon.
- fe80::220:b3f:f0e0:29: Incorrect. This changes the structure and values of the original address.
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290: Incorrect. It changes the structure and values of the original address and does not accurately represent the original blocks.
- fe80:9ea0::2020::bf:e0:9290: Incorrect and invalid. It has multiple uses of the double colon (::) and does not accurately reflect the original address’s values.
Therefore, the first option,
fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290, is the correctly compressed format of the given IPv6 address.
-
Which is the compressed format of the IPv6 address fe80:9ea0:0000:2020:0000:00bf:00e0:9290?
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290
- fe80:9:20::b000:290
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029
-
Explanation & Hint: To compress the IPv6 address
fe80:9ea0:0000:2020:0000:00bf:00e0:9290, the following rules should be applied:- Leading zeros within each 16-bit block of the address can be omitted.
- Consecutive blocks of zeros can be replaced with a double colon (::), but this can only be done once in the address.
Applying these rules, the compressed format of the IPv6 address is:
fe80:9ea0:0:2020:0:bf:e0:9290Explanation of the options:
- fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290: Correct. It omits leading zeros and replaces a single block of zeros with a double colon.
- fe80:9:20::b000:290: Incorrect. This changes the structure and values of the original address, not accurately representing it.
- fe80:9ea:0:2200::fe0:290: Incorrect. This does not match the structure or values of the original address.
- fe80::0220:0b3f:f0e0:0029: Incorrect. This also changes the original address’s structure and values, not accurately reflecting it.
The first option,
fe80:9ea0::2020:0:bf:e0:9290, correctly represents the compressed format of the given IPv6 address.
-
What ACPI power state describes when the CPU and RAM are off and the contents of RAM have been saved to a temporary file on the hard drive?
- S4
- S1
- S2
- S3
-
Explanation & Hint: The ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) power state that describes the condition where the CPU and RAM are off, and the contents of RAM have been saved to a temporary file on the hard drive, is known as S4.
In the S4 state, also known as “hibernation,” the system saves the contents of the memory to a hard drive or other non-volatile storage. This allows the computer to turn off completely, which means the CPU, RAM, and most of the other components are powered down. When the system is powered back on, it can resume from where it left off by reading the saved data from the hard drive.
-
What ACPI power state describes when the CPU and RAM are still receiving power but unused devices are powered down?
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the CPU is off, but the RAM is refreshed?
- S2
- S1
- S3
- S4
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the computer is off?
- S5
- S1
- S2
- S3
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the computer is off?
- S5
- S1
- S2
- S4
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the CPU is off and the RAM is set to a slow refresh rate, often called suspend mode?
- S3
- S4
- S2
- S5
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the computer is on and the CPU is running?
- S0
- S4
- S3
- S5
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the CPU and RAM are still receiving power but unused devices are powered down?
- S1
- S4
- S3
- S5
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the CPU and RAM are off and the contents of RAM have been saved to a temporary file on the hard drive?
- S4
- S3
- S2
- S5
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
What ACPI power state describes when the computer is off?
- S5
- S4
- S3
- S2
-
Explanation & Hint:
-
A photographer is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer issues a “Document failed to print” message. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- A cable is loose or disconnected.
- The printer is no longer shared.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
- The laser printer is emitting too much radiation.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
-
Explanation & Hint: - A cable is loose or disconnected: This is a common and straightforward issue. If the connection between the printer and the computer (or network) is not secure due to a loose or disconnected cable, it can prevent the printer from receiving print jobs. Ensuring all cables are properly connected is an essential step in troubleshooting printer issues.
- The printer is no longer shared: In a network environment, especially in offices or shared spaces, printers are often set up as shared devices. If the printer sharing settings are altered or if the printer is somehow removed from the network sharing options, it could lead to an inability to print, especially from other computers on the network. Restoring the printer’s shared status or ensuring that network sharing settings are correctly configured can resolve this issue.
These two causes are indeed plausible and can be relatively common in different printing environments. Checking and addressing both can help in resolving the printing issue.
-
A reporter is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer is printing unknown characters. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The wrong or an outdated printer driver is installed.
- The printer has a loose connection.
- The laser printer is emitting too much radiation.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a printer starts printing unknown characters, it’s typically related to issues with communication or data interpretation between the computer and the printer. Two possible causes for this issue could be:
- The wrong or an outdated printer driver is installed: If the printer driver is incorrect or outdated, it may not translate the document data correctly for the printer, leading to the printing of unknown or garbled characters. Ensuring that the correct, up-to-date driver for the specific printer model is installed is crucial.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port: If the printer is configured to use a port that it’s not actually connected to, or if the port settings are incorrect, this can result in communication problems, leading to printing errors like unknown characters.
The other options listed are less likely to be direct causes of this specific issue. A loose connection might stop the printer from working altogether but is less likely to cause it to print unknown characters. The notion of a laser printer emitting too much radiation is not relevant to the issue of printing unknown characters. Lastly, a flimsy paper tray would typically cause paper jams or misfeeds, not issues with the characters being printed.
-
A manager is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer is printing incorrect colors. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The print heads might need to be cleaned and calibrated.
- An incorrect cartridge could be installed.
- The printer is using the wrong cable.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a printer is printing incorrect colors, it’s typically an issue related to the ink or toner and the printer’s ability to accurately apply them. Two possible causes for this issue could be:
- The print heads might need to be cleaned and calibrated: Over time, print heads can become clogged or misaligned, especially in inkjet printers. This can result in colors not being printed correctly. Cleaning and calibrating the print heads can often resolve these color accuracy issues.
- An incorrect cartridge could be installed: If a cartridge is not the right type for the printer, or if it’s a color cartridge that’s been installed in the wrong slot, this can lead to incorrect colors being printed. Checking that all cartridges are correct for the model and are installed in the proper slots is important.
The other options listed are less likely to be related to the issue of incorrect colors. The type of cable used or the specific port to which the printer is connected generally does not affect color output. Likewise, the quality or condition of the paper tray is not typically related to color printing issues.
-
A technician is complaining about the following printer issue: The print appears faded on the paper. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The toner cartridge is low.
- The paper might be incompatible with the printer.
- The wrong printer type has been selected.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
-
Explanation & Hint:
- The Toner Cartridge is Low: A low toner cartridge is a common cause of faded prints in printers. When the toner level is low, the printer is unable to apply a sufficient amount of toner to the paper, leading to lighter or uneven printing. Replacing or refilling the toner cartridge is the standard solution to this problem.
- The Paper Might be Incompatible with the Printer: Using paper that is not compatible with the printer can also result in faded prints. Different printers are designed to work with specific types of paper, and using the wrong kind can affect print quality. For example, inkjet printers require different paper types compared to laser printers to achieve optimal print quality. Ensuring that the paper used is suitable for the specific printer model can help in resolving print quality issues.
The other provided options are less likely to cause faded prints:
- The Wrong Printer Type has been Selected: While this can affect overall print quality, it typically doesn’t result in faded prints.
- The Printer has been Installed on the Wrong Port: This would affect the printer’s ability to communicate with the computer, not the quality of the prints.
- The Paper Tray is Flimsy: A flimsy paper tray might lead to paper feed issues, but it’s not a direct cause of faded printing.
In summary, checking the toner levels and verifying the compatibility of the paper with the printer are key steps in addressing the issue of faded prints.
-
A librarian is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer control panel displays no image. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The contrast of the screen may be set too low.
- The printer is not turned on.
- The room temperature is above normal.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
-
Explanation & Hint:
The issue of the printer control panel displaying no image can be attributed to a couple of possible causes. Based on the options provided, the two most likely causes are:- The Contrast of the Screen May be Set Too Low: If the contrast on the printer’s control panel is set too low, it might make the display appear blank or very faint. Adjusting the contrast settings could resolve this issue and bring back the display image.
- The Printer is Not Turned On: This might seem basic, but it’s a common oversight. If the printer is not properly turned on, the control panel will not display any image. Checking the power connection and ensuring that the printer is switched on is a fundamental step in troubleshooting this issue.
The other options are less likely to be the cause of a blank control panel screen:
- The Room Temperature is Above Normal: While extreme temperatures can affect electronic devices, a slightly elevated room temperature is unlikely to cause the printer’s control panel to display no image. This issue would more likely arise under more extreme conditions.
- The Printer has been Installed on the Wrong Port: The port through which the printer is connected to a computer impacts data transmission for printing tasks, not the display of the printer’s control panel.
- The Paper Tray is Flimsy: The condition of the paper tray is unrelated to the display functionality of the printer’s control panel. A flimsy paper tray might cause paper feed issues, but it would not affect the control panel display.
In summary, checking the contrast settings of the screen and ensuring that the printer is actually turned on are practical first steps to address the issue of the printer control panel displaying no image.
-
A teacher is complaining about the following printer issue: The paper is creased after printing. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The paper-feed tray might not be firmly adjusted against the edges of the printer.
- The paper might be loaded incorrectly.
- Print jobs are being sent to the wrong printer.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
-
Explanation & Hint:
The issue of paper being creased after printing can be attributed to a couple of possible causes. Based on the options provided, the two most likely causes are:- The Paper-Feed Tray Might Not be Firmly Adjusted Against the Edges of the Printer: If the paper-feed tray is not properly aligned or firmly adjusted, it can lead to misfeeds or skewed feeding of the paper through the printer. This misalignment can cause the paper to crease as it passes through the printer’s internal mechanisms.
- The Paper Might be Loaded Incorrectly: Incorrectly loaded paper can easily lead to creases. This can happen if the paper is not placed squarely in the tray, is overloaded, or if different sizes or types of paper are mixed in the tray. Ensuring that the paper is loaded correctly and in alignment with the printer’s specifications is crucial to avoid such issues.
The other options are less likely to cause paper creasing:
- Print Jobs are Being Sent to the Wrong Printer: Sending a print job to the wrong printer would not result in paper creasing. It would either result in no printout or a printout from a different printer.
- The Printer has been Installed on the Wrong Port: The port through which the printer is connected to a computer affects data transmission and has no impact on the physical process of printing, such as paper handling.
- The Paper Tray is Flimsy: While a flimsy paper tray might contribute to paper feed issues, it is less likely to be a direct cause of paper creasing compared to improper adjustment of the paper-feed tray or incorrect paper loading.
In summary, ensuring that the paper-feed tray is properly adjusted and that the paper is loaded correctly are important steps in resolving the issue of paper creasing after printing.
-
A receptionist is complaining about the following printer issue: My impact printer produces faded or light characters. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The ribbon may be worn out.
- The ribbon may be damaged.
- The print queue is overloaded.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
-
Explanation & Hint:
For the issue of an impact printer producing faded or light characters, the two most likely causes are:- The Ribbon May be Worn Out: In impact printers, the ribbon is an essential component for transferring ink onto the paper. Over time and with extensive use, the ribbon can become worn out, leading to faded or light characters being printed. Replacing the worn-out ribbon with a new one should resolve this issue.
- The Ribbon May be Damaged: Besides general wear and tear, the ribbon can also be damaged or have defects. Damage to the ribbon, such as tears, creases, or inconsistent ink distribution, can result in poor print quality, including faded or light characters. Inspecting the ribbon for damage and replacing it if necessary is a recommended step.
The other options are less likely to be the cause of this specific issue:
- The Print Queue is Overloaded: While an overloaded print queue can lead to delays in printing or errors in print jobs, it does not directly affect the quality of the print itself, such as causing faded or light characters.
- The Printer has been Installed on the Wrong Port: The port through which the printer is connected to a computer affects its ability to receive data for printing jobs. This would not typically impact the physical quality of the print, such as the intensity of the characters.
- The Paper Tray is Flimsy: The condition of the paper tray is unlikely to affect the quality of printing in terms of ink intensity. Issues with a flimsy paper tray are more likely to lead to paper jams or misalignment, not faded printing.
In summary, checking and potentially replacing the printer’s ribbon, whether due to wear or damage, are key steps in addressing the issue of faded or light characters in impact printer output.
-
A photographer is complaining about the following printer issue: The paper is not being fed into the printer. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The paper may be wrinkled.
- The printer could be set to print to a different paper size than is currently loaded.
- The paper tray is flimsy.
- The printer has been installed on the wrong port.
- The printer service is stopped or not working properly.
-
Explanation & Hint:
For the issue of paper not being fed into the printer, the two most likely causes are:- The Paper May be Wrinkled: If the paper loaded into the printer is wrinkled, it can prevent proper feeding into the printer. Wrinkled paper can jam or misalign within the printer’s feeding mechanism, leading to the paper not being fed at all. Ensuring that the paper is smooth and free of wrinkles before loading it into the printer can help resolve this issue.
- The Printer Could be Set to Print to a Different Paper Size than is Currently Loaded: If the printer’s settings are configured for a different paper size than the size of the paper actually loaded in the tray, this can cause feeding issues. The printer might attempt to feed paper from a different tray or fail to pick up the paper altogether. Adjusting the printer settings to match the actual paper size loaded in the tray is essential for proper functioning.
The other options are less likely to be the cause of this specific issue:
- The Paper Tray is Flimsy: While a flimsy or damaged paper tray could potentially cause issues with paper alignment or stability, it is less directly related to the problem of paper not being fed into the printer compared to issues with the paper itself or printer settings.
- The Printer has been Installed on the Wrong Port: The port through which the printer is connected to a computer affects its ability to receive print jobs, not the mechanical process of feeding paper.
- The Printer Service is Stopped or Not Working Properly: Issues with the printer service would typically affect the printer’s ability to process print jobs or communicate with the computer, rather than the mechanical feeding of paper.
In summary, ensuring that the paper is not wrinkled and that the printer settings match the loaded paper size are important steps in resolving the issue of paper not being fed into the printer.
-
A reporter is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer is printing unknown characters. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The wrong or an outdated printer driver is installed.
- The printer has a loose connection.
- The printer lid has not been closed securely.
- The room temperature is above normal.
- The printer does not have enough RAM.
-
Explanation & Hint: Understood, the two possible causes for the issue of a printer printing unknown characters, based on the provided options, are:
- The Wrong or an Outdated Printer Driver is Installed: This is a common cause of printing issues. Printer drivers are crucial for the proper communication between the computer and the printer. If the driver is incorrect or outdated, it may not translate the print commands correctly, leading to the printer outputting unknown or garbled characters. Updating or reinstalling the correct printer driver often resolves this problem.
- The Printer has a Loose Connection: A loose connection between the printer and the computer can result in incomplete or erratic data transmission. This can lead to the printer receiving incomplete or corrupt data, resulting in the printing of unknown characters. Checking and securing all cables and connections between the printer and the computer (or network, if applicable) is important for ensuring reliable communication and proper printing.
The other provided options are less likely to cause this specific issue:
- The Printer Lid has Not Been Closed Securely: While important for the operation of some printers, an unsecured lid typically leads to mechanical issues (like paper jams) rather than the printing of unknown characters.
- The Room Temperature is Above Normal: While extreme temperatures can affect hardware performance, a slightly elevated room temperature is unlikely to cause a printer to output unknown characters.
- The Printer Does Not Have Enough RAM: Insufficient RAM in a printer might lead to issues with processing large or complex documents, but it’s more likely to slow down printing or cause incomplete prints rather than the printing of unknown characters.
Ensuring that the printer driver is up to date and correct for the printer model, along with checking for secure and proper connections, are the key steps in resolving the issue of unknown characters being printed.
-
A manager is complaining about the following printer issue: The printer is printing incorrect colors. What are two possible causes of this issue? (Choose two.)
- The print heads might need to be cleaned and calibrated.
- An incorrect cartridge could be installed.
- The printer service is stopped or not working properly.
- The printer does not have enough RAM.
- The print queue is overloaded.
-
Explanation & Hint: The issue of a printer printing incorrect colors can be attributed to a couple of possible causes. Based on the options provided, the two most likely causes are:
- The Print Heads Might Need to be Cleaned and Calibrated: Over time, print heads can become clogged with ink or dust, which can affect their ability to accurately dispense ink. This can lead to incorrect colors being printed. Additionally, if the print heads are misaligned (a calibration issue), it can also result in color inaccuracies. Cleaning and calibrating the print heads are common solutions to this problem.
- An Incorrect Cartridge Could be Installed: If an incorrect ink or toner cartridge is installed in the printer, it could lead to wrong color output. This can happen if the cartridge is not compatible with the printer model or if it is a color cartridge placed in the wrong slot. Ensuring that the correct cartridges are installed and properly seated can resolve this issue.
The other options are less likely to be the cause of incorrect color printing:
- The Printer Service is Stopped or Not Working Properly: While a stopped or malfunctioning printer service could lead to printing issues, it is more likely to result in no print output or error messages rather than incorrect colors.
- The Printer Does Not Have Enough RAM: Insufficient printer RAM can affect the processing of large or complex print jobs but is less likely to be the direct cause of incorrect color output. It might slow down the printing or cause incomplete prints.
- The Print Queue is Overloaded: An overloaded print queue can lead to delays in printing or mixed-up print jobs but does not typically cause a change in the color output of the prints.
In summary, checking and maintaining the print heads and ensuring the correct ink or toner cartridges are installed are crucial steps in resolving the issue of a printer producing prints with incorrect colors.
-
A laptop has an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive (D:). When the user tries to save a spreadsheet to the D: drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not there. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel.
- Use the Msconfig utility.
- Boot into UEFI/BIOS and see if the drive appears.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the D: drive (the mechanical hard drive) is recognized by the operating system, the technician should follow these steps:
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: This is the first and most straightforward step. The Disk Management tool in Windows provides a clear view of all the storage devices connected to the system and their status. Here’s how to access it:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
Windows Key + Xand select “Disk Management.” - In the Disk Management window, look for the mechanical hard drive. It should be listed with its capacity and partitions. If the drive is shown but does not have a drive letter, it can be assigned one right from this tool.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
- Boot into UEFI/BIOS and See if the Drive Appears: If the drive does not appear in Disk Management, the next step is to check if it is recognized at a hardware level. This involves restarting the computer and entering the UEFI/BIOS setup:
- Restart the computer and enter the UEFI/BIOS setup (this usually involves pressing a key like F2, Del, or Esc during boot-up, but the exact key can vary depending on the manufacturer).
- Once in the UEFI/BIOS, navigate to the section where it lists the storage devices. If the mechanical hard drive is not listed here, it indicates a potential hardware issue or connection problem.
The other options, while possible, are less immediate or practical as initial steps:
- Use the Msconfig Utility: The System Configuration utility (msconfig) is more related to startup processes and services and is not typically used for managing or viewing storage devices.
- Remove the Drive and Attach it to the SATA Port Used by the SSD: This is a more advanced step and should be performed only if the above methods fail to recognize the drive. It involves physically swapping the drives’ connections, which can be helpful in diagnosing a faulty port or cable. However, this should be done cautiously and is typically a last resort after software-level checks have been exhausted.
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: This is the first and most straightforward step. The Disk Management tool in Windows provides a clear view of all the storage devices connected to the system and their status. Here’s how to access it:
-
A computer has two mechanical hard drives. The second drive (D:) is used for data storage. When trying to save an email attachment to the local hard drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the second mechanical hard drive (D:) is recognized by the operating system, the technician should take the following steps:
- Use File Explorer: The simplest and first step is to check if the drive is visible in File Explorer. Here’s how to do it:
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Windows Key + Eor clicking on the File Explorer icon on the taskbar. - Look under “This PC” or “Computer” (depending on the Windows version) to see if the D: drive is listed. If it is listed, it indicates the operating system recognizes the drive. If it’s not listed, there could be an issue with the drive or its connection.
- Open File Explorer by pressing
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: If the drive is not visible in File Explorer, the next step is to check Disk Management. This tool provides a detailed view of all storage devices connected to the system:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
Windows Key + Xand select “Disk Management.” - In Disk Management, look for the second mechanical hard drive. It should appear with its capacity and partitions. If it’s there but doesn’t have a drive letter, you can assign one. If it’s not showing up at all, this could indicate a hardware connection issue or a drive failure.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
The other options provided are not relevant for checking the status of a hard drive:
- Swap the Data Cables of the Mechanical Drive and the SSD: This step is more intrusive and should be considered only if there’s a suspicion of a faulty cable or port. It involves physically changing the connections, which should be done cautiously and generally only after software checks (like the ones above) have been completed.
- Open a Web Browser and Type
http://127.0.0.1: This address is a loopback address for the local host, typically used in network testing and does not provide information about hard drives. - Bring Up a Command Prompt and Type
ipconfig: Theipconfigcommand is used for displaying network configuration information and is not relevant for checking local hard drive status.
In summary, the technician should first use File Explorer and then the Disk Management tool to check if the D: drive is recognized by the operating system.
- Use File Explorer: The simplest and first step is to check if the drive is visible in File Explorer. Here’s how to do it:
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Check the Startup folder.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the missing drive is recognized by the operating system, the technician should take the following steps:
- Use Device Manager: The technician can use Device Manager to check if the drive is recognized by the operating system at a hardware level. Here’s how to do it:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager,” or press
Windows Key + Xand choose “Device Manager.” - In Device Manager, expand the “Disk drives” section to see if the missing drive is listed. If the drive is listed, it indicates that the drive is recognized at a hardware level. If it’s not listed, this could indicate a hardware connection issue or a drive failure.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager,” or press
- Use the Disk Management Tool: If the drive is not visible in Device Manager or for more detailed information, the technician should check the Disk Management tool. This tool provides a comprehensive view of all connected storage devices and their status:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
Windows Key + Xand select “Disk Management.” - In Disk Management, look for the missing drive. It should appear with its capacity and partitions. If it’s visible here but not in the application’s save options, there might be an issue with drive letter assignment or the application itself. If the drive is not visible in Disk Management, this points towards a hardware issue.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
The other options are not directly relevant for checking the status of a hard drive:
- Check the Startup Folder: The Startup folder contains programs that run on startup and is not relevant for checking the status of a hard drive.
- Bring Up a Command Prompt and Type
ipconfig: Theipconfigcommand is used to display network configuration information and is not useful for diagnosing hard drive issues. - Swap the Data Cables of the Mechanical Drive and the SSD: This is a more advanced step and should only be considered if there’s a suspicion of a faulty cable or port. It involves physically altering the hardware connections and should be done cautiously, typically after software-level checks have been exhausted.
In summary, the technician should first use Device Manager and then the Disk Management tool to check if the missing drive is recognized by the operating system.
- Use Device Manager: The technician can use Device Manager to check if the drive is recognized by the operating system at a hardware level. Here’s how to do it:
-
A computer has two mechanical hard drives. The second drive (D:) is used for data storage. When trying to save an email attachment to the local hard drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Determine if the hard drive service is set to start automatically.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To check if the second mechanical hard drive (D:) is recognized by the operating system, the technician should follow these steps:
- Use File Explorer: The first and simplest step is to check if the drive is visible in File Explorer. Here’s how to do it:
- Open File Explorer by pressing
Windows Key + Eor clicking on the File Explorer icon on the taskbar. - Look under “This PC” or “Computer” (depending on the Windows version) to see if the D: drive is listed. If it is listed, it indicates the operating system recognizes the drive. If it’s not listed, there could be an issue with the drive or its connection.
- Open File Explorer by pressing
- Use the Disk Management Tool: If the drive is not visible in File Explorer, the next step is to check Disk Management. This tool provides a detailed view of all storage devices connected to the system:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
Windows Key + Xand select “Disk Management.” - In Disk Management, look for the second mechanical hard drive. It should appear with its capacity and partitions. If it’s there but doesn’t have a drive letter, you can assign one. If it’s not showing up at all, this could indicate a hardware connection issue or a drive failure.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
The other options provided are not as directly relevant to the issue:
- Determine if the Hard Drive Service is Set to Start Automatically: There isn’t a specific “hard drive service” in Windows that needs to start for drives to be recognized. The operating system inherently manages hard drives without the need for a user-specified service.
- Bring Up a Command Prompt and Type
ipconfig: Theipconfigcommand is used for displaying network configuration information and is not relevant for checking local hard drive status. - Swap the Data Cables of the Mechanical Drive and the SSD: While this could be a step to diagnose a faulty cable or port, it’s more invasive and should only be considered after the above software checks have been completed. It involves physically altering the hardware, which should be done cautiously.
In summary, the technician should first use File Explorer and then the Disk Management tool to check if the D: drive is recognized by the operating system.
- Use File Explorer: The first and simplest step is to check if the drive is visible in File Explorer. Here’s how to do it:
-
A computer has an SSD for the operating system and applications and uses another mechanical hard drive for data storage. The user reports that data can no longer be saved to the mechanical hard drive. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a user is unable to save data to a mechanical hard drive in a system that also has an SSD for the operating system and applications, the first step a technician should take is to use File Explorer. Here’s how and why this approach is appropriate:
- Open File Explorer: File Explorer in Windows is the primary interface through which users interact with files and drives. By opening File Explorer, the technician can quickly check if the mechanical hard drive (likely designated as the D: drive) is visible.
- Check for the Drive’s Presence: If the mechanical hard drive is listed in File Explorer, it means the operating system recognizes the drive, but there may be other issues preventing data from being saved, such as permission problems or file system errors.
- Identify Possible Issues:
- If the drive is visible but access is denied, it could be a permissions issue.
- If the drive appears but shows errors, it might be a file system problem or the drive could be failing.
- If the drive does not appear at all, it could indicate that the drive is not properly connected, has failed, or there is an issue with its configuration in the system (like a missing drive letter).
- Further Actions Based on Findings:
- Drive Visible but Access Denied: The technician might need to adjust permissions or ownership settings.
- Drive Visible with Errors: Running disk checking tools like
chkdskmight be necessary. - Drive Not Visible: This would necessitate a deeper investigation, possibly involving Disk Management or checking BIOS/UEFI settings, and potentially looking into physical connections or hardware issues.
Using File Explorer is a simple, non-invasive first step that provides immediate insights into whether the operating system recognizes the mechanical hard drive and can guide further troubleshooting steps based on the observation.
-
A user reports that a drive is no longer there. The technician asks the user to demonstrate the problem. Within the application, the user demonstrates that the drive, that was present in the save options yesterday, is now no longer an option. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Use the Msconfig utility.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To check if the missing drive is recognized by the operating system, the technician should follow these steps:
- Use Device Manager: The Device Manager can be used to see if the drive is being recognized by the system at a hardware level. Here’s how to do it:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager,” or press
Windows Key + Xand choose “Device Manager.” - In Device Manager, expand the “Disk drives” section. If the missing drive is listed here, it indicates that the drive is recognized at a hardware level. If it’s not listed, this could indicate a hardware connection issue or a drive failure.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Device Manager,” or press
- Use the Disk Management Tool: If the drive is visible in Device Manager or for more detailed information, the technician should use Disk Management. This tool provides a comprehensive view of all connected storage devices and their status:
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
Windows Key + Xand select “Disk Management.” - In Disk Management, look for the missing drive. If it’s visible here but not in the application’s save options, it might be an issue with drive letter assignment or the application itself. If the drive is not visible in Disk Management, this could indicate a hardware issue.
- Right-click on the Start button and select “Disk Management,” or press
The other options provided are not as directly relevant for this issue:
- Use the Msconfig Utility: The System Configuration utility (msconfig) is used for startup processes and services, not for managing or viewing storage devices.
- Bring Up a Command Prompt and Type
ipconfig: Theipconfigcommand displays network configuration information and is not relevant for checking the status of a hard drive. - Swap the Data Cables of the Mechanical Drive and the SSD: While this could be a step to diagnose a faulty cable or port, it’s more invasive and should be considered only after confirming the drive isn’t recognized through software checks. This step involves physically altering the hardware connections and should be done cautiously.
In summary, the technician should use Device Manager and the Disk Management tool to check if the missing drive is recognized by the operating system.
- Use Device Manager: The Device Manager can be used to see if the drive is being recognized by the system at a hardware level. Here’s how to do it:
-
A laptop has an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive (D:). When the user tries to save a spreadsheet to the D: drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not there. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To determine if the D: drive (mechanical hard drive) is recognized by the operating system when it’s not appearing while trying to save a spreadsheet, the technician should follow these steps:
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: This is the first and most direct approach. Disk Management is a Windows utility that lets you view and manage disk drives attached to your computer. It will show all the drives recognized by the operating system, including any that are not currently assigned a drive letter. To access Disk Management, the technician can right-click on the Start menu, select “Disk Management,” or type “diskmgmt.msc” in the Run dialog box (accessed by pressing Windows key + R).
- Other Options Mentioned:
- Open a web browser and type http://127.0.0.1: This action will not help in this context. The address 127.0.0.1 refers to the localhost of your own computer and is used primarily for network testing or web development purposes. It won’t provide information about hard drives.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: This command is used to display the IP configuration of a computer, specifically network-related information. It will not provide any information about the status or presence of hard drives.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: This is a hardware troubleshooting step that could be considered if the drive is not visible in Disk Management. However, it’s a bit more advanced and should be done with caution. Swapping cables might help determine if the issue is with the cable or the port on the motherboard.
The initial and most straightforward step is to check the Disk Management utility. If the drive does not appear there, further hardware troubleshooting (like cable swapping) or checking BIOS/UEFI settings might be required.
-
A computer has an SSD for the operating system and applications and uses another mechanical hard drive for data storage. The user reports that data can no longer be saved to the mechanical hard drive. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use Device Manager.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
- Open a web browser and type the following: http://127.0.0.1. Verify if both drives appear in the list.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
-
Explanation & Hint: To troubleshoot the issue where data can no longer be saved to the mechanical hard drive on a computer that also has an SSD for the operating system and applications, the technician should follow these steps:
- Use Device Manager: This is a good initial step. Device Manager in Windows shows all the hardware components that are installed on the computer, including hard drives. If the mechanical hard drive is not showing up in Device Manager, it could indicate a hardware issue with the drive itself or its connection. To open Device Manager, right-click on the Start menu and select “Device Manager,” or type “devmgmt.msc” in the Run dialog box (accessed by pressing Windows key + R).
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD: This is a more advanced troubleshooting step. If the drive is not recognized in Device Manager, swapping the SATA ports can help determine if the issue is with the hard drive, the SATA port, or the cable. However, this should be done with caution, especially ensuring that the computer is powered off and unplugged before making any hardware changes.
- Other Options Mentioned:
- Open a web browser and type http://127.0.0.1: This action will not assist in this scenario. The address 127.0.0.1 is a loopback address for the local machine and is unrelated to hard drive management or detection.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: This command is used for displaying network configuration information and will not provide any details about the status or presence of hard drives.
If the mechanical hard drive is not visible in both Device Manager and Disk Management, it suggests a more serious hardware issue, such as a drive failure, a disconnected or faulty cable, or a problem with the motherboard’s SATA port. Further hardware diagnostics or professional assistance might be required in such cases.
-
A laptop has an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive (D:). When the user tries to save a spreadsheet to the D: drive, the user notices that the D: drive is not there. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel.
- Determine if the hard drive service is set to start automatically.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
-
Explanation & Hint: To troubleshoot the issue where a laptop with an NVMe drive (C:) and a mechanical hard drive (D:) is not showing the D: drive when trying to save a spreadsheet, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Use the Disk Management Control Panel: This is the most appropriate first step. Disk Management will show all the storage devices recognized by the operating system, including any that are not currently assigned a drive letter or are offline. To access Disk Management, right-click on the Start menu and select “Disk Management,” or type “diskmgmt.msc” in the Run dialog box (accessed by pressing Windows key + R). If the drive is visible here but not in File Explorer, it may need a drive letter assigned or be reactivated.
- Determine if the hard drive service is set to start automatically: This step typically isn’t necessary for standard internal drives like an NVMe drive or a mechanical hard drive. Services related to automatic starting are generally more relevant to network drives or external storage solutions. However, checking system services for any abnormalities can be a secondary step if the primary methods do not resolve the issue.
- Other Options Mentioned:
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig: This command is irrelevant in this context. Ipconfig is used for network configuration information and does not provide any insights into storage device management or recognition.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD: This step is not applicable for a laptop, as laptops typically do not have user-serviceable data cables for their internal drives like desktops do. NVMe drives and mechanical hard drives in laptops use different connectors and are not interchangeable. Additionally, accessing internal components of a laptop may void the warranty and should be done cautiously and preferably by qualified personnel.
The most effective approach is to start with the Disk Management tool to verify if the operating system recognizes the mechanical hard drive. If the drive does not appear there, it could indicate a hardware issue, and the laptop may need to be serviced by a professional.
-
A computer has an SSD for the operating system and applications and uses another mechanical hard drive for data storage. The user reports that data can no longer be saved to the mechanical hard drive. What should the technician do to see if the drive is recognized by the operating system?
- Use File Explorer.
- Swap the data cables of the mechanical drive and the SSD.
- Bring up a command prompt and type ipconfig.
- Remove the drive and attach it to the SATA port used by the SSD. Reboot the computer and see if the drive is recognized.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a user is unable to save data to a mechanical hard drive in a system that also has an SSD for the operating system and applications, the first step a technician should take is to use File Explorer. Here’s how and why this approach is appropriate:
- Open File Explorer: File Explorer in Windows is the primary interface through which users interact with files and drives. By opening File Explorer, the technician can quickly check if the mechanical hard drive (likely designated as the D: drive) is visible.
- Check for the Drive’s Presence: If the mechanical hard drive is listed in File Explorer, it means the operating system recognizes the drive, but there may be other issues preventing data from being saved, such as permission problems or file system errors.
- Identify Possible Issues:
- If the drive is visible but access is denied, it could be a permissions issue.
- If the drive appears but shows errors, it might be a file system problem or the drive could be failing.
- If the drive does not appear at all, it could indicate that the drive is not properly connected, has failed, or there is an issue with its configuration in the system (like a missing drive letter).
- Further Actions Based on Findings:
- Drive Visible but Access Denied: The technician might need to adjust permissions or ownership settings.
- Drive Visible with Errors: Running disk checking tools like
chkdskmight be necessary. - Drive Not Visible: This would necessitate a deeper investigation, possibly involving Disk Management or checking BIOS/UEFI settings, and potentially looking into physical connections or hardware issues.
Using File Explorer is a simple, non-invasive first step that provides immediate insights into whether the operating system recognizes the mechanical hard drive and can guide further troubleshooting steps based on the observation.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and the GPS is not functioning. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- A service is disabled.
- The GPU is overheating.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration.
- The screen refresh rate is too low.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and the GPS is not functioning, the most probable cause from the given options is:
A service is disabled: Many laptops that include GPS functionality rely on specific services running in the operating system to enable and manage the GPS hardware. If the relevant service is disabled, the GPS will not function properly. The technician should check the operating system’s services to ensure that any service related to GPS or location tracking is enabled.
The other options are less likely to be related to GPS functionality:
- The GPU is overheating: While an overheating GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) can cause several issues, primarily related to graphics and display, it is unlikely to directly affect the GPS functionality of a laptop.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration: Screen resolution and calibration issues would affect the display quality and accuracy but would not impact the functionality of the GPS.
- The screen refresh rate is too low: The screen refresh rate impacts how smoothly content is displayed on the screen and is not related to the functionality of GPS hardware.
Therefore, the first step the technician should take is to verify that all necessary services for GPS functionality are running correctly in the laptop’s operating system.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and the GPS is not functioning. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- Airplane mode is turned on.
- The GPU is overheating.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration.
- The screen refresh rate is too low.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and finds that the GPS is not functioning, the most probable cause from the given options is that Airplane mode is turned on. When Airplane mode is enabled, it disables all wireless communication functions of the device, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and often GPS, to comply with airline regulations. If Airplane mode is accidentally left on, it would prevent the GPS from functioning properly.
The other options are less likely to affect the GPS functionality:
- The GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) overheating: An overheating GPU can cause issues primarily related to graphics processing, display output, and system stability. It is not directly related to the functioning of GPS.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration: Screen resolution and calibration are related to the visual display and touch input accuracy (if it’s a touchscreen) but do not impact GPS functionality.
- The screen refresh rate is too low: The refresh rate of the screen affects how smoothly content is displayed and is unrelated to GPS functionality.
Therefore, the technician should first check if Airplane mode is active and turn it off if necessary to see if that resolves the GPS issue.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and the GPS is not functioning. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- Airplane mode is turned on.
- Wi-Fi is turned off.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration.
- The screen refresh rate is too low.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and the GPS is not functioning, the most probable cause from the given options is that Airplane mode is turned on. When Airplane mode is enabled, it generally disables all wireless communications, which can include not only Wi-Fi and Bluetooth but also GPS in some laptops, particularly if the GPS functionality is integrated with other wireless communication hardware.
The other options are less likely to affect GPS functionality:
- Wi-Fi is turned off: While turning off Wi-Fi disables wireless internet connectivity, it typically does not affect the GPS functionality directly. However, it’s worth noting that some devices use Wi-Fi networks to assist in location determination (known as Wi-Fi triangulation), but this is different from true GPS functionality.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration: The screen resolution and calibration are related to visual display and touch input accuracy (if it’s a touchscreen) but do not impact the functionality of the GPS system.
- The screen refresh rate is too low: The refresh rate of the screen affects the smoothness of visual content display and is not related to the functioning of the GPS system.
So, the first step the technician should take is to check if Airplane mode is activated and turn it off if it is. This could potentially restore GPS functionality if the laptop’s GPS is indeed affected by this mode.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and the GPS is not functioning. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- Airplane mode is turned on.
- More than one app is open simultaneously.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration.
- The screen refresh rate is too low.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and finds that the GPS is not functioning, the most probable cause from the provided options is that Airplane mode is turned on. When Airplane mode is enabled on a laptop, it typically disables all wireless communication functions, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and in some cases, GPS. This is done to prevent interference with sensitive equipment, particularly in airplanes, hence the name. If Airplane mode is accidentally activated, it could prevent the GPS from functioning properly.
The other options are less likely to be related to GPS functionality issues:
- More than one app is open simultaneously: Generally, having multiple apps open at the same time should not directly affect the functionality of GPS on a laptop. Modern laptops are designed to multitask, and the GPS functionality should work independently of how many apps are running.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration: Issues with screen resolution and calibration affect the visual display and, if it’s a touchscreen, the touch input accuracy. However, these issues do not impact the GPS functionality of the laptop.
- The screen refresh rate is too low: The refresh rate of the screen influences how smoothly content is displayed on the screen. It does not have any impact on the functionality of the GPS system.
Given these options, the technician should first check if Airplane mode is activated and, if it is, turn it off to see if this resolves the GPS issue.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an app is not loading. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- An app needs to be restarted.
- More than one app is open simultaneously.
- The screen resolution needs recalibration.
- The screen refresh rate is too low.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and encounters an issue where an app is not loading, the probable causes from the given options are:
- An app needs to be restarted: This is a common and likely cause for an app not loading properly. Sometimes, apps can encounter issues due to temporary glitches, memory leaks, or other problems that can be resolved by simply restarting the app. This should be the first step in troubleshooting.
- More than one app is open simultaneously: While modern laptops are generally capable of handling multiple apps running at the same time, if the system resources (like RAM or CPU) are overextended, it could potentially cause issues with apps loading. This is more likely if the laptop has limited resources and several resource-intensive apps are running concurrently.
The other options are less likely to be the cause of an app not loading:
- The screen resolution needs recalibration: Issues with screen resolution and calibration mainly affect the visual display and, if it’s a touchscreen, the touch input accuracy. These issues generally do not prevent apps from loading.
- The screen refresh rate is too low: The refresh rate of the screen affects how smoothly content is displayed. It does not typically impact the ability of an app to load or function properly.
In summary, the technician should first try restarting the problematic app. If the issue persists, checking the system’s resource usage to see if too many apps are running simultaneously and consuming excessive resources could be another step. If neither of these approaches solves the problem, further investigation into other potential causes would be necessary.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an app is not loading. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- An app needs to be restarted.
- The Num Lock key is depressed.
- The GPU is overheating.
- Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and encounters an issue where an app is not loading, the probable causes from the given options are:
- An app needs to be restarted: This is a common and likely cause for an app not loading properly. Applications can occasionally encounter bugs or glitches that prevent them from loading correctly. Restarting the app can often resolve these issues by resetting its state and clearing temporary data.
The other options are less likely to be directly related to an app not loading:
- The Num Lock key is depressed: The Num Lock key’s status typically affects only the functionality of the numeric keypad on a keyboard. It does not usually have any impact on the loading or functioning of applications.
- The GPU is overheating: While an overheating GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) can cause system-wide issues, especially with graphically intensive tasks, it is less likely to be the sole reason for a specific app not loading, unless the app is highly graphics-intensive. However, if the laptop is experiencing overall performance issues due to overheating, it could indirectly affect the operation of applications.
- Wi-Fi is turned off: If the app in question requires an internet connection to function or load content, then having Wi-Fi turned off could prevent the app from loading properly. This is especially true for cloud-based apps or apps that rely on online data.
Given these options, the most straightforward initial step is to restart the app. If the issue persists and the app requires internet access, the technician should ensure that Wi-Fi is enabled. If there’s suspicion of hardware-related issues, such as overheating, further investigation into the laptop’s thermal management might be necessary.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an app is not responding. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- An app needs to be restarted.
- The battery is low.
- The GPU is overheating.
- Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and an app is not responding, the probable causes from the given options are:
- An app needs to be restarted: This is often the most common cause of an app not responding. Applications can encounter issues due to various reasons like software bugs, memory leaks, or conflicts with other processes. Restarting the app can reset its state and potentially resolve any temporary glitches it’s experiencing.
- The GPU is overheating: If the app is graphically intensive (like a video game or a high-resolution video editing software), an overheating GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) could cause performance issues or crashes. When a GPU overheats, it may throttle its performance to reduce heat, leading to application instability or non-responsiveness.
The other options are less likely to be directly related to an app not responding:
- The battery is low: While a low battery can affect overall laptop performance, especially if the laptop enters a power-saving mode, it’s less likely to specifically cause an app to become unresponsive. However, in some cases, power-saving settings can reduce processing power, potentially impacting app performance.
- Wi-Fi is turned off: If the app relies on an internet connection to function (like cloud-based apps or apps that stream data from online sources), then Wi-Fi being turned off could impact its functionality. However, this typically wouldn’t cause an app to become unresponsive; instead, it might prevent the app from accessing online content or updating.
In this scenario, the technician should first attempt to restart the app. If the issue persists and the app is resource-intensive, checking the laptop’s temperature and ensuring it’s not overheating would be a good step. If the app requires internet access, ensuring that Wi-Fi is turned on is also important.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an app is not responding. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- An app needs to be restarted.
- The display setting is incorrect.
- The GPU is overheating.
- Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician is working on a laptop and encounters an app that is not responding, the probable causes from the given options are:
- An app needs to be restarted: This is a common and likely cause for an app not responding. Applications can encounter various issues, such as bugs, memory leaks, or conflicts with other system processes, leading them to become unresponsive. Restarting the app often resolves these temporary problems by resetting its state and clearing any problematic data or processes.
- The GPU is overheating: If the app is graphically intensive (like a video game or advanced graphic design software), an overheating GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) could cause performance issues or lead to the app becoming unresponsive. Overheating can result in thermal throttling where the GPU slows down its performance to reduce temperature, potentially affecting the stability and responsiveness of graphics-intensive applications.
The other options are less likely to be directly related to an app not responding:
- The display setting is incorrect: While incorrect display settings can affect the visibility or layout of an app, they usually don’t cause an app to become unresponsive. However, if the settings are significantly misconfigured, it might affect the app’s ability to render correctly, though this is less common.
- Wi-Fi is turned off: If the app relies on an internet connection to function (for example, cloud-based services, streaming, or online data retrieval), then having Wi-Fi turned off could impact its functionality. However, this generally wouldn’t cause an app to become unresponsive; instead, it might prevent the app from accessing online content or performing tasks that require internet access.
In this situation, the technician should first attempt to restart the app. If the problem persists, particularly with a graphically intensive app, it would be prudent to check for overheating issues. If the app requires internet access, ensuring that Wi-Fi is enabled is also a good step to consider.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an error message about decryption appears when opening an email. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- A digital certificate is missing.
- The display setting is incorrect.
- The GPU is overheating.
- Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician encounters an error message about decryption when opening an email on a laptop, the most probable cause from the given options is:
A digital certificate is missing: Email encryption and decryption often rely on digital certificates for security. If the necessary digital certificate is not present, expired, or incorrectly configured on the laptop, it can lead to decryption errors when attempting to open encrypted emails. This is because the digital certificate contains the necessary keys for decrypting the encrypted content of the email.
The other options are less likely to be related to an email decryption issue:
- The display setting is incorrect: Incorrect display settings can affect how content is visually rendered on the screen, but they would not typically result in decryption errors in an email application.
- The GPU is overheating: An overheating GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) can cause performance issues, especially in tasks that are graphics-intensive, but it is unlikely to be the cause of a decryption error in an email.
- Wi-Fi is turned off: While having Wi-Fi turned off would prevent the laptop from receiving new emails, it would not cause decryption errors in attempting to open an email that has already been downloaded to the laptop.
In this case, the technician should investigate the status and configuration of digital certificates on the laptop, ensuring they are correctly installed and up-to-date, which is essential for the proper decryption of encrypted emails.
-
A technician is working on a laptop and an error message about decryption appears when opening an email. What is a probable cause for this situation?
- A digital certificate is missing.
- The screen refresh rate is too low.
- The GPU is overheating.
- Wi-Fi is turned off.
-
Explanation & Hint: If a technician encounters an error message about decryption when trying to open an email on a laptop, the most probable cause from the given options is:
A digital certificate is missing: Digital certificates are essential for the encryption and decryption of emails. They include the necessary keys for securely encrypting and decrypting email messages. If a required digital certificate is missing, expired, or not properly installed, the laptop will not be able to decrypt the email, leading to an error message. This is a common issue in environments where email encryption is used for security.
The other options are less likely to cause a decryption error in an email:
- The screen refresh rate is too low: The refresh rate of the screen affects how smoothly content is displayed and has no bearing on the decryption capabilities of the email client or the laptop. Low refresh rates can lead to screen flickering or motion blur but won’t cause decryption errors.
- The GPU is overheating: While an overheating GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) can cause various system performance issues and graphical problems, it is not related to the decryption process of emails. Decryption errors are typically related to software issues, not hardware like the GPU.
- Wi-Fi is turned off: If Wi-Fi is off, it would prevent new emails from being received, but it wouldn’t cause an error in decrypting an email that has already been downloaded to the laptop. Decryption is a process that happens independently of the network status once the email is received.
In this scenario, the technician should focus on checking the digital certificate status associated with the email account. This involves ensuring that the certificate is present, valid, and properly configured to facilitate the decryption of the email content.
-
A technician has just completed a preventive maintenance on the department printer. Users are now complaining that the printer is no longer available. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Check that the printer is plugged into a power source.
- Replace the pickup roller.
- Update the BIOS.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Update the OS.
-
Explanation & Hint: When addressing the issue of a department printer not being available to users after preventive maintenance, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Check that the printer is plugged into a power source: This is a basic but crucial step. The technician should ensure that the printer is properly plugged in and turned on. Sometimes, cables can be inadvertently unplugged or loose during maintenance activities.
- Connect the printer using wireless (if applicable): If the printer is designed to operate over a wireless network and was previously set up this way, the technician should verify that the wireless connection is active and properly configured. Preventive maintenance might have included resetting the printer, which could have disrupted its network settings.
Other options are less likely to be the immediate solution for the issue:
- Replace the pickup roller: The pickup roller is a component that helps feed paper into the printer. While it’s important for the physical operation of the printer, replacing it would not typically address an issue related to the printer’s availability to users on the network.
- Update the BIOS: BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) updates are related to the computer’s firmware and are not directly related to printer functionality or network availability.
- Update the OS (Operating System): While keeping the operating system updated is generally good practice, it’s unlikely to be the immediate solution unless the issue is specifically related to compatibility or driver issues after an OS update. This is a more complex solution and typically not the first step unless there’s a known issue related to the OS.
The most likely causes of the printer not being available post-maintenance are related to power or network connectivity issues. The technician should first ensure the printer is powered on and then check the network connections, whether wired or wireless, to ensure the printer is correctly connected to the network and visible to users.
-
A user complains that recently every printed document has vertical lines and streaks on the paper. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Distribute the toner more evenly within the cartridge.
- Update the BIOS.
- Update the OS.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Power cycle the printer.
-
Explanation & Hint: When addressing an issue where a user reports that every printed document has vertical lines and streaks on the paper, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Distribute the toner more evenly within the cartridge: This is a common solution for laser printers experiencing issues with print quality, such as streaks or lines. Over time, toner can settle or clump, especially if the printer or toner cartridge has been sitting idle. Removing the toner cartridge and gently shaking it can help redistribute the toner evenly, potentially resolving the issue.
- Power cycle the printer: Sometimes, simply turning the printer off and then on again can resolve temporary glitches or errors. This process can clear out any stuck print jobs or minor software issues that might be affecting print quality.
The other options are less likely to resolve the issue of vertical lines and streaks on printed documents:
- Update the BIOS: Updating the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is relevant for computers and their firmware, not printers. BIOS updates do not address printer quality issues.
- Update the OS (Operating System): While keeping the operating system of your computer updated is important, it is unlikely to directly resolve print quality issues unless there is a specific driver issue. However, driver issues usually affect printer functionality rather than the quality of the prints.
- Connect the printer using wireless: The method of connecting the printer (wireless or wired) would not typically affect the quality of the prints. Connectivity issues might prevent printing altogether but wouldn’t cause streaks or lines on printed documents.
In summary, the technician should first try redistributing the toner in the cartridge and power cycling the printer. If these steps do not resolve the issue, further investigation into the printer’s maintenance and servicing might be required, such as cleaning or replacing parts like the drum unit or the toner cartridge.
-
Students who use the same printer are complaining that recently printed documents contain unknown characters. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Re-install the printer driver.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Reset the page counter.
- Install a USB hub.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
-
Explanation & Hint: When students are complaining that recently printed documents contain unknown characters, the technician should consider the following steps to resolve the issue:
- Re-install the printer driver: This is the most likely solution. Corrupted or outdated printer drivers can cause various printing issues, including the appearance of unknown or garbled characters in printed documents. Re-installing or updating the printer driver on the computers that are experiencing this issue can often resolve these kinds of problems.
The other options are less likely to be effective in this scenario:
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This option does not apply to common printer issues. Crystal vibrations are more relevant in the context of precision electronics and timekeeping devices, not standard printing issues.
- Reset the page counter: The page counter on a printer keeps track of how many pages have been printed, often for maintenance or supply management purposes. Resetting it would not typically affect the quality or content of the printed documents.
- Install a USB hub: A USB hub expands the number of USB ports available and is useful if you need to connect multiple devices. However, it wouldn’t address an issue with unknown characters appearing in printed documents.
- Connect the printer using wireless: The connection method (wireless or wired) is generally not related to the content of the printed documents. Changing the connection method won’t typically resolve an issue with unknown characters appearing in printouts.
Therefore, the technician should focus on updating or re-installing the printer driver, as this is the most likely cause of the issue with unknown characters appearing in printed documents.
-
Students who use the same printer are complaining that recently printed documents contain unknown characters. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Re-install the printer driver.
- Install a USB hub.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Update the BIOS.
-
Explanation & Hint: When dealing with the issue of printed documents containing unknown characters from a printer used by multiple students, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Re-install the printer driver: This is the most appropriate first action. Printer drivers are software components that allow the computer’s operating system to communicate with the printer. If the driver is corrupted, outdated, or incompatible, it could lead to issues like misinterpreted data, resulting in unknown characters appearing in printed documents. Re-installing or updating the printer driver can often resolve these kinds of printing problems.
The other options are less likely to resolve this specific issue:
- Install a USB hub: A USB hub is used to expand the number of USB ports available. This would be useful if there are not enough ports to connect all necessary devices, but it wouldn’t typically resolve a problem related to the quality of printing or the appearance of unknown characters in printouts.
- Connect the printer using wireless: The method of connecting the printer (whether wireless or wired) generally doesn’t impact the nature of the content being printed. While changing the connection method might be useful for addressing connectivity issues, it’s unlikely to fix problems related to the appearance of unknown characters in printouts.
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This suggestion doesn’t apply to standard printer troubleshooting. Crystal vibrations are a consideration in highly specialized electronics and do not relate to the functionality of typical printers.
- Update the BIOS: Updating the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is relevant to computer firmware and is unrelated to issues with a printer. BIOS updates affect the computer’s hardware interactions and do not typically resolve printing problems, especially those related to document content.
In summary, re-installing or updating the printer driver is the most relevant and likely solution to address the issue of unknown characters appearing in printed documents from a shared printer.
-
An office assistant in a law firm is trying to print many large legal documents but is getting “memory overload” error messages from the printer. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Add more memory to the printer.
- Install a USB hub.
- Connect the printer using wireless.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Update the BIOS.
-
Explanation & Hint: When an office assistant in a law firm is encountering “memory overload” error messages from the printer while trying to print large legal documents, the most effective step for a technician to resolve the issue would be to:
- Add more memory to the printer: Printers, especially those used for professional purposes like in a law firm, often have the capability to expand their memory. Large documents can require significant memory for processing, and if the printer’s memory is insufficient, this can lead to overload errors. Adding more memory to the printer can help it handle larger documents more efficiently.
The other options are less likely to address the specific issue of a memory overload error:
- Install a USB hub: A USB hub is used to increase the number of USB ports available on a computer and does not affect a printer’s memory capacity or its ability to process large documents.
- Connect the printer using wireless: The method of connection (wireless or wired) to the printer does not typically influence the printer’s internal memory capacity. While switching to a wireless connection might offer convenience, it will not resolve memory overload issues.
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This is not a relevant step in printer troubleshooting. Crystal vibrations pertain to highly specialized electronic contexts and are not applicable to resolving printer memory issues.
- Update the BIOS: BIOS updates are related to the computer’s firmware and do not impact the memory or processing capabilities of a printer. A BIOS update would not resolve a memory overload issue in a printer.
Therefore, the recommended action is to explore the option of adding more memory to the printer, which should enable it to handle larger print jobs without encountering memory overload errors.
-
An office assistant in a law firm is trying to print many large legal documents but is getting “memory overload” error messages from the printer. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Add more memory to the printer.
- Rewind the ribbon.
- Clean the printer.
- Reset the page counter.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
-
Explanation & Hint: When an office assistant in a law firm is experiencing “memory overload” error messages while trying to print large legal documents, the technician should take the following steps to resolve the issue:
- Add more memory to the printer: This is the most direct and effective solution to address the memory overload error. Printers have a finite amount of memory, and large documents, particularly those with complex graphics or formatting, can require more memory than the printer has available. Adding additional memory to the printer can help it process these larger documents more effectively.
The other options are less likely to resolve a memory overload issue:
- Rewind the ribbon: This action is relevant for printers that use ribbons (like dot matrix printers or some thermal printers), but it would not address a memory overload issue. Ribbon rewinding is typically related to print quality issues or continuous feed problems.
- Clean the printer: While regular cleaning is good for maintaining printer functionality and print quality, it will not solve a problem related to the printer’s memory capacity.
- Reset the page counter: The page counter in a printer tracks the number of pages printed for maintenance and supply management purposes. Resetting it does not impact the printer’s memory or its ability to process large print jobs.
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This suggestion is not applicable to standard printer troubleshooting. Crystal vibrations are a consideration in specific, highly specialized electronic contexts and do not relate to the functionality of typical office printers.
In summary, to resolve the memory overload error, the technician should focus on expanding the printer’s memory. This solution is directly targeted at increasing the printer’s capacity to handle larger documents, which is the root cause of the memory overload issue.
-
A user is complaining that the printer is printing pages with no image on them. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Replace the toner cartridge.
- Rewind the ribbon.
- Clean the printer.
- Reset the page counter.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
-
Explanation & Hint: When a user reports that the printer is printing pages with no image on them, the technician should consider the following steps to resolve the issue:
- Replace the toner cartridge: This is the most likely solution if the printer is a laser printer. When a toner cartridge is empty or near empty, it can result in blank pages being printed. Replacing the toner cartridge with a new one should resolve the issue.
- Rewind the ribbon: If the printer is a dot matrix printer or a thermal printer that uses a ribbon, then rewinding or replacing the ribbon might be necessary. An expended or incorrectly seated ribbon can result in blank pages.
- Clean the printer: Sometimes, dust or debris inside the printer can interfere with the printing process. Cleaning the printer can help, especially if the issue is related to blocked nozzles in inkjet printers. However, this is more likely to result in poor quality prints or streaks, rather than completely blank pages.
The other options are less likely to resolve the issue of printing blank pages:
- Reset the page counter: The page counter is a feature in printers that tracks the number of pages printed. Resetting it is usually done for maintenance tracking purposes and does not typically impact the printing process itself.
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This suggestion is not relevant to standard printer troubleshooting. Vibrations of crystals are a consideration in specific, highly specialized electronic contexts and are unrelated to typical printer operations.
In summary, the first step should be to check the printer’s supply levels (toner or ribbon, depending on the type of printer) and replace them if necessary. If the problem persists, further troubleshooting, such as cleaning the printer, might be required.
-
Students who use the same printer are complaining that recently printed documents contain unknown characters. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Re-install the printer driver.
- Reset the page counter.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Install a USB hub.
- Clean the printer.
-
Explanation & Hint: When students complain that recently printed documents from a shared printer contain unknown characters, the most effective steps the technician should consider are:
- Re-install the printer driver: This is often the most likely solution for the issue of unknown characters appearing in printed documents. Printer drivers are software components that allow the computer to communicate with the printer. If the driver is outdated, corrupted, or incompatible, it can lead to printing errors, including the appearance of unknown characters. Re-installing or updating the printer driver on the affected computers can resolve these issues.
- Clean the printer: While less likely to be the cause of unknown characters in the printouts, it’s still a good practice to maintain the printer’s cleanliness. In some cases, especially with inkjet printers, clogged nozzles or accumulated debris can affect print quality. However, this typically results in streaks or poor-quality prints rather than unknown characters.
The other options are less likely to address the specific issue:
- Reset the page counter: The page counter in a printer is used for maintenance tracking, such as determining when to perform certain servicing tasks. Resetting this counter does not typically have any impact on the content of printed documents.
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This suggestion is not applicable to standard printer troubleshooting. Crystal vibrations are relevant in highly specialized electronic contexts and do not relate to common printing issues.
- Install a USB hub: A USB hub is used to expand the number of available USB ports on a computer. This would be helpful if there are insufficient ports for necessary peripherals, but it would not resolve issues related to the appearance of unknown characters in printouts.
In summary, the first step to address the problem is to re-install or update the printer driver on the computers that are experiencing the issue. This is the most direct approach to resolving problems related to data interpretation and printing errors such as unknown characters appearing in documents.
-
Students who use the same printer are complaining that recently printed documents contain unknown characters. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Re-install the printer driver.
- Reset the page counter.
- Check the vibration of the crystals.
- Install a USB hub.
- Replace the pickup roller.
-
Explanation & Hint: When students report that a shared printer is producing documents with unknown characters, the technician should consider the following steps:
- Re-install the printer driver: This is often the most likely solution for the issue of unknown characters appearing in printed documents. Printer drivers are crucial software components that facilitate communication between the computer and the printer. If a driver is outdated, corrupted, or incompatible with the current system or printer model, it can result in printing errors, such as the appearance of unknown or garbled characters. Re-installing or updating the printer driver on the computers using this printer can often resolve these types of issues.
The other options are less likely to address the specific issue of unknown characters in printouts:
- Reset the page counter: The page counter on a printer keeps track of the number of pages printed for maintenance purposes. Resetting it is generally for tracking and servicing the printer and does not usually affect the quality or content of the printed documents.
- Check the vibration of the crystals: This suggestion is not relevant to standard printer troubleshooting. Crystal vibrations are a consideration in specific, highly specialized electronic devices and contexts and do not relate to the functionality of standard office printers.
- Install a USB hub: While a USB hub expands the number of available USB ports on a computer, this would not be a solution to a problem involving unknown characters appearing in printouts. USB hubs are useful when there is a need for more USB connections but do not influence the data processing of a printer.
- Replace the pickup roller: The pickup roller is a component in printers that helps feed paper into the machine. Issues with the pickup roller might lead to paper jams or feed issues but would not cause unknown characters to appear in printed documents.
In this situation, the recommended action is to re-install or update the printer driver, as this is most directly related to the issue of data interpretation and print quality, particularly when it comes to the appearance of unknown characters in printed
-
Users have noticed that the colors on their printed documents are different from the colors that they see on their computer screens. What should the technician do to resolve the issue?
- Calibrate the printer.
- Configure the printer for duplex printing.
- Power cycle the printer.
- Update the OS.
- Replace the pickup roller.
-
Explanation & Hint: When users notice that the colors on their printed documents are different from the colors on their computer screens, the technician should consider the following steps to resolve the issue:
- Calibrate the printer: This is the most relevant and likely solution. Printer calibration involves adjusting the printer’s settings to produce output that matches a specific standard or expectation. This can include color calibration, which aligns the colors produced by the printer with what is expected or seen on the screen. Color discrepancies are often due to differences in how monitors display colors and how printers interpret them, so calibrating the printer to more closely match the monitor’s display can significantly improve color accuracy.
The other options are less likely to resolve the issue of color discrepancies:
- Configure the printer for duplex printing: Duplex printing refers to printing on both sides of the paper. This setting does not affect the color accuracy or quality of the prints and is unrelated to the issue at hand.
- Power cycle the printer: While power cycling (turning the printer off and then on again) can resolve many electronic and software glitches, it is unlikely to fix issues related to color accuracy unless the issue is a temporary glitch in the printer’s color processing.
- Update the OS: Updating the operating system of the computer can resolve various issues and is generally good practice, but it’s unlikely to directly affect the color accuracy of prints from a printer, unless the issue is specifically related to printer drivers or color profiles managed by the OS.
- Replace the pickup roller: The pickup roller is responsible for feeding paper into the printer. Issues with the pickup roller can lead to paper jams or feed problems but would not cause color discrepancies between the screen and printed documents.
Therefore, the recommended first step is to calibrate the printer to improve the color match between the printed documents and the screen display. This process might involve using specific calibration tools or software provided by the printer manufacturer.
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Final - Mid-term - Cert | |
| Chapter 1 -9 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Chapter 10 - 14 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1001 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1002 | Online Test |