ITE 8.01 – ITE v7.02 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 7.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Answers 2024
ITE v8.01 – ITE v7.02 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 7.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Answers 2024 Full 100%
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Final - Mid-term - Cert | |
| Chapter 1 -9 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Chapter 10 - 14 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1001 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1002 | Online Test |
Cisco Netacad ITE 8 and ITE v7 – IT Essentials (Version 8.00) – IT Essentials 7.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Exam Answers 2024
-
Which two tools are available to transfer user data and settings from an old Windows computer to a Windows operating system on a new computer? (Choose two.)
- Windows Easy Transfer
- Windows User Manager
- Windows Upgrade Assistant
- Windows Upgrade Advisor
- User State Migration tool
Explanation: When a new operating system is being installed, existing user data and settings need to be migrated from the old to the new operating system. The User State Migration Tool and the Windows Easy Transfer Tool are available to perform this task on the Windows Vista, 7, and 8 operating systems.
-
A user wants to extend a primary partition formatted with the NTFS file system with the unallocated space on the hard disk. What must the user do after the primary partition is extended to make it usable?
- Convert the disk type to dynamic.
- Ensure that the disk type is basic.
- Format the disk with the FAT64 file system.
- Partition the new space as a basic disk.
Explanation: A partition must be formatted with the NTFS file system in order to extend it by using the unallocated space on the disk. Once the partition has been extended, the disk type must be converted to a dynamic disk in order for the new partition to be accessible.
-
Why is a full format more beneficial than a quick format when preparing for a clean OS installation?
- A full format is the only method of installing Windows 8.1 on a PC that has an operating system currently installed.
- A full format will delete files from the disk while analyzing the disk drive for errors.
- A full format will delete every partition on the hard drive.
- A full format uses the faster FAT32 file system, whereas a quick format uses the slower NTFS file system.
Explanation: A full format removes files from a partition while scanning the disk for bad sectors. A quick format will remove files from a partition but does not scan a disk for bad sectors.
-
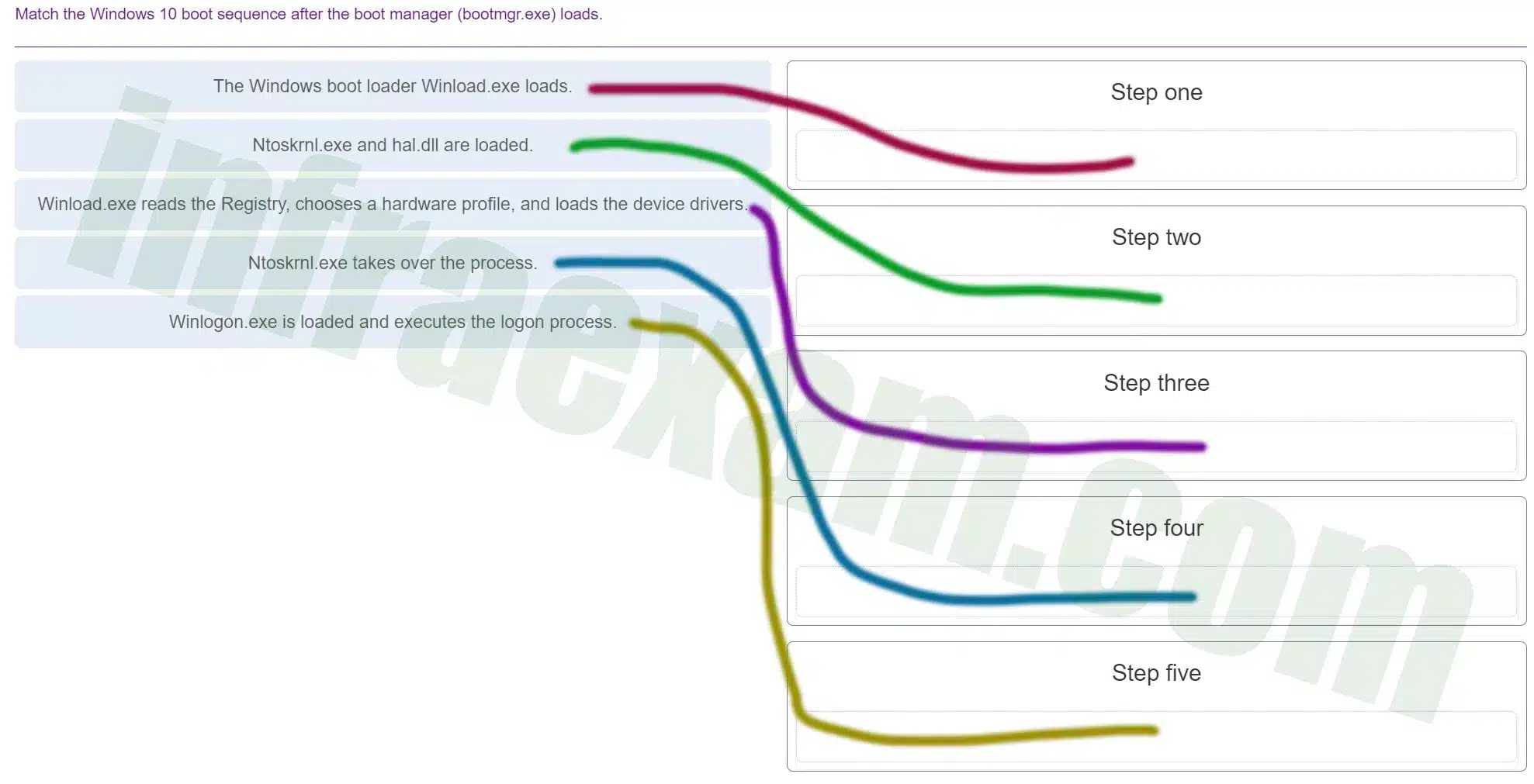
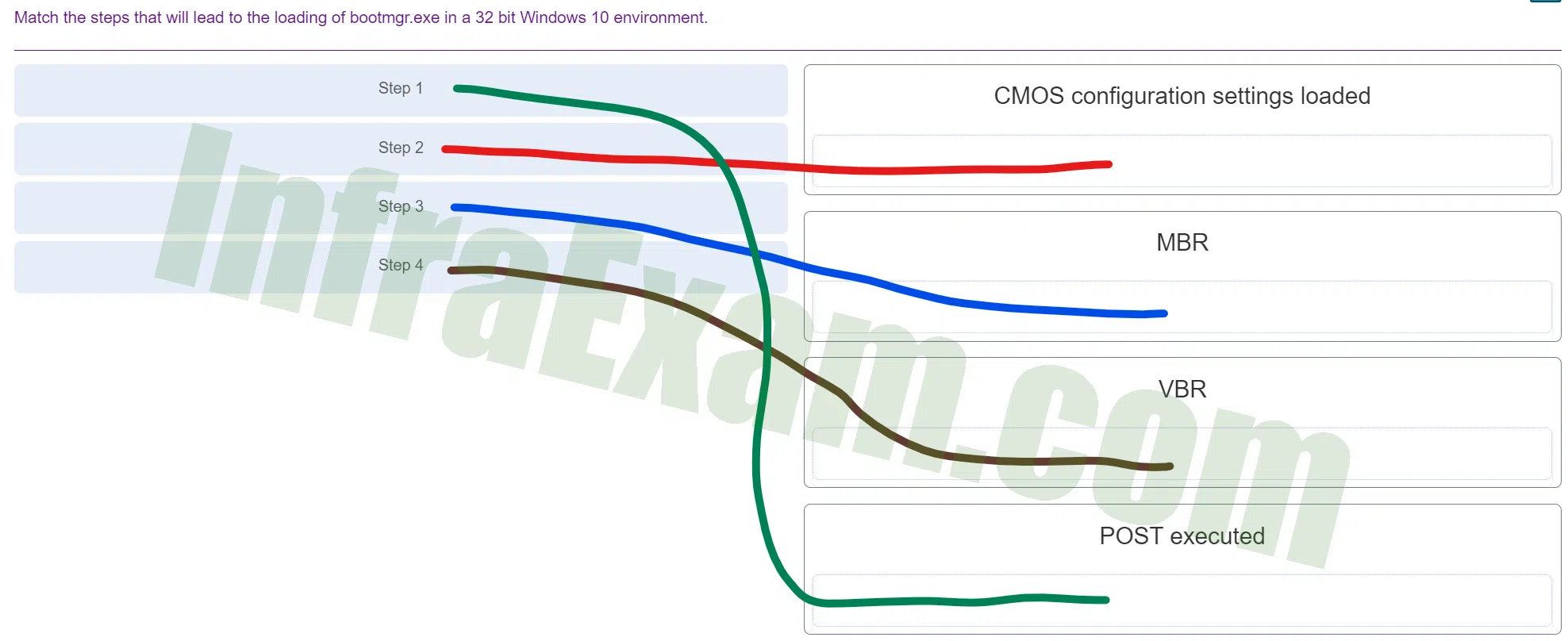
Match the Windows 10 boot sequence after the boot manager (bootmgr.exe) loads.
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 003 -
Explanation & Hint: Here’s the usual sequence for Windows 10 booting after the boot manager (
bootmgr.exe) has done its job:- The Windows Boot Loader (Winload.exe) loads. This is the first step after the boot manager has determined which operating system to start. It involves loading the necessary files to begin the boot process.
- Ntoskrnl.exe and hal.dll are loaded.
Ntoskrnl.exeis the Windows NT operating system kernel, andhal.dllis the Hardware Abstraction Layer. Both are essential for Windows to operate and interact with the system hardware. - Winload.exe reads the Registry, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers. At this point, Windows is loading the system registry and initializing the hardware profiles and device drivers needed for the basic hardware components to communicate with the software.
- Ntoskrnl.exe takes over the process. Once the basic drivers and kernel are in place, control is handed over to
ntoskrnl.exe, which continues the boot process by starting system services and further initializing the operating system. - Winlogon.exe is loaded and executes the logon process. This is one of the final steps in the boot process where the Windows Logon Application (
winlogon.exe) is responsible for handling the user logon.
-
-
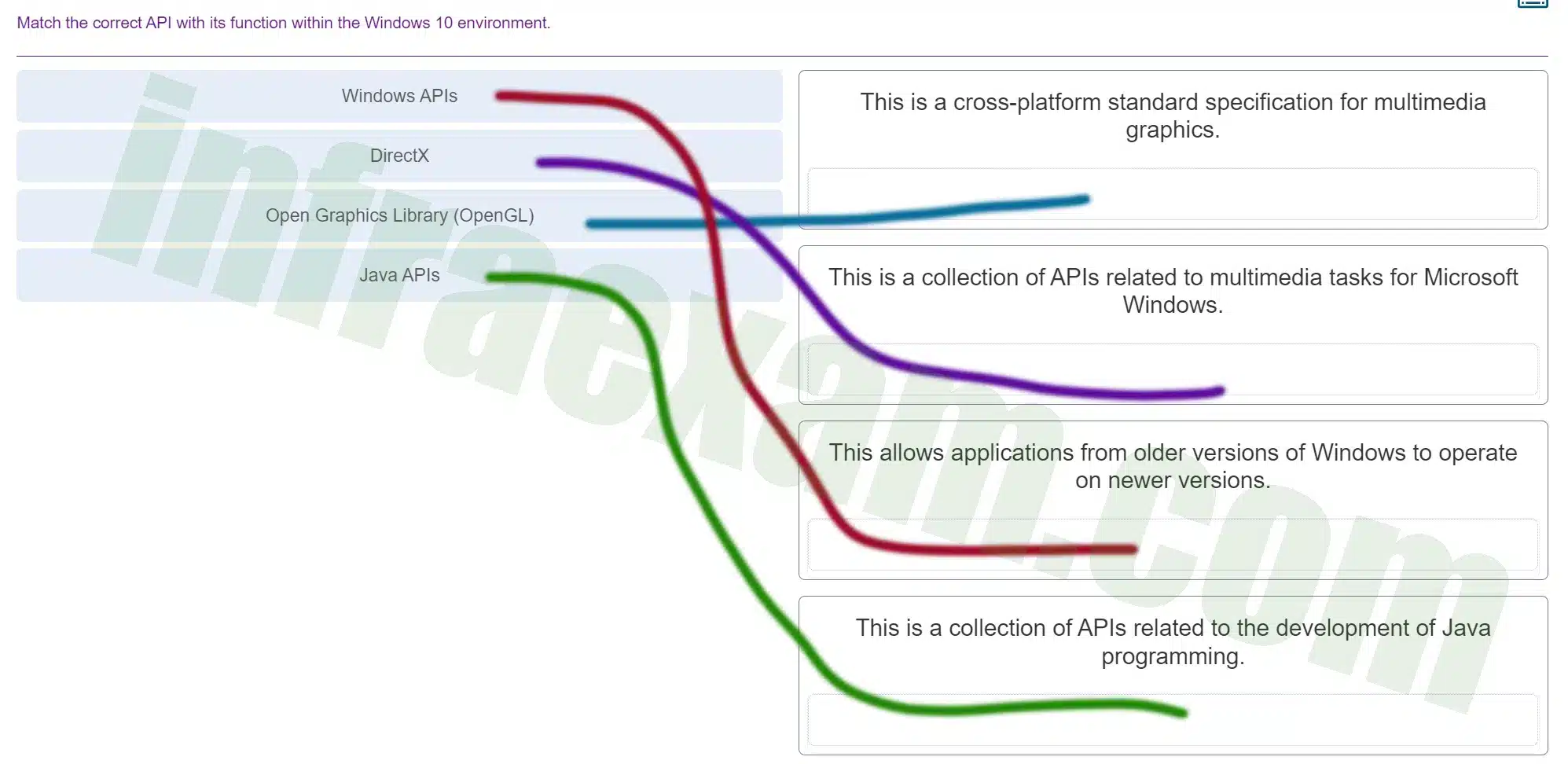
Match the correct API with its function within the Windows 10 environment.
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 004 -
Explanation & Hint: - Windows APIs: These are the interfaces provided by Microsoft that allow developers to interact with the Windows operating system. Windows APIs cover a wide range of Windows functionalities, including file handling, device input, networking, and graphical rendering.
- DirectX: This is a collection of APIs designed for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. DirectX includes APIs for rendering 2D and 3D graphics, processing audio and video, and managing input devices.
- Open Graphics Library (OpenGL): OpenGL is a cross-platform API for rendering 2D and 3D vector graphics. While it’s not exclusively for Windows—it’s used in various systems—it allows for the development and deployment of graphics across different platforms.
- Java APIs: These are not specific to Windows but are a set of APIs for the Java programming language that provide the capability for a wide range of functionalities, from basic functions to complex networking and graphical interfaces.
-
-
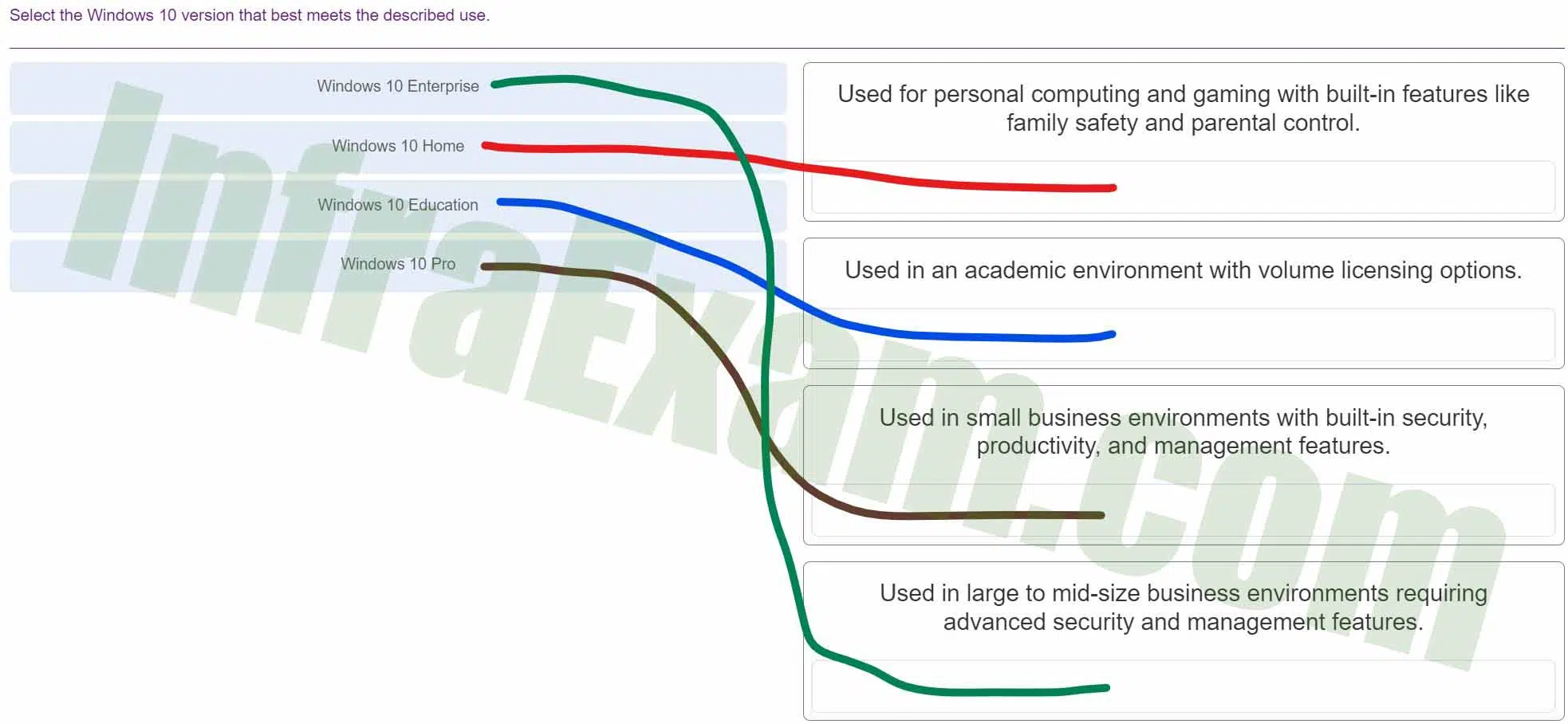
A technician wishes to prepare the computers in the network for disaster recovery. The network consists of a variety of desktops and laptops from different vendors. All the computers are running either a 32-bit version of Windows 10 Pro or a 64-bit version of Windows 10 Pro. How would the technician prepare the recovery media?
- Prepare one 64-bit recovery disc for all the computers.
- Prepare one 32-bit recovery disc for all the computers.
- Prepare individual recovery discs for all the computers.
- Prepare one image restore for all the computers.
Explanation: All the PCs are from different vendors and thus have dissimilar hardware configurations. Furthermore, all the PCs have a variety of 32-bit Windows 10 and 64-bit Windows 10. Because the PCs have different versions of the OS and dissimilar hardware, you cannot use the same image on all the PCs . In order to use a single image, Sysprep must be used to strip out machine specific information like the SID, and all PCs must have the same hardware configuration and the same version of the Windows operating system.
-
A technician wishes to deploy Windows 10 Pro to multiple PCs through the remote network installation process. The technician begins by connecting the new PCs to the network and booting them up. However, the deployment fails because the target PCs are unable to communicate with the deployment server. What is the possible cause?
- The wrong network drivers are loaded in the image file.
- The SID has not been changed in the image file.
- The NIC cards on the new PCs are not PXE-enabled.
- Sysprep was not used before building the image file.
Explanation: The NIC cards on the new PCs have to be PXE-enabled in order for them to communicate with the remote installation services on the server.
-
Which condition is required when planning to install Windows on a GPT disk?
- The computer must be UEFI-based.
- Only one primary partition can contain an OS.
- The maximum partition size cannot exceed 2 TB.
- The maximum number of primary partitions that can co-exist is 4.
Explanation: The globally unique identifier (GUID) partition table (GPT) makes use of a number of modern techniques to expand on the older MBR partitioning scheme. GPT is commonly used in computers with UEFI firmware. For Windows 10 to be installed on, and boot, from a GPT disk UEFI must be used.
-
A technician wishes to perform a customized unattended network installation of Windows 10 on a PC. The requirements include the installation of specific applications and device drivers through the use of an answer file. What would the technician use to create the answer file?
- Recovery partition
- Windows SIM
- disk cloning
- System Restore
Explanation: To perform a custom Windows Unattended installation, setup.exe must be run with the user options found in the answer file. Additional packages, such as applications or drivers, can be added to the answer file. The Windows System Image Manager (SIM) is used to create the setup answer file.
-
An organization has purchased a custom application for the sales staff that can only be installed on a 64-bit Windows operating system. Each member of the sales staff has a Windows 8.1 32-bit PC. What must the IT department do in order to install and run the application on the sales staff computers?
- Downgrade the 32-bit Windows 8.1 to 64-bit Windows 7.
- Upgrade the 32-bit Windows 8.1 to 64-bit Windows 10.
- Perform a clean installation of 64-bit Windows 10.
- Download and install 64-bit hardware drivers in the current OS.
Explanation: A 32-bit OS cannot be upgraded to a 64-bit OS. In this case a clean install of Windows 64-bit would be the only option because the application requires a 64-bit Windows environment to work.
-
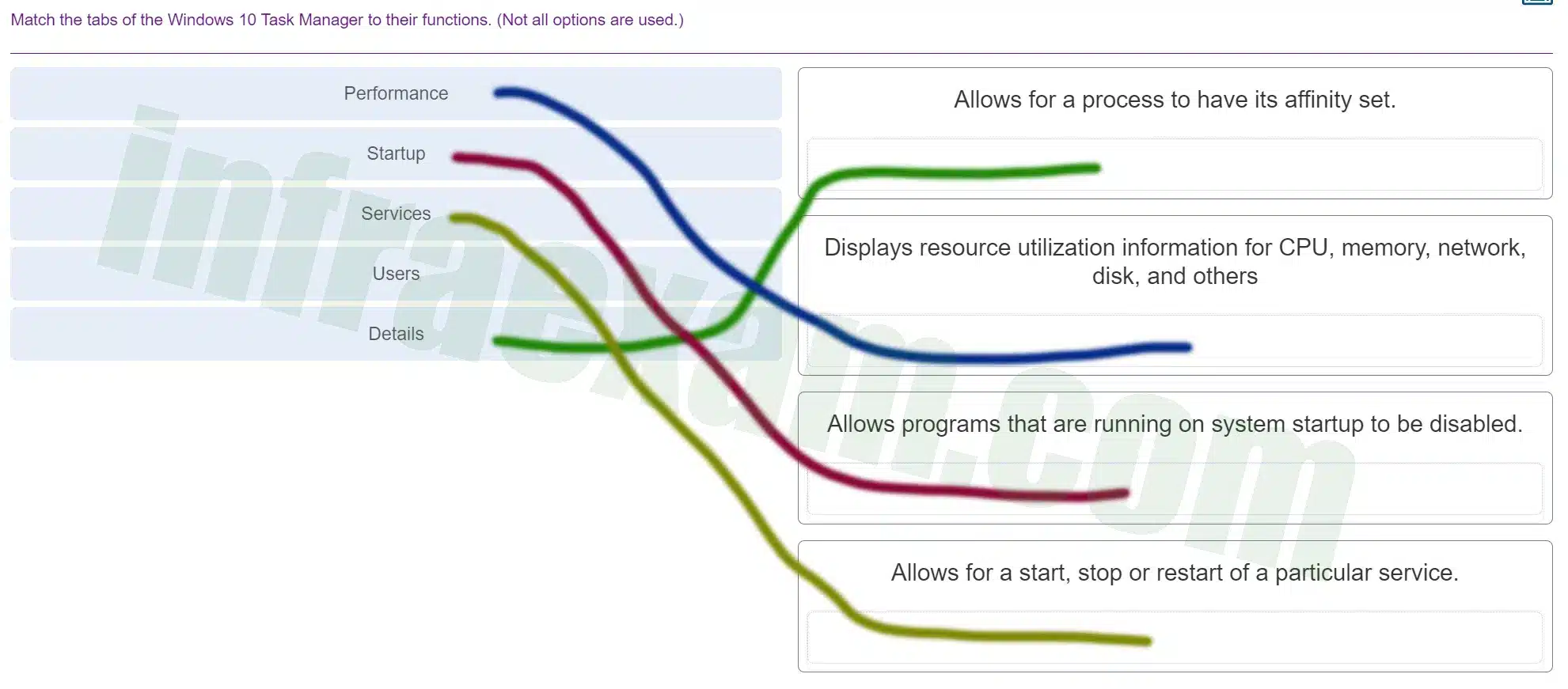
Match the tabs of the Windows 10 Task Manager to their functions. (Not all options are used.)
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 005 -
Explanation & Hint: - Performance: This tab displays real-time graphs and information about the hardware resources’ usage, including CPU, memory, disk, Ethernet, and potentially other resources like GPU. The details can help users understand how system resources are being utilized at any given time.
- Startup: In the Startup tab, you can see a list of applications and services that are set to run when the computer boots up. Users can enable or disable these programs to affect the startup process, which can improve the boot time and overall system performance.
- Services: This tab provides a list of all services, both running and stopped. From here, users can start, stop, or restart services. It is also possible to open the Services application for more detailed management options.
- Users: The Users tab shows all users currently logged onto the computer. You can see the processes running under each user and can manage their sessions, including logging off or switching users.
- Details: The Details tab provides in-depth information about each process running on your system. It is similar to the Processes tab but offers more technical details and allows advanced operations such as setting the priority of a process or its affinity (which CPUs the process can run on).
-
-
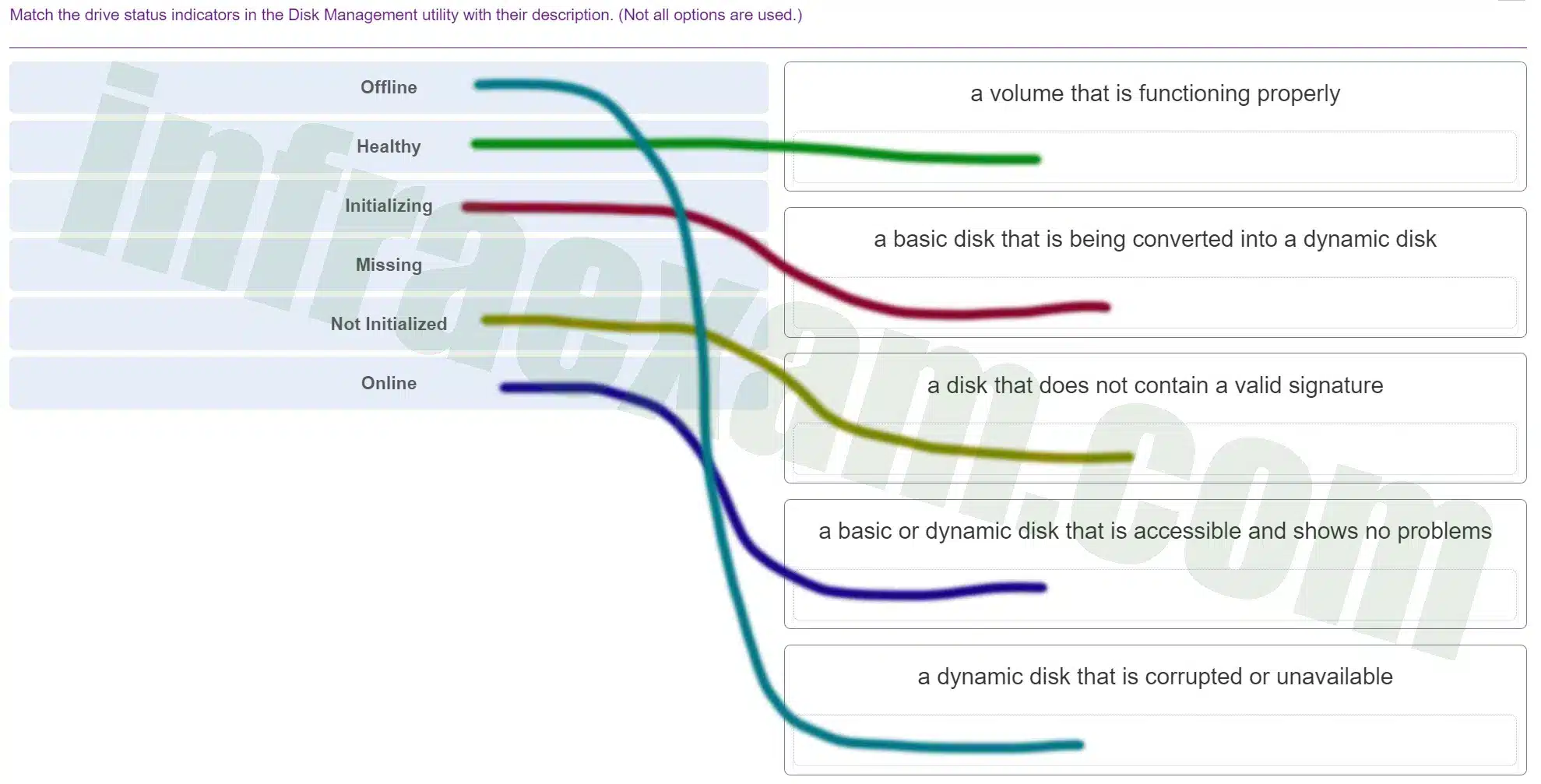
Match the drive status indicators in the Disk Management utility with their description. (Not all options are used.)
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 006 -
Explanation & Hint: - Healthy: Indicates a volume that is functioning properly with no underlying issues.
- Initializing: The process of preparing a new disk to be used, which often includes creating a new volume and formatting it. This status should not last long; once the disk is initialized, it moves to another status.
- Missing: A disk that is expected to be present but cannot be detected by the system. This can happen if a disk is removed or if it fails and is no longer communicating with the system.
- Not Initialized: Indicates a disk that has not yet been prepared for use by the operating system. A disk must be initialized before it can be formatted and used to store data.
- Offline: A disk that is not accessible by the operating system. Disks can be manually set to offline status or could be offline due to a problem like a missing signature.
- Online: A basic or dynamic disk that is accessible and functioning properly. An online disk is ready for use and shows no problems.
-
-
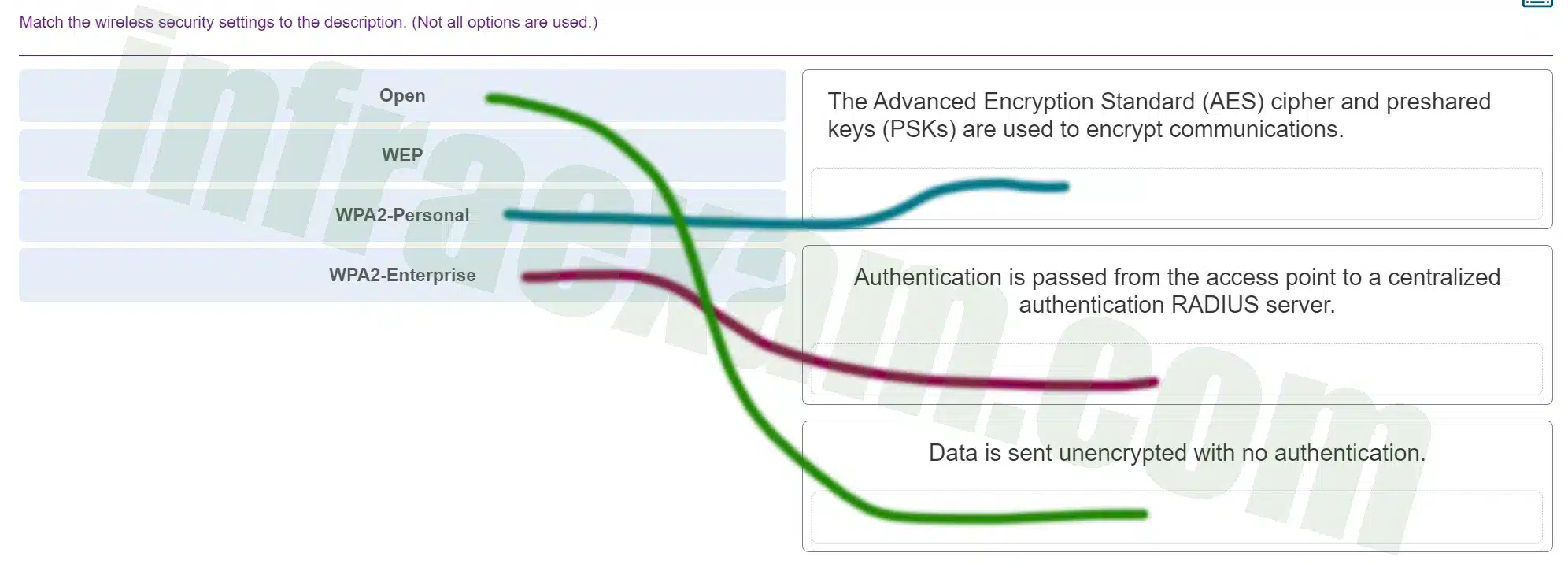
Match the wireless security settings to the description. (Not all options are used.)
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 007 -
Explanation & Hint: - Open: An open network does not encrypt data and does not require authentication to connect. This is the least secure option as it allows anyone to connect and intercept the data transmitted over the network.
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy): This is an outdated security protocol that was designed to provide a wireless network with a level of security and privacy comparable to what is usually expected of a wired network. However, it is no longer considered secure due to vulnerabilities in how it encrypts data.
- WPA2-Personal (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Personal): This security protocol uses the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and pre-shared keys (PSKs) to encrypt communications. It is designed for home and small office networks and requires a passphrase for network access.
- WPA2-Enterprise: This is similar to WPA2-Personal but is designed for enterprise networks. It uses a RADIUS server for centralized authentication, which provides additional security by managing user credentials and policies.
-
-
What are two possible solutions to any Windows computer restarting continuously and never displaying the desktop? (Choose two.)
- Upgrade the processor.
- Press F8 to open the Advanced Options menu and choose Disable Automatic Restart on System Failure.
- Access the BIOS and change the boot order options.
- Run chkdsk /F /R from the recovery console.
- Upgrade the video card.
- Reset the hard drive jumpers.
Explanation: Upgrading the processor, upgrading the video card, or resetting the hard drive jumper would not fix this problem. Boot order settings cannot cause the system to reboot continuously.
-
A technician uses Microsoft Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool to create a Windows image file on one of the workstations running Windows 10. When the technician tries to clone another workstation with the image file, the workstation exhibits network connectivity issues on completion. What could cause this?
- The SID of the original PC is not cleared when creating the image with DISM.
- The technician used the wrong tool to create the image file.
- The network drivers were not added to the image file.
- The Sysprep utility should have been turned off prior to the creation of the image file.
Explanation: The technician must use Sysprep to clean up the local specific configuration, such as the SID, otherwise the cloned systems will not work properly.
-
A user complains that user files cannot be synced with the network file server while the user is traveling out of the office. The user had access to the internet but no access to the company network server. How can this be addressed?
- Ensure that the user only uses a single device and not multiple devices when accessing networked files.
- Turn off the activation of Offline Files feature in the Sync Center.
- Setup a Sync partnership with the networked file location.
- Setup a Sync partnership between the network server, Microsoft OneDrive, and the user.
Explanation: Because the user has access to the internet, access to the Microsoft OneDrive cloud based service is possible and thus the user can sync with Microsoft OneDrive, which in turn can sync with the company network server from across the internet.
-
A technician has connected a new internal hard drive to a Windows 10 PC. What must be done in order for Windows 10 to use the new hard drive?
- Initialize the new hard drive.
- Extend the partition on an existing hard drive to the new hard drive.
- Run chkdsk on the new hard drive.
- Mount the new hard drive.
Explanation: The new hard drive needs to be initialized before it can be used in Windows. This will involve formatting the disk which will erase any existing data on the drive.
-
What service does PRINT$ provide?
- It provides a network share for accessing shared printers.
- It provides printer drivers for printer administrators.
- It provides a group of hidden printers that only administrative users have permissions to send print jobs to.
- It provides an administrative Printer share accessible by all local user accounts.
Explanation: PRINT$ is a hidden share for printer drivers. It is shared by default and used to access remote shared printers or provide drivers to clients when sharing a printer.
-
A technician is troubleshooting a Windows 10 laptop infected with a virus that has damaged the master boot record. The technician has booted the laptop using the installation media and is attempting to repair the laptop from the command line interface. Which command can the technician use to repair the corrupt master boot record?
- bootrec /fixmbr
- chkdsk
- msconfig
- sfc /scannow
Explanation: The sfc /scannow command is used to check the integristy of the system files. The msconfig command allows for viewing the startup configuration mode, while the chkdsk command is used to repair the Windows file system. The bootrec /fixmbr command is used to repair a corrupt master boot record in a Windows 10 environment.
-
A user reports that a Windows 10 PC displays the error message “Invalid Boot Disk” during the boot process. The IT technician attempts to boot the computer and finds that the error message occurs immediately after the POST. What could be the possible cause?
- A recently installed device driver is incompatible with the boot controller.
- BOOTMGR is corrupted.
- The MBR/GPT is corrupted.
- A service failed to start during the booting process.
Explanation: The message “invalid Boot Disk” could be a symptom of a missing or damaged MBR/GPT, a missing or damaged Boot Configuration Data file, a boot sector virus, a boot order not set correctly in BIOS, media without an operating system being in a drive, a hard drive not detected or damaged, or the absence of an installed operating system.
-
Which port number is used by Virtual Network Computing (VNC) to provide remote screen sharing between devices?
- 22
- 23
- 389
- 3389
- 5900
Explanation: Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a freeware product that is similar in functionality to RDP and works over port 5900.
-
Which feature is included with macOS and provides the ability for a remote user to view and change files, folders, and applications on the local computer?
- Screen Sharing
- Remote Assistance
- Virtual Network Computing
- Remote Desktop
Explanation: In macOS, remote access functionality is provided by the Screen Sharing feature, which is based on Virtual Network Computing (VNC). VNC is a freeware product that is similar in functionality to RDP and works over port 5900.
-
Which area of concern falls under the operations and planning category in IT documentation?
- inventory management
- disaster recovery policies and procedures
- logical and physical network topology diagrams
- end-user manual for hardware and software
Explanation: There are four broad categories of IT documentation: Policies, Operations, Projects, and User documentation. Operations is concerned with inventory management.
-
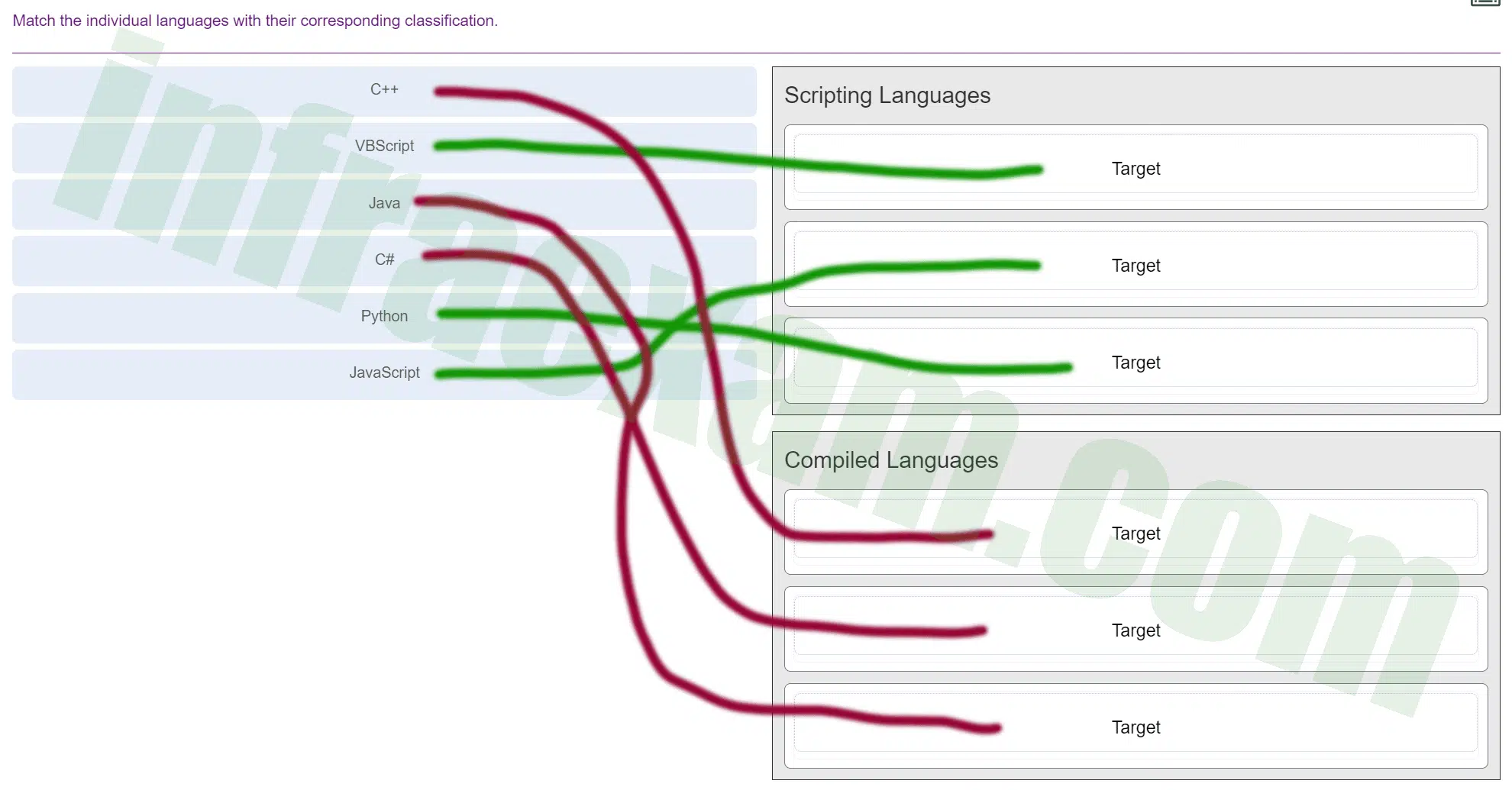
Match the individual languages with their corresponding classification.
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 011 Explanation: Scripting languages include Windows batch files, PowerShell, Linux shell script, VBScript, JavaScript, and Python. Compiled languages include C, C++, C#, and Java.
-
Which two actions should a technician take if illegal content, such as child pornography, is discovered on the hard drive of a customer computer? (Choose two.)
- Confront the customer immediately.
- Remove and destroy the hard drive.
- Contact a first responder.
- Shut down the computer until authorities arrive.
- Document as much information as possible.
Explanation: If illegal content is found, begin documentation to build a chain of custody and contact a first responder immediately.
-
What are three pieces of information a level one technician should gather from a customer? (Choose three.)
- contact information
- description of the problem
- details of any recent changes to the computer
- output from diagnostic software
- output from a remote connection to the customer computer
- current CMOS settings
Explanation: A level one technician should gather information from the customer and solve simple problems. For more advanced diagnostics, opening the computer case, running diagnostics software, and performing remote connections, the problem should be escalated to a level two technician.
-
What two actions are appropriate for a support desk technician to take when assisting customers? (Choose two.)
- Interrupt customers if they start to solve their own problems.
- Comfort a customer by minimizing the customer problem.
- Let a customer finish talking before asking additional questions.
- If you have to put the customer on hold, ask the customer for permission.
- As soon as you detect customer anger, pass the angry customer to the next level.
Explanation: When dealing with customers, a technician should show professionalism in all aspects. A technician should observe the process before putting a customer on hold. First, let the customer finish speaking. Then, explain that there is need to put the customer on hold for a short period, and ask the customer for permission to do so. Tell the customer that it will be only a few minutes and explain what you will do during the period. When the customer agrees to be put on hold, thank the customer.
-
A support desk technician is dealing with an angry customer. Which two approaches should the technician take in dealing with the customer? (Choose two.)
- Ask socially related questions to direct the customer away from the problem.
- Work to redirect the conversation to solving the problem.
- Immediately transfer the customer to a higher level technician.
- Reply to the customer with the same level of anger.
- Let the customer explain the problem without interrupting.
Explanation: Angry customers should be allowed to explain the problem, then be redirected to discussing how the problem can be solved. Transferring the customer, replying in a rude tone, and asking unrelated questions will usually increase, not ease, the anger being expressed by the customer.
-
What two kinds of problems should be escalated from a level one technician to a level two technician? (Choose two.)
- problems that require rebooting the equipment
- problems that can be solved in a short time
- problems that are complicated and will take a long time to resolve
- problems that do not fit into the “down call” category
- problems that are beyond the scope of the knowledge of the level one technician
Explanation: A problem should be escalated to a level two technician when the problem is going to take a long time to fix, is affecting a large number of users, or requires knowledge or expertise that the level one technician does not possess.
-
An IT technician in a service company has provided extensive remote IT support with product deployment for a customer. After the completion of the contract, a complaint is filed against the IT technician for not following company policy by sending unsolicited emails about services and products that are not related to the contract. What two things should the IT support technician have done differently? (Choose two.)
- The IT technician should have researched the company policy about personal communication with customers on company time.
- The IT technician should have used encryption to hide the purpose of the emails.
- The IT technician should have added the customer to a chain letter with many recipients instead.
- The IT technician should have asked the customer if the customer was interested in receiving information regarding other new services and products.
- The IT technician should have requested permission from a supervisor to send the customer emails.
Explanation: While working with customers both briefly and over an extended period of time, it is possible to form friendly relationships. It is important to always follow company policy and never send unsolicited messages to a customer. Also do not send unsolicited mass mailings or chain letters to customers from a company email address. Any personal relationships should be kept via personal email accounts and should not reflect the IT organization of the employer.
-
A third-party security firm is performing a security audit of a company and recommends the company utilize the Remote Desktop Protocol. What are two characteristics of the Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)? (Choose two.)
- RDP connects on TCP port 22.
- RDP requires a Windows client.
- RDP uses an encrypted session.
- RDP is a command-line network virtual terminal protocol.
- RDP connects on TCP port 3389.
Explanation: The Remote Desktop protocol (RDP) is used to remotely access a Windows OS. It is a client/server protocol.The port number for RDP is TCP port 3389 and it uses encryption.
-
Which subject area describes collecting and analyzing data from computer systems, networks, and storage devices, as part of an investigation of alleged illegal activity?
- cyber law
- computer forensics
- cryptography
- disaster recovery
Explanation: The field of computer forensics involves collecting and analyzing data from computer systems, networks, wireless communications, and storage devices.
-
In a computer forensics investigation, which type of data is considered volatile data and can be lost if power is removed from the computer?
- data stored on magnetic disks
- data stored on an internal drive
- data in transit between RAM and the CPU
- data stored on an external drive
Explanation: Volatile data is a data that is lost when power is turned off, and is located in temporary storage such as RAM, cache, CPU or in transit between them.
-
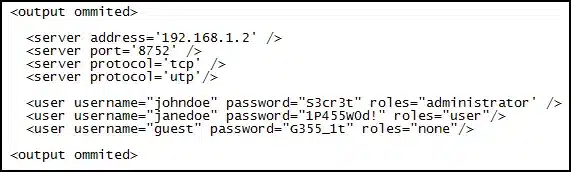
Refer to the exhibit. During the troubleshooting of software that is installed on a computer system, a level one technician requires help from a level two technician. The file shown in the exhibit must be sent to the level two technician. How should the level one technician deliver this file?
ITE v8.0 – IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8 Final Exam 1 – 14 Answers 01 - This file should not be shared with the level two technician.
- Replace all passwords in the file with <password omitted> before emailing the file and then supply the passwords by secure means, if required.
- Send the file as it is to the level two technician.
- Deliver the file in printed format only.
Explanation: Customer privacy should be maintained. The easiest way to preserve it is removing any occurrence of passwords from the documentation that is being sent to another technician.
If a client password is required to solve the problem, it should be sent to another technician through a specific document.
-
What skill is essential for a level one technician to have?
- the ability to gather relevant information from the customer and pass it to the level two technician so it can be entered into the work order
- the ability to ask the customer relevant questions, and as soon as this information is included in the work order, escalate it to the level two technician
- the ability to translate a description of a customer problem into a few succinct sentences and enter it into the work order
- ability to take the work order prepared by the level two technician and try to resolve the problem
Explanation: The level one technician must be able to translate the description of a customer problem into a succinct sentence or two that is entered into the work order.
-
What is used to control illegal use of software and content?
- chain of custody
- service level agreement
- End User License Agreement
- digital rights management
Explanation: Digital rights management, or DRM, is software that is designed to prevent illegal access to digital content.
-
What determines the level of support that a call center technician will provide to an individual customer?
- Support is based on the SLA for that customer.
- All customers receive the same level of support by the call center.
- A level one technician will provide a higher level of support than a level two technician.
- An individual call center technician chooses the level of support based on the time available to assist the customer.
Explanation: A call center technician must provide the level of support that is outlined in the SLA for that individual customer.
-
A bench technician enters the server room and finds the backup server computer case open. The hard drives containing patient medical data are all physically disconnected from the motherboard and the SATA data cables are hanging outside the case. Which step should the technician immediately take?
- Reconnect the SATA data cables to ensure continued data backup.
- Disconnect the SATA power cables to prevent the loss of persistent data.
- Place the hard drives in an external enclosure and begin backing up the data before releasing the drives to first responders.
- Locate an employee qualified to collect evidence.
- Dust the server computer case for fingerprints.
Explanation: When a potential crime scene is found, a chain of custody must be observed and followed. The technician should immediately locate another employee who is qualified to collect evidence. Disconnecting or reconnecting the drives or attempting to move data may adversely affect the chain of custody.
-
What is the difference between a scripting language and a compiled language?
- Scripting languages need to be converted into executable code using a compiler, while compiled languages are interpreted as they are executed.
- Compiled languages are executed by the operating system, while scripting languages are executed by the CPU.
- Scripting languages are interpreted and executed line by line when a script is run, while compiled languages need to be converted into executable code.
- Compiled languages are executed by a command interpreter, while scripting languages are executed by the CPU.
Explanation: A scripting language is different than a compiled language because each line is interpreted and then executed when the script is run. Compiled languages need to be converted into executable code using a compiler. Another difference between the two types of languages is that compiled languages are executed by the CPU while scripting languages are executed by a command interpreter or by the operating system.
-
Which methods can be used to implement multifactor authentication?
- VPNs and VLANs
- IDS and IPS
- passwords and fingerprints
- tokens and hashes
Explanation: A cybersecurity specialist must be aware of the technologies available that support the CIA triad.
-
When responding to a call from a customer who is experiencing problems with a computer, the technician notices that a number of system files on the computer have been renamed. Which two possible solutions could the technician implement to resolve the problem? (Choose two.)
- Use antivirus software to remove a virus.
- Restore the computer from a backup.
- Change the folder and file permissions of the user.
- Reset the password of the user.
- Upgrade the file encryption protocol.
Explanation: Renamed system files are usually the result of a virus on the computer. Removing the virus and restoring the computer from a backup are the only two possible solutions in this case.
-
A technician suspects that a security issue is causing problems with a computer. What two actions could be performed to test theories of probable cause when troubleshooting the PC? (Choose two.)
- Log in as a different user.
- Disconnect the computer from the network.
- Search helpdesk repair logs for more information.
- Discuss solutions with the customer.
- Ask the customer open-ended questions about the problem.
Explanation: Several actions can be taken by a technician when security issues are suspected as the possible cause of a problem with a computer. Logging in as a different user or disconnecting the PC from the network to isolate the cause of the problem are two possible actions.
-
The CIO wants to secure data on company laptops by implementing file encryption. The technician determines the best method is to encrypt each hard drive using Windows BitLocker. Which two things are needed to implement this solution? (Choose two.)
- at least two volumes
- USB stick
- password management
- TPM
- EFS
- backup
Explanation: Windows provides a method to encrypt files, folders, or entire hard drives depending on need. However, certain BIOS settings and configurations are necessary to implement encryption on an entire hard disk.
-
What is an accurate description of asymmetric encryption technology?
- Asymmetric encryption is an encryption process that compares traffic on both ends to make sure the traffic has not been altered.
- It is an encryption process that uses identical keys on both ends to establish the VPN.
- It is an encryption protocol that is used to encrypt data as the data is sent over the VPN.
- It is an encryption process that uses a public and private key pair to encrypt/decrypt data.
-
Explanation & Hint: Certainly! Let’s break down each option and identify whether they are correct or incorrect:
- “It is an encryption process that uses a public and private key pair to encrypt/decrypt data.”
- Correct. Asymmetric encryption involves a pair of keys – a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption, and the corresponding private key is used for decryption. This method ensures that only the holder of the private key can decrypt the message, providing a secure means of communication.
- “It is an encryption process that compares traffic on both ends to make sure the traffic has not been altered.”
- Incorrect. This description more closely aligns with the concept of integrity checks or digital signatures rather than asymmetric encryption. Integrity checks and digital signatures ensure that the data has not been tampered with during transmission but do not specifically describe the process of encrypting and decrypting data using key pairs.
- “It is an encryption process that uses identical keys on both ends to establish the VPN.”
- Incorrect. This describes symmetric encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption. In symmetric encryption, both parties must have access to the same secret key, which differs from the public-private key pair mechanism used in asymmetric encryption.
- “It is an encryption protocol that is used to encrypt data as the data is sent over the VPN.”
- Incorrect. While this statement might describe the use of encryption in a VPN context, it does not specifically detail asymmetric encryption. VPNs can use various types of encryption methods, including both symmetric and asymmetric encryption. This statement is too broad and does not capture the unique characteristics of asymmetric encryption, specifically the use of a public and private key pair.
In summary, asymmetric encryption is uniquely characterized by the use of two different keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption – ensuring secure communication where only the intended recipient can decrypt the message.
- “It is an encryption process that uses a public and private key pair to encrypt/decrypt data.”
-
Which type of security threat can be transferred through email and is used to gain sensitive information by recording the keystrokes of the email recipient?
- adware
- Trojan
- worm
- virus
- grayware
Explanation: Adware does not record keystrokes. A worm self-replicates across the network. A Trojan appears to be a legitimate program while carrying malware, and grayware is a general term for software that may be malware.
-
A manager reports that unusual things are happening on a Windows computer. The technician determines that malware is the culprit. What can the technician do to remove stubborn malware?
- Ensure that the computer is connected to the wired network so that antimalware updates can be installed.
- Enter Safe Mode and do a system restore.
- Install adware protection.
- Train the user on identifying trusted and untrusted sources.
Explanation: Booting the computer in Safe Mode prevents most drivers from loading. Additional antimalware software can then be installed to remove or quarantine malware. Sometimes the storage drive must be wiped, the operating system reinstalled, and data restored from a backup.
-
An employee that has worked at the company for many years has started a home-based business selling crafts. While leaving an office meeting, a company supervisor notices the employee buying supplies for the personal crafting business of the employee. What section of the security policy should the supervisor review when determining how to handle this situation?
- acceptable use policies
- identification and authentication policies
- incident handling policies
- remote access policies
Explanation: The acceptable use policies section of a security policy commonly identifies network resources and usages that are acceptable to the organization. They might also state the ramifications that can occur if this security policy is violated.
-
What Windows utility should be used to configure password rules and account lockout policies on a system that is not part of a domain?
- Event Viewer security log
- Local Security Policy tool
- Active Directory Security tool
- Computer Management
Explanation: A technician must be aware of the technologies and measures that are used as countermeasures to protect the organization from threats and vulnerabilities. A Windows Domain Security Policy is used and applied when a user logs in to a computer that is on a corporate network. A Windows Local Security Policy is used for stand-alone computers to enforce security settings.
-
A customer brings in a computer that is asking for a password as soon as it powers on, even before the operating system boots. Which type of password is enabled?
- BIOS
- login
- multifactor
- network
- synchronous
Explanation: A BIOS password is configured by entering the BIOS Setup program. If unknown, it can be removed by placing a jumper over two motherboard pins. Some motherboards support BIOS password removal by removing the CMOS battery, but if this is done, all BIOS settings will be reset to the default values.
-
When attempting to improve system performance for Linux computers with a limited amount of memory, why is increasing the size of the swap file system not considered the best solution?
- A swap file system only supports the ex2 file system.
- A swap file system does not have a specific file system.
- A swap file system cannot be mounted on an MBR partition.
- A swap file system uses hard disk space to store inactive RAM content.
Explanation: The swap file system is used by Linux when it runs out of physical memory. When needed, the kernel moves inactive RAM content to the swap partition on the hard disk. Storing and retrieving content in the swap partition is much slower than RAM is, and therefore using the swap partition should not be considered the best solution to improving system performance.
-
What are three features of GPS on mobile devices? (Choose three.)
- phone number lookup
- navigation
- specialized search results
- device tracking
- remote wipe
- gas mileage calculations
Explanation: Navigation, specialized search results, and device tracking are features of GPS on mobile devices. Remote wipe may be a feature on some mobile devices, but is not related to GPS. Phone number lookup and gas mileage calculations are not GPS features.
-
Which three components are used to assign file and directory permissions in Linux systems? (Choose three.)
- root
- group
- owner
- all users
- super group
- admin group
Explanation: In Linux, file and directory permissions are assigned as follows:
- Owner – the owner user of the file or directory
- Group – the user group that has been assigned to the file or directory
- All users – all other users on the system
-
A user downloads a widget onto his Android phone but is puzzled to see that when the widget is touched an app is launched. What is a possible cause?
- The user has downloaded a virus.
- The widget is corrupt.
- The security settings of the Android OS have been compromised.
- The widget is associated with the app and this is the normal behavior.
Explanation: Widgets are programs that when installed associate with the application they were built for. This will cause the application to launch when the widget icon is touched on the touchscreen of the Android device.
-
What is the purpose of running mobile device apps in a sandbox?
- to enable the phone to run multiple operating systems
- to prevent malicious programs from infecting the device
- to enable separate app icons to be displayed on the home screen
- to bypass phone carrier restrictions that prevent access to unauthorized apps
Explanation: Mobile device apps are run in a sandbox that isolates them from other resources. Bypassing the phone carrier from preventing access to unauthorized apps is jailbreaking or rooting the device.
-
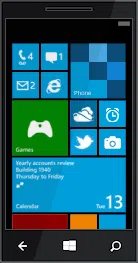
Refer to the exhibit. What is true of this mobile device screen?
ITE 8.01 – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Exam Answers 01 - Tapping and holding the arrow at the bottom left will display the Home screen.
- Text messages, news, photos and other content can be displayed in the different tiles.
- Icons and buttons are used to represent the different apps on the phone.
- Unpinning an app from this view will uninstall the app from the phone.
- Tile sizes depend on the size of the app.
Explanation: The Windows Phone interface uses tiles to represent apps. Tiles are rectangular areas of a screen that identify the app and may also contain active content such as text messages, news feeds, and photos.
-
Which built-in tool is available on a Mac OS X machine to perform disk backups?
- Disk Utility
- Deja Dup
- Finder
- Time Machine
Explanation: Time Machine is an automatic backup utility in the Mac OS. The Mac Disk Utility allows an administrator to configure disk backups. The Deja Dup tool is a tool built into the Linux OS for backing up data. Finder is similar to the Windows File Explorer tool and is used to navigate the Mac OS file system.
-
A user calls the help desk reporting that a laptop with Linux freezes on startup and displays kernel panic. What could cause this problem?
- A driver has become corrupted.
- GRUB or LILO has been deleted.
- GRUB or LILO has been corrupted.
- An application is using a resource that has become unavailable.
Explanation: A corrupted driver or failing hardware could cause kernel panic for Linux or Mac OS. The laptop will not be able to boot successfully. Either GRUB or LILO corruption or GRUB or LILO deletion would cause the stop screen to display a “Missing GRUB” or “Missing LILO” message. A resource unavailable to an application will cause the application to stop responding, but not prevent a laptop from starting up.
-
A user calls the help desk to report that a mobile device exhibits very slow performance. What could cause this problem?
- The touchscreen is not calibrated.
- An app is not compatible with the device.
- The operating system is corrupt.
- A power-intensive app is running in the background.
Explanation: A power-intensive app that is running in the background could consume most of the CPU cycles and thus the device would exhibit very slow performance for other apps. If an app is not compatible with the device, the device operating system would freeze. If the operating system has encountered an error, the device will fail to respond.
-
Which term describes a partition that is used to store and boot an operating system by default?
- logical drive
- active partition
- basic disk
- extended partition
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct term is:
- Active partition: This is the partition that the computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware considers to be the source for booting the operating system. The active partition is marked as such and is typically where the bootloader for the operating system resides. In a Master Boot Record (MBR) disk, there can only be one active partition at a time, which is used to boot the system.
The incorrect terms are:
- Logical drive: This is not the correct term for a bootable partition. A logical drive is a partition within an extended partition on a hard drive that uses the MBR partitioning scheme. Logical drives are typically used to extend the number of partitions beyond the limit of four primary partitions on an MBR disk, but they are not marked as active for booting purposes.
- Basic disk: This term refers to a storage disk that is not divided into volumes that span across several disks. Basic disks can contain both primary and extended partitions, where primary partitions can be marked as active to boot an operating system. However, the term “basic disk” itself does not denote a bootable partition.
- Extended partition: An extended partition is a type of partition on MBR disks that acts as a container for logical drives. It’s not bootable by itself; rather, it’s used to create more partitions than the limit of four primary partitions on an MBR disk. An extended partition cannot be set as active.
-
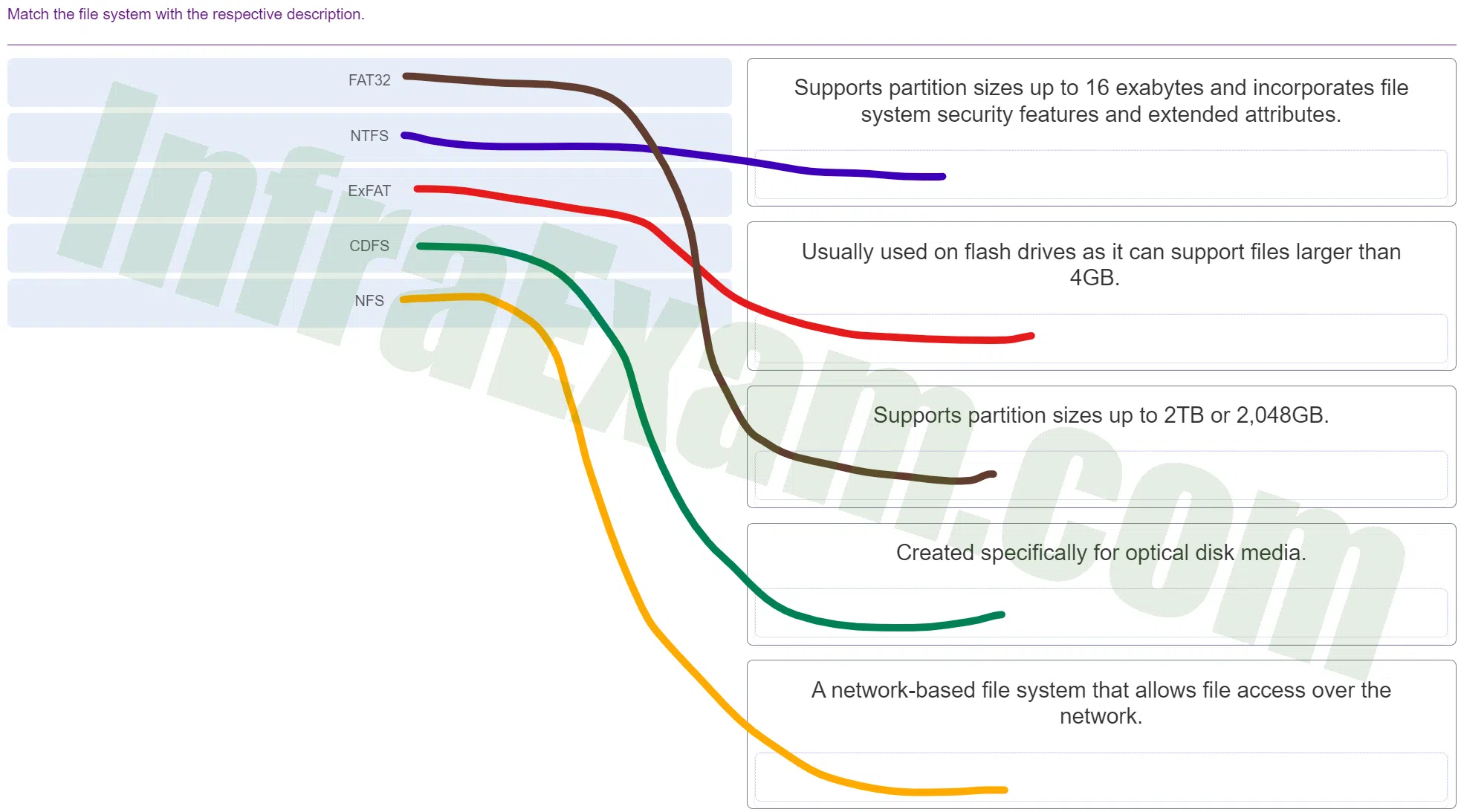
Which term describes a file system that supports a partition size up to 16 exabytes?
- extended partition
- NTFS
- logical drive
- active partition
-
Explanation & Hint: The term that describes a file system capable of supporting partition sizes up to 16 exabytes is:
- NTFS (New Technology File System)
NTFS is a file system developed by Microsoft. It is the standard file system for Windows NT and its later versions, including Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10. It includes features not found in FAT and exFAT file systems, such as support for metadata, use of advanced data structures to improve performance, reliability, and disk space utilization, plus additional extensions, such as security access control lists (ACL) and file system journaling.
The incorrect terms are:
- Extended partition: This refers to a type of partition on a Master Boot Record (MBR) disk. An extended partition is a container that can hold multiple logical drives within it. It does not refer to a file system or to the maximum size of a partition.
- Logical drive: This is a partition within an extended partition on an MBR disk. A logical drive itself can be formatted with any file system, but the term does not specify a file system nor the maximum partition size it supports.
- Active partition: This term refers to the primary partition from which the computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware starts the operating system’s bootloader. It does not refer to a file system or define the maximum size of a partition.
-
Which term describes a file system for USB flash drives that supports files larger than 4 GB?
- extended partition
- exFAT
- logical drive
- active partition
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct term is:
- exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table): This file system is designed for flash drives and is used when large capacity and large file sizes are required. Unlike FAT32, exFAT does not have the 4 GB file size limitation, making it ideal for large files.
The incorrect terms are:
- Extended partition: This is a type of partition on a Master Boot Record (MBR) disk that is not itself a file system; it’s a container that can hold logical drives, which are then formatted with a file system such as FAT, FAT32, exFAT, or NTFS.
- Logical drive: This refers to a partition within an extended partition on an MBR disk. It’s a segment of a hard drive that is treated as a separate volume, and like an extended partition, it’s not a file system. A logical drive can be formatted with any supported file system, including exFAT.
- Active partition: This term identifies the primary partition from which the system’s BIOS or UEFI firmware will boot the operating system. It is related to boot processes and not to the file system format of the partition or drive.
-
Which term describes a partition that supports up to 23 logical drives?
- logical drive
- extended partition
- basic disk
- active partition
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct term is:
- Extended partition: This is the type of partition on an MBR disk that does not hold files directly. Instead, it can contain multiple logical drives within it. The extended partition allows you to bypass the limitation of four primary partitions on an MBR disk. While there is no set limit to the number of logical drives that can be created within an extended partition, the number of drive letters available in Windows (C through Z, as A and B are reserved for floppy drives) limits the number of logical drives you can easily access to 23.
The incorrect terms are:
- Logical drive: This is not a type of partition, but rather a subdivision within an extended partition. A single logical drive cannot support additional logical drives within it.
- Basic disk: This term refers to a storage disk that is not split into volumes that span multiple disks. A basic disk can contain primary partitions and an extended partition with logical drives, but the term itself does not denote the capability to support multiple logical drives.
- Active partition: This refers to the primary partition on a disk that the computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware uses to boot the operating system. It does not refer to the capacity to contain multiple logical drives. An active partition is a bootable partition and is not directly related to the concept of supporting multiple logical drives.
-
Which term describes a file system for optical disk media?
- extended partition
- CDFS
- logical drive
- active partition
-
Explanation & Hint: The term that describes a file system for optical disk media is:
- CDFS (Compact Disc File System)
CDFS is an acronym for Compact Disc File System, which is a file system for optical disc media. It is used for the storage of files on compact discs and is a standard part of the ISO 9660 format.
The incorrect terms are:
- Extended partition: This term is related to hard drive partitioning in the Master Boot Record (MBR) scheme and has nothing to do with file systems for optical media.
- Logical drive: This term refers to a subdivision of an extended partition on a hard disk, not to a file system for optical discs.
- Active partition: This term is used to describe the bootable partition from which the computer starts the operating system, and is not specific to optical media file systems.
-
Which term describes a type of partition that would only exist on a hard disk that has an MBR?
- extended partition
- logical drive
- basic disk
- active partition
-
Explanation & Hint: The terms that describe a type of partition that would only exist on a hard disk that has an MBR (Master Boot Record) are:
- Extended partition: This is a specific type of partition on an MBR disk that can contain logical drives. It provides a way to bypass the limitation of four primary partitions imposed by the MBR partitioning scheme.
- Logical drive: This refers to a subdivided partition within an extended partition on an MBR disk. Logical drives are created to expand the number of partitions beyond the four primary partitions allowed by the MBR.
The terms that are not exclusive to an MBR disk are:
- Basic disk: This term refers to a disk that is not using a RAID configuration or isn’t a dynamic disk. Both MBR and GPT disks can be basic disks.
- Active partition: This term refers to the primary partition that the computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware uses to boot the operating system. This concept applies to both MBR and GPT disks, although GPT uses a different method for booting.
-
Which term describes a type of storage device that supports a partition to be extended into adjacent unallocated space as long as it is contiguous?
- NTFS
- basic disk
- FAT32
- formatting
-
Explanation & Hint: The term that describes a type of storage device that allows a partition to be extended into adjacent unallocated space, as long as it is contiguous, is:
- Basic disk
A basic disk in Windows supports extending a partition into contiguous unallocated space on the same disk. This feature allows users to increase the size of an existing partition, provided there is unallocated space immediately following it on the disk.
The incorrect terms are:
- NTFS: This is a file system used in Windows operating systems. While NTFS allows for large file sizes and includes features like security permissions, it does not itself define the ability of a partition to be extended; this is a function of the disk type (basic or dynamic).
- FAT32: This is another file system and, like NTFS, it defines how data is stored and retrieved from a storage medium. The ability to extend a partition is not a feature of the FAT32 file system but of the disk’s management system.
- Formatting: Formatting is the process of preparing a storage device for data storage, setting up a file system like NTFS or FAT32. It does not relate to extending partitions on a disk.
-
Which term describes a general name for physical areas on a hard drive?
- NTFS
- partition
- FAT32
- formatting
-
Explanation & Hint: The term that describes a general name for physical areas on a hard drive is:
- Partition
A partition is a distinct region of a hard drive that can be managed separately. When a hard drive is partitioned, it is divided into one or more regions that can be formatted with a file system and used for storing data. Each partition functions as if it were a separate hard drive.
The incorrect terms are:
- NTFS (New Technology File System): This is a file system used by Windows operating systems. It defines how data is stored and organized on a partition, but it does not refer to the physical areas on a hard drive.
- FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32): Similar to NTFS, FAT32 is a file system, but it does not refer to physical areas on a hard drive. It’s an older file system with limitations compared to NTFS, especially in terms of maximum file size and partition size.
- Formatting: This is the process of preparing a partition with a specific file system (like NTFS or FAT32) so it can store data. Formatting sets up the data structures needed by the file system but does not describe the physical areas of a hard drive.
-
Which term describes a partition scheme that takes a portion of disk space of 512 bytes long and that contains the boot loader?
- NTFS
- MBR
- FAT32
- formatting
-
Explanation & Hint: The term that describes a partition scheme where a portion of disk space, 512 bytes long, contains the boot loader is:
- MBR (Master Boot Record)
The Master Boot Record is a type of boot sector at the very beginning of partitioned computer mass storage devices like hard disks. It contains information about how the logical partitions, containing file systems, are organized on that medium. The MBR itself is 512 bytes long and includes a bootloader and a partition table.
The incorrect terms are:
- NTFS (New Technology File System): This is a file system used by Windows operating systems for storing and retrieving files on a hard disk. NTFS does not refer to the boot sector or partition scheme of a disk.
- FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32): FAT32 is another type of file system, but like NTFS, it does not describe a boot sector or partition scheme. It’s an older file system format used for data storage.
- Formatting: This is the process of preparing a storage device (like a hard disk or USB drive) for data storage by setting up a file system. Formatting does not directly relate to the boot sector or the partition scheme of a disk.
-
Which term describes a type of storage device that supports a volume that can span across more than one disk?
- NTFS
- dynamic disk
- FAT32
- formatting
-
Explanation & Hint: The correct term is:
- Dynamic disk: This type of disk configuration in Windows allows for the creation of volumes that can extend across more than one disk. It provides features like spanning a volume across multiple disks, creating RAID-5 volumes, and the ability to resize volumes without rebooting the system. Dynamic disks offer more flexibility compared to basic disks, especially in managing large and complex storage solutions.
The incorrect terms are:
- NTFS (New Technology File System): This is a file system format used by Windows operating systems. NTFS is known for supporting large volumes and files, security features, and data recovery capabilities, but it does not inherently support volumes spanning across multiple disks. It defines how data is stored on a disk, not the structure or management of the disk itself.
- FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32): Like NTFS, FAT32 is a file system format. It’s an older system with limitations in terms of maximum file and partition sizes compared to NTFS. FAT32 does not have the capability to manage volumes across multiple disks.
- Formatting: This process involves preparing a storage device with a specific file system, such as NTFS or FAT32. Formatting sets up the necessary data structures for the file system to store and retrieve data on a disk. It does not pertain to the disk’s capability to span volumes across multiple disks.
-
A technician is booting a laptop that has Windows 10 installed with 2 GB RAM. The boot process is currently working on the following step: NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.
- Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.
-
Explanation & Hint: At the stage where NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE during the Windows 10 boot process, the next step that will happen is:
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen.
In the Windows boot process, after the kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) has been loaded and starts the WINLOGON.EXE, the next step is for WINLOGON.EXE to present the Windows Welcome screen. This screen is where users are prompted to enter their credentials, such as a password or PIN, to access the system.
The other steps mentioned occur at different stages of the boot process:
- “WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.” This step occurs earlier in the boot process, where the Windows Boot Loader (Winload.exe) loads the essential system files including the kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) and the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL.DLL).
- “WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.” This is also an earlier step, where Winload.exe sets up the system environment by reading the registry and loading necessary drivers.
- “Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.” This is one of the first steps in the boot process, where the Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) identifies the boot partition and instructs Winload.exe to start loading Windows.
-
A user is booting a tablet that has Windows 10 installed. The boot process is currently working on the following step: WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.
- Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.
-
Explanation & Hint: When the Windows 10 boot process is at the stage where WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen on a tablet, the next step in the boot process is not explicitly defined as a single step, but it involves user authentication and the initialization of the user environment. Here’s what generally happens next:
- User logs in and the user environment is initialized. After the Windows Welcome screen is displayed by WINLOGON.EXE, the user is prompted to enter their credentials, such as a password or PIN. Upon successful authentication, the system loads the user’s personal settings and initializes the desktop environment, effectively completing the boot process and making the system ready for use.
The other steps mentioned occur at different stages of the boot process:
- “WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.” This step occurs much earlier in the boot process. It’s when the Windows Boot Loader (Winload.exe) loads the essential system files, including the kernel and the Hardware Abstraction Layer.
- “WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.” This also happens earlier than the WINLOGON.EXE stage. Here, Winload.exe prepares the system environment by reading the registry and loading necessary drivers.
- “Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.” This is one of the initial steps in the boot process, where the Windows Boot Manager (BOOTMGR) locates the boot partition and begins the process of starting Windows.
-
A manager is booting a tablet that has Windows 8 installed. The boot process is currently working on the following step: POST. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- BIOS locates and reads the configuration settings that are stored in the CMOS memory.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.
-
Explanation & Hint: During the boot process of a computer with Windows 8, after the Power-On Self-Test (POST), the next step is typically for the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) to locate and read the configuration settings stored in the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) memory. Here’s a brief overview of the steps:
- POST: This is the initial step where the system checks the basic hardware components to ensure they are functioning properly.
- BIOS locates and reads the configuration settings stored in the CMOS memory: After POST, the BIOS searches for and reads the system configuration settings stored in the CMOS. This includes information about hardware like the boot order, which determines from which device the system will start the operating system.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers (later step): This occurs after the BIOS hands over control to the Windows Boot Manager and the Windows loader (WinLoad) begins its process.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL (also a later step): This is a part of the operating system loading phase, where the Windows kernel and Hardware Abstraction Layer are loaded into memory.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process (final step): This is the last phase of the boot process where the Windows kernel takes full control, initializing the rest of the operating system and user environment.
So, the next step after POST in your scenario would be for the BIOS to read the configuration settings from the CMOS memory.
-
An accountant is booting a PC that has Windows 8 installed. The boot process is currently working on the following step: BIOS locates and reads the configuration settings that are stored in the CMOS memory. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- The BIOS boots the computer using the first drive that contains a valid boot sector.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.
-
Explanation & Hint: The next step in the boot process after the BIOS locates and reads the configuration settings stored in the CMOS memory is “The BIOS boots the computer using the first drive that contains a valid boot sector.”
Here’s a brief overview of the steps following this:
- BIOS locates and reads the configuration settings stored in the CMOS memory: This step involves the BIOS checking the system settings and hardware configurations.
- The BIOS boots the computer using the first drive that contains a valid boot sector: After reading the CMOS settings, the BIOS proceeds to identify the bootable drive as per the boot order specified in the settings. It looks for a valid boot sector to initiate the loading of the operating system.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers (subsequent step): After the BIOS hands over control to the boot loader, in this case, WinLoad, it begins by reading the system registry files, selecting a hardware profile, and loading necessary device drivers.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL (following step): This is where WinLoad loads the core components of the Windows operating system, namely the NT kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) and the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL.DLL).
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process (final step): In this last phase, the Windows kernel is fully operational, managing the complete startup of the operating system and transitioning to the user logon process.
Therefore, the immediate next step is for the BIOS to find and boot from the drive with a valid boot sector.
-
A network analyst is booting a PC that has Windows 7 installed with 2 GB RAM. The boot process is currently working on the following step: The code in the boot sector is executed and the control of the boot process is given to Windows Boot Manager. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.
-
Explanation & Hint: After the code in the boot sector is executed and control of the boot process is given to Windows Boot Manager in a Windows 7 environment, the next step is:
“Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.”
Here’s a brief overview of the sequence in the boot process following this step:
- The code in the boot sector is executed, and control is given to Windows Boot Manager: This step is where the system begins transitioning from the basic input/output operations performed by the BIOS to the specific operations needed to load the Windows operating system.
- Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition: At this point, Windows Boot Manager, which was invoked by the boot sector, uses the information provided by the BOOTMGR (Boot Manager) to locate the Winload program on the boot partition.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers (subsequent step): Winload, now in control, reads the necessary registry files, selects the appropriate hardware profile for the system, and begins loading the necessary device drivers.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL (following step): In this step, Winload loads the NT kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) and the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL.DLL), which are critical for the Windows operating system to function.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process (final step): After the core components are loaded, the control is handed over to the Windows kernel, which completes the process of starting up the operating system.
Thus, the immediate next step after the boot sector code execution and the control given to Windows Boot Manager is for Winload to use the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition.
-
An analyst is booting a desktop that has Windows 7 installed with 4 GB RAM. The boot process is currently working on the following step: Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
-
Explanation & Hint: After Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition on a desktop with Windows 7, the next step in the boot process is:
“WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL.”
Here’s a more detailed look at the sequence of events:
- Winload uses the path specified in BOOTMGR to find the boot partition: This step involves Winload locating the correct partition where the Windows operating system is installed.
- WinLoad loads two files that make up the core of Windows: NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL: At this point, Winload loads the Windows NT kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) and the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL.DLL). These are essential for the operating system to function and manage both software and hardware interaction.
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE (subsequent step): Once the kernel and HAL are loaded, the control is passed to NTOSKRNL.EXE, which then starts the login process, primarily managed by WINLOGON.EXE.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen (following step): This is the part of the boot process where the Windows login screen (Welcome screen) is displayed, prompting the user to enter credentials or select a user account.
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete (not accurate): The boot process is not complete at this point; there are further steps involved post-login, where the user environment is set up.
Therefore, the immediate next step is for WinLoad to load NTOSKRNL.EXE and HAL.DLL, which are critical for the Windows operating system’s core functionality.
-
A gamer is booting a desktop that has Windows 7 installed on dynamic drives. The boot process is currently working on the following step: WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
-
Explanation & Hint: NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
- Correct: This is the accurate next step. After the initial steps of reading registry files, choosing a hardware profile, and loading device drivers, the Windows NT operating system kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) takes the next step. It initiates the Windows Logon process by starting WINLOGON.EXE. This process is responsible for handling the user logon screen and loading the user profile.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process: This statement is somewhat misleading. The Windows kernel, represented by NTOSKRNL.EXE, is already actively involved in the boot process at this stage. It doesn’t just “take over”; it continues its role by starting the WINLOGON.EXE process.
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete: This is incorrect. The boot process is not complete after the device drivers are loaded. There are several more steps involved, including user authentication and the starting of essential services and programs.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen: While WINLOGON.EXE is indeed responsible for displaying the Windows Welcome screen, this is not the immediate next step. First, WINLOGON.EXE needs to be started by NTOSKRNL.EXE, and only after it’s initiated does it go on to display the Welcome screen.
-
A technician is booting a laptop that has Windows 10 installed with 2 GB RAM. The boot process is currently working on the following step: The Windows kernel takes over the boot process. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
-
Explanation & Hint: NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
- Correct: After the Windows kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) takes over the boot process, the next step is for it to start the WINLOGON.EXE process. This process is crucial for managing user logins and displaying the logon UI, leading to the user authentication phase of the boot process.
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete: This is incorrect. The boot process is not yet complete at this stage. Following the kernel’s takeover, several more steps occur, including user authentication and the initialization of various system processes and services.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen: While eventually true, this step comes after WINLOGON.EXE is initiated by NTOSKRNL.EXE. It’s not the immediate next step following the kernel’s takeover. WINLOGON.EXE must first be started, and then it proceeds to display the Welcome screen.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process: This statement is redundant in this context, as the kernel’s takeover is already mentioned as the current step in the boot process. The next step involves the actions taken by the kernel, namely starting WINLOGON.EXE.
-
A user is booting a laptop that has Windows 10 installed. The boot process is currently working on the following step: WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- There are no more steps, the boot process is complete.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
-
Explanation & Hint: There are no more steps, the boot process is complete.
Explanation: Once WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen, it indicates that the boot process of Windows 10 is essentially complete. At this point, the system has loaded all necessary services, drivers, and the Windows kernel. The Welcome screen is where users can log in to their accounts, signaling that the system is ready for use.
Incorrect Options:
- WINLOGON.EXE displaying the Windows Welcome screen is the step in question, so it’s not the next step.
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starting the login file called WINLOGON.EXE occurs earlier in the boot process. NTOSKRNL.EXE is the kernel of Windows and is responsible for various system services. It loads before WINLOGON.EXE.
- The Windows kernel taking over the boot process is an earlier step. NTOSKRNL.EXE, the Windows kernel, is fundamental in the boot process and initiates much earlier than the Welcome screen.
-
A manager is booting a tablet that has Windows 8 installed. The boot process is currently working on the following step: The Windows kernel takes over the boot process. What is the next step that will happen in the boot process?
- NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
- The Windows kernel takes over the boot process.
- WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers.
- WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen
-
Explanation & Hint: NTOSKRNL.EXE starts the login file called WINLOGON.EXE.
Explanation: When a tablet with Windows 8 is booting, and the process is at the stage where the Windows kernel (NTOSKRNL.EXE) has taken over, the next step is for NTOSKRNL.EXE to start the login file, which is WINLOGON.EXE. This step is crucial as WINLOGON.EXE is responsible for managing the login process and subsequently displaying the Windows Welcome screen where users can log into their accounts.
Incorrect Options:
- “The Windows kernel takes over the boot process” is the step that has just been completed.
- “WinLoad reads the registry files, chooses a hardware profile, and loads the device drivers” is a step that occurs earlier in the boot process, before the kernel takes over.
- “WINLOGON.EXE displays the Windows Welcome screen” happens after NTOSKRNL.EXE starts WINLOGON.EXE.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker was using a specific technique that affected the TCP three-way handshake. What is the type of network attack?
- SYN flood
- DDoS
- DNS poisoning
- zero-day
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack that specifically affects the TCP three-way handshake is a SYN flood.
Explanation:
- A SYN flood is a form of Denial-of-Service attack in which an attacker sends a succession of SYN requests to a target’s system in an attempt to consume enough server resources to make the system unresponsive to legitimate traffic. It targets the TCP three-way handshake mechanism by not completing the handshake process, leading to a buildup of half-open connections.
Incorrect Options:
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) is a broader category of attack that can include SYN floods but is not specific to the TCP three-way handshake disruption.
- DNS poisoning is an attack that corrupts DNS server data to redirect traffic to malicious sites.
- A zero-day attack refers to exploiting vulnerabilities that are unknown or unaddressed by the software vendor, and it does not specifically target the TCP three-way handshake.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker is using a technique that compares hashed passwords to potential hashes the hacker has. What is the type of network attack?
- rainbow table
- DDoS
- DNS poisoning
- SYN flood
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where an attacker compares hashed passwords to potential hashes they have, is a rainbow table attack.
Explanation:
- A rainbow table attack involves using a precomputed table for reversing cryptographic hash functions, primarily for cracking password hashes. Attackers use rainbow tables to compare hashed passwords found in a system with the hashes in their table, allowing them to find matches and thus determine the original password.
Incorrect Options:
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) is an attack that aims to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming it with a flood of internet traffic.
- DNS poisoning involves corrupting the DNS resolution process to redirect users to malicious sites.
- A SYN flood is a form of DoS attack that specifically targets the TCP three-way handshake, not password hashing.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the DNS server was sent with an enormous amount of false requests, thus overwhelming the server. What is the type of network attack?
- DoS
- DNS poisoning
- SYN flood
- zero-day
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where a DNS server is overwhelmed with an enormous amount of false requests, is a DoS (Denial of Service) attack.
Explanation:
- A DoS attack is characterized by an attempt to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users. This is often achieved by overwhelming the targeted server or infrastructure with a flood of traffic or requests, as described in the scenario with the DNS server.
Incorrect Options:
- DNS poisoning involves corrupting the DNS resolution process, typically by inserting false information into the DNS system, to redirect users to malicious sites. It doesn’t typically involve overwhelming the server with requests.
- A SYN flood is a specific type of DoS attack that targets the TCP three-way handshake process, not the DNS server.
- A zero-day attack exploits unknown vulnerabilities in software or hardware, which is not described in the scenario focused on overwhelming the DNS server with requests.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker is using a vulnerability that is known to the software vendor, but not patched yet. What is the type of network attack?
- zero-day
- DDoS
- DNS poisoning
- SYN flood
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where an attacker exploits a vulnerability that is known to the software vendor but not yet patched, is a zero-day attack.
Explanation:
- A zero-day attack refers to exploiting vulnerabilities in software or hardware that are known but have not been addressed or patched by the vendor. The term “zero-day” indicates that the vendor or the public has had zero days to fix or mitigate the vulnerability since it became known.
Incorrect Options:
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) involves overwhelming a system or network with traffic, making it unavailable to its intended users, and does not specifically relate to exploiting known software vulnerabilities.
- DNS poisoning involves corrupting the DNS resolution process to redirect users to malicious sites, not exploiting known unpatched vulnerabilities.
- A SYN flood is a specific type of DoS attack that targets the TCP three-way handshake process and is unrelated to exploiting known software vulnerabilities.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that zombies were used to attack the firewall. What is the type of network attack?
- DDoS
- DNS poisoning
- SYN flood
- zero-day
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where zombies are used to attack the firewall, is a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack.
Explanation:
- In a DDoS attack, multiple compromised computer systems, often referred to as “zombies,” are used to target a single system, such as a server or firewall. These zombies, which are part of a botnet, flood the target with an overwhelming amount of traffic, rendering it incapable of handling legitimate requests and potentially causing it to become unavailable to users.
Incorrect Options:
- DNS poisoning is an attack that involves corrupting the DNS resolution process to redirect users to malicious sites, not using zombies to attack a firewall.
- A SYN flood is a specific type of DoS attack targeting the TCP three-way handshake process, and while it can use multiple systems, it is more specifically focused on the TCP protocol aspect rather than the broad use of zombies.
- A zero-day attack refers to exploiting vulnerabilities that are unknown or unpatched, which is different from using a network of compromised devices to launch an attack.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that zombies were used to attack the firewall. What is the type of network attack?
- DDoS
- zero-day
- dictionary
- SYN flood
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where zombies are used to attack the firewall, is a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack.
Explanation:
- A DDoS attack involves the use of multiple compromised systems, often referred to as “zombies,” to flood a target, such as a firewall, with an overwhelming amount of traffic. This orchestrated attack overloads the target’s capabilities, leading to degraded performance or complete unavailability for legitimate users.
Incorrect Options:
- A zero-day attack exploits vulnerabilities that are unknown or unpatched, which is different from using a network of compromised devices to launch an attack.
- A dictionary attack is a method used to breach passwords by systematically entering every word in a predefined list (like a dictionary). It’s unrelated to using zombies to attack a firewall.
- A SYN flood is a specific type of DoS attack that targets the TCP three-way handshake process. While it can involve multiple systems, it specifically focuses on exploiting the SYN part of the TCP handshake, rather than the broad use of zombies in a DDoS attack.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker is using a table of words that potentially could be used as passwords. What is the type of network attack?
- dictionary
- SYN flood
- zero-day
- DNS poisoning
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where an attacker uses a table of words that potentially could be used as passwords, is a dictionary attack.
Explanation:
- A dictionary attack involves trying to break into a password-protected system or decrypt a file by systematically entering every word in a pre-compiled list of likely passwords. This list, often referred to as a “dictionary,” contains common words, phrases, and potentially commonly used passwords.
Incorrect Options:
- A SYN flood is a specific type of DoS attack targeting the TCP three-way handshake process, unrelated to password cracking.
- A zero-day attack exploits vulnerabilities that are unknown or unpatched, which is different from trying to guess passwords using a dictionary.
- DNS poisoning involves corrupting the DNS
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker injected false records on the server that translates IP addresses to domain names. What is the type of network attack?
- DNS poisoning
- zero-day
- dictionary
- SYN flood
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where an attacker injects false records into the server that translates IP addresses to domain names, is DNS poisoning.
Explanation:
- DNS poisoning, also known as DNS spoofing, involves corrupting the Domain Name System (DNS) data. This attack leads to the DNS server returning incorrect results, redirecting users to malicious sites or servers instead of the intended destinations. It is achieved by inserting false records into the DNS system.
Incorrect Options:
- A zero-day attack refers to exploiting vulnerabilities that are unknown or unpatched, which is different from manipulating DNS records.
- A dictionary attack involves trying to guess passwords using a pre-compiled list of likely passwords, unrelated to DNS manipulation.
- A SYN flood is a type of DoS attack targeting the TCP three-way handshake process, not related to DNS operations.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker is using a technique that compares hashed passwords to potential hashes the hacker has. What is the type of network attack?
- rainbow table
- SYN flood
- zero-day
- DNS poisoning
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where an attacker compares hashed passwords to potential hashes they have, is a rainbow table attack.
Explanation:
- A rainbow table attack involves using a precomputed table for reversing cryptographic hash functions, primarily for cracking password hashes. Attackers use rainbow tables to compare hashed passwords found in a system with the hashes in their table, allowing them to find matches and thus determine the original password.
Incorrect Options:
- A SYN flood is a type of DoS attack that specifically targets the TCP three-way handshake process and is unrelated to password hash cracking.
- A zero-day attack exploits unknown or unpatched vulnerabilities in software or hardware, which is not directly related to password hash comparison.
- DNS poisoning involves corrupting the DNS resolution process to redirect users to malicious sites, not cracking password hashes.
-
Users in a company have complained about network performance. After investigation, the IT staff has determined that the attacker was using a specific technique that affected the TCP three-way handshake. What is the type of network attack?
- SYN flood
- zero-day
- dictionary
- DNS poisoning
-
Explanation & Hint: The type of network attack described, where the attacker is using a specific technique that affects the TCP three-way handshake, is a SYN flood.
Explanation:
- A SYN flood is a form of Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack that targets the TCP three-way handshake mechanism. In this attack, the attacker sends a succession of SYN requests to a target’s system in an attempt to consume enough server resources to make the system unresponsive to legitimate traffic. It specifically disrupts the handshake process by not completing it, leading to a buildup of half-open connections.
Incorrect Options:
- A zero-day attack refers to exploiting vulnerabilities that are unknown or unpatched, which is different from targeting the TCP handshake process.
- A dictionary attack involves trying to guess passwords using a pre-compiled list of likely passwords, unrelated to the TCP handshake process.
- DNS poisoning involves corrupting the DNS resolution process to redirect users to malicious sites, not disrupting the TCP handshake.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for a company that wants a device to monitor incoming and outgoing traffic and stop any malicious activity. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Buy an IPS.
- Implement a RAID.
- Provide security awareness training.
- Use SSL.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend buying an IPS (Intrusion Prevention System).
Explanation:
- An Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is designed to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic. It actively analyzes the traffic for malicious activities and known threats and can take immediate action to stop these threats. This makes it an ideal solution for a company looking to monitor and protect its network from various cyber threats.
Incorrect Options:
- Implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage virtualization technology primarily used for data redundancy and performance improvement. It is not a security solution for monitoring and stopping malicious network traffic.
- Providing security awareness training is crucial for educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, but it does not directly monitor or stop malicious network traffic.
- Using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) helps secure communications over a computer network and is essential for protecting data in transit. However, SSL alone does not monitor or stop malicious traffic across a network.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for a machine where the antimalware software cannot remove all of the malware. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Use Windows Safe Mode.
- Implement a RAID.
- Provide security awareness training.
- Use SSL.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend using Windows Safe Mode.
Explanation:
- Windows Safe Mode is a diagnostic mode of a computer operating system (OS). It can be very useful for troubleshooting problems with programs and drivers that might not start correctly or that might prevent Windows from starting correctly. When dealing with malware that cannot be removed by antimalware software under normal operating conditions, booting into Safe Mode can be effective. In Safe Mode, only essential system programs and services are loaded, which can prevent malware from loading, making it easier to remove.
Incorrect Options:
- Implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology used for data storage and redundancy. It is not a solution for removing malware.
- Providing security awareness training is important for preventing security breaches and educating users on best practices, but it does not help in the actual process of removing existing malware.
- Using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is for securing data in transit over a network. While it is an important security measure, it does not assist in removing malware from a machine.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for a machine where the antimalware software cannot remove all of the malware. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Use Windows Safe Mode.
- Implement a RAID.
- Provide security awareness training.
- Use encryption.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend using Windows Safe Mode.
Explanation:
- Windows Safe Mode is a special diagnostic mode in Windows operating systems that starts the computer with a minimal set of drivers and services. In Safe Mode, because only the essential system processes are running, it’s often easier to remove malware. Malware and other unwanted programs that automatically start with Windows often do not run in Safe Mode, making it easier for antimalware tools to clean the system effectively.
Incorrect Options:
- Implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology focused on data storage and redundancy, not on malware removal.
- Providing security awareness training is essential for educating users on how to avoid malware and other security threats, but it doesn’t help in removing malware that’s already present on a system.
- Using encryption is a method to secure data by encoding it, which is important for protecting data from unauthorized access. However, encryption does not help in the removal of malware from an infected system.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for preventing tailgating. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Use a mantrap.
- Implement a RAID.
- Provide security awareness training.
- Use encryption.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend using a mantrap.
Explanation:
- A mantrap is a physical security measure designed to prevent unauthorized access to secure areas. It typically consists of two sets of interlocking doors. An individual enters the first door and must authenticate their identity before the second door opens. This system effectively prevents tailgating, which is when an unauthorized person follows someone with legitimate access into a restricted area.
Incorrect Options:
- Implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology focused on data storage and redundancy, not on preventing physical security breaches like tailgating.
- Providing security awareness training is vital in educating employees about various security threats, including tailgating, but it does not physically prevent the act.
- Using encryption protects data from unauthorized electronic access but does not address the physical security issue of tailgating.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for drive redundancy. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Implement a RAID.
- Provide security awareness training.
- Disable ports.
- Implement dual authentication.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend Implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks).
Explanation:
- RAID is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This technology is specifically designed to create redundancy, ensuring data is duplicated across multiple drives. In case of a drive failure, the system can continue to operate using the redundant data.
Incorrect Options:
- Providing security awareness training is important for educating users on security best practices, but it does not address the issue of drive redundancy.
- Disabling ports is a security measure to prevent unauthorized access through physical connections, but it doesn’t provide drive redundancy.
- Implementing dual authentication is a security practice that requires two forms of verification to access resources, but it does not relate to drive redundancy.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for drive redundancy. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Implement a RAID.
- Buy an ASA.
- Use a VPN.
- Implement dual authentication.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend Implementing a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks).
Explanation:
- RAID is a data storage virtualization technology specifically designed for drive redundancy and performance improvement. It combines multiple physical disk drives into one or more logical units. Depending on the RAID level, it can provide redundancy, ensuring that data is copied or mirrored across multiple drives, which protects against data loss in case of a drive failure.
Incorrect Options:
- Buying an ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) relates to network security and firewall solutions, not to drive redundancy.
- Using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a method to secure network traffic, especially over unsecured networks, and does not address drive redundancy.
- Implementing dual authentication, while important for security, involves requiring two forms of user verification to access systems or data and is not related to drive redundancy.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for phishing. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Provide security awareness training.
- Buy an ASA.
- Use a VPN.
- Employ ping sweeps.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend Provide security awareness training.
Explanation:
- Security awareness training is one of the most effective methods to combat phishing. This training educates employees about the dangers of phishing attacks, how to recognize phishing emails or messages, and what to do if they suspect a phishing attempt. Since phishing often relies on social engineering tactics to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information, informed users are a crucial line of defense.
Incorrect Options:
- Buying an ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) is more focused on network security and does not directly address the human element exploited in phishing attacks.
- Using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) secures internet connections and protects data in transit but does not specifically address the issue of identifying and avoiding phishing attacks.
- Employing ping sweeps is a network scanning technique used to determine which of a range of IP addresses map to live hosts. It’s not relevant to protecting against phishing attacks.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for protecting a computer used to log in at a dental clinic from someone using a bootable disk containing hacking tools. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Disable ports.
- Buy an ASA.
- Use a VPN.
- Employ ping sweeps.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend Disable ports.
Explanation:
- Disabling ports, particularly USB or other external device ports on the computer, is an effective way to prevent someone from using a bootable disk or USB containing hacking tools. This measure prevents unauthorized users from booting the computer from external devices, which is a common method for bypassing the operating system’s security mechanisms.
Incorrect Options:
- Buying an ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) provides network security and firewall solutions but does not prevent booting from an external device with hacking tools.
- Using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) secures internet connections and protects data in transit, but it does not address the issue of booting from external devices with hacking tools.
- Employing ping sweeps is a technique used to determine which IP addresses correspond to live hosts in a network, and it is not relevant to preventing someone from using a bootable disk with hacking tools on a physical computer.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for protecting a computer used to log in at a dental clinic from someone using a bootable disk containing hacking tools. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Disable ports.
- Buy an ASA.
- Use a VPN.
- Run vulnerability scanners.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend Disable ports.
Explanation:
- Disabling ports, particularly USB or other external device ports on the computer, is an effective way to prevent someone from using a bootable disk or USB containing hacking tools. By disabling the ports, unauthorized external devices cannot be connected and used to boot the computer, thereby protecting it from such intrusion attempts. This is particularly relevant in a dental clinic or any environment where the computer might be left unattended and vulnerable to physical access.
Incorrect Options:
- Buying an ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) is primarily for network security and firewall solutions. While important, it does not address the issue of booting from unauthorized external devices.
- Using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is great for securing internet connections and protecting data in transit, but it does not prevent booting from external devices with hacking tools.
- Running vulnerability scanners is a proactive security measure to identify and fix vulnerabilities in a system. However, it does not directly prevent someone from using a bootable disk to access a computer.
-
A PC technician has been asked by a supervisor to recommend a security solution for a manager traveling who needs access to internal corporate resources. Which security technique should the technician recommend?
- Use a VPN.
- Buy an ASA.
- Disable ports.
- Run vulnerability scanners.
-
Explanation & Hint: The PC technician should recommend Use a VPN (Virtual Private Network).
Explanation:
- A VPN is an ideal solution for a manager who needs secure access to internal corporate resources while traveling. VPNs create a secure, encrypted tunnel between the manager’s device and the corporate network, allowing for safe and private access to internal resources over the internet. This ensures that sensitive data is protected from eavesdropping and interception, which is especially important when using potentially insecure public Wi-Fi networks.
Incorrect Options:
- Buying an ASA (Adaptive Security Appliance) can enhance overall network security but is not a portable solution for a traveling manager needing remote access.
- Disabling ports is a security measure to prevent unauthorized physical access to a system but does not facilitate remote access to internal resources.
- Running vulnerability scanners is important for identifying security weaknesses in a network or system but does not provide a means for secure remote access.
-
Why would a gamer need to use the move command?
- to relocate a file from one Windows directory to another one
- to prepare a hard drive to accept Windows files
- to manage a PCs drives, disks, partitions, volumes, and virtual drives
- to copy files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another
-
Explanation & Hint: A gamer would need to use the move command to relocate a file from one Windows directory to another one.
Explanation:
- The move command in Windows is primarily used to transfer files and directories from one location to another within the file system. For a gamer, this could be useful for organizing game files, moving game saves or configuration files to different directories, or relocating entire game folders to different drives or locations for better file management or system performance.
Incorrect Options:
- Preparing a hard drive to accept Windows files typically involves formatting or partitioning, which is not accomplished with the move command.
- Managing a PC’s drives, disks, partitions, volumes, and virtual drives is usually done through disk management tools, not with the move command.
- The move command does move files, directories, and subdirectories, but it relocates them rather than creating a copy. The copy command would be used to create copies of files in another location.
-
Why would a gamer need to use the copy command?
- to move that file to a different Windows directory while also leaving the file in the current location
- to prepare a hard drive to accept Windows files
- to manage a PCs drives, disks, partitions, volumes, and virtual drives
- to copy files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another
-
Explanation & Hint: A gamer would need to use the copy command to move that file to a different Windows directory while also leaving the file in the current location.
Explanation:
- The copy command in Windows is used to create a duplicate of files, directories, and subdirectories in a different location, while also retaining the original files in their current location. For a gamer, this can be useful for creating backups of game saves, configuration files, or mods before making changes, ensuring that the original files remain intact and can be restored if needed.
Incorrect Options:
- Preparing a hard drive to accept Windows files generally involves formatting or partitioning, not something achieved with the copy command.
- Managing a PC’s drives, disks, partitions, volumes, and virtual drives is done through disk management tools, not the copy command.
- Although the copy command does copy files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another, the key aspect for a gamer would be the ability to keep the original files in their current location while creating a duplicate in another location.
-
Why would a university student need to use the robocopy command?
- to copy a group of files from one Windows directory to another
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A university student would need to use the robocopy command to copy a group of files from one Windows directory to another.
Explanation:
- Robocopy (Robust File Copy) is a command-line directory and file replication command in Windows. It is used to copy files and directories from one location to another, offering more options and better performance compared to the standard copy command. It’s particularly useful for copying large sets of data, mirroring directories, and handling complex file structures, which can be beneficial for a university student managing large or numerous files for their studies.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not robocopy. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, one would typically use commands like
shutdownor remote management tools, not robocopy. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not robocopy.
-
Why would a university student need to use the xcopy command?
- to copy files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A university student would need to use the xcopy command to copy files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another.
Explanation:
- The xcopy command in Windows is a powerful command-line tool used for copying files, directories, and subdirectories from one location to another. It offers more options than the basic copy command, such as the ability to copy directory structures, file attributes, and handle read-only files. This can be particularly useful for a university student who needs to organize or back up large amounts of data, like research materials, projects, or documents.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not xcopy. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, commands like
shutdownor remote management tools are used, not xcopy. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not xcopy.
-
Why would a technical support representative need to use the format command?
- to prepare a hard drive to accept Windows files
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A technical support representative would need to use the format command to prepare a hard drive to accept Windows files.
Explanation:
- The format command in Windows is used to prepare a hard drive or other storage device for use by erasing all of the data on the drive and setting up a file system. This is essential before a new installation of the Windows operating system or when repurposing an old drive for new data. Formatting a drive creates a clean, empty file system (like NTFS or FAT32) that can store files and applications, including the Windows operating system files.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not the format command. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, commands like
shutdownor remote management tools are used, not the format command. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not the format command.
-
Why would a technical support representative need to use the bootrec command?
- to help to repair the MBR that is suspected of having issues
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A technical support representative would need to use the bootrec command to help to repair the MBR (Master Boot Record) that is suspected of having issues.
Explanation:
- The bootrec command (Bootrec.exe) is a tool used in Windows recovery environments to repair and rebuild the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) and Master Boot Record. This tool is essential when dealing with boot issues such as when the system fails to start due to MBR corruption. It offers various options like
fixmbr,fixboot, andrebuildbcdto address different boot problems.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not bootrec. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, commands like
shutdownor remote management tools are used, not the bootrec command. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not the bootrec command.
- The bootrec command (Bootrec.exe) is a tool used in Windows recovery environments to repair and rebuild the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) and Master Boot Record. This tool is essential when dealing with boot issues such as when the system fails to start due to MBR corruption. It offers various options like
-
Why would a technical support representative need to use the ipconfig command?
- to display the IPv6 address of the PC
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A technical support representative would need to use the ipconfig command to display the IPv6 address of the PC.
Explanation:
- The ipconfig (Internet Protocol Configuration) command in Windows is a console application that displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. It can be used to display a PC’s IP address, including both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, subnet mask, and default gateway. This is crucial for troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not ipconfig. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, commands like
shutdownor remote management tools are used, not the ipconfig command. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not the ipconfig command.
-
Why would a user need to use the netstat command?
- to verify activity on the PC by displaying all active TCP connections on the device
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A user would need to use the netstat command to verify activity on the PC by displaying all active TCP connections on the device.
Explanation:
- The netstat (network statistics) command is a useful tool in various operating systems, including Windows, that displays network connections for the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), routing tables, and a number of network interface and network protocol statistics. It is commonly used to check incoming and outgoing connections to the device, which can be crucial for diagnosing network issues or monitoring network activity.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not netstat. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, commands like
shutdownor remote management tools are used, not the netstat command. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not the netstat command.
-
Why would a user need to use the nslookup command?
- to query the Domain Name Sysytem (DNS) to get domain names and mapping information
- to scan and verify the integrity of all protected system files and replace incorrect versions with correct versions
- to shutdown several remote computers one at a time
- to repair, prepare, and fix Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: A user would need to use the nslookup command to query the Domain Name System (DNS) to get domain names and mapping information.
Explanation:
- The nslookup (Name Server Lookup) command is a network tool used to query DNS servers and retrieve information about domain names, IP addresses, and DNS records. It allows users to look up domain names and obtain DNS-related information, such as the IP address associated with a domain or the mail server responsible for a specific email domain. This is helpful for troubleshooting network and DNS-related issues or verifying DNS configurations.
Incorrect Options:
- Scanning and verifying the integrity of all protected system files and replacing incorrect versions with correct Microsoft versions is done using the System File Checker tool (
sfc /scannow), not nslookup. - To shutdown several remote computers one at a time, commands like
shutdownor remote management tools are used, not the nslookup command. - Repairing, preparing, and fixing Windows images and the recovery image within an installation of the operating system is typically done using tools like DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management), not the nslookup command.
-
Why would a manager need to use the ping command?
- to quickly verify connectivity by sending echo-request messages to the destination and receiving a series of echo-reply messages from that destination
- to change from the current working folder to another folder
- to create a new Windows directory
- to remove an empty directory
-
Explanation & Hint: A manager would need to use the ping command to quickly verify connectivity by sending echo-request messages to the destination and receiving a series of echo-reply messages from that destination.
Explanation:
- The ping command is a network utility used to test the reachability of a host or network device on an IP network. It works by sending ICMP echo-request packets to the target device and waiting for echo-reply packets in response. This process helps determine whether the target device is reachable and responsive. Managers often use ping to check network connectivity, diagnose network issues, and ensure that critical network resources are available.
Incorrect Options:
- Changing from the current working folder to another folder is typically done using the
cd(Change Directory) command in a command-line interface, not the ping command. - Creating a new Windows directory is done using the
mkdir(Make Directory) command or through the Windows File Explorer, not the ping command. - Removing an empty directory is done using the
rmdir(Remove Directory) command or through the Windows File Explorer, not the ping command.
-
Which two statements are true regarding 64-bit processor architecture? (Choose two.)
- It supports a maximum of 4GB RAM memory.
- It supports both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems.
- It has additional registers for 64-bit address space.
- It has only 64-bit registers.
- It only supports 64-bit operating systems.
-
Explanation & Hint: The 64-bit processor architecture contains additional 64-bit registers to support 64-bit address space. This allows it to run both 32-bit and 64-bit operating systems and applications.
-
A technician wishes to start Windows 10 in safe mode to troubleshoot it. What key or key combination would begin this process?
- recycle power and hold down the F8 key
- recycle power and hold down the del key
- ctrl + F6 and restart
- hold the Shift key and select the Restart option in the Power menu
-
Explanation & Hint: Hold the Shift key and select the Restart option in the Power menu. This will display the Choose an Option screen. To get the startup settings, select Troubleshoot, then from the next screen, select Advanced options. Inside Advanced options, select Startup settings, then on the next screen, select Restart. The computer will then restart and display the Startup Settings menu from which you can select enable Safe Mode.
-
What is a possible situation when it might be necessary to boot Windows 10 from a bootable recovery USB device?
- to disable background services
- to delete registry keys
- to partition the hard drive
- to repair the operating system
-
Explanation & Hint: You can boot Windows 10 from a repair boot USB drive and repair your computer with corresponding recovery tools, such as bootrec commands. A Windows 10 repair boot USB is a bootable recovery drive made with USB.
-
Select the Windows 10 version that best meets the described use.
ITE 8.01 – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Exam Answers 01 - Windows 10 Enterprise ==> Used in large to mid-size business environments requiring advanced security and management features.
- Windows 10 Home ==> Used for personal computing and gaming with built-in features like family safety and parental control.
- Windows 10 Education ==> Used in an academic environment with volume licensing options.
- Windows 10 Pro ==> Used in small business environments with built-in security, productivity, and management features.
-
Explanation & Hint: To select the appropriate version of Windows 10 for your needs, consider the primary use and environment in which it will be used:
- Windows 10 Enterprise: This version is ideal for large to mid-size business environments. It offers advanced security and management features, making it suitable for organizations that require robust security measures and centralized control over their IT infrastructure.
- Windows 10 Home: Best suited for personal computing and gaming. It includes built-in features like family safety and parental controls, making it a good choice for household use where these features might be beneficial.
- Windows 10 Education: Specifically designed for use in academic environments. It offers volume licensing options, which can be cost-effective for educational institutions. This version typically includes features beneficial in a school or university setting.
- Windows 10 Pro: A good fit for small business environments. It offers built-in security, productivity, and management features that can help small business owners manage their operations more efficiently and securely.
In summary:
- Choose Enterprise for large or mid-size businesses needing advanced security and management.
- Choose Home for personal use, especially if family safety features are important.
- Choose Education for academic institutions requiring volume licensing and education-specific features.
- Choose Pro for small businesses needing a balance of security, productivity, and management features.
-
Match the file system with the respective description.
ITE 8.01 – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Exam Answers 02 - FAT32 ==> Supports partition sizes up to 2TB or 2,048GB.
- NTFS ==> Supports partition sizes up to 16 exabytes and incorporates file system security features and extended attributes.
- ExFAT ==> Usually used on flash drives as it can support files larger than 4GB.
- CDFS ==> Created specifically for optical disk media.
- NFS ==> A network-based file system that allows file access over the network.
-
Explanation & Hint: - FAT32: Usually used on flash drives as it can support files larger than 4GB. FAT32 is a popular file system for USB flash drives and other external media due to its compatibility with a wide range of operating systems and devices. However, it has a limitation of a maximum file size of 4GB.
- NTFS: Supports partition sizes up to 16 exabytes and incorporates file system security features and extended attributes. NTFS is commonly used in Windows operating systems and is known for its support for large files and partitions, as well as its advanced features like file encryption and disk quotas.
- ExFAT: Supports partition sizes up to 2TB or 2,048GB. ExFAT is an updated version of the FAT file system, designed to overcome the limitations of FAT32, particularly for large files and large storage devices like modern USB drives and SDXC cards.
- CDFS: Created specifically for optical disk media. CDFS, or Compact Disc File System, is designed for storing and accessing data on CDs. It is widely used for CD-ROMs and audio CDs.
- NFS: A network-based file system that allows file access over the network. NFS, or Network File System, enables file sharing across a network, allowing users to access files as if they are stored locally on their own system. It is commonly used in Unix/Linux environments.
-
Match the steps that will lead to the loading of bootmgr.exe in a 32 bit Windows 10 environment.
ITE 8.01 – IT Essentials 8.0 Final Exam Ch 10 – 14 Exam Answers 03 - Step 1 ==> POST executed
- Step 2 ==> CMOS configuration settings loaded
- Step 3 ==> MBR
- Step 4 ==> VBR
-
Explanation & Hint: To understand the sequence of steps leading to the loading of
bootmgr.exein a 32-bit Windows 10 environment, let’s break down each step:- POST (Power-On Self-Test) executed: This is the first step when a computer is turned on. POST is a diagnostic testing sequence run by the computer’s firmware (BIOS or UEFI) to check the hardware components like memory, disk drives, and other hardware to ensure they are working correctly.
- CMOS configuration settings loaded: After the POST, the BIOS/UEFI firmware loads the CMOS configuration settings. CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) stores information like system time, date, and hardware settings. The BIOS/UEFI uses these settings to understand the system’s configuration.
- MBR (Master Boot Record): The MBR is the first sector of the hard drive that the BIOS/UEFI reads after it has determined which storage device to boot from based on the CMOS settings. The MBR contains information on how the hard drive is partitioned, as well as a small amount of code to start the boot process.
- VBR (Volume Boot Record): After reading the MBR, the system proceeds to read the VBR of the active partition. The VBR, also known as a partition boot sector, contains the code to load the operating system’s bootloader. In the case of Windows 10, this bootloader is
bootmgr.exe.
So, the correct order to load
bootmgr.exein a 32-bit Windows 10 environment is:- POST executed.
- CMOS configuration settings loaded.
- MBR read.
- VBR read, leading to the loading of
bootmgr.exe.
-
Which statement is true regarding mobile devices using the Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN)?
- They require an adapter to link to a cellular provider’s network through the nearest base station or transmitter.
- They require a 64-bit operating system.
- They can only be connected through external WWAN USB adapters.
- The bandwidth available over WWAN connections is fixed and is independent of the technologies supported by the adapter and the transmitter.
-
Explanation & Hint: Mobile devices use Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) or cellular Internet access technology. WWAN requires using an adapter to link to a cellular provider network through the nearest base station or transmitter. WWAN adapters can be internally or externally connected by USB. The bandwidth available over WWAN connections depends on technologies supported by the adapter and the transmitter, such as 3G or 4G. Connection to the WWAN is automatic once the adapter and adapter software are installed.
-
A Windows 10 computer locks up with a stop error during startup and then automatically reboots. The automatic restart setting is making it difficult to see any error messages. What can be done so that the error messages can be viewed?
- Use the System Recovery options to restart the operating system.
- Use the Command Prompt option to research the stop error messages.
- View the error messages and recover the system using the System Image Recovery tool.
- Access the System and Security options menu in the control panel and disable the auto restart function.
-
Explanation & Hint: The error messages are difficult to read so the best solution is to first try to disable the auto restart function. To disable auto restart, follow these steps:
- Open Control Panel and navigate to Control Panel\System and Security\System (copy paste in the Control Panel address bar)
- Click ‘Advanced system settings’ and click ‘Settings…’ under the Startup and Recovery section
- Under System Failure, uncheck Automatically Restart
- Click ‘OK’ and ‘OK’ again to close the window
-
Which statement is true regarding libraries in Windows 10?
- Libraries allow Windows 10 to support file names longer than 20 characters.
- Libraries allow Windows 10 to link mutiple different directories.
- Libraries allow Windows 10 to enforce the EFS file system.
- Libraries allow Windows 10 to index files faster.
-
Explanation & Hint: Libraries in Windows 10 allow multiple different directories to be linked together in one location.
-
A user notes that the username and password are automatically populated in the Microsoft Edge browser when logging into a secure site. When the user tries to log into the same site using Google Chrome, the username and password do not save automatically. Why is this occurring?
- Google Chrome does not support that secure site.
- The certificate for that site has not been authenticated.
- Google Chrome does not automatically save web credentials.
- The Google Chrome browser is corrupt.
-
Explanation & Hint: Web credentials do not save for sites accessed by browsers other than Internet Explorer and Edge. Credentials created with other browsers must be managed from within that browser.
-
A system administrator has been asked to protect the sensitive data on Windows 10 computers of all management employees. Which Windows 10 feature can be used to selectively encrypt individual files within the user accounts of each manager?
- BitLocker
- EFS
- TPM
- Windows Update
-
Explanation & Hint: Encrypting File System (EFS) is a Windows 10 feature that can be used to encrypt files and folders linked to a specific user account. BitLocker is a Windows 10 feature that can be used to encrypt the entire hard drive volume. TPM is a specialized chip on the motherboard that stores information specific to the computer system such as encryption keys, digital certificates, and passwords. Windows Update is used to update the operating system, not to encrypt data.
-
A corporation would like to use three or more factors for the password authentication policy. How can this be achieved?
- 2FA
- SFA
- bitlocker
- MFA
-
Explanation & Hint: MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication) requires users to present at least two, if not more, types of authentication. 2FA (Two-Factor authentication), also sometimes referred to as 2-step verification, is a security approach requiring users to present two factors for authentication for accessing an account. SFA (Single-Factor Authentication) requires users to authenticate with only one type of evidence for authentication, usually a password. Bitlocker encrypts drives.
| IT Essentials 8 | |
| IT Essentials 8 Final - Mid-term - Cert | |
| Chapter 1 -9 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Chapter 10 - 14 Skills Assessment | NA |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Practice Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 1 - 9 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Answers Ch 10 - 14 | Online Test |
| Final Exam Composite Answers Ch 1 - 14 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1001 | Online Test |
| A+ 220-1002 | Online Test |