312-50 : CEH Certified Ethical Hacker (312-50v9) : Part 16
-
A penetration tester is conducting a port scan on a specific host. The tester found several ports opened that were confusing in concluding the Operating System (OS) version installed. Considering the NMAP result below, which of the following is likely to be installed on the target machine by the OS?
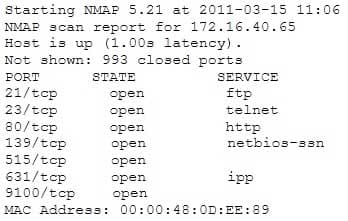
312-50 Part 16 Q01 015 - The host is likely a printer.
- The host is likely a Windows machine.
- The host is likely a Linux machine.
- The host is likely a router.
Explanation:
The Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) uses port 631. -
Which of the following is the least-likely physical characteristic to be used in biometric control that supports a large company?
- Height and Weight
- Voice
- Fingerprints
- Iris patterns
Explanation:
There are two main types of biometric identifiers:
– Physiological characteristics: The shape or composition of the body.
– Behavioral characteristics: The behavior of a person.Examples of physiological characteristics used for biometric authentication include fingerprints; DNA; face, hand, retina or ear features; and odor. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of the behavior of a person, such as typing rhythm, gait, gestures and voice.
-
Which of the following is not a Bluetooth attack?
- Bluedriving
- Bluejacking
- Bluesmacking
- Bluesnarfing
Explanation:
Incorrect Answers:
B: Bluejacking is the sending of unsolicited messages over Bluetooth to Bluetooth-enabled devices such as mobile phones, PDAs or laptop computers, sending a vCard which typically contains a message in the name field (i.e., for bluedating or bluechat) to another Bluetooth-enabled device via the OBEX protocol.
C: BlueSmack is a Bluetooth attack that knocks out some Bluetooth-enabled devices immediately. This Denial of Service attack can be conducted using standard tools that ship with the official Linux Bluez utils package.
D: Bluesnarfing is the unauthorized access of information from a wireless device through a Bluetooth connection, often between phones, desktops, laptops, and PDAs (personal digital assistant.). This allows access to a calendar, contact list, emails and text messages, and on some phones, users can copy pictures and private videos. -
This phase will increase the odds of success in later phases of the penetration test. It is also the very first step in Information Gathering, and it will tell you what the “landscape” looks like.
What is the most important phase of ethical hacking in which you need to spend a considerable amount of time?
- footprinting
- network mapping
- gaining access
- escalating privileges
Explanation:
Footprinting is a first step that a penetration tester used to evaluate the security of any IT infrastructure, footprinting means to gather the maximum information about the computer system or a network and about the devices that are attached to this network. -
The purpose of a __________ is to deny network access to local area networks and other information assets by unauthorized wireless devices.
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention System
- Wireless Access Point
- Wireless Access Control List
- Wireless Analyzer
Explanation:
A wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS) is a network device that monitors the radio spectrum for the presence of unauthorized access points (intrusion detection), and can automatically take countermeasures (intrusion prevention). -
> NMAP -sn 192.168.11.200-215
The NMAP command above performs which of the following?
- A ping scan
- A trace sweep
- An operating system detect
- A port scan
Explanation:
NMAP -sn (No port scan)
This option tells Nmap not to do a port scan after host discovery, and only print out the available hosts that responded to the host discovery probes. This is often known as a “ping scan”, but you can also request that traceroute and NSE host scripts be run. -
You are using NMAP to resolve domain names into IP addresses for a ping sweep later.
Which of the following commands looks for IP addresses?
- >host -t a hackeddomain.com
- >host -t soa hackeddomain.com
- >host -t soa hackeddomain.com
- >host -t AXFR hackeddomain.com
Explanation:
The A record is an Address record. It returns a 32-bit IPv4 address, most commonly used to map hostnames to an IP address of the host. -
Which of the following is a command line packet analyzer similar to GUI-based Wireshark?
- tcpdump
- nessus
- etherea
- Jack the ripper
Explanation:
tcpdump is a common packet analyzer that runs under the command line. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network to which the computer is attached. -
The configuration allows a wired or wireless network interface controller to pass all traffic it receives to the central processing unit (CPU), rather than passing only the frames that the controller is intended to receive.
Which of the following is being described?
- promiscuous mode
- port forwarding
- multi-cast mode
- WEM
Explanation:
Promiscuous mode refers to the special mode of Ethernet hardware, in particular network interface cards (NICs), that allows a NIC to receive all traffic on the network, even if it is not addressed to this NIC. By default, a NIC ignores all traffic that is not addressed to it, which is done by comparing the destination address of the Ethernet packet with the hardware address (a.k.a. MAC) of the device. While this makes perfect sense for networking, non-promiscuous mode makes it difficult to use network monitoring and analysis software for diagnosing connectivity issues or traffic accounting. -
Which of the following is an extremely common IDS evasion technique in the web world?
- unicode characters
- spyware
- port knocking
- subnetting
Explanation:
Unicode attacks can be effective against applications that understand it. Unicode is the international standard whose goal is to represent every character needed by every written human language as a single integer number. What is known as Unicode evasion should more correctly be referenced as UTF-8 evasion. Unicode characters are normally represented with two bytes, but this is impractical in real life.
One aspect of UTF-8 encoding causes problems: non-Unicode characters can be represented encoded. What is worse is multiple representations of each character can exist. Non-Unicode character encodings are known as overlong characters, and may be signs of attempted attack. -
Which of the following is the structure designed to verify and authenticate the identity of individuals within the enterprise taking part in a data exchange?
- PKI
- single sign on
- biometrics
- SOA
Explanation:
A public key infrastructure (PKI) is a set of roles, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates[1] and manage public-key encryption. The purpose of a PKI is to facilitate the secure electronic transfer of information for a range of network activities such as e-commerce, internet banking and confidential email. -
Which of the following is a design pattern based on distinct pieces of software providing application functionality as services to other applications?
- Service Oriented Architecture
- Object Oriented Architecture
- Lean Coding
- Agile Process
Explanation:
A service-oriented architecture (SOA) is an architectural pattern in computer software design in which application components provide services to other components via a communications protocol, typically over a network. -
Which mode of IPSec should you use to assure security and confidentiality of data within the same LAN?
- ESP transport mode
- AH permiscuous
- ESP confidential
- AH Tunnel mode
Explanation:
When transport mode is used, IPSec encrypts only the IP payload. Transport mode provides the protection of an IP payload through an AH or ESP header. Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) provides confidentiality (in addition to authentication, integrity, and anti-replay protection) for the IP payload.Incorrect Answers:
B: Authentication Header (AH) provides authentication, integrity, and anti-replay protection for the entire packet (both the IP header and the data payload carried in the packet). It does not provide confidentiality, which means that it does not encrypt the data. -
Which of the following is assured by the use of a hash?
- Integrity
- Confidentiality
- Authentication
- Availability
Explanation:
An important application of secure hashes is verification of message integrity. Determining whether any changes have been made to a message (or a file), for example, can be accomplished by comparing message digests calculated before, and after, transmission (or any other event). -
Which of the following is the greatest threat posed by backups?
- A backup is the source of Malware or illicit information.
- A backup is unavailable during disaster recovery.
- A backup is incomplete because no verification was performed.
- An un-encrypted backup can be misplaced or stolen.
Explanation:
If the data written on the backup media is properly encrypted, it will be useless for anyone without the key. -
An incident investigator asks to receive a copy of the event logs from all firewalls, proxy servers, and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) on the network of an organization that has experienced a possible breach of security. When the investigator attempts to correlate the information in all of the logs, the sequence of many of the logged events do not match up.
What is the most likely cause?
- The network devices are not all synchronized.
- Proper chain of custody was not observed while collecting the logs.
- The attacker altered or erased events from the logs.
- The security breach was a false positive.
Explanation:
Time synchronization is an important middleware service of distributed systems, amongst which Distributed Intrusion Detection System (DIDS) makes extensive use of time synchronization in particular. -
In Risk Management, how is the term “likelihood” related to the concept of “threat?”
- Likelihood is the probability that a threat-source will exploit a vulnerability.
- Likelihood is a possible threat-source that may exploit a vulnerability.
- Likelihood is the likely source of a threat that could exploit a vulnerability.
- Likelihood is the probability that a vulnerability is a threat-source.
Explanation:
The ability to analyze the likelihood of threats within the organization is a critical step in building an effective security program. The process of assessing threat probability should be well defined and incorporated into a broader threat analysis process to be effective. -
The chance of a hard drive failure is once every three years. The cost to buy a new hard drive is $300. It will require 10 hours to restore the OS and software to the new hard disk. It will require a further 4 hours to restore the database from the last backup to the new hard disk. The recovery person earns $10/hour. Calculate the SLE, ARO, and ALE. Assume the EF = 1 (100%).
What is the closest approximate cost of this replacement and recovery operation per year?
- $146
- $1320
- $440
- $100
Explanation:
The annualized loss expectancy (ALE) is the product of the annual rate of occurrence (ARO) and the single loss expectancy (SLE).
Suppose than an asset is valued at $100,000, and the Exposure Factor (EF) for this asset is 25%. The single loss expectancy (SLE) then, is 25% * $100,000, or $25,000.
In our example the ARO is 33%, and the SLE is 300+14*10 (as EF=1). The ALO is thus: 33%*(300+14*10) which equals 146. -
A network administrator discovers several unknown files in the root directory of his Linux FTP server. One of the files is a tarball, two are shell script files, and the third is a binary file is named “nc.” The FTP server’s access logs show that the anonymous user account logged in to the server, uploaded the files, and extracted the contents of the tarball and ran the script using a function provided by the FTP server’s software. The ps command shows that the nc file is running as process, and the netstat command shows the nc process is listening on a network port.
What kind of vulnerability must be present to make this remote attack possible?
- File system permissions
- Privilege escalation
- Directory traversal
- Brute force login
Explanation:
To upload files the user must have proper write file permissions. -
While performing online banking using a Web browser, a user receives an email that contains a link to an interesting Web site. When the user clicks on the link, another Web browser session starts and displays a video of cats playing a piano. The next business day, the user receives what looks like an email from his bank, indicating that his bank account has been accessed from a foreign country. The email asks the user to call his bank and verify the authorization of a funds transfer that took place.
What Web browser-based security vulnerability was exploited to compromise the user?
- Cross-Site Request Forgery
- Cross-Site Scripting
- Clickjacking
- Web form input validation
Explanation:
Cross-site request forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding and abbreviated as CSRF or XSRF, is a type of malicious exploit of a website where unauthorized commands are transmitted from a user that the website trusts.Example and characteristics
If an attacker is able to find a reproducible link that executes a specific action on the target page while the victim is being logged in there, he is able to embed such link on a page he controls and trick the victim into opening it. The attack carrier link may be placed in a location that the victim is likely to visit while logged into the target site (e.g. a discussion forum), sent in a HTML email body or attachment.Incorrect Answers:
C: Clickjacking (User Interface redress attack, UI redress attack, UI redressing) is a malicious technique of tricking a Web user into clicking on something different from what the user perceives they are clicking on, thus potentially revealing confidential information or taking control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous web pages. It is a browser security issue that is a vulnerability across a variety of browsers and platforms. A clickjack takes the form of embedded code or a script that can execute without the user’s knowledge, such as clicking on a button that appears to perform another function.